Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Planning Grid Construction Studies
Uploaded by
api-6062576980 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views3 pagesThis document contains a planning grid for a senior cycle construction studies class. The grid outlines 4 weeks of topics, including [1] built heritage awareness and conservation, [2] planning development, [3] foundations, and [4] floors and radon protection. Each week covers relevant learning outcomes, learning intentions, teaching methodologies, assessment methods, and key vocabulary. The class has 22 students and aims to build students' understanding of architecture, planning policies, foundation types, and radon gas prevention through hands-on projects, worksheets, and demonstrations.
Original Description:
Original Title
planning grid construction studies
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a planning grid for a senior cycle construction studies class. The grid outlines 4 weeks of topics, including [1] built heritage awareness and conservation, [2] planning development, [3] foundations, and [4] floors and radon protection. Each week covers relevant learning outcomes, learning intentions, teaching methodologies, assessment methods, and key vocabulary. The class has 22 students and aims to build students' understanding of architecture, planning policies, foundation types, and radon gas prevention through hands-on projects, worksheets, and demonstrations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views3 pagesPlanning Grid Construction Studies
Uploaded by
api-606257698This document contains a planning grid for a senior cycle construction studies class. The grid outlines 4 weeks of topics, including [1] built heritage awareness and conservation, [2] planning development, [3] foundations, and [4] floors and radon protection. Each week covers relevant learning outcomes, learning intentions, teaching methodologies, assessment methods, and key vocabulary. The class has 22 students and aims to build students' understanding of architecture, planning policies, foundation types, and radon gas prevention through hands-on projects, worksheets, and demonstrations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
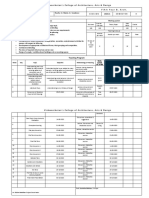
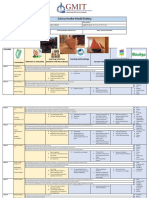
Senior Cycle Construction Studies Planning Grid
Student Name: Darren Hegarty School: Dunmore Community School Class teacher: Mr Carlos O’Gara
ID: No: G00393203 No of Pupils: 22 Length of Lesson: 1 hour
Class profile
Diversity (Gender, Ethnicity etc.) Other relevant information
Schedule Topic/ Relevant LC Outcomes Learning Intentions
Success Criteria
Chapter (students will learn Teaching Methodology Assessment Method Key Words
about)
Week 1 Built Heritage 1. appreciate how the architecture and Identify and distinguish Worksheets Students distinguish various Questions Settlement
awareness and technologies of the past influence various forms of PowerPoint forms of architecture. Students Traffic light system Shelter
conservation contemporary designs and the general architecture heritage in Models can identify how architecture Posters Environment
built environmen Ireland. Demonstrations has changed over time and Heritage
4. understand and evaluate a variety of Gain an understanding of have an insight into the Conservation
Icebreaker
building types and systems in the how architectural styles conservation buildings
Socratic questioning
context of design and aesthetics, have developed over
architectural appropriateness, as well time.
