Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Immune Gas Exchange Markscheme
Uploaded by
yt kOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Immune Gas Exchange Markscheme
Uploaded by
yt kCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
define antigen: antigens are foreign molecules(usually protein) that can
generate immune response when detected by the body
2. describe phagocytosis:
a. recognse antigen
b. engulf pathogen
c. enclose in vacuole(phagosome
d. fuses with lysosome
e. lysosome contain enzyme (hydrolytic enzyme) -> hydrolyse pathogen
f. antigen (from virus) are displayed on the cell membrane
3. define antibody:a protein which binds to specific antigens to form
antigen-antibody complex made from b-cells
4. monoclonal antibody : identical to b-cells
5. define pathogen: any microorganism which can cause disease
6. explain why antibodies are only effective against a specific pathogen
a. antibody is protein which have a unique tertiary structure
b. that is complementary to 1 type of antigen only(antigens also have a
specific shape
7. Describe how HIV is replicated.(4 marks)
a. attachment protein bind to t helper cell receptor protein
b. Rna goes inside to the host cell
c. reverse transcriptase makes double strand dna from rna
d. insert human dna
e. viral protein assemble and released
8. When a vaccine is given to a person, it leads to the production of antibodies
against a disease-causing organism. Describe how.(5)
vaccine contain antigen
macrophage have the antigen on its surface
binds to a T helper cell with complementary receptor protein
T helper cell activates the B-cell clones itself
complementary to antigen
b-cell release lots of antibody
and the clone of b-cell(plasma cell) also produce the same antibody
b-cell to memory cell and release ab faster when inflected
8.Describe the difference between active and passive immunity
active involve memory cell but passive does not
active takes longer time to have protection than passive
active have the process of produce antibody from memory cell
passive introduced into the body from vaccines or breast milk…
active have a long term protection because antibody is produced
passive short term because antibody given broken down
9.Suggest and explain two further investigations that should be done before this
ADC is tested on human breast cancer patients
test on other mammals for safety
investigate different conc to find the suitable dose
test on healthy human repeat the epxperiment
10.Suggest and explain how the viruses became able to infect other species of frog.
mutation in genetic materials
alter the shape of attachment protein
can bind with receptor of other species
11.
Antibody has specific tertiary structure
Complementary (shape / fit) to receptor protein
Prevents GF binding
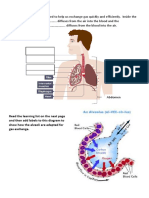
1.Describe and explain one feature of the alveolar epithelium that makes the
epithelium well adapted as a surface for gas exchange. Do not refer to surface area
or moisture in your answer
Single layer of cells; Reduces diffusion distance/Permeable; 4. Allows diffusion of
oxygen/carbon dioxide
2.Explain two ways in which the structure of fish gills is adapted for efficient gas
exchange.
● large surface area provided by lamellae and gill filament
● thin layer of cell (capillaries in lamellae) = short diffusion pathway
3.Explain how the counter current mechanism in fish gills ensures the maximum
amount of the oxygen passes into the blood flowing through the gills.
● water and blood flow in opposite direction
● to make sure the O2 conc in water > blood
● to maintain a steep conc gradient along the whole length
4.Explain three ways in which an insect’s tracheal system is adapted for efficient gas
exchange.
● tracheole have thin ways so short diffusion pathway
● large number of tracheole gives high SA
● highly branched tracheole short diffusion pathway to the cell
● tracheal provide full tube of air so fast diffusion
● rhythmic abdominal to maintain concentration gradient for oxygen
5.The damselfly larva is a carnivore that actively hunts prey. It has gills to obtain
oxygen from water. Explain how the presence of gills adapts the damselfly to its way
of life.
● high metabolic rate = more respiration= more oxygen required
7.Describe and explain the mechanism that causes lungs to fill with air.
● Diaphragm (muscle) contracts and external intercostal muscles contract;
Ignore ribs move up and out
● (Causes volume increase and) pressure decrease;
● Air moves down a pressure gradient
● – trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
8.Explain why death of alveolar epithelium cells reduces gas exchange in human
lungs.
