Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PAYMENT (Amount, Email Id, Mobile Banking, Cash On Delivery, Status)
Uploaded by
Wa 13 Extreme0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesOriginal Title
PAYMENT(amount,email id, mobile banking,cash on delivery, status)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesPAYMENT (Amount, Email Id, Mobile Banking, Cash On Delivery, Status)
Uploaded by
Wa 13 ExtremeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ASSIGNMENT - 01
NAME : Abdullah Ibna Siddiquie
ID : 21301591
COURSE : CSE320
SECTION : 07
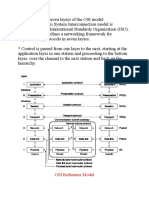
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI):
Open Systems Interconnection or the OSI model is used to understand and standardize
the functions of a telecommunication. It divides data communication into seven layers
and each is responsible for specific tasks.The OSI model was originally developed to
facilitate interoperability between vendors and to define clear standards for network
communication. There are seven layer of this model.
Layer 1: Physical Layer
The lowest layer of the OSI model is the Physical Layer. It deals with the actual
hardware, transmission, and reception of raw binary data over a physical medium. It
defines the physical characteristics of the network, such as cables, connectors, and the
transmission rate. This layer is concerned with bit-level transmission, It defines a range
of aspects, including:
1. Different types of Topologies such as Bus, Star, Ring, and Mesh.
2. Data transmission performance, such as Bit Rate and Bit Synchronization.
3. Common protocols including Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and others
4. Networking devices such as antennas, cables, modem, and intermediate devices
such as repeaters and hubs.
5. Communication modes such as Simplex, Half Duplex, and Full Duplex
6. Ensuring that data can be physically transmitted and received without errors.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
The second layer of the OSI model is The Data Link Layer. It is responsible for creating
a reliable link between two directly connected nodes. It takes the raw stream of bits from
the Physical Layer and organizes them. It defines a range of aspects, including;
1. It handles error detection and correction,
2. Ensure error-free and accurate data transmission between the network nodes.
3. Ensuring data integrity during transmission.
4. Manages access to the physical medium .
5. Performs MAC (Media Access Control) addressing.
6. Expects acknowledgement for the encapsulated raw data sent between the nodes.
Layer 3: Network Layer
The third layer of the OSI model is the Network Layer . It is concerned with the logical
addressing of devices and the efficient routing of data. It defines a range of aspects,
including:
1. Protocols such as Internet (IPv4) Protocol version 4 and Internet Protocol version
6 (IPv6).
2. The network layer implements logical addressing for data packets between the
source and destination ..
3. Routers operate at this layer.
4. End-to-end communication across multiple networks.
Layer 4: Transport Layer
The fourth layer of the OSI model is the Transport Layer. It manages end-to-end
communication and ensures the reliable delivery of data between devices. It defines a
range of aspects, including:
1. Error detection, flow control, and retransmission of lost or corrupted data.
2. It involves the service-point addressing function to ensure that the packet is sent in
response to a specific process (via a port address).
3. This layer establishes, maintains, and terminates connections.
4. Also Offering both connection-oriented (TCP) and connectionless (UDP) services.
Layer 5: Session Layer
The fifth layer of the OSI model is the Session Layer. It establishes, maintains, and
terminates communication sessions between applications. It defines a range of aspects,
including:
1. It manages the dialogue control between different processes.
2. Allow exchange of data and coordinate their communication.
3. Ensuring that data is properly organized into manageable chunks.
4. Include HTTPS sessions that allow users to visit and browse websites.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
The sixth layer of the OSI model is the Presentation Layer. It is responsible for
translating, encrypting, or compressing data . It defines a range of aspects, including:
1. Ensure that it can be properly understood by the application layer.
2. It deals with data format conversions, character encoding, and
encryption/decryption.
3. This layer enhances interoperability between different systems with varying data
formats.
Layer 7: Application Layer
The seven layer of the OSI model is the Application Layer. It is the topmost layer and
interacts directly with end-users and application software.It defines a range of aspects,
including:
1. It provides network services directly to end-users and applications
2. offer a platform-independent interface.
3. This layer includes protocols for tasks such as email, file transfer, and remote
access.
Network administrators and engineers must comprehend the OSI model in order to
diagnose problems, create effective networks, and guarantee system interoperability.
Every layer contributes to the smooth transfer of data across various networks and is
essential to the entire communication process.