as their environmental and ecological Have an insight into the
impact conservation of heritage
21. model buildings and their buildings
components and/or restore or
reproduce artefacts and furnishings
Week 2 Planning 4. understand and evaluate a variety of Appreciate and Working drawing Students comprehend the Name game Planning
development building types and systems in the understand the different Video factors that impact urban and Visual inspection policies
context of design and aesthetics, factors that impact on PowerPoint rural development Questioning Sustainability
architectural appropriateness, as well urban and rural Demonstrations Zoning
as their environmental and ecological development. Blackboard Urban and
impact Understand the main quiz rural
30. have an awarenessof aesthetic elements that go into development
valuesand considerations relating to creating urban and rural Planning
the built environment communities. permission
33. appreciate design considerations Explain planning
appropriate to various environments guidelines and how they
are used to integrate
new developments into
the landscape
Week 3 Foundations 25. understand considerations in Understand the functions PowerPoint Students appreciate the Visual inspection Foundations
designing for manufacture and multiple of foundations. Video functions of foundations and Exit cards Settlement
production Be able to identify Demonstration create accurate models of Questioning Bulb of
21. model buildings and their different types of Peer teaches. foundations Socratic questioning pressure
components and/or restore or foundations. Circle of learning Strip
reproduce artefacts and furnishings Select suitable Demo foundation
22. appreciate the influence of foundation types for Traffic lights Raft
available materials and technologies on different categories of foundation
both past and contemporary soil. Pile
architectural design practices Draw neatly annotated foundation
sectional diagrams of Reinforcement
various foundations
installations
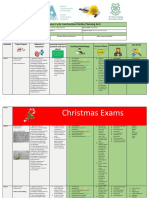
Week 4 Floors and radon 12. understand the societal and Understand what radon PowerPoint Students produces neat Visual assessment Radon
environmental impact of building and gas is where it occurs Video accurate models and sketches Socratic questioning Radium
architectural technologies and name and describe Worksheet of floors and peer teach one Self-assessment Barrier
21. model buildings and their methods of protecting Think pair share. another Meeting individuals Floors
components and/or restore or against it Student Demonstration Suspended
reproduce artefacts and furnishings Illustrate various ground Solid
13. apply design principles on a sound floor types describe their Concrete
scientific basis and in the context of advantages and Hardcore
contemporary building and safety disadvantages and Wall plate
regulations graphically describe how DPC
they are constructed Sub floor
Describe how upper
floors are constructed
and the different
methods used
Week 5 Walls and plastering 21. model buildings and their Understands the PowerPoint Students comprehend the Load bearing
components and/or restore or functions of walls. Video functions of walls. Students list Visual assessment Non load
reproduce artefacts and furnishings Be familiar with the main Worksheet the different components Socratic questioning bearing
32. understand the procedures and components involved in Think pair share. involved in making a wall Self-assessment Rising wall
requirements in obtaining permission building a wall. Student Demonstration Meeting individuals Cavity wall
to build Understand the Party wall
31. understand the principles of difference between load Wall tie
sustainable architecture in the location, bearing and non-load Bonding
design and construction of buildings bearing walls. Noggin
Be able to sketch timber Stud
frame Headplate
Lintel
Week 6 Timber frame 22. appreciate the influence of Understand the main Small group instructions Students differentiate the Summative assessment Timber frame
building available materials and technologies on differences between PowerPoint difference between block and Exit cards Panels
both past and contemporary block buildings and Corroboration leaning timber wall. Visual inspection Plasterboard
architectural design practices timber frame buildings. Reflection journal Kahoot Vapour
21. model buildings and their Be able to draw a Think pair share External assessment membrane
components and/or restore or sectional model through Wall tie
reproduce artefacts and furnishings a timber frame building. Insulation
20. recognise the relevance and Understand the parts Plywood
importance of elements associated that make up timber
with conservation and refurbishment frame panels and the
of buildings and associated artefacts functions they serve
and furnishings
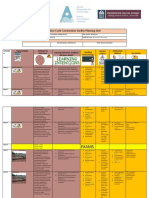
Week 7 Roofs 31. understand the principles of Know the main functions PowerPoint Student can appreciate the Exit cards. Roof
sustainable architecture in the location, of roofs. Think pair share. functions of roofs and Pier teaches. Pitched roof.
design and construction of buildings Be able to name various Demonstration identify the differences Visual inspection Truss roof
31. understand the principles of roof types. Small group exercise between different Socratic questioning Cut roof.
sustainable architecture in the location, Understand how pitched types of roofs. Lean to roof.
design and construction of buildings roofs are constructed. Students create neat Flat roof
35. model real or imaginary rural and Be able to draw to scale sketches that are Hip
urban site layouts various aspects of a roof labelled clearly Valley
Gutter
Fascia
Eaves gable
Week 8 Stairs 16. appreciate the way in which good Understand the various PowerPoint Students produce neat Visual inspection Tread
architecture enhances the quality of types of stairs that can Demonstration accurate models of stairs and Meeting induvial Riser
life of individuals and the community be constructed in a Exit cards. present it Infront of the class Self-assessment Handrail
31. understand the principles of home. Small group instructions Socratic questioning Stairwell
sustainable architecture in the location, Neatly sketch design Landing string
design and construction of buildings features of a stairs Nosing
32. understand the procedures and Carry out a calculation to Step
requirements in obtaining permission find the ideal rise and
to build going for a stair.