● Reduced surface area;
● Increased distance for diffusion;
● Reduced rate of gas exchange;
9,Use your knowledge of gas exchange in leaves to explain why plants grown in soil
with very little water grow only slowly.
● Stomata close;
● Less carbon dioxide (uptake) for less photosynthesis/glucose production
10.Describe the pathway taken by an oxygen molecule from an alveolus to the
blood.
● (Across) alveolar epithelium;
● Endothelium / epithelium of capillary;
1.Using the information provided, explain how two features of the body of the tubifex
worm allow efficient gas exchange
● Thin/small so short diffusion pathway
● Flat/long/small/thin so large surface area to volume ratio
2.Explain the advantage for larger animals of having a specialised system that
facilitates oxygen uptake.
● Large(r) organisms have a small(er) surface area:volume
● Overcomes long diffusion pathway
3.Use your knowledge of surface area to volume ratio to explain the higher metabolic
rate of a mouse compared to a h-*-orse
● larger surface area to volume ratio
● More/faster heat loss
● respiration/metabolism releases heat
4.explain why cant draw conclusion
no statistic information
information lack
cant compare the stages
5.
You might also like
- Soln123 BioDocument2 pagesSoln123 Biothe_truth_94No ratings yet
- Short Answers Chapter 1 Page 3Document42 pagesShort Answers Chapter 1 Page 3Leen AlodatNo ratings yet
- IB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Document35 pagesIB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Naz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- Fall Semester Review 2020Document5 pagesFall Semester Review 2020api-521781723No ratings yet
- Analysis of Past Question PapersDocument72 pagesAnalysis of Past Question PapersShamaNo ratings yet
- Role of tissue fluid and breathing measurementsDocument4 pagesRole of tissue fluid and breathing measurementsTamer A. DakkakNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Gas Exchange and The Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesPart 2 Gas Exchange and The Respiratory Systemrongelandrew.gilbolingoNo ratings yet
- Bio sp3Document9 pagesBio sp3imrupnarayanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Integration: Lymphatic & Respiratory SystemsDocument13 pagesClinical Integration: Lymphatic & Respiratory SystemsJoseph KimNo ratings yet
- Topic3 ImprovementsDocument8 pagesTopic3 Improvementsmahmood.mNo ratings yet
- Markscheme: (125 Marks)Document33 pagesMarkscheme: (125 Marks)Naz GümüşlüoğluNo ratings yet
- DLaboratory Actiivty 3 - Cellular Basis of LifeDocument5 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 3 - Cellular Basis of LifeSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- NMAT Biology Practice Questions Set 3Document7 pagesNMAT Biology Practice Questions Set 3Nurshayma JalilNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument21 pagesFinal Revisionsam.cool.boy2021123No ratings yet
- GCSE Biology RevisionDocument2 pagesGCSE Biology RevisionsannnnnNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer of Animal PhysiologyDocument14 pagesQuestion and Answer of Animal PhysiologyNuni Rismayanti NurQalbi0% (1)
- BTEC First Applied Science: Unit 3: Biology and Our EnvironmentDocument2 pagesBTEC First Applied Science: Unit 3: Biology and Our Environmentabu imaanNo ratings yet
- Biocomp Exam 2009Document12 pagesBiocomp Exam 2009martynapet100% (1)
- Cells Introduction SHODocument5 pagesCells Introduction SHOshamshadNo ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2006Document24 pagesAIIMS May 2006Deepak MainiNo ratings yet
- bio workDocument7 pagesbio workRiddhi TullooNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pathophysiology 8th Edition by MccanceDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Pathophysiology 8th Edition by MccanceMichaelNguyenwgok100% (39)
