Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agriculture Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 4 (PDF)
Uploaded by
dreamritika22Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Agriculture Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 4 (PDF)
Uploaded by
dreamritika22Copyright:
Available Formats
Revision Notes
Class-8 Social Science Geography
Chapter 04- Agriculture
Agriculture is that branch of science that deals with the plants and products
derived from plants. The products can be used to as food as well as in other
forms of valuable resources. Agriculture also has the distinction of an economic
activity, infect in the riverine nations which also includes India, it is the primary
occupation of the majority of people. Moreover, the half of the world’s
population livelihood also depends on the agriculture.
CBSE class 8 Geography Chapter 4 provides an elaborate discussion of the
agriculture, main crops, types of farming and the agricultural development that
has occurred in the country till now.
Highlights
• Despite the fact that plants grow on every type of land but still agriculture
is not a feasible activity on all lands. Agricultural activity requires
specific climatic and topological conditions in order to be carried out
properly.
• The land suitable for the cultivation of crops is known as arable lands.
• Farm systems are just like the other systems of production which requires
some inputs to get the desired outputs.
• The inputs needed are seeds, water, climatic conditions, land, fertilizers
etc.
• Ploughing, harvesting, sowing and irrigation etc. are some of the
processes that ensures input produces the desired outputs.
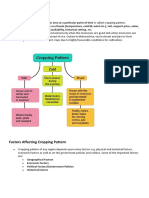
Types of Farming
Agriculture is practiced all over the world but still farmers do not adopt
the same practices worldwide. Factors play a very significant role in this
for ex: Labor, geographical location, demand for production etc. are
different for the different farmers. Based on these factors, there are two
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 1
significant types of farming: Commercial Farming and Subsistence
Farming.
• Subsistence Farming: It is practiced where there is limited availability
of the labor for the production of crops. It is not aimed to meet the high
demands of production and they also use low levels of technology.
• Types of Subsistence Farming: They are further classified into intensive
subsistence farming or the Primitive Subsistence Farming.
▪ Intensive Subsistence farming: In this type of farming, a small
piece of land is cultivated with the help of small tools. It also
requires more labor as compared to other modes of farming.
It is practiced in the places which have quiet long summers as
compared and have rich fertility of the soil.
Rice is the major crop that is grown in this type of farming. Other
crops include wheat, oilseeds, maize, pulses. This farming is
mostly practiced in the regions of South Asia, East Asia and South-
East Asia.
▪ Primitive Subsistence Farming: As the name only suggests that it
is an old type of farming where farmers cultivate different stretches
of land at only one time. After production of one crop, farmers then
move to the next stretch of land.
▪ Two major forms of Primitive Subsistence farming are the shifting
cultivation as well as the nomadic herding.
▪ Shifting Cultivation: It is practiced in regions of very high rainfall
and dense forestation. For Ex: Southeastern Asia, Northeastern
India and the Amazon Basin.
In this type of cultivation, a land is chosen by a farmer and then
they cut all trees of that land. The ashes of the trees are then mixed
with the soil of the land which increases its fertility. The farmer
then grows crops on that cleared land till it does not lose its
fertility. After that they move to the next piece of land and repeat
the entire process again.
▪ Nomadic Herding: This type of herding is mostly practiced in the
semi -arid regions of the Sahara, parts of Asia and the dry regions
of Jammu and Kashmir and Rajasthan.
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 2
Due to adverse climatic condition of the region, the farmers select
a certain route for themselves so that they can sustain. In the way,
they practice the herding on the different areas of the same route.
• Commercial Farming:
▪ It helps in the cultivation of large amounts of crops along with
animals with the purpose of selling in the market.
▪ A large area of land is used for the cultivation of large amount of
production with the help of advanced machineries.
▪ It requires high amount of capital as compared to the subsistence
farming.
▪ There are varieties of Commercial Farming also:
➢ Commercial Grain Farming
➢ Mixed Farming
➢ Plantation
▪ Commercial Grain Farming: Crops are produced on the large
patch of land for the commercial purposes.
➢ Wheat and Maize are grown through this farming.
➢ Mostly practiced in the temperate grassland regions of
Europe, Asia and Northern America.
