Professional Documents
Culture Documents
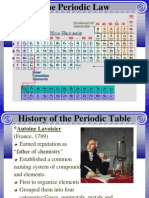
A Periodic Table Logic Problem
Uploaded by
kjj77600 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views2 pagesA Periodic Table Logic Problem
Uploaded by
kjj7760Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
A Periodic Table Logic Problem
Purpose: In this activity you will use a set of clues to identify a set of unknown
elements in a periodic table. The elements are the elements with atomic numbers
1-20 and 31-36. A letter of the alphabet is used to represent each unknown
element. The letter designation is not related to an element’s chemical symbol.
Each clue refers to a property of an element or a relationship an element has to
other elements in the periodic table. Along with logic and knowledge of
properties, you will use the periodic trends to solve the puzzle.
Grade: Neatness and completeness count.
Procedure: Use the following trend clues to place the elements in their proper
places on the provided periodic table. Try to identify the elements with direct
clues first. For example, B is a direct clue because it identifies only one element.
Group 1 Group 2 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 Group 18
Work copy
Group Group Group Group Group Group Group Group
1 2 13 14 15 16 17 18
A – Has one of the highest electronegativities on the table.
B – Has one electron in a 3p orbital.
C – Has five electrons in the 4th energy level.
D – Forms the smallest 2+ ion.
E – Tends to gain one electron.
F – Electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
G – The most electronegative element.
H – An ion of this element with a 2+ charge has 18 electrons.
I – Its second ionization energy is large compared to its first ionization energy.
Perodic table properties
J – Its highest occupied energy level is full.
K – This nonmetal is likely to form an ion with a 3- charge.
L – Has the highest 1st ionization energy in the table.
M – Has the smallest atomic radius in the 3rd period.
N – Is the smallest atom in its family.
O – The first element with an electron in the 2nd energy level.
P – The only nonmetal in a group of highly reactive metals.
Q – Has eight fewer protons than its “groupmate” H.
R – The most likely element of the ones included to lose an electron.
S – A metalloid in period 4.
T – Its ionic radius is larger than its atomic radius.
U – The ion with a 2- charge that it forms has 18 electrons.
V – Atomic number is 34.
W – Metalloid that forms an anion with a 3+ charge.
X – Has characteristics of both a metal and a nonmetal.
Y – Has a lower 1st ionization energy than S.
Z – Has a 1st ionization energy that is higher than T but lower than M.
Ready to turn in?: Copy the clues with the corresponding answers and the filled
in chart into your lab book..
Group Group Group Group Group Group Group Group
1 2 13 14 15 16 17 18
Your partners:
1.
2.
3.
Perodic table properties
You might also like
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Kids | Elements, Acid-Base Reactions and Metals Quiz Book for Kids | Children's Questions & Answer Game BooksFrom EverandChemistry for Kids | Elements, Acid-Base Reactions and Metals Quiz Book for Kids | Children's Questions & Answer Game BooksNo ratings yet
- Chemis IX Chapter-04 PDFDocument5 pagesChemis IX Chapter-04 PDFJsusNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Presentation1Document37 pagesPeriodic Table Presentation1AnonymousGodiswithyouNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic Table of ElementsDocument5 pagesModern Periodic Table of ElementsAriful Hassan SaikatNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements - KPDocument4 pagesClassification of Elements - KPKiran KiruNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument58 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsMichelle Casayuran - RegalaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Law InstructionsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Law InstructionsHazel Ann Orevillo AuditorNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3Document12 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3Bijay SchoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 4 Periodicity of ElementsDocument4 pagesChapter # 4 Periodicity of ElementsCadet HadeedNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument10 pagesPeriodic Tableapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Science Booklet Prep 2 First Term 2015-2016Document59 pagesScience Booklet Prep 2 First Term 2015-2016Zeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument8 pagesPeriodic Tablechaitramallu.mNo ratings yet
