Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Efecto de Un Choque Eléctrico
Uploaded by
geav25653855Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Efecto de Un Choque Eléctrico
Uploaded by
geav25653855Copyright:
Available Formats
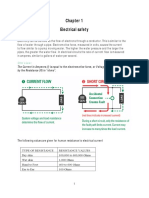
EFFECTS OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK
Electric shock is the physical stimulation that occurs when
electric current flows through the human body. The distribution
of current flow through the body depends on the resistance of the
various paths that the current flows through. The final trauma
associated with the electric shock is determined by the most
critica! path called the Shock Circuit.
Burns: caused by electric current occur from the inside of the body. Electric current burns
typically impact vital interna! organs, destroying tissue and growth centers. Externa!
damage to skin results in third-degree burns, blistering and scarring.
Cell Wall Damage; cell death can result from the enlargement of cellular pores due to high
intensity electrical pulse through the cells, known as "electrop oration". This process allows
ions to flow freely through the cell membranes, causing cell death.
Current Flow: Electrical shock current flow tends to follow the same current paths used by
the body's central nervous system. Since the externa! current is much higher than the
body's normal current flow, damage is done to the nervous system, including deterioration
of destruction of the myelin sheath which covers and protects nerves.
Damage- Nervous System: Electrical current destroys neurons, melanon, and nerve
synap ses. Since the nervous system is the communications pathway used to control the
muscles, nerve damage can result in loss of senses such as touch, smell and taste, or
muscle function.
Damage - Muscles: Currents as low as 5 amps will cause muscle and tissue damage.
Electrical current results in deep muscle damage which may not present as a complication
for days or months until the muscle tissue begins to shrink or atrophy. The heart is a
muscle and, like any muscle, it can become paralyzed and damaged if externa! current
flows through it.
Electric Hold: The reaction of muscles to uncontrollably contract when an electric current
passes through them. Your muscles clench to anything you are holding or touching and
you cannot let go. Consequently, the electric shock will continue until the current is cut-off
or another person intervenes and physically frees you from the contact with the current.
The flow of current through tissue causes heating which will make the body's resistance
drop, resulting in an increase in the current.
Fibrillation: This is the rapid and inefficient contraction of muscle fibers of the heart caused
by disruption of nerve imp ulses. lf the heart can not regain normal rhythm quickly, it will
stop beating altogether.
Electrical shock effects the body in a variety of damaging ways.
You might also like
- Quantum EducationDocument32 pagesQuantum Educationnamkay_tenzyn100% (1)
- Hormone Chart: The Body's Chemical MessengersDocument3 pagesHormone Chart: The Body's Chemical MessengersRNStudent1100% (1)
- 2007 Tap CatalogDocument142 pages2007 Tap Cataloggeav25653855No ratings yet
- The Healing Potency Of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy: Chronic Pain | Fibromyalgia | Arthritis | Multiple SclerosisFrom EverandThe Healing Potency Of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy: Chronic Pain | Fibromyalgia | Arthritis | Multiple SclerosisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Basics of Electricity: An Informational Overview of The Hazards of Electrical Contact and How To Avoid ThemDocument26 pagesBasics of Electricity: An Informational Overview of The Hazards of Electrical Contact and How To Avoid ThemRv RejuvenatedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety HazardDocument73 pagesElectrical Safety Hazardanpuselvi125100% (1)
- 1 Clinical Veterinary Advisor - Dogs and Cats 1-100 - RemovedDocument49 pages1 Clinical Veterinary Advisor - Dogs and Cats 1-100 - RemovedArieromNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-ObjectivesDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-ObjectivesJustine May Balinggan DelmasNo ratings yet
- Astm A700Document40 pagesAstm A700geav25653855No ratings yet