Be able to sketch
diagrams of key features
of staircase
Week 9 Windows and doors 15. appropriately record and Understand the PowerPoint Students comprehend the Self-assessment rubric Window
communicate architectural/building importance of windows Demonstration importance of having windows Evaluation sheet Door
detail and design ideas and use CAD and doors in dwellings. Exit cards. and the functions of the Exam questions Casement
systems to model design ideas and Be able to explain the Small group instructions windows Summative assessment Glazing
solutions. main functions of both Observation Lintel
32. understand the procedures and windows and doors. Solid core
requirements in obtaining permission Draw to scale vertical Lock
to build sections through Hinge
21. model buildings and their windows and doors.
components and/or restore or Explain how windows
reproduce artefacts and furnishings and doors are installed
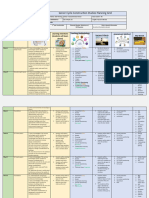
Week 10 U values 36. through appropriate investigation, Understand U values and PowerPoint Students calculate the U Value Visual inspection U value
derive solutions to environmental know the maximum u Demonstration and illustrate why U value is Meeting induvial Heat
problems. values for specific Exit cards. very important within the Self-assessment Kelvin
20. recognise the relevance and elements. Small group instructions house Socratic questioning Celsius
importance of elements associated Be able to calculate U Conductivity
with conservation and refurbishment values having been given Resistivity
of buildings and associated artefacts material thickness and
and furnishings resistivity.
23. explore the properties of a variety Further calculate
of materials including wood, metals, monetary gains and
plastics, ceramics and composites losses based on U value
results
You might also like
- Study Plan - Studio 2C - 2021Document7 pagesStudy Plan - Studio 2C - 2021Jade LauNo ratings yet
- RPKPS Permukiman Ekologis Sarwadi PDFDocument5 pagesRPKPS Permukiman Ekologis Sarwadi PDFSalsa Ayu Puspa1018No ratings yet
- Theories of Architectureurbanism Module Outline March 2018Document13 pagesTheories of Architectureurbanism Module Outline March 2018api-292463251No ratings yet
- Building System Design Module 1 21 CopiesDocument45 pagesBuilding System Design Module 1 21 CopiesRichelle Gonzales PilapilNo ratings yet
- Vishwaniketan's College of Architecture, Arts & Design Lesson Plan Fifth Year B. ArchDocument2 pagesVishwaniketan's College of Architecture, Arts & Design Lesson Plan Fifth Year B. Archvaibhavee baneNo ratings yet
- Planning Grid Leaving Cert Construction Studies STPDocument7 pagesPlanning Grid Leaving Cert Construction Studies STPapi-598398993No ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus B.arch R 2021Document108 pagesRevised Syllabus B.arch R 2021MANIMEGALAI PRASANNANo ratings yet
- DESIGN 1 Syllabus A4 Aug12'20Document9 pagesDESIGN 1 Syllabus A4 Aug12'20Mike Jacson BautistaNo ratings yet
- B.arch R2021Document121 pagesB.arch R2021nivetha109shanmugamNo ratings yet
- College of Architecture and Fine Arts: Olytechnic Niversity of The HilippinesDocument5 pagesCollege of Architecture and Fine Arts: Olytechnic Niversity of The HilippinesTiara OyardoNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Group ADocument2 pagesScheme of Work Group Aapi-385355126No ratings yet
- Ibs SyllabusDocument3 pagesIbs Syllabusapi-726085240No ratings yet
- Micro Teaching: Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) Spesifikasi Dan Karakteristik CatDocument32 pagesMicro Teaching: Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) Spesifikasi Dan Karakteristik CatPutri AprilliaNo ratings yet
