Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V
Uploaded by
bsuma.jeevuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V
Uploaded by
bsuma.jeevuCopyright:
Available Formats
UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS
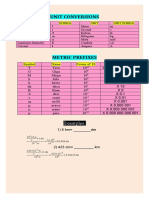
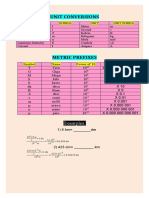
Common SI prefixes:
Multiples and Submultiples Prefixes Symbols
1 000 000 000 000 tera T
1000 000 000 giga G
1 000 000 mega M
1000 kilo k
100 hecto h
10 deka da
Base unit: 1
0.1 deci d
0.01 centi c
0.001 milli m
0.000 001 micro
0.000 000 001 nano n
0.000 000 000 001 pico p
0.000 000 000 000 001 femto f
0.000 000 000 000 000 001 atto a
Measurement of length: Length of various objects or distances between the objects differ widely
ranging from the radius of proton of about 10-15m to the average size of the universe with a radius
of about 1026m.
Some of the simple measurement of length involves the use of
a) A metre scale for lengths from 10-3m to 102m.
b) Vernier callipers for lengths to accuracy of about 10-4m.
c) A screw gauge or spherometer to measure lengths of the order of 10-5m.
In order to measure lengths beyond these ranges some special indirect methods are adopted.
One of them is the parallax method.
Parallax: It is the change in the position of an object to its background, when the object is seen
from two different positions.
The distance between the two different points of observation is called the Basis.
Measurement of large distance by parallax method:
Let and are the two positions of observation of a distant object .
Let be the distance between the distant object and the earth.
The distance between and be
be the angle made by two opposite ends and .
Then,
Where is in radian and is called parallactic angle.
U N Swamy, Lecturer in Physics, GPUC Aranakatte, Hiriyur Taluk Page | 3
You might also like
- Gen Physics 1Document2 pagesGen Physics 1Clyde SingsonNo ratings yet
- Q2 - MeasurementsDocument4 pagesQ2 - MeasurementsgundamstrikejusticeNo ratings yet
- English To Metric Sytem ConversionDocument1 pageEnglish To Metric Sytem ConversionRanz RodgerNo ratings yet
- Converting Units of Base QuantityDocument2 pagesConverting Units of Base QuantityZi SongNo ratings yet
- Converting Units of Base QuantityDocument2 pagesConverting Units of Base QuantityZi Song100% (1)
- PHYSICS1111Document201 pagesPHYSICS1111Kaone LakayNo ratings yet
- The Metric SystemDocument2 pagesThe Metric SystemtaiNo ratings yet
- Metric PrefixesDocument2 pagesMetric PrefixesmichaelcviennaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ScienceBrandon LawNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversion Factors: Shuhong WangDocument5 pagesUnits and Conversion Factors: Shuhong Wangoblex99No ratings yet
- Basics - Study GuideDocument7 pagesBasics - Study GuideVũ NamNo ratings yet
- Banner Data Tables PDFDocument11 pagesBanner Data Tables PDFpotNo ratings yet
- Jhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1Document308 pagesJhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1Thoko SimbeyeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Booklet Triple AwardDocument202 pagesPHYSICS Booklet Triple Awardrose tebogoNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversions PDFDocument33 pagesUnits and Conversions PDFiayamaeNo ratings yet
- ฟิสิกส์Document17 pagesฟิสิกส์nukul angsopaNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion and Scientific NotationDocument7 pagesUnit Conversion and Scientific NotationGanda SuriaNo ratings yet
- General Physics Week 1 4Document23 pagesGeneral Physics Week 1 4Yona SpadesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Units and Conversion FactorsDocument6 pagesEngineering Units and Conversion Factorssyira_syahirahNo ratings yet
- Notes On Measurements1Document9 pagesNotes On Measurements1tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Chapter # 01 Short Questions: ScientiaDocument9 pagesChapter # 01 Short Questions: ScientiaAhmed MalikNo ratings yet
- Math FormulasDocument173 pagesMath Formulasrajkumar.manjuNo ratings yet
- Units of Measurement: LessonDocument26 pagesUnits of Measurement: Lessongavint skynardNo ratings yet