You might also like
- Network 2Document19 pagesNetwork 2jhn75070No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledJoven Andrei R. LagahitNo ratings yet
- CNDocument2 pagesCNweirdshers07No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2trapti191967No ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument3 pagesOSI ModelManasa VanamNo ratings yet
- MPDFDocument8 pagesMPDFTommy ElmaghrabyNo ratings yet
- Networking 2: It 219: Lesson IvDocument19 pagesNetworking 2: It 219: Lesson IvKlim Hazel Racal LumansocNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Any One Layer of OSI ModelDocument8 pagesCase Study On Any One Layer of OSI ModelDharmesh VaishNo ratings yet
- Explain OSI Model and All Seven LayersDocument7 pagesExplain OSI Model and All Seven Layerskhan.hassanijazNo ratings yet
- Network Model ArchitectureDocument15 pagesNetwork Model ArchitectureMahiNo ratings yet
- PhishingDocument2 pagesPhishingFrancis FinanNo ratings yet
- Polangui Campus: Republic of The Philippines Bicol UniversityDocument4 pagesPolangui Campus: Republic of The Philippines Bicol Universitymark carlo SanorjoNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument10 pagesOSI ModelRajkumar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Osi Model-AnubhavDocument8 pagesOsi Model-AnubhavAvnit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Osi Model: Neeraj Kumar Jangid B.Tech ECE 3 Year A2 Roll - no:-09MUBECE049Document17 pagesOsi Model: Neeraj Kumar Jangid B.Tech ECE 3 Year A2 Roll - no:-09MUBECE049neerajjangidNo ratings yet
- Datacomm AssDocument4 pagesDatacomm AssKicave BlogNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument97 pagesOSI Modelchowsaj9No ratings yet
- Network Protocol and OSI ModelDocument4 pagesNetwork Protocol and OSI Modelwhen your pizza rolls are goneNo ratings yet
- Network Protocol and OSI ModelDocument4 pagesNetwork Protocol and OSI ModelmerricpremantonyNo ratings yet
- The OSI Reference Model PDFDocument10 pagesThe OSI Reference Model PDFm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument18 pagesOSI ModelShashank Tewari100% (1)
- OSI ModelDocument15 pagesOSI ModelRiajiminNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Cn: Syeda Pakiza ImranDocument5 pagesAssignment-Cn: Syeda Pakiza Imrannauman tariqNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Networks 15B11EC611: Dr. Bhagirath Sahu Assistant Professor, JIIT, NoidaDocument15 pagesTelecommunication Networks 15B11EC611: Dr. Bhagirath Sahu Assistant Professor, JIIT, NoidaMOHAMMED FAYEZ KHANNo ratings yet
- Iso Osi TCP IpDocument18 pagesIso Osi TCP Ipkrishna kant yadav 088No ratings yet
- Presentation of Osi ModelDocument18 pagesPresentation of Osi ModelSahil KrazzyoneNo ratings yet
- Explain ISO - OSI, Seven Layer Network Architecture Giving The Functions of Each LayerDocument1 pageExplain ISO - OSI, Seven Layer Network Architecture Giving The Functions of Each LayerAbdulhaq SadiqiNo ratings yet
- Rakibul Hasan EmonDocument3 pagesRakibul Hasan EmonRakibul Hasan EmonNo ratings yet
- OSI 7 LayerDocument14 pagesOSI 7 LayervictorNo ratings yet
- The Open System InterconnectionDocument2 pagesThe Open System InterconnectionRohitha6lasanthaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication S: Lecture - 3Document42 pagesData Communication S: Lecture - 3Fr Sunny100% (1)
- Osi Model: Communication ArchitectureDocument6 pagesOsi Model: Communication ArchitecturetharunkuttiNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument16 pagesOSI ModelPratik SapkalNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument5 pagesOSI ModelWasif QaziNo ratings yet
- He OSI Model - Features, Principles and LayersDocument6 pagesHe OSI Model - Features, Principles and LayersLALITHA BALASUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- Communication: FundamentalsDocument17 pagesCommunication: FundamentalsBobbyNo ratings yet
- OSI 7 Layers Reference Model For Network CommunicationDocument1 pageOSI 7 Layers Reference Model For Network CommunicationShaneDmxNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument3 pagesOsi ModelTaonaishe Hastings MuzavaziNo ratings yet
- Iso Osi ModelDocument7 pagesIso Osi ModelSasiNo ratings yet
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument22 pagesNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineeringআসিফ রেজাNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument32 pagesOSI ModelBhanu Singh0% (1)
- OSI Reference Model With 7 LayersDocument5 pagesOSI Reference Model With 7 LayersDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OSI ModelDocument13 pagesChapter 5 OSI ModelMem MemNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument1 pageOSI Modelomerkhadim2No ratings yet
- BCA4010 Computer NetworkingDocument8 pagesBCA4010 Computer NetworkingNaveen TirthaniNo ratings yet