- Idiopathic Intracranial HypertensionDocument21 pagesIdiopathic Intracranial HypertensionJorge Dornellys LapaNo ratings yet
- NSG 330 NCLEX Kaplan Med Surg 2 Final Exam Predictor TestDocument18 pagesNSG 330 NCLEX Kaplan Med Surg 2 Final Exam Predictor TestabbieNo ratings yet
- Plain Chest X RayDocument154 pagesPlain Chest X RaySamuel Gamadey100% (3)
- Electric HazardsDocument60 pagesElectric HazardsVarsha PraburamNo ratings yet
- Steel SAE O-Rings AdaptersDocument3 pagesSteel SAE O-Rings Adaptersgeav25653855No ratings yet
- The A To Z of The HeartDocument259 pagesThe A To Z of The HeartAspenPharma100% (2)
- Electrical SafetyDocument51 pagesElectrical SafetyDIANA QUINONESNo ratings yet
- Practical Data For MetallurgistsDocument154 pagesPractical Data For MetallurgistsGuillermo Cordero100% (1)
- 2010 IMCO CatalogDocument170 pages2010 IMCO Cataloggeav25653855No ratings yet
- Electricution ShockDocument4 pagesElectricution ShockQuinta HiiNo ratings yet
- ElectrocutionDocument68 pagesElectrocutionShi_DMS100% (1)
- MS Critical Thinking DrillsDocument18 pagesMS Critical Thinking DrillsSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZ100% (1)
- Legal Medicine NewDocument19 pagesLegal Medicine Newmhilet_chiNo ratings yet
- GD&T Pocket GiudeDocument33 pagesGD&T Pocket Giudepepe51100% (2)
- Physical Injuries or Death by LIGHTNING AND ELECTRICITY PDFDocument2 pagesPhysical Injuries or Death by LIGHTNING AND ELECTRICITY PDFVincent De Vera100% (1)
- Festo Didactic: LabVolt Series Training Systems A Whole New Range of PossibilitiesDocument60 pagesFesto Didactic: LabVolt Series Training Systems A Whole New Range of PossibilitiesBharat Singh Rajpurohit50% (2)
- Festo Didactic: LabVolt Series Training Systems A Whole New Range of PossibilitiesDocument60 pagesFesto Didactic: LabVolt Series Training Systems A Whole New Range of PossibilitiesBharat Singh Rajpurohit50% (2)
- Festo Didactic: LabVolt Series Training Systems A Whole New Range of PossibilitiesDocument60 pagesFesto Didactic: LabVolt Series Training Systems A Whole New Range of PossibilitiesBharat Singh Rajpurohit50% (2)
- Understanding Variable Speed Drives (Part 1)Document4 pagesUnderstanding Variable Speed Drives (Part 1)geav25653855No ratings yet
- Understanding Variable Speed Drives (Part 1)Document4 pagesUnderstanding Variable Speed Drives (Part 1)geav25653855No ratings yet
- Physiological Effect of Electric ShocksDocument7 pagesPhysiological Effect of Electric ShocksMohammed Jalaluddin RayeenNo ratings yet
- Lec5 PDFDocument73 pagesLec5 PDFvenkatesh801No ratings yet
- Physiological Effects of Electricity (2335)Document2 pagesPhysiological Effects of Electricity (2335)susana salazarNo ratings yet
- Physiological. Electric ShockdocxDocument6 pagesPhysiological. Electric ShockdocxRam LamaNo ratings yet
- 2018- Year 10 Electricity LI1 Safety WorksheetDocument8 pages2018- Year 10 Electricity LI1 Safety Worksheetpablo forbesNo ratings yet
- Physics ReportDocument12 pagesPhysics ReportBryandelaPeñaNo ratings yet
- PATHO-202: Submitted To:-Dr. Imtiaz Ahmed KhanDocument4 pagesPATHO-202: Submitted To:-Dr. Imtiaz Ahmed KhanAltaf HusainNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 5-6docxDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 5-6docxrichie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1Document18 pagesCh. 1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Electric Shock Dangers and First AidDocument6 pagesElectric Shock Dangers and First AidMilos VirijevicNo ratings yet
- ChronaxymetryDocument9 pagesChronaxymetryYasin TuncNo ratings yet
- Effects of Electric Current On The Human BodyDocument6 pagesEffects of Electric Current On The Human BodygNo ratings yet
- Electrodiagnostics Chronaxymetry: Honorata Nawrocka-Bogusz, Marek Tuliszka, Leszek KubiszDocument9 pagesElectrodiagnostics Chronaxymetry: Honorata Nawrocka-Bogusz, Marek Tuliszka, Leszek KubiszRamboNo ratings yet
- Andrey Ricch GarinDocument1 pageAndrey Ricch GarinAbu Saro DimasangkaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety: Understanding the DangersDocument2 pagesElectrical Safety: Understanding the DangersRomeo MougnolNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Electricity IIDocument8 pagesUnit 8 Electricity II03152788No ratings yet
- Effect of Electricity in Your BodyDocument1 pageEffect of Electricity in Your BodyKish SivaNo ratings yet
