Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isotopes
Uploaded by
hanniisme30000 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesIsotopes
Uploaded by
hanniisme3000Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Science 8 Study Guide
ISOTOPES
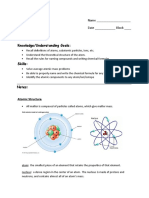
• Are different version of an element or atom.
• It occurs when atoms have the same atomic number and protons but different numbers of
neutrons in the nucleus.
o The numbers of neutrons in an atom does not affect the way
an element behaves chemically, but it does affect the way it
behaves physically. The protons in the nucleus are held together
by the strong nuclear force which overcomes the electrostatic
repulsion between individual protons.
o Neutron helps provide stability to the nucleus of an atom.
Positively charged protons repel each other, but neutrons lessen the
effect of that repulsion by getting between them, essentially.
o The strong nuclear force also binds neutrons to protons.
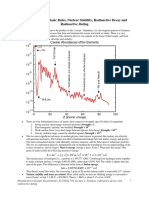
o Too many or too few neutrons can affect the stability of the nucleus
causing radioactive decay to occur and new elements to be formed.
• All elements have isotopes.
o There are two main types of isotopes: stable and unstable (radioactive).
■ An atom is stable if the forces among the particles (protons and neutrons) that makeup the nucleus
are balanced.
■ An atom is unstable (radioactive) if the forces among the particles (protons and neutrons) that
makeup the nucleus are unbalanced.
❖ Radioisotopes are the unstable form of an element that emit radiation to transform into a more
stable form. Radiation is easily traceable and can cause changes in the substance it falls upon.
These special attributes make radioisotopes useful in medicine, industry, and other area.
❖ The radiation emitted is energetic and can be of different types, most often alpha (a), beta (b) and
gamma (g). Their behavior differs from one another, though all the three causes some ionization and
carry some penetration power.
❖ During radioactivity, particles like alpha, beta & gamma rays are emitted by an atom, due to
unstable atom trying to gain stability. Hence, the atoms eventually decay by emitting a particle that
transforms when they are unstable and transforms the nucleus into a lower energy state. This
process of decaying continues till the nucleus attains a stable stage.
ISOTOPIC NOTATION (nuclear notation)
• It is significant because it allows us to quickly calculate an isotope's mass number, atomic number,
and the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus using a visual symbol rather than using a
lot of words.
• Is a shorthand notation that use a hyphen to separate the mass number and the atomic number.
For example: U-235. This represents a uranium isotope with a mass number of 235 and an atomic
number of 92.
• is a shorthand notation for isotopes and atoms that provide a concise way to represent the
composition of an element, specifying its mass number, atomic number, and chemical symbol.
You might also like
- Radioactivity: Instructor: MR Toba Al-Kheir Islamic Girls' SeminaryDocument86 pagesRadioactivity: Instructor: MR Toba Al-Kheir Islamic Girls' SeminarySalehe TobaNo ratings yet
- GenPhy2 - Lesson 4.2 - Atomic and Nuclear PhenomenaDocument12 pagesGenPhy2 - Lesson 4.2 - Atomic and Nuclear PhenomenaKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity and Thermionic Emission Notes 2Document22 pagesRadioactivity and Thermionic Emission Notes 2lawrenceNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic DefinitionsDocument75 pagesIntroduction and Basic Definitionsma9858056No ratings yet
- What Is Radioactivity?Document27 pagesWhat Is Radioactivity?Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ModelDocument11 pagesNuclear Modelzeamayf.biasNo ratings yet
- A-Level Edexcel ChemistryDocument22 pagesA-Level Edexcel ChemistryElyssa Mcpe100% (1)
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument46 pagesNuclear PhysicsAmit PaulNo ratings yet
- The Mighty NucleusDocument3 pagesThe Mighty NucleusSenio, Lexis Jan A.No ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Synthesis of New Elements, Nuclear ReactionDocument58 pagesAtomic Number and Synthesis of New Elements, Nuclear ReactionJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- IG Chem - Nuclear MatterDocument1 pageIG Chem - Nuclear MatterRyno BredenkampNo ratings yet
- Aqa A-Level Chemistry Cheatsheet PDFDocument23 pagesAqa A-Level Chemistry Cheatsheet PDFRiri Findlay100% (1)