- SI UnitsDocument1 pageSI UnitsluameiacheiaNo ratings yet
- Physics 5024 Complete 2Document225 pagesPhysics 5024 Complete 2Sechelanji siwilaNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Metric System UnitsDocument3 pagesCommonly Used Metric System UnitsPaola Andrea Fdezds Abdul-RahimNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Chemistry - For - Engineers - 1 - Basic - Concepts - Topic - 02 - Student - Review - On - MeasurementDocument12 pages2.2 Chemistry - For - Engineers - 1 - Basic - Concepts - Topic - 02 - Student - Review - On - MeasurementJay GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- ADMModule STEM GP12EU-Ia-1Document8 pagesADMModule STEM GP12EU-Ia-1Kirby MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Annie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 M 2.1aDocument18 pagesUnit 2 M 2.1amarisNo ratings yet
- GP1 - MeasurementsDocument19 pagesGP1 - MeasurementsMark Anthony AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Science 5124 (Physics) Final-1 PDFDocument56 pagesScience 5124 (Physics) Final-1 PDFMapalo Chirwa100% (2)
- 1 Physical QuantitiesJannyDocument64 pages1 Physical QuantitiesJannyChristian PustanesNo ratings yet
- Metric System: Prefix Symbol Multiplication Factor Scientific NotationDocument2 pagesMetric System: Prefix Symbol Multiplication Factor Scientific Notationjohn FlanneryNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditDocument19 pagesFundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditMohamad Radhahudin100% (1)
- The SI Prefixes or Metric Prefixes Are An Indicator That Precedes A Basic Unit of Measure To Indicate A Multiple or Sub-Multiple of The UnitDocument3 pagesThe SI Prefixes or Metric Prefixes Are An Indicator That Precedes A Basic Unit of Measure To Indicate A Multiple or Sub-Multiple of The UnitMathilda YapNo ratings yet
- Units of Measurement ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnits of Measurement ObjectivesErienne IbanezNo ratings yet
- Physics 5054 PDFDocument60 pagesPhysics 5054 PDFWilfred PhiriNo ratings yet
- Appendix I: Si and English Units and Conversion FactorsDocument7 pagesAppendix I: Si and English Units and Conversion FactorsAdi CunNo ratings yet
- Ge Elect 110 Module 1Document5 pagesGe Elect 110 Module 1Hassel AbayonNo ratings yet
- UnitsDocument27 pagesUnitsKithminaNo ratings yet
- Topic: Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementDocument13 pagesTopic: Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementKripa mariam JosephNo ratings yet
- Measurement LessonDocument15 pagesMeasurement LessonMatthew SonntagNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionsDocument1 pageUnit ConversionsemilieNo ratings yet
- Phy NotesDocument222 pagesPhy NotesNunu KheesNo ratings yet
- Conversion Chart: Length Units How To ConvertDocument2 pagesConversion Chart: Length Units How To Convertdaisuke ʕ•ᴥ•ʔNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Gen ChemDocument10 pagesModule 4 Gen ChemMaster BeaterNo ratings yet
- 5124 PhysicsDocument176 pages5124 PhysicsChristine BandaNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionsDocument1 pageUnit ConversionsemilieNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionsDocument1 pageUnit ConversionsemilieNo ratings yet
- General-Physics-1 Q1 W1 M1 LDS Measurements ALG RTPDocument13 pagesGeneral-Physics-1 Q1 W1 M1 LDS Measurements ALG RTPKaye Cee GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Conversion TableDocument3 pagesConversion TableCrystL SnowNo ratings yet
- MetrologyDocument132 pagesMetrologyAd Man GeTig0% (1)
- Number Scales - Ten Hundred Thousand Million Billion Milli MicroDocument1 pageNumber Scales - Ten Hundred Thousand Million Billion Milli MicroRAJAMANICKAMNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - MechanicsDocument4 pagesWeek 6 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- App1Document7 pagesApp1Duy Hoai TranNo ratings yet
- Metric PrefixesDocument1 pageMetric PrefixesKaitlynne Mae GamboaNo ratings yet
- Si Units Metric Prefixes Sci NotationDocument2 pagesSi Units Metric Prefixes Sci NotationJenna McAdamNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 1B NovDocument1 page1B Novbsuma.jeevuNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument1 pageMotion Along A Straight Linebsuma.jeevuNo ratings yet