- Martianperiodicactivity 1Document2 pagesMartianperiodicactivity 1api-356360575No ratings yet
- Periodic LawDocument2 pagesPeriodic LawThea KyutNo ratings yet
- The Periodic LawDocument33 pagesThe Periodic Lawviolaplayer09No ratings yet
- PMT CH (4) 1d) The Periodic Table PDFDocument3 pagesPMT CH (4) 1d) The Periodic Table PDFEric TTLNo ratings yet
- 29-03CBSE10th (N A)Document32 pages29-03CBSE10th (N A)Namrata GoelNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table (QuestionsDocument11 pagesPeriodic Table (QuestionsDiya ChandaniNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Imp ch3 2 PDFDocument5 pages11 Chemistry Imp ch3 2 PDFSandeep JainNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 LESSON 13 Periodic Relationships Among ElementsDocument22 pagesCHEM1 LESSON 13 Periodic Relationships Among ElementsLoraine CastroNo ratings yet
- Science Prep.2Document64 pagesScience Prep.2Mayar DahyNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table - PPT 2019 ClassDocument22 pagesThe Periodic Table - PPT 2019 Classgn28tkxph6No ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2021 112746435Document12 pagesMUCLecture 2021 112746435Talent of galaxyNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument21 pagesPeriodic TableSanyam jainNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table WorksheetDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table Worksheetadela50% (2)
- Class XI Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties NotesDocument5 pagesClass XI Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- Science BookletDocument91 pagesScience Bookletmarc.habib2010No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument44 pagesPeriodic TableKithminiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument58 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNevin ShajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Atoms and MatterDocument44 pagesChapter 2-Atoms and MatterNajma AqilahNo ratings yet
- Color Coding The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesColor Coding The Periodic TableEthanTranNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Nov. 16 Chemical Bonding Grade 9Document11 pagesLesson Plan in Nov. 16 Chemical Bonding Grade 9Edessa Masinas100% (1)
- The Periodic TableDocument33 pagesThe Periodic TableIra MunirahNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument17 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elementsapi-24735088286% (7)
- Periodic Classification of Elements X NotesDocument5 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements X NotesVenkatesan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Booklet Prep Two First TermDocument81 pagesBooklet Prep Two First Termfmjcy8bqs5No ratings yet
- 3 - Classification of ElementsDocument10 pages3 - Classification of ElementsV̶a̶i̶s̶h̶n̶a̶v̶No ratings yet
- Periodic Table PowerpointDocument26 pagesPeriodic Table PowerpointCindy De Guzman TandocNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements (Chemistry Notes)Document4 pagesAtoms and Elements (Chemistry Notes)wlkernanNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Groups Periods Atomic Number Explained 7b24244bDocument14 pagesThe Periodic Table Groups Periods Atomic Number Explained 7b24244bmithiraiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure Notes by Aung Kyaw SwarDocument9 pagesElectronic Structure Notes by Aung Kyaw Swarေအာင္ ေက်ာ္ စြာNo ratings yet
- Identify The Demarcation of The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesIdentify The Demarcation of The Periodic TableRana Irfan100% (1)
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic TableufazgymNo ratings yet
- Lesson - The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesLesson - The Periodic TableramyaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 1 NotesDocument7 pages2 2 1 Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementDocument7 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elementkrushnakadam0029No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument21 pagesPeriodic Tableapi-449002661No ratings yet
- Periodic Table MysteryDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table MysteryBei Cab0% (2)
- The Organization of The Periodic Table Directions: 18 GroupsDocument7 pagesThe Organization of The Periodic Table Directions: 18 GroupsArin ATANo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Atoms & The Peiodic Table - Topic BDocument36 pagesElectronic Structure of Atoms & The Peiodic Table - Topic Bphonepyaehtut2006No ratings yet
- Physics and Chemistry Unit 4Document2 pagesPhysics and Chemistry Unit 4sērgîö :DNo ratings yet