➢ The area selected for this is usually a field and that too in
sparsely populated area.
➢ Due to the harsh conditions in winter season, there can be
only successful cultivation of only one crop.
▪ Mixed farming: This method is used for the growing of crops
alongside the rearing of animals for the purpose of sale in the
markets. Argentina, South Africa, New Zealand, Eastern USA,
Southeastern Australia etc. are the regions where this farming is
practiced.
▪ Plantation: Only one crop is used to grow throughout the year
over the large areas.
➢ Major Plantation crops are the coffee, tea, rubber and the
cashew nuts.
➢ The produce can be easily processed in the farms or the
nearby factories.
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 3
➢ The regions where plantation farming is practiced is Sri
Lanka, India, Brazil, Malaysia etc.
• Major Crops: A large varieties of crops are grown in different
regions of world to meet the requirements of growing population.
Some of the important crops are:
• Rice: It is a staple food in the tropical and sub-tropical climatic
conditions.
▪ Climatic Requirements: It requires high rainfall, high humidity
and high temperature.
▪ For the cultivation of rice, alluvial soils are best as they can
easily retain the water.
▪ The major rice growing regions are China (Largest producer),
India (Second Largest Producer) along with Bangladesh, Japan
and Egypt.
• Wheat:
▪ It is consumed throughout the world to meet the growing
demands of the population.
▪ Climatic Requirements: It requires bright sunlight during
harvesting, moderate temperature as well as rainfall in the
growing season.
▪ The best soil for the cultivation of wheat is the loamy soil
as it is well-drained.
▪ Major wheat growing areas are Russia, Canada, Australia,
India, Argentina, Ukraine, USA.
• Maize:
▪ Maize is also known by the name of corn.
▪ Climatic Requirements: It requires moderate rainfall and
temperature with a lot of sunshine.
▪ Well-drained fertile soil is needed for the cultivation of
maize.
▪ Major maize growing regions are: China, North America,
Russia, Canada, Brazil, Mexico and India.
• Millets: It also includes a number of different crops like
Jowar, bajra and Ragi.
▪ They can be very easily grown on the sandy soils or the
less fertile soil. They are hard in the structure.
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 4
▪ Climatic Requirements: High to moderate temperature as
well as low rainfall.
▪ Millets are grown in China, India and Nigeria.
• Cotton:
▪ Climatic Requirements: It requires bright sunshine, 210
frost-free days with light rainfall and high temperature.
Black and alluvial soils are best for the cultivation of
cotton.
▪ It is mainly grown in the regions of India, Pakistan, Brazil,
USA and China.
• Jute: It is also known as the golden fiber.
▪ Climatic Requirements: It requires very high rainfall,
humidity as well as temperature.
▪ Alluvial Soil is the best soil for the production of Jute.
▪ India and Bangladesh are the largest producers of jute.
• Coffee: It’s a beverage which is most common and consumed
worldwide.
▪ Climatic Requirements: It requires adequate rainfall with
high temperature.
▪ It requires hill slopes along with the well-drained loamy
soil.
▪ The leading producers of the coffee are the India,
Columbia and Brazil.
• Tea:
▪ Climatic Requirements: it needs cool climate with
proportionate distribution of rainfall all throughout the
year.
▪ Like coffee, it also needs hill slopes and well-drained
loamy soils.
▪ There is a lot of labor requirement in the harvesting of tea.
▪ The largest producers of tea are the India, China and
Kenya.
• Agricultural Development:
▪ It is the development in the field of agricultural production
in order to meet the current increasing demand. The logic
is to increase the food security. For the development, it
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 5
includes, HYV seeds, fertilizers as well as improvement in
the irrigation facilities.
▪ In developing nations like India, the farmers still use
primitive methods like tube wells, tractors, bullock
ploughing etc.
▪ Whereas on the other hand, developed countries like USA
differs a lot from the developing nations. For ex: they
conduct soil testing and then sent samples in the
laboratory. The use of chemical fertilizers is based on the
Scientific Fertilizer Programs that were undertaken.