- Electrical InjuryDocument5 pagesElectrical InjuryCandilicious10No ratings yet
- MT 6312 Current PresentationsDocument30 pagesMT 6312 Current PresentationsJames Haki MazikuNo ratings yet
- EEAC 112 BOSH Module II Lesson 2Document12 pagesEEAC 112 BOSH Module II Lesson 2aspillagaarnelNo ratings yet
- Effect of High Voltage On BodyDocument10 pagesEffect of High Voltage On BodyAbraham PanickerNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Electric ShockDocument9 pagesBab 2 Electric ShockrusnaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment - GEN120Document9 pagesAssignment - GEN120aboubakr soultanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety GuideDocument5 pagesElectrical Safety Guideyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy in The HomeDocument4 pagesElectrical Energy in The HomewasaiyanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 5Document9 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 5richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 16Document8 pagesPresentation 16Titos TRNo ratings yet
- Electrical Injury and Death Causes, Effects and IdentificationDocument17 pagesElectrical Injury and Death Causes, Effects and IdentificationRocky PangerapanNo ratings yet
- ANESKEY-Lightning and Electrical InjuriesDocument7 pagesANESKEY-Lightning and Electrical InjuriesJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electrical Safety ManagementDocument90 pages1 - Electrical Safety ManagementMohammad Hassan JawedNo ratings yet
- PAE AssignmentDocument4 pagesPAE AssignmentHuzaifa HabibNo ratings yet
- Appendix E - Electrical Shock and Injuries: A. "Simply Shocking" July 2001 Chevron Shipping Safety BulletinDocument2 pagesAppendix E - Electrical Shock and Injuries: A. "Simply Shocking" July 2001 Chevron Shipping Safety BulletinRol2No ratings yet
- Understanding Electrical HazardsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Electrical Hazardsshani mughalNo ratings yet
- Collective Task 2 - Effects of The Electric Current. Property of The Eye.Document2 pagesCollective Task 2 - Effects of The Electric Current. Property of The Eye.ibrahimjahangir1No ratings yet
- Post-Mortem Appearance Electrical InjuryDocument2 pagesPost-Mortem Appearance Electrical InjuryMade YogiswaraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety: Assistant Electrical Inspector Electrical Inspectorate Govt. of KeralaDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety: Assistant Electrical Inspector Electrical Inspectorate Govt. of Keralaramiz razaNo ratings yet
- Easwari Engineering College 6Document14 pagesEaswari Engineering College 6PreethikaaNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES TO ELECTRICAL CURRENTSDocument22 pagesPHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES TO ELECTRICAL CURRENTSzainabnoorNo ratings yet
- hEART RatE & diSeaSeSDocument2 pageshEART RatE & diSeaSeSdivijaNo ratings yet
- MERCK MANUAL-Electrical InjuriesDocument6 pagesMERCK MANUAL-Electrical InjuriesJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- BEEE ManualDocument99 pagesBEEE ManualPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- Hazards of Electricity: Eng. Sami Abu-ShararDocument39 pagesHazards of Electricity: Eng. Sami Abu-Shararsufian olimatNo ratings yet
- Forms of Faradic CurrentDocument5 pagesForms of Faradic CurrentAdebayo Tob AdeyinkaNo ratings yet
- Electric Shock: Electrical InjuryDocument2 pagesElectric Shock: Electrical InjuryracNo ratings yet
- Essential Guide to Electricity and Electronics SafetyDocument32 pagesEssential Guide to Electricity and Electronics SafetyAlfred KuwodzaNo ratings yet
- Electrical CurrentsDocument66 pagesElectrical Currentsbikedet268No ratings yet
- Electrotherapy AllDocument342 pagesElectrotherapy Allbikedet268No ratings yet
- Uso Del Analizador de FasesDocument2 pagesUso Del Analizador de Fasesgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Mtto 1Document1 pageMtto 1geav25653855No ratings yet
- Cap 3 ElectrocuciónDocument18 pagesCap 3 Electrocucióngeav25653855No ratings yet
- Conversao Transformacao Polegada Milesimal Milimetro Polegada Fracionaria ExerciciosDocument1 pageConversao Transformacao Polegada Milesimal Milimetro Polegada Fracionaria Exerciciosgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Coursera Specialization on Embedding Sensors and Motors Enclosure Types (ESM_C2M2V3Document16 pagesCoursera Specialization on Embedding Sensors and Motors Enclosure Types (ESM_C2M2V3geav25653855No ratings yet