- Chapter 6 A Tour of The CellDocument3 pagesChapter 6 A Tour of The CellMohammad Mahrus Bin AshfaqNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 1Document5 pages5090 Nos SW 1gizzarNo ratings yet
- Questions MarksDocument18 pagesQuestions MarksJenkins CK TsangNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Chapter 2: Organelles, Tissues, CellsDocument33 pagesCell Biology Chapter 2: Organelles, Tissues, CellsJs TeoNo ratings yet
- STEM General Biology2 3-4Document13 pagesSTEM General Biology2 3-4Jp menorNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1Document20 pagesBiology Unit 1Serene NassifNo ratings yet
- 6, Life Processes: NCERT (CBSE) Textbook Exercise QuestionsDocument5 pages6, Life Processes: NCERT (CBSE) Textbook Exercise QuestionsTarique WaliNo ratings yet
- 1st 9 WeekreviewDocument5 pages1st 9 Weekreviewapi-262368188No ratings yet
- Essay QuestionsDocument3 pagesEssay QuestionsAytheaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Study GuideDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Study GuideCesar MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesLife Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes QuestionsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes QuestionsDeepakNo ratings yet
- Final Answer Key-WebsiteDocument6 pagesFinal Answer Key-Websiteapi-292258241No ratings yet
- AP Biology Student Growth ObjectivesDocument5 pagesAP Biology Student Growth ObjectivesIrina ShutovskyNo ratings yet
- Physio 1 Day MainDocument302 pagesPhysio 1 Day Mainanup raoNo ratings yet
- Simple Notes - Paper I PhysiologyDocument147 pagesSimple Notes - Paper I PhysiologyArrya DSNo ratings yet
- Ib Biology Topic 1 CellsDocument10 pagesIb Biology Topic 1 Cellswee100% (1)
- B7 Knowledge ChecklistDocument9 pagesB7 Knowledge ChecklisthabuelmagdNo ratings yet
- C9e Answers Active Reading 07Document7 pagesC9e Answers Active Reading 07Daniel DHizzy Hizgilov83% (18)
- Problems SolutionDocument3 pagesProblems SolutionJanelle Jabby ReidNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- Rewrite sentences for clarity and correctnessDocument1 pageRewrite sentences for clarity and correctnessRabiul SikderNo ratings yet
- Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 6 Life ProcessesDocument14 pagesKarnataka SSLC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 6 Life ProcessessumeshmirashiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy Evidence To Practice 5th Edition Frownfelter Test BankDocument25 pagesCardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy Evidence To Practice 5th Edition Frownfelter Test Bankturnoutlection80nqy100% (18)
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Document26 pagesANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)ajdNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review ANSWERSDocument7 pagesCell Transport Review ANSWERSAnonymous pUJNdQNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Plasma Membranevvgnzdbkf100% (1)
- SL Paper 2: Do Not Accept Energy StorageDocument73 pagesSL Paper 2: Do Not Accept Energy StoragemanrajNo ratings yet
- Bone InjuryDocument16 pagesBone Injuryfhenrique77No ratings yet
- Biology Keystone Exam ReviewDocument58 pagesBiology Keystone Exam ReviewLian LzNo ratings yet
- Protein Adsorption and Cell Migration on HydrogelsDocument3 pagesProtein Adsorption and Cell Migration on HydrogelsCurtis LamNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology AnswersDocument30 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Human Biology AnswersAvrinox88% (48)
- A Unifying Theory For The Crypt: News & ViewsDocument2 pagesA Unifying Theory For The Crypt: News & ViewsJesus A. Arzola FloresNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and BloodDocument5 pagesGas Exchange and Bloodsemirah anthonyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Elasmobranch Fishes: Internal ProcessesFrom EverandPhysiology of Elasmobranch Fishes: Internal ProcessesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Immunity and DiseasesDocument11 pagesLesson Plan Immunity and DiseasesAnalyn ValentinNo ratings yet