- Chemistry Assignment 1Document4 pagesChemistry Assignment 1joegabriel901No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Study NotesDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 4Document9 pagesPDF Document 4harbhjans911No ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument44 pagesLearning ObjectivesDia KhamelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Radiation ScienceDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Radiation ScienceHam ZaNo ratings yet
- 7b Modern Atomic Theory, Subatomic Particles and Structure of AtomDocument32 pages7b Modern Atomic Theory, Subatomic Particles and Structure of AtomMaaz WaseemNo ratings yet
- Isotopes Radioactive IsotopesDocument16 pagesIsotopes Radioactive Isotopesapi-272083070No ratings yet
- Isotopes and IsobarsDocument16 pagesIsotopes and IsobarsAdityakingdomNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument6 pagesAtomsshreyaNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument2 pagesAtomsJullienne Noreen AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - : ElectronDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure - : ElectronAinne Joy DimapilisNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Handout 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Handout 2Roxan Oxima ClabriaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- 2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Document12 pages2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Keshia KatarinaNo ratings yet
- Atoms Are The Foundation ofDocument2 pagesAtoms Are The Foundation ofAnonymous 3zzvu1No ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument22 pagesPhysics AssignmentanessnabelaNo ratings yet
- 12.744/12.754 The Basic Rules, Nuclear Stability, Radioactive Decay and Radioactive DatingDocument8 pages12.744/12.754 The Basic Rules, Nuclear Stability, Radioactive Decay and Radioactive Datingshawnah jamesNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument14 pagesNuclear Physics NotesJonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- 12 RadioactivityDocument62 pages12 RadioactivityAMRA IQBALNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StabilityDocument7 pagesNuclear StabilityWaqas SaeedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- Victoria Catholic School: Submitted By: Jessica V. MarceloDocument4 pagesVictoria Catholic School: Submitted By: Jessica V. MarceloEric CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology: 2.1 Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of All Matter in The UniverseDocument50 pagesChapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology: 2.1 Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of All Matter in The UniverseShemmy Delotina DadulaNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument12 pagesAtomatgimale.comNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic StructureFandyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PDFDocument16 pagesNuclear PDFAlisha AkramNo ratings yet
- The Atomic StructureDocument22 pagesThe Atomic StructureDeonLeo CuencaNo ratings yet
- Interatomic BondingDocument43 pagesInteratomic BondingJessica Laine TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Aqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3Document24 pagesAqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3David AdigboNo ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of The AtomDocument9 pagesStructure and Properties of The AtomenesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructreDocument18 pagesAtomic StructreAndre GreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gen ChemDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Gen ChemJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Mse Group 2Document100 pagesMse Group 2Nicko CortoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesAtomic StructurejagpatvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument2 pagesNuclear Energyapi-307043468No ratings yet
- Basic Rad Phy1Document99 pagesBasic Rad Phy1Rashmi RajanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesUnit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDanyel Rodriguez RomeraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and EnergyDocument18 pagesNuclear Chemistry and EnergyJm EscobarNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Chemistry 2023 2Document60 pagesYr 9 Chemistry 2023 2mkkit2105No ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Lesson1Document21 pagesBiology Unit 1 Lesson1AvakoalaNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsDocument23 pagesFormation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsHIA GS AACNo ratings yet