- CSB 2uby20 Ferris - Assessment Program Planner 2017Document2 pagesCSB 2uby20 Ferris - Assessment Program Planner 2017api-263403037No ratings yet
- Planning Grid Leaving Cert Construction StudiesDocument4 pagesPlanning Grid Leaving Cert Construction Studiesapi-545610225No ratings yet
- 21Sch Year2-5SyllabusDocument226 pages21Sch Year2-5SyllabusGagana B K MSANo ratings yet
- 46 Building and Environmental Planning - RPS - RE - RT (Eng)Document20 pages46 Building and Environmental Planning - RPS - RE - RT (Eng)M Ainur RidloNo ratings yet
- Programme Specification: BA (Hons) Interior Design Environment ArchitecturesDocument20 pagesProgramme Specification: BA (Hons) Interior Design Environment ArchitectureslisaconnollyNo ratings yet
- Planning Grid Weebly Leaving Cert Construction Studies PracticeDocument4 pagesPlanning Grid Weebly Leaving Cert Construction Studies Practiceapi-726332798No ratings yet
- Aesthetics For Interior Design-1st Tri SY 2023-2024Document17 pagesAesthetics For Interior Design-1st Tri SY 2023-2024Ashley LabisteNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design Studio V Arc 60306 - Module Outline - March 2018 ApprovedDocument15 pagesArchitectural Design Studio V Arc 60306 - Module Outline - March 2018 Approvedapi-289083087No ratings yet
- Unit Title Unit Code Programme Credits Level Unit Status Contact TimeDocument7 pagesUnit Title Unit Code Programme Credits Level Unit Status Contact TimelisaconnollyNo ratings yet
- Department Course Name Course Code Semester Credit Coordinator LecturerDocument20 pagesDepartment Course Name Course Code Semester Credit Coordinator LecturerHwang Ha YoungNo ratings yet
- MArs 2021.heritage Management - Semester Learning Plan - ENGDocument5 pagesMArs 2021.heritage Management - Semester Learning Plan - ENGaswarNo ratings yet
- Unit of Work Design TechnologyDocument5 pagesUnit of Work Design Technologyapi-389000148No ratings yet
- Principles of Reinforced ConcreteDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Reinforced Concreteiking_balonNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design Studio V Arc 60306 - Module Outline - August 2018Document15 pagesArchitectural Design Studio V Arc 60306 - Module Outline - August 2018api-289042707100% (1)
- PLANING 423 - SYLLABUS - 2nd Semester - 2021-2022Document9 pagesPLANING 423 - SYLLABUS - 2nd Semester - 2021-2022Angelo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer InteriorDocument8 pagesReviewer InteriorLaurence Emmanuel BenedictosNo ratings yet
- Planning Grid Ty ConstructionDocument4 pagesPlanning Grid Ty Constructionapi-544281074No ratings yet
- Architectural Design 1Document6 pagesArchitectural Design 1hope jirehNo ratings yet
- UC-CEA-SYL-2027 - Research Method and Statistics - SyllabusDocument5 pagesUC-CEA-SYL-2027 - Research Method and Statistics - SyllabusAlven BactadNo ratings yet
- Subject Course Unit Title DurationDocument13 pagesSubject Course Unit Title Durationapi-511779674No ratings yet
- Construction Studies Planning GridDocument3 pagesConstruction Studies Planning Gridapi-601842277No ratings yet
- Curriculum GridDocument5 pagesCurriculum Gridapi-404604545No ratings yet
- Planning 1 Syllbus For EditDocument9 pagesPlanning 1 Syllbus For Editmedi BanayatNo ratings yet
- Unit Title Unit Code Programme Credits Level Unit Status Contact TimeDocument5 pagesUnit Title Unit Code Programme Credits Level Unit Status Contact TimelisaconnollyNo ratings yet
- B.arch 2022 NEP Scheme Syllabus - DraftDocument265 pagesB.arch 2022 NEP Scheme Syllabus - DraftNeha AlbertNo ratings yet