- Immunology of Pregnancy (Gil Mor) PDFDocument338 pagesImmunology of Pregnancy (Gil Mor) PDFherdhika100% (1)
- Cancer ImmunotherapyDocument7 pagesCancer ImmunotherapyKamu RajiNo ratings yet
- BIOC39 Lecture 1 Intro PDFDocument63 pagesBIOC39 Lecture 1 Intro PDFPriya NathNo ratings yet
- London, 18 October 2006 EMEA/CHMP/VWP/164653/2005: European Medicines AgencyDocument19 pagesLondon, 18 October 2006 EMEA/CHMP/VWP/164653/2005: European Medicines AgencyAntonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Micro Lec Ars Sessions 17 23Document9 pagesMicro Lec Ars Sessions 17 23rica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- 143 SG 9Document43 pages143 SG 9cake girlsNo ratings yet
- FDA Combating COVID-19 With Medical Devices-082520Document39 pagesFDA Combating COVID-19 With Medical Devices-082520el multicolor de videosNo ratings yet
- C. J. Mieny, U. Mennen: Principles of Surgical Patient Care - Volume II Chapter 13: Organ Transplantation Principles of Organ Transplantation J. R. Botha and L. P. MargoliusDocument28 pagesC. J. Mieny, U. Mennen: Principles of Surgical Patient Care - Volume II Chapter 13: Organ Transplantation Principles of Organ Transplantation J. R. Botha and L. P. MargoliusGordana UzelacNo ratings yet
- Colostrum BenefitsDocument8 pagesColostrum BenefitsjcenizalNo ratings yet
- Pfizer-Biontech COVID-19 Vaccine Briefing DocumentDocument92 pagesPfizer-Biontech COVID-19 Vaccine Briefing DocumentDavid CaplanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vaccines, Vaccine Development and ProductionDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Vaccines, Vaccine Development and ProductionAni IoanaNo ratings yet
- DL Biotech 2024Document3 pagesDL Biotech 2024sriNo ratings yet
- BAMU B.pharmcy Second Year Syllabus 2007Document37 pagesBAMU B.pharmcy Second Year Syllabus 2007Gajanan VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Immunology Questions 1903Document4 pagesImmunology Questions 1903microkannan100% (5)
- Autoimmune Protocol Ebook 6 19Document306 pagesAutoimmune Protocol Ebook 6 19Hrvoje100% (11)
- Innoculations The True Weapons of Mass DestructionDocument3 pagesInnoculations The True Weapons of Mass DestructionRedza100% (3)
- Immunology QuizDocument29 pagesImmunology QuizRa A GulNo ratings yet
- Adoptive Immunotherapy - Methods and Protocols - B. Ludewig, M. Hoffmann (Humana, 2005) WW PDFDocument517 pagesAdoptive Immunotherapy - Methods and Protocols - B. Ludewig, M. Hoffmann (Humana, 2005) WW PDFSilviuNo ratings yet
- Harnessing Oncolytic Virus-Mediated Antitumor ImmunityDocument111 pagesHarnessing Oncolytic Virus-Mediated Antitumor ImmunityhigginscribdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology, Lecture# 4 (Dr. Adeela Naureen)Document6 pagesIntroduction To Immunology, Lecture# 4 (Dr. Adeela Naureen)arissa noorNo ratings yet
- Immuno 2013 Course SyllabusDocument56 pagesImmuno 2013 Course Syllabusapi-239521627No ratings yet
- Jurnal Imunologi Kanker PDFDocument32 pagesJurnal Imunologi Kanker PDFwildan pratamaNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Word Document-1Document23 pagesHypersensitivity Word Document-1Dan 04No ratings yet
- Veterinary Immunology HypersensitivityDocument36 pagesVeterinary Immunology HypersensitivityBEKUMA SHIBIRUNo ratings yet
- Communicative English Final (@TMHRT - Minister)Document7 pagesCommunicative English Final (@TMHRT - Minister)Abd KedirNo ratings yet
- Biology Immunology Course HighlightsDocument34 pagesBiology Immunology Course HighlightsAhmed Asaad Majid Al Mousawi100% (1)
- Notes Pack 11.1Document4 pagesNotes Pack 11.1diahemaNo ratings yet
- Vasectomy in Men With Primary Progressive Aphasia: WZ W Z W Z y yDocument4 pagesVasectomy in Men With Primary Progressive Aphasia: WZ W Z W Z y yAdrián KupczyszynNo ratings yet
- 9700 s02 QP 2 PDFDocument12 pages9700 s02 QP 2 PDFIG UnionNo ratings yet