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument22 pagesNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringJoyNo ratings yet
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument22 pagesNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringBlue BloodNo ratings yet
- The OSI ModelDocument15 pagesThe OSI ModelTariku MehdiNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Osi ModelDocument11 pagesGroup 3 - Osi ModelRhynne T.No ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument10 pagesOSI ModelJayalle PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Physical (Layer 1) : Stack That Consists of The Following LayersDocument9 pagesPhysical (Layer 1) : Stack That Consists of The Following LayersZahoor ahmedNo ratings yet
- The OSI Model - Features, Principles and LayersDocument7 pagesThe OSI Model - Features, Principles and LayersJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Network Support LayersDocument3 pagesNetwork Support LayersAbdelrhman AhmedNo ratings yet
- 02 - OSI Model ReviewDocument2 pages02 - OSI Model ReviewQosai ZoubiNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument17 pagesOsi ModelPiyush RajputNo ratings yet
- Reference Models in Communication NetworksDocument7 pagesReference Models in Communication NetworksPRODIP DEBNo ratings yet
- CN KCS-603 Important Questions SolvedDocument162 pagesCN KCS-603 Important Questions SolvedVikas RajpootNo ratings yet
- OSI Model EssayDocument9 pagesOSI Model EssayKyle BeestMode Lynch100% (1)
- Welcome To Politeknik Tuanku Sultanah Bahiyah.: For PLC and CX-Programmer Training CourseDocument33 pagesWelcome To Politeknik Tuanku Sultanah Bahiyah.: For PLC and CX-Programmer Training CoursemajitraNo ratings yet
- Kerberos ChartDocument1 pageKerberos ChartkshehzadNo ratings yet
- BArring PArametersDocument5 pagesBArring PArametersQasim Abbas AlviNo ratings yet
- Deploying AMI SolutionsDocument6 pagesDeploying AMI SolutionsPithoon UngnaparatNo ratings yet
- TmaDocument3 pagesTmaSteveAbonyiNo ratings yet
- Instalar Win Desde USB WinSetupFromUSB 1Document3 pagesInstalar Win Desde USB WinSetupFromUSB 1luisabetoNo ratings yet
- IMP - Step by Step Guide To Install SAProuterDocument2 pagesIMP - Step by Step Guide To Install SAProuterRashed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Short QuestionDocument4 pagesCyber Security Short QuestionDharmanshu MerNo ratings yet
- RFC 3551Document6 pagesRFC 3551jupivipaNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide: Dell EMC Integrated Data Protection Appliance DP4400Document18 pagesInstallation Guide: Dell EMC Integrated Data Protection Appliance DP4400Emre Halit POLATNo ratings yet
- VPN - Direct Connection Using The 2ndDocument18 pagesVPN - Direct Connection Using The 2ndmozzpunkzNo ratings yet
- Inter MSC HandoffDocument2 pagesInter MSC HandoffMrinal MondalNo ratings yet
- HP Z4 G4 WorkstationDocument73 pagesHP Z4 G4 WorkstationMArceloNo ratings yet
- SS7 SignalingDocument97 pagesSS7 SignalingvigneshNo ratings yet
- NPort W2150 W2250 PlusDocument4 pagesNPort W2150 W2250 PlusToroomNo ratings yet
- Culture, Communication and Media: How Do Media Shape Our Views of Others?Document18 pagesCulture, Communication and Media: How Do Media Shape Our Views of Others?Ngân LêNo ratings yet
- P1001071-01-Rev 01-Varian Oncology Services Installation Instructions and Configuration Guide ARIA OISDocument30 pagesP1001071-01-Rev 01-Varian Oncology Services Installation Instructions and Configuration Guide ARIA OISmemo muroNo ratings yet
- Cyclades ACS ManualDocument210 pagesCyclades ACS ManualMatthew Omogbai EhiwereNo ratings yet
- ToolsNet 4000 Installation Guide (9836418101)Document72 pagesToolsNet 4000 Installation Guide (9836418101)Anton KazakovNo ratings yet
- Spring Cloud SleuthDocument31 pagesSpring Cloud SleuthtejpremiumNo ratings yet
- SE1213 - Xightor PRO Product DatasheetDocument1 pageSE1213 - Xightor PRO Product Datasheetleanh121No ratings yet
- Kerberos Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesKerberos Seminar ReportNaveen Krishnan100% (2)
- Pres June2010Document44 pagesPres June2010iklan amirNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeDevesh BharathanNo ratings yet
- Yealink - SIP-T21P-E2 - Datasheet - by LATNOK CDDocument2 pagesYealink - SIP-T21P-E2 - Datasheet - by LATNOK CDCoko Mirindi MusazaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 3Document5 pagesResearch Paper 3anon_899268215No ratings yet
- CP Unc Ta21pl3 GP yDocument5 pagesCP Unc Ta21pl3 GP yDesign TeamNo ratings yet
- Scientific Atlanta DPC2100 CableModem XSRFDocument2 pagesScientific Atlanta DPC2100 CableModem XSRFNexus VyasNo ratings yet
- Brkarc 2031Document115 pagesBrkarc 2031tuan anh nguyenNo ratings yet
- Experiment Title.: Scope of IT Audit of UniversityDocument3 pagesExperiment Title.: Scope of IT Audit of UniversityDraKon GamingNo ratings yet