- Year 7 s2 - Cutting BoardDocument5 pagesYear 7 s2 - Cutting Boardapi-521819507No ratings yet
- CMPE 30052 - Data Structures and Algorithm - PUP OBE Syllabus - For Revised Curriculum 2018 - SAMPLE TEMPLATESDocument8 pagesCMPE 30052 - Data Structures and Algorithm - PUP OBE Syllabus - For Revised Curriculum 2018 - SAMPLE TEMPLATESjscansinoNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Obe SyllabusDocument7 pagesData Structure Obe SyllabusRige Mae MuescoNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes 2022Document9 pagesLearning Outcomes 2022emet baqsNo ratings yet
- STEN 43053 Dam EngineeringDocument10 pagesSTEN 43053 Dam EngineeringClarize MikaNo ratings yet
- Design 3 Lecture Note 1 - Precedent Study - Rev00Document17 pagesDesign 3 Lecture Note 1 - Precedent Study - Rev00Syee Khor100% (1)
- Assessment 2Document39 pagesAssessment 2api-320762430No ratings yet
- Planning Grid-Galway Hooker Model MakingDocument3 pagesPlanning Grid-Galway Hooker Model Makingapi-385077225No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Surveying 1 (Lab)Document15 pagesFundamentals of Surveying 1 (Lab)Crate AngsterNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesPolytechnic University of The PhilippinesCrate AngsterNo ratings yet
- Thesis PPT Presentation SampleDocument47 pagesThesis PPT Presentation SampleArmand Kyle AbadNo ratings yet
- Structures: Mixed-Ability NeedsDocument39 pagesStructures: Mixed-Ability NeedsMiquel Mulet AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Plan 309/646 Site Planning and Design Studio Course Syllabus - Fall 2017Document12 pagesLearning Objectives: Plan 309/646 Site Planning and Design Studio Course Syllabus - Fall 2017Chau TruongNo ratings yet
- BSC and MArch Architecture 96dpi Spreads With CoverDocument66 pagesBSC and MArch Architecture 96dpi Spreads With CoverapisavuNo ratings yet
- CEEdSD - (Lumbera - Track B) PICE National Convention Ver 12nov2022-1Document42 pagesCEEdSD - (Lumbera - Track B) PICE National Convention Ver 12nov2022-1LERIS PENOTELNo ratings yet
- A History of Instructional Design and Technology 2 Fv1icDocument12 pagesA History of Instructional Design and Technology 2 Fv1iccaoy8844No ratings yet
- Space Planning and ErgonomicDocument17 pagesSpace Planning and ErgonomicDominikus ChristopherNo ratings yet
- BCE-221 - Coursepack Edited 3Document12 pagesBCE-221 - Coursepack Edited 3SHALOM EMMANUEL OHAONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2 Mwangi Ivy WDocument18 pagesChapter 1 & 2 Mwangi Ivy WIvy MwangiNo ratings yet
- QAAC - Course Syllabus - ARCG 510 - 22-23 - 1 - Rev2Document12 pagesQAAC - Course Syllabus - ARCG 510 - 22-23 - 1 - Rev2Noha GhareebNo ratings yet
- 2019 Arch S0102 SyllabusDocument19 pages2019 Arch S0102 SyllabusZoljargal DorjooNo ratings yet
- Architect Skills and Qualities: Guide to Becoming a Good ArchitectFrom EverandArchitect Skills and Qualities: Guide to Becoming a Good ArchitectNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Paper Code of ConductDocument4 pagesTutorial Paper Code of Conductapi-606257698No ratings yet
- Es Essay My Philophy Statement g00393203Document8 pagesEs Essay My Philophy Statement g00393203api-606257698No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Work SheetDocument1 pageLesson 1 Work Sheetapi-606257698No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 PowerpointDocument6 pagesLesson 5 Powerpointapi-606257698No ratings yet
- 2nd Year Wood ProjectDocument20 pages2nd Year Wood Projectapi-606257698No ratings yet
- Speech FailureDocument2 pagesSpeech FailureJay AustriaNo ratings yet