- Notes For Science Diagnostic GR 8Document19 pagesNotes For Science Diagnostic GR 8Ma Simone Alexine CasaoNo ratings yet
- 3.classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Some Important Points and Terms of The ChapterDocument7 pages3.classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Some Important Points and Terms of The ChapterShivaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3Document11 pagesThe Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3المونتاج الاخيرNo ratings yet
- Outline CH 3Document4 pagesOutline CH 3lexusredpbNo ratings yet
- C3 - The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesC3 - The Periodic TableEdward HarveyNo ratings yet
- 10 TH CBSEDocument29 pages10 TH CBSENamrata GoelNo ratings yet
- Headout Ticket - 10898242Document6 pagesHeadout Ticket - 10898242kjj7760No ratings yet
- 27452-WAL Chemistry 06 ResultsDocument1 page27452-WAL Chemistry 06 Resultskjj7760No ratings yet
- 27437-WAL Chemistry 03 CarbonCycleGame WorksheetDocument1 page27437-WAL Chemistry 03 CarbonCycleGame Worksheetkjj7760No ratings yet
- Killer Backs' MovesDocument8 pagesKiller Backs' Moveskjj7760No ratings yet
- We Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 2 (Chemistry) : Build A Molecule GameDocument1 pageWe Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 2 (Chemistry) : Build A Molecule Gamekjj7760No ratings yet
- We Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 6 (Chemistry) : Using UV Beads To Investigate Reaction RatesDocument2 pagesWe Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 6 (Chemistry) : Using UV Beads To Investigate Reaction Rateskjj7760No ratings yet
- We Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 8 (Chemistry) Ice Core AnalysisDocument13 pagesWe Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 8 (Chemistry) Ice Core Analysiskjj7760No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Problem Set 2 Reactions of BenzeneDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry II Problem Set 2 Reactions of Benzenekjj7760No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Problem Set 7 Solutions Synthesis: C O CL H CDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Problem Set 7 Solutions Synthesis: C O CL H Ckjj7760No ratings yet
- We Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 8 (Chemistry) : Could Life Exist in This Ice Core?Document1 pageWe Are Aliens! - Class Room Activity 8 (Chemistry) : Could Life Exist in This Ice Core?kjj7760No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Problem Set 1-5 Reactions of Benzene DerivativesDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry II Problem Set 1-5 Reactions of Benzene Derivativeskjj7760No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Problem Set 3 Reaction of Substituted BenzeneDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Problem Set 3 Reaction of Substituted Benzenekjj7760No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Problem Set 7 Synthesis: C O CL H CDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Problem Set 7 Synthesis: C O CL H Ckjj7760No ratings yet
- Subject ChemistryDocument17 pagesSubject Chemistrykjj7760No ratings yet
- Introduction To VSEPR Theory and Molecular GeometryDocument10 pagesIntroduction To VSEPR Theory and Molecular Geometrykjj7760No ratings yet
- Chapter: Chemical EqulibriumDocument13 pagesChapter: Chemical Equlibriumkjj7760No ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument71 pages1.0 Introduction To Organic Chemistrykjj7760No ratings yet
- The Common Core English Language Arts Standards (CCELA)Document2 pagesThe Common Core English Language Arts Standards (CCELA)kjj7760No ratings yet
- Detailed List of Effect PacksDocument14 pagesDetailed List of Effect Packskjj7760No ratings yet
- Development of Augmented Reality Teaching Materials of Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Augmented Reality Teaching Materials of Chemical Bondingkjj7760No ratings yet
- A Survey of Augmented Reality-AzumaDocument48 pagesA Survey of Augmented Reality-AzumaGuilherme Teles da MotaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On Alkane Nomenclature: CH CHDocument2 pagesPractice Problems On Alkane Nomenclature: CH CHRishav Sasmal100% (1)
- C1 - PCCDocument8 pagesC1 - PCCkjj7760No ratings yet
- TEST YOURSELF 1 Answers OnlyDocument1 pageTEST YOURSELF 1 Answers Onlykjj7760No ratings yet
- Literature Summary TableDocument1 pageLiterature Summary Tablekjj7760No ratings yet
- Poster Pertandingan InovasiDocument1 pagePoster Pertandingan Inovasikjj7760No ratings yet
- Epson EB-600x Series (NoAddress)Document12 pagesEpson EB-600x Series (NoAddress)Anonymous gMgeQl1SndNo ratings yet
- C1 - PCCDocument8 pagesC1 - PCCkjj7760No ratings yet