- 1.nuclear PharmacyDocument40 pages1.nuclear PharmacySheetal MeeniaNo ratings yet
- Dr.S.Balamurugan.,Bpharm, Pharmd Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kmch-CopDocument31 pagesDr.S.Balamurugan.,Bpharm, Pharmd Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kmch-CopbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- C18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsDocument106 pagesC18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2From EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- El-Moasser - Chemistry - Third Secondary - 2022 - Main BookDocument403 pagesEl-Moasser - Chemistry - Third Secondary - 2022 - Main BookMartria EhabNo ratings yet
- Chem Poject XII FinalDocument23 pagesChem Poject XII Finalsashankpandey9No ratings yet
- SS400 Plate SpecificationDocument1 pageSS400 Plate Specificationthiruprema100% (2)
- NovaTec Pro 147172TEDocument6 pagesNovaTec Pro 147172TEMichele LamNo ratings yet
- Brochure EngDocument2 pagesBrochure EngGustavo LafritolaNo ratings yet
- Certificado de Calidad TerminalesDocument4 pagesCertificado de Calidad TerminalesJerson CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical VIVA Question XIIDocument3 pagesChemistry Practical VIVA Question XIIAmaan Ali khan100% (1)
- The Versatility of Outotec's Ausmelt Process For Lead ProductionDocument12 pagesThe Versatility of Outotec's Ausmelt Process For Lead ProductionMatthew PrattNo ratings yet
- June 2016 - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument16 pagesJune 2016 - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEJanice 123No ratings yet
- Chapter 5.1Document6 pagesChapter 5.1api-19624513No ratings yet
- Class 7 Work Book Answers Acid Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesClass 7 Work Book Answers Acid Bases and SaltsGaurav SethiNo ratings yet
- Four Way Galvanic Cell 2Document7 pagesFour Way Galvanic Cell 2Mike OrtillaNo ratings yet
- AWS Abbreviations Oxyfuel Cutting - OFC Oxyacetylene Cutting - OFC-A Oxyfuel Cutting - Process and Fuel GasesDocument8 pagesAWS Abbreviations Oxyfuel Cutting - OFC Oxyacetylene Cutting - OFC-A Oxyfuel Cutting - Process and Fuel GasesahmedNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 First Long Exam Student's Copy (Edited)Document10 pagesChem 16 First Long Exam Student's Copy (Edited)Craig Juliene NavaltaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL EQUATIONS-NotesDocument31 pagesCHEMICAL EQUATIONS-NotesNOELIE IBACARRANo ratings yet
- (1996) Placid-A Clean Process For Recycling Lead From BaterriesDocument3 pages(1996) Placid-A Clean Process For Recycling Lead From BaterriesYeimy Vivar LobosNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Product NameDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet: Product NameakbarNo ratings yet
- Nfpa 704Document1 pageNfpa 704Perdro 10No ratings yet
- 1-Ial WCH11 01 Oct19Document24 pages1-Ial WCH11 01 Oct19Phoe SawNo ratings yet
- Chelating AgentsDocument5 pagesChelating AgentsSalil MukundanNo ratings yet
- A+ EDUCARE CLASS 8-CHEMISTRY Chemical Changes. (EM)Document5 pagesA+ EDUCARE CLASS 8-CHEMISTRY Chemical Changes. (EM)Arkeshwar I V80% (5)
- 11 HalfDocument6 pages11 HalfsgrnaharantuNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent ProblemsDocument2 pagesLimiting Reagent ProblemsMarijan VrhovácNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base Quick Question IGCSEDocument4 pagesAcid and Base Quick Question IGCSELei YinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions SAT Questions 3-6Document8 pagesChemical Reactions SAT Questions 3-6balalaNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument24 pagesStainless SteelsmrutiNo ratings yet
- Borates in Wire Drawing: Technical BulletinDocument4 pagesBorates in Wire Drawing: Technical BulletinNguyen Thanh TrungNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7a - Redox Process and Equilibrium K23Document36 pagesLecture 7a - Redox Process and Equilibrium K23Hải MinhNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 3 Metals and Non-Metals - Class 10th Science Study RankersDocument9 pagesNotes of CH 3 Metals and Non-Metals - Class 10th Science Study Rankerssamy100% (1)
- Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Document6 pagesBixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Teacher OliNo ratings yet