Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Distribution of Active Volcanoes Around The World Is Influenced by Various Geological Factors
The Distribution of Active Volcanoes Around The World Is Influenced by Various Geological Factors
Uploaded by
rachel adavan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document discusses how different types of plate boundaries and hotspots influence the global distribution of active volcanoes. Convergent plate boundaries like subduction zones produce many of the world's most explosive volcanoes, forming arcs and mountain chains parallel to the boundaries. Divergent boundaries create less explosive shield volcanoes as plates move apart and magma rises. Transform boundaries generally do not show volcanic activity but localized volcanism can occur where stresses are extensional or compressional. Hotspots unrelated to plate motions also contribute to volcanism in places like Hawaii.
Original Description:
Original Title
The distribution of active volcanoes around the world is influenced by various geological factors
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses how different types of plate boundaries and hotspots influence the global distribution of active volcanoes. Convergent plate boundaries like subduction zones produce many of the world's most explosive volcanoes, forming arcs and mountain chains parallel to the boundaries. Divergent boundaries create less explosive shield volcanoes as plates move apart and magma rises. Transform boundaries generally do not show volcanic activity but localized volcanism can occur where stresses are extensional or compressional. Hotspots unrelated to plate motions also contribute to volcanism in places like Hawaii.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe Distribution of Active Volcanoes Around The World Is Influenced by Various Geological Factors
The Distribution of Active Volcanoes Around The World Is Influenced by Various Geological Factors
Uploaded by
rachel adavanThe document discusses how different types of plate boundaries and hotspots influence the global distribution of active volcanoes. Convergent plate boundaries like subduction zones produce many of the world's most explosive volcanoes, forming arcs and mountain chains parallel to the boundaries. Divergent boundaries create less explosive shield volcanoes as plates move apart and magma rises. Transform boundaries generally do not show volcanic activity but localized volcanism can occur where stresses are extensional or compressional. Hotspots unrelated to plate motions also contribute to volcanism in places like Hawaii.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
The distribution of active volcanoes around the world is influenced by various geological
factors, primarily related to tectonic plate boundaries and hotspot activity. Here's an
overview of the different types of plate boundaries and hotspots and how they
contribute to the distribution of active volcanoes:
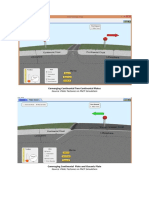
1. Convergent Boundaries (Subduction Zones):
Many of the world's most explosive and active volcanoes are found along
convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another
in a process known as subduction.
Subduction zone volcanoes often form arcs of volcanic islands or mountain
chains parallel to the boundary. Examples include the Pacific Ring of Fire, which
encircles the Pacific Ocean, and the Andes Mountains in South America.
These volcanoes typically produce highly explosive eruptions due to the
interaction between water-rich subducted oceanic crust and the overlying
continental crust.
2. Divergent Boundaries:
Divergent plate boundaries are areas where tectonic plates move away from each
other, allowing magma from the mantle to rise and create new crust.
Volcanism at divergent boundaries tends to be less explosive and more effusive,
characterized by basaltic lava flows and shield volcanoes.
Examples of divergent boundary volcanoes include those along the Mid-Atlantic
Ridge and the East African Rift.
3. Transform Boundaries:
Transform boundaries are where tectonic plates slide past each other
horizontally. While these boundaries are not typically associated with volcanic
activity, some localized volcanic activity can occur where there is extensional or
compressional stress.
Examples of transform boundary volcanoes include those in regions like the San
Andreas Fault in California.