- QUIZ#01Document8 pagesQUIZ#01kjj7760No ratings yet
- PT Ws 2 GlencoepttransparencieskeyDocument2 pagesPT Ws 2 Glencoepttransparencieskeykjj7760No ratings yet
- 1 Ajrc 5 11 2012 PDFDocument9 pages1 Ajrc 5 11 2012 PDFRaga BimaNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument10 pagesMetalsPeterNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of ChemistryDocument16 pagesSome Basic Concept of ChemistryInsane insaanNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Phytochemical Analysis of Various Parts of Bamboo (Bambusa Balcooa) For Possible Therapeutic Usages in Bovine Reproductive DisordersDocument5 pagesQualitative Phytochemical Analysis of Various Parts of Bamboo (Bambusa Balcooa) For Possible Therapeutic Usages in Bovine Reproductive DisordersMarie Del CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Data Sheet Stage 2 and Stage 3 2015Document2 pagesChemistry Data Sheet Stage 2 and Stage 3 2015serena123456No ratings yet
- Unit 14Document61 pagesUnit 14KerredaiNo ratings yet
- Topic II Basic Principles of Extraction of Metals From Ores & PurificationDocument31 pagesTopic II Basic Principles of Extraction of Metals From Ores & PurificationKing of KingsNo ratings yet
- Alloys in FPDDocument6 pagesAlloys in FPDharshita parasharNo ratings yet
- Acid and Alkali Soal 3Document1 pageAcid and Alkali Soal 3Adipta MartulandiNo ratings yet
- Flue Gas Desulfurization at High Temperatures: A ReviewDocument24 pagesFlue Gas Desulfurization at High Temperatures: A ReviewHuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Electropolishing: Process Considerations: Better Chemistry. Better BusinessDocument3 pagesElectropolishing: Process Considerations: Better Chemistry. Better Businessjuan carlos pulidoNo ratings yet
- The Potentials of Henna (L) Leaves Extracts As Counter Stain in Gram Staining ReactionDocument5 pagesThe Potentials of Henna (L) Leaves Extracts As Counter Stain in Gram Staining ReactionAna Virginia MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Sundow Polymers Co., LTD.: Surpren SN244Document1 pageSundow Polymers Co., LTD.: Surpren SN244Phuong The NguyenNo ratings yet
- SCH4U Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesSCH4U Exam Reviewtaya guyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Extra Edge Topics For NEET 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesChemistry - Extra Edge Topics For NEET 2020 PDFalishNo ratings yet
- S Block ChemhaackDocument13 pagesS Block ChemhaackDrushya SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Dapus Rekristalisasi.Document35 pagesDapus Rekristalisasi.RamaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry: A Suitable Detection Technique in Speciation Studies For Arsenic, Selenium, Antimony and MercuryDocument15 pagesAtomic Fluorescence Spectrometry: A Suitable Detection Technique in Speciation Studies For Arsenic, Selenium, Antimony and MercuryZain Shah Zain ShahNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic BrochureDocument33 pagesCosmetic BrochureJorgeNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Carbon and Its Compound DPP - 01Document1 pageCH 4 Carbon and Its Compound DPP - 01HemantBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Polymeric Materials From Petroleum ModDocument21 pagesChapter 9 Polymeric Materials From Petroleum ModAbdurabu AL-MontaserNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Test Plan (Itp) : PilingDocument3 pagesInspection & Test Plan (Itp) : PilingLOPA THANDARNo ratings yet
- AOCS-Da2a - 48 Moisture and Volatile Matter in Soap and Soap Products, Air Oven Method PDFDocument3 pagesAOCS-Da2a - 48 Moisture and Volatile Matter in Soap and Soap Products, Air Oven Method PDFwilNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks Igneous Rock: There Are Two Basic TypesDocument4 pagesTypes of Rocks Igneous Rock: There Are Two Basic TypesBELENNo ratings yet
- Synonyms Module 1Document2 pagesSynonyms Module 1Ark Olfato ParojinogNo ratings yet
- Ind Biotech...Document27 pagesInd Biotech...Mario ForeverNo ratings yet
- Silicone Resin Binders: Silsan® WR1750 WR1800 HSB Hsb-Gs WRF MSR 6575Document7 pagesSilicone Resin Binders: Silsan® WR1750 WR1800 HSB Hsb-Gs WRF MSR 6575Deiby AraujoNo ratings yet
- C5 Chemical Changes Exam Question Pack: 119 Minutes 119 MarksDocument28 pagesC5 Chemical Changes Exam Question Pack: 119 Minutes 119 MarksequakeroatsNo ratings yet
- Spec I Task 4 Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesSpec I Task 4 Classification of MatterJERIEL MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Silver SulphateDocument5 pagesElectrolysis of Silver SulphateJackson_de_Roz_6005100% (1)