- High-precision chuck and collet catalog featuring micro and mini tool holding solutionsDocument0 pagesHigh-precision chuck and collet catalog featuring micro and mini tool holding solutionsgeav25653855No ratings yet
- RoundingDocument6 pagesRoundinggeav25653855No ratings yet
- RoundingDocument6 pagesRoundinggeav25653855No ratings yet
- Astm A370 1977Document58 pagesAstm A370 1977Waseem Saif DarNo ratings yet
- Steel Heat Treatment Metallurgy and TechnologiesDocument832 pagesSteel Heat Treatment Metallurgy and TechnologiesSUNDRAMNAGANo ratings yet
- BIG Daishowa BIG-PLUS Tooling SystemDocument0 pagesBIG Daishowa BIG-PLUS Tooling Systemgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Rugosimetro MAHRDocument8 pagesRugosimetro MAHRHenryMonteagudoParedesNo ratings yet
- BIG Daishowa BIG-PLUS Tooling SystemDocument0 pagesBIG Daishowa BIG-PLUS Tooling Systemgeav25653855No ratings yet
- BIG Daishowa Profit Maker ToolsDocument40 pagesBIG Daishowa Profit Maker Toolsgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Metric Machine Screws Tap & DrillsDocument6 pagesMetric Machine Screws Tap & Drillsgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Reliable Bench Hardness Tester for Metal and Alloys /TITLEDocument1 pageReliable Bench Hardness Tester for Metal and Alloys /TITLEgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Screw Thread Diameter ChartDocument2 pagesScrew Thread Diameter Chartgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Thread Screw Drill & Tap ChartDocument2 pagesThread Screw Drill & Tap Chartgeav25653855No ratings yet
- NC NF NefDocument4 pagesNC NF Nefgeav25653855No ratings yet
- Chapter 111 - Congenital and Acquired Atresia of The External Auditory CanalDocument20 pagesChapter 111 - Congenital and Acquired Atresia of The External Auditory CanalYousef AlalawiNo ratings yet
- Prelim AnatomyDocument17 pagesPrelim AnatomyAji Nikka AngelesNo ratings yet
- Explaining - Stroke - BrochureDocument20 pagesExplaining - Stroke - BrochureNipun ShamikaNo ratings yet
- 04.0 HydrocephalusDocument41 pages04.0 HydrocephalusBaraka SayoreNo ratings yet
- Truamatic Brain InjuryDocument22 pagesTruamatic Brain InjuryH SHABANANo ratings yet
- I. Learning Objective:: /endocrine-System-Lesson-Plan-Final-Na-FinalDocument10 pagesI. Learning Objective:: /endocrine-System-Lesson-Plan-Final-Na-FinalGabilan Rose JeanNo ratings yet
- Athar Abdallatif Progress Report and Conversion ProposalDocument72 pagesAthar Abdallatif Progress Report and Conversion ProposalAthar MazenNo ratings yet
- Cancer Types & Classification: A Guide to NeoplasmsDocument53 pagesCancer Types & Classification: A Guide to NeoplasmsNooria ButtNo ratings yet
- Chapter SixDocument182 pagesChapter Sixtadele10No ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis of The Cervical SpineDocument6 pagesMultiple Sclerosis of The Cervical SpineAmajida RizkyNo ratings yet
- Textbook ReadingDocument275 pagesTextbook ReadingNovitasari EkaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Medical Language 3rd Edition Allan Test BankDocument143 pagesEssentials of Medical Language 3rd Edition Allan Test BankDebbieCollinsokpzd100% (14)
- Krishna2019 ReferenceWorkEntry CiliaDocument5 pagesKrishna2019 ReferenceWorkEntry CiliaWinada ReyhanNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Analysis OnDocument70 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Analysis OnAngelica RelanaNo ratings yet
- Pain Management: Ins, Kmu FON-2 Chap-4Document31 pagesPain Management: Ins, Kmu FON-2 Chap-4Saqlain M.No ratings yet
- CT BrainDocument230 pagesCT BrainpraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Complications Following Head InjuryDocument6 pagesComplications Following Head InjuryKiran ShelkeNo ratings yet
- ThymusDocument5 pagesThymusmeccha ella sojorNo ratings yet
- Child Growth and DevelopmentDocument60 pagesChild Growth and DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument14 pagesDiagnosing Thoracic Outlet SyndromeolaNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument27 pagesDental AnatomyMc Philip Gabay DamoclesNo ratings yet
- Winkler - Chapter 8. Khalid AlshareefDocument4 pagesWinkler - Chapter 8. Khalid AlshareefKhalid Bin FaisalNo ratings yet