4. Hotspots:
Hotspots
You might also like
- Distribution of VolcanoesDocument9 pagesDistribution of VolcanoesRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Filipino 10Document12 pagesFilipino 10MJ BotorNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonic Theoryrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Science, Option 2Document4 pagesScience, Option 2alyssaNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries Are The Zones Where The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Boundaries Are The Zones Where The Earthrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- VolcanismDocument6 pagesVolcanismWraith WrathNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries ActivityDocument5 pagesPlate Boundaries ActivityMaestro de GrapicoNo ratings yet
- Subject:: ModèleDocument10 pagesSubject:: ModèleAnouar ChraibiNo ratings yet
- Distribution of VolcanosDocument3 pagesDistribution of Volcanoskakozipascal2No ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument5 pagesPlate BoundariesMaria Sophia ManuelNo ratings yet
- The Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesThe Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate Boundariesrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- CH5 VolcanismDocument8 pagesCH5 VolcanismNovie GraceNo ratings yet
- Science DraftDocument4 pagesScience Draftmaster dilucNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesLesson 1 - Plate BoundariesVincent GarciaNo ratings yet
- New AgendaDocument2 pagesNew AgendaVinay YadavNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EpicentersDocument1 pageEarthquake Epicentersrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Pacific Ring of FireDocument1 pagePacific Ring of Firekrishnasri neelapuNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument6 pagesPlate Boundarieswaterresourcesyear1No ratings yet
- Volcanoes and EarthquakesDocument104 pagesVolcanoes and EarthquakesAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- g10 - Science-Sl 4 Plate Boundaries Ay 2021-2022Document4 pagesg10 - Science-Sl 4 Plate Boundaries Ay 2021-2022Mark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- Formation of VolcanoesDocument14 pagesFormation of VolcanoesLouise LawNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Epicenters Are Located in Areas With Volcanoes and Mountain RangesDocument1 pageEarthquake Epicenters Are Located in Areas With Volcanoes and Mountain Rangesoszel june balanayNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Volcanoes: VolcanoDocument18 pagesDistribution of Volcanoes: VolcanoAnne BethNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Volcanoes: VolcanoDocument18 pagesDistribution of Volcanoes: VolcanoAnne BethNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic LandformsDocument52 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic LandformsSudesh Karad0% (1)
- Earth Science 1Document1 pageEarth Science 1Rucild SurrigaNo ratings yet
- Volcanis1Document10 pagesVolcanis1Malik JawadNo ratings yet
- Els Plate-BoundariesDocument1 pageEls Plate-BoundariesMaria Pauline AsiNo ratings yet
- ValcanoDocument1 pageValcanoKeyankjNo ratings yet
- Subduction PDFDocument48 pagesSubduction PDFThea Rusia100% (1)
- Science NotesDocument55 pagesScience NotesSheila Marie U. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience Reviewereugene domingoNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries and EffectsDocument3 pagesPlate Boundaries and EffectsjnlljoyNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument16 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDemon bbyNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Week 1Document56 pagesPlate Tectonics Week 1liza rimpaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceCris Gery DiazNo ratings yet
- 3a .Physiographic Features of EarthDocument5 pages3a .Physiographic Features of EarthAzaz Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Geographical Phenomena Handout 1Document8 pagesGeographical Phenomena Handout 1kershama.charlemagneNo ratings yet
- Effects of Divergent BoundaryDocument9 pagesEffects of Divergent Boundaryalaiza cabilladaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Earth's Moving Plates What Causes VolcanoesDocument4 pagesVolcanoes and Earth's Moving Plates What Causes VolcanoesJovz BumohyaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Modules For One WeekDocument6 pagesScience 10 Modules For One WeekRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- AtarNotes Work UploadDocument57 pagesAtarNotes Work UploadKaira JogNo ratings yet
- VolvanoDocument6 pagesVolvanoZarinaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 10 ReviewerArgie Mabag100% (2)
- Caribbean Studies - Plate TectonicsDocument24 pagesCaribbean Studies - Plate TectonicsJamion Knight100% (1)
- Plate BoundariesDocument17 pagesPlate BoundariesKyle Krizzia Esplana IINo ratings yet
- On Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orDocument5 pagesOn Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orrituNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument16 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesTadiwa MawereNo ratings yet
- VOLCANODocument2 pagesVOLCANOBernadeth A. UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1663507508465 6977256196788546956-3Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1663507508465 6977256196788546956-3Brenda Ongogan DollienteNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: Natural Disasters By:Josh RahimDocument12 pagesVolcanoes: Natural Disasters By:Josh Rahimjordan rahim100% (1)
- Characteristics of Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Plate BoundariesIsla VermilionNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument5 pagesVolcanokirthmolosNo ratings yet
- Converging Continental Two Continental Plates: Source: Plate Tectonics in Phet SimulationDocument11 pagesConverging Continental Two Continental Plates: Source: Plate Tectonics in Phet SimulationanaNo ratings yet
- TraduçãoDocument3 pagesTraduçãoLeny MaziveNo ratings yet
- Seismicity Vulcanicity Associated Landforms 85Document10 pagesSeismicity Vulcanicity Associated Landforms 85Sanjana DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Some Descriptions of The Ring of Fire (Grade 11 Earth Science)Document2 pagesSome Descriptions of The Ring of Fire (Grade 11 Earth Science)Stephen BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?Document43 pagesReview Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?maris100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument14 pagesPlate TectonicsCarl AducaNo ratings yet
- The Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesThe Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate Boundariesrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EpicentersDocument1 pageEarthquake Epicentersrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument1 pageAcid and Basesrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Forming HypothesisDocument1 pageForming Hypothesisrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non MetalsDocument1 pageMetal and Non Metalsrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell Legends of LearningDocument6 pagesParts of A Cell Legends of Learningrachel adavanNo ratings yet