- F 1Document1 pageF 1bsuma.jeevuNo ratings yet
- WDocument1 pageWbsuma.jeevuNo ratings yet
- 1 Puc Notes PDFDocument185 pages1 Puc Notes PDFbsuma.jeevuNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Grammar Teaching On Writing Development PDFDocument18 pagesThe Effect of Grammar Teaching On Writing Development PDFRIANNo ratings yet
- Def ReadingDocument1 pageDef ReadingJembus WedutNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Science 4 Activity Sheet No. 6Document2 pagesQuarter 1 Science 4 Activity Sheet No. 6karol melendezNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Portal Frame Structure With ETABS PDFDocument19 pagesAnalysis of Portal Frame Structure With ETABS PDFAnonymous OynOOfNo ratings yet
- Ais For PROTONDocument18 pagesAis For PROTONAfaf RadziNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp C1 U4 Lang Test BDocument2 pagesGold Exp C1 U4 Lang Test Bmaituti1No ratings yet
- Intelligent Control LED Integrated Light Source: Features and BenefitsDocument6 pagesIntelligent Control LED Integrated Light Source: Features and BenefitsRazvy StoianNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Midterms GRASPSDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Midterms GRASPSAlbert RoseteNo ratings yet
- Data Mining in The Insurance Industry - Solving Business Problems Using SAS Enterprise Miner SoftwareDocument20 pagesData Mining in The Insurance Industry - Solving Business Problems Using SAS Enterprise Miner SoftwareShehan1No ratings yet
- Rapport - FEEDBACK INFRA - ODIENNE - V01 - ANGLAISDocument25 pagesRapport - FEEDBACK INFRA - ODIENNE - V01 - ANGLAISabertoNo ratings yet
- AI Learning ResourcesDocument6 pagesAI Learning Resourcesrip asawNo ratings yet
- Chrome OS Recovery - Does Not Detect Image - Foros de Productos de GoogleDocument6 pagesChrome OS Recovery - Does Not Detect Image - Foros de Productos de GoogleIsrael MarinoNo ratings yet
- DLL Format LandscapeDocument2 pagesDLL Format Landscapewilflor romeroNo ratings yet
- Anth 1020 Natural Selection Lab ReportDocument4 pagesAnth 1020 Natural Selection Lab Reportapi-272845435No ratings yet
- Sedimentary Basins of IndiaDocument90 pagesSedimentary Basins of IndiaSrikanta Khuntia100% (6)
- Daftar BukuDocument6 pagesDaftar Bukuretnopamungkas55yahoNo ratings yet
- International Baccalaureate ProgrammeDocument5 pagesInternational Baccalaureate Programmeapi-280508830No ratings yet
- Kriging InterpolationDocument49 pagesKriging InterpolationJimmy MaharadjaNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE Class VIII Practice PaperDocument8 pagesFIITJEE Class VIII Practice PaperD Samy100% (1)
- Science Investigatory Project PDFDocument2 pagesScience Investigatory Project PDFNick john CaminadeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsJssy May71% (17)
- Chapter One 1.1. Background of The Study: Iloilo City's Heritage Tourist Destinations Are Worth Keeping ForDocument2 pagesChapter One 1.1. Background of The Study: Iloilo City's Heritage Tourist Destinations Are Worth Keeping ForCrisNo ratings yet
- Glickman (1) - Ethical and Scientific Implications of The Globalization of Clinical Research NEJMDocument8 pagesGlickman (1) - Ethical and Scientific Implications of The Globalization of Clinical Research NEJMMaria BernalNo ratings yet
- Lec21 2011Document25 pagesLec21 2011ireall3017No ratings yet
- Informatica Certification Prep ListDocument5 pagesInformatica Certification Prep ListRabindra P.SinghNo ratings yet
- Mayo Medical School: College of MedicineDocument28 pagesMayo Medical School: College of MedicineDragomir IsabellaNo ratings yet
- Mpeg-1 11172-1Document46 pagesMpeg-1 11172-1Hana HoubaNo ratings yet
- Netapp Powershell CommandsDocument74 pagesNetapp Powershell CommandsravishankarNo ratings yet
- Lecture15 Analysis of Single PilesDocument32 pagesLecture15 Analysis of Single PilesJulius Ceasar SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Practice Types of SentenceDocument6 pagesPractice Types of SentenceTrần Hồ Quỳnh HươngNo ratings yet