- LP 16Document3 pagesLP 16Alya QistinaNo ratings yet
- Agile MethodologyDocument16 pagesAgile MethodologyubadjateNo ratings yet
- DLP-Math 8 2017 - 1st QuarterDocument42 pagesDLP-Math 8 2017 - 1st QuarterIan Santos Salinas100% (1)
- Child NeglectDocument6 pagesChild Neglectalutus2006No ratings yet
- The Magic of Short Books MasterclassDocument59 pagesThe Magic of Short Books MasterclassNIKNo ratings yet
- The Power of Positive AttitudeDocument3 pagesThe Power of Positive AttitudeSiyaa Singh100% (1)
- Software Requirement Specification For Online Shopping SystemDocument8 pagesSoftware Requirement Specification For Online Shopping Systempawansingh100% (1)
- Determination of Malingering in Disability Evaluations - Good (1) (Inglés)Document18 pagesDetermination of Malingering in Disability Evaluations - Good (1) (Inglés)Michu AguilarNo ratings yet
- Study of Punctuality Among School Going Adolescents in Relation To Their Home EnvironmentDocument7 pagesStudy of Punctuality Among School Going Adolescents in Relation To Their Home EnvironmentAnonymous CwJeBCAXp100% (2)
- Pes1ug21ec106 CLP A 3Document2 pagesPes1ug21ec106 CLP A 3Gowri MatadhNo ratings yet
- Sri Ramana Paravidyopanishad PDFDocument101 pagesSri Ramana Paravidyopanishad PDFantiX LinuxNo ratings yet
- ENG001 Elementary English Solved Final Term Paper 01Document8 pagesENG001 Elementary English Solved Final Term Paper 01syedkhi92No ratings yet
- IWAR May 2 - May 6, 2022Document2 pagesIWAR May 2 - May 6, 2022gelma furing lizalizaNo ratings yet
- Scribd 3Document6 pagesScribd 3anirudh modhalavalasaNo ratings yet
- Netfind The Volume of Each Solid FigureDocument29 pagesNetfind The Volume of Each Solid FigureFynn NiallNo ratings yet
- National College of Business Administration and Economics: Department of Management SciencesDocument5 pagesNational College of Business Administration and Economics: Department of Management SciencestahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Creation of A New DisciplineDocument46 pagesChapter 2 - The Creation of A New DisciplineAndréina PessoaNo ratings yet
- Personality ClassificationDocument6 pagesPersonality ClassificationMunir AhmedNo ratings yet
- BU-F-GS-4 Request For Dropping and Adding SubjectsDocument1 pageBU-F-GS-4 Request For Dropping and Adding Subjectsdaren.tejadaNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Key Concepts PDFDocument281 pagesPsychology - Key Concepts PDFSolly Seid100% (1)
- Fms Question BankDocument4 pagesFms Question BankAli Arun100% (1)
- GRADE 7 Peace and Val Ed Catch Up PlanDocument8 pagesGRADE 7 Peace and Val Ed Catch Up Plancarlkevinval.ybanez029No ratings yet
- Quality Management, Ethics, and Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument13 pagesQuality Management, Ethics, and Corporate Social ResponsibilityJoyce FranciscoNo ratings yet
- MIS500 - Assessment 2 BriefDocument11 pagesMIS500 - Assessment 2 BriefWarisha KhanNo ratings yet
- The Sociological Perspective: "Seeing The General in The Particular"Document34 pagesThe Sociological Perspective: "Seeing The General in The Particular"Cassandra OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Response Inhibition IdeasDocument2 pagesResponse Inhibition Ideasapi-2470445450% (1)
- MathdlpDocument10 pagesMathdlpPearl DiansonNo ratings yet
- Genres and Academic WritingDocument3 pagesGenres and Academic WritingYamith José FandiñoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Loyalty Programs in Behavioral and Affective LoyaltyDocument11 pagesThe Role of Loyalty Programs in Behavioral and Affective LoyaltyNoam MaoniNo ratings yet