Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pythagorean Theorem
Uploaded by
Mehdi KhyriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pythagorean Theorem
Uploaded by
Mehdi KhyriCopyright:
Available Formats
Pythagorean Theorem
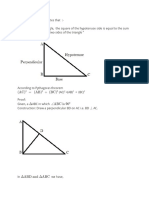
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length
of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares
of the lengths of the other two sides.
Let's consider a right-angled triangle with sides �a, �b, and hypotenuse �c.
We want to prove that �2+�2=�2a2+b2=c2.
Using the area of squares constructed on each side, we have:
Area of square on side �a = �2a2
Area of square on side �b = �2b2
Area of square on side �c = �2c2
Now, we can see that the area of the square on side �c is equal to the sum of the areas
of the squares on sides �a and �b, since the square on �c is formed by joining
squares on �a and �b.
Therefore, �2+�2=�2a2+b2=c2, which proves the Pythagorean Theorem.
You might also like
- What is the Pythagoras theoremDocument2 pagesWhat is the Pythagoras theoremVenuNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument61 pagesTRIGONOMETRYMapurisa TriciahNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Property ExplainedDocument4 pagesPythagorean Property ExplainedventyemmachahyantiNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem ProofDocument12 pagesPythagorean Theorem ProofVibhu GoelNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras Theorem ProofDocument5 pagesPythagoras Theorem Proofburgesss87No ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument7 pagesPythagoras Theoremananya9119afmcNo ratings yet
- What Is The Pythagorean TheoremDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Pythagorean Theoremapi-150547803No ratings yet
- PythogDocument5 pagesPythogJonathanNo ratings yet
- What Is Pythagorean TheoremDocument4 pagesWhat Is Pythagorean Theoremapi-140032165No ratings yet
- James Garfield's Proof of The Pythagorean TheoremDocument4 pagesJames Garfield's Proof of The Pythagorean TheoremBlaise09No ratings yet
- Trigonometry and Analytical Geometry EssentialsDocument88 pagesTrigonometry and Analytical Geometry EssentialsSakote Tobiloba IsaacNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8Document27 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8Nilofer AnjumNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction To Trigonometry 2Document169 pagesNcert Solution For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction To Trigonometry 2Ashif RahmanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Trigonometry SolutionsDocument9 pagesNCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Trigonometry SolutionsCurious 00 guyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - INTRO TO TRIGODocument5 pagesCHAPTER 8 - INTRO TO TRIGOBlessed ChildNo ratings yet
- ااااااااااااااااااااااDocument3 pagesااااااااااااااااااااااhussenman1234No ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument15 pagesPythagoras TheoremShikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Trignometry BasicDocument16 pagesTrignometry BasicRAJENDRA GAJULANo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths March28 Chapter 8 Introduction To Trigonometry 1Document29 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths March28 Chapter 8 Introduction To Trigonometry 1Google UserNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras Theorem Statement-: Hypotenuse Perpendicular + BaseDocument2 pagesPythagoras Theorem Statement-: Hypotenuse Perpendicular + BaseRISHIK GUPTANo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document6 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- What Is The Pythagorean TheoremDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Pythagorean Theoremapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument16 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigonometrychristian tamparongNo ratings yet
- Rezolvari EGMO 2014 Ziua 1Document9 pagesRezolvari EGMO 2014 Ziua 1Raluca PantaziNo ratings yet
- Kimberly Nichole CDocument3 pagesKimberly Nichole CCharles Jonard palispisNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument5 pages2 PDFanonymous personNo ratings yet
- 14right Angle TrigonometryDocument12 pages14right Angle TrigonometryMhai MabantaNo ratings yet
- Geometry ProblemsDocument10 pagesGeometry ProblemsAphrocamsieNo ratings yet
- 17 Ganitasarasangraha III (MSS)Document46 pages17 Ganitasarasangraha III (MSS)Srinivas VamsiNo ratings yet
- Foundations of TrigonometryDocument8 pagesFoundations of TrigonometryGenevieve MerroNo ratings yet
- Right angled triangles: properties, theorems and examples (35Document5 pagesRight angled triangles: properties, theorems and examples (35Mana GargiNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem SolverDocument6 pagesPythagorean Theorem SolverTunay Na Karl OlimpoNo ratings yet
- An Elegant Proof of The Pythagoras Theorem PDFDocument7 pagesAn Elegant Proof of The Pythagoras Theorem PDFRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem ExplainedDocument3 pagesPythagorean Theorem ExplainedElizabethNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry Law of Cosines TrigonometryDocument3 pagesSpherical Trigonometry Law of Cosines TrigonometryFaisal SaleemNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: TrigonometryDocument58 pagesUnit 1: TrigonometryLyssaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Guided Notes To TrigonometryDocument10 pagesChapter 1 - Guided Notes To TrigonometryfallonNo ratings yet
- 15 Spherical TrigonometryDocument9 pages15 Spherical TrigonometrySadiq SarfarazNo ratings yet
- (AC) = (AB) + (BC) Δ ∠ABC is 90 ⊥Document3 pages(AC) = (AB) + (BC) Δ ∠ABC is 90 ⊥Sidham JainNo ratings yet
- Synergetics in The PlaneDocument27 pagesSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- MATH12 Spherical Trigonometry by JohnsonDocument19 pagesMATH12 Spherical Trigonometry by JohnsonPaolo GochingcoNo ratings yet
- Coc-Pen Math1 Study Guide of Trigonometry 01 Easy Way (How To Learn Trigonometry Faster)Document9 pagesCoc-Pen Math1 Study Guide of Trigonometry 01 Easy Way (How To Learn Trigonometry Faster)Marlon AmpoNo ratings yet
- MATHS PROJECT Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Chakeri Kanpur, InDIADocument57 pagesMATHS PROJECT Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Chakeri Kanpur, InDIASAURABH VERMA83% (6)
- Pythagorean Theorem ExplainedDocument3 pagesPythagorean Theorem ExplainedPranayaNo ratings yet
- Final Project ##Document11 pagesFinal Project ##shoshoadnan25No ratings yet
- Area of The TriangleDocument6 pagesArea of The Triangleapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Tartar 2Document2 pagesTartar 2TrungNguyễnChíNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document17 pagesLecture 01David OrtegaNo ratings yet
- PythagorasDocument16 pagesPythagorasGiridharanNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras's TheoremDocument6 pagesPythagoras's TheoremRita NovitaNo ratings yet
- Classifying triangles by internal anglesDocument1 pageClassifying triangles by internal anglesRatulKumarMajumdarNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras Theorem PresentationDocument8 pagesPythagoras Theorem PresentationFarzin98No ratings yet
- CongnumberDocument17 pagesCongnumbersab108No ratings yet
- Math 113 Handout No. 1Document1 pageMath 113 Handout No. 1Nova Mae Quillas AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document2 pagesProject 2api-261605819No ratings yet
- Euclidean Geometry NotesDocument170 pagesEuclidean Geometry NoteseisatoponNo ratings yet