Important Questions and Answers:
1. State the differences between Commercial and Subsistence Farming.
Commercial Farming Subsistence Farming
1. Crops are grown for trading 1. Crops are grown for the
purpose personal consumption.
2. It is capital-intensive. 2.It is labor intensive.
3. It requires large area 3.Small area is needed
4. It uses high doses of modern 4.It uses manure.
inputs.
5. Cash crops and cereals are 5.Vegetables and fruits are
grown in this type of grown here.
farming.
6. It does not depend on 6.It depends on monsoon.
monsoon.
2. Write a short note on Primitive Farming.
Ans: It is practiced in the small areas using primitive tools like digging
sticks, bow, hoe etc. It depends on the rainfall and family members cultivates
the field and do other associated work in the Primitive Subsistence Farming.
This type of agriculture faces very low land productivity giving rise to quiet
meagre yields. It is done solely for the consumption purpose as nothing left
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 6
to be sold in the market. The size of farms is very small and in this type of
farming only selected crops are grown.
3. What are the requirements of growing different main crops?
Crop Climatic Soil required Regions of
requirement s cultivation
Rice High Alluvial soil China, India,
temperature, Egypt, Japan and
high rainfall, Bangladesh.
high humidity.
Wheat Moderate Loamy soil USA, Ukraine,
temperature, Russia, Canada,
bright sunlight Argentina,
(during Australia and
harvesting) and India.
rainfall (in the
growing season)
Maize Moderate Loamy soil China, North
temperature, America, Russia,
rainfall and a lot Canada, Brazil,
of sunshine Mexico and
India.
Millets Low rainfall, Sandy soil China, USA,
high to moderate Brazil, India and
temperature Pakistan
Coffee High Loamy soil Brazil, Columbia
temperature and and India.
adequate rainfall.
Tea A cool climate Loamy soil Kenya, India,
and well China
distributed high
rainfall all
through the year.
Cotton High Black and USA, India and
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 7
temperature light alluvial soil Pakistan.
rainfall 210
Frost-free days
and bright
sunlight for
growth.
Jute High Alluvial soil India,
temperature, Bangladesh.
high rainfall and
high humidity.
4. Discuss the disadvantages of shifting cultivation.
Ans: The disadvantages of shifting cultivation are:
1. It leads to deforestation as once the fertility of land drops, farmers shift to
the other patch of land which have high fertility.
2. Because of this, soil erosion takes place and the chances of desertification
increases. It leads to the damage to the natural environment as well as the
biodiversity.
3. It destroys watersheds which is very uneconomical in the nature.
4. It restricts the intensity of land-use and leads to water pollution.
5. Discuss the importance of agriculture.
Ans: Agriculture contributes to the national income of a developing country
however, for developed nations it contributes very less. It is important for the
food and fodder demand of the population as well as animals. Agriculture
contributes in the marketable surplus. With the development of a country
more people get engaged to the non-agricultural sectors like the mining,
manufacturing etc. As agriculture expands, it leads to the expansion of a
marketable surplus which the nation can also export to the different
countries.
Class VIII Geography www.vedantu.com 8
You might also like
- Agriulture VIIIDocument43 pagesAgriulture VIIISakshi ShrutiNo ratings yet
- Geography Class XDocument64 pagesGeography Class XAbhilash100% (1)
- Ch.4 AgricultureDocument30 pagesCh.4 AgricultureMiten shahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AgricultureDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Agriculturesadiyaarchive22No ratings yet
- G D Goenka Public School, Sector-22, Rohini Subject-Geography Class-X Ch-4-Agriculture Outline of The ChapterDocument15 pagesG D Goenka Public School, Sector-22, Rohini Subject-Geography Class-X Ch-4-Agriculture Outline of The Chaptervikas aggarwalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 AgricultureDocument8 pagesCBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculturegargij2011No ratings yet
- Akshit Manhas 121001061645 Phpapp01Document37 pagesAkshit Manhas 121001061645 Phpapp01Sunsong31No ratings yet
- Agriculture - Key NotesDocument9 pagesAgriculture - Key NotesJRNo ratings yet
- 8th Ncert 4th CHPTDocument19 pages8th Ncert 4th CHPTThe masteroNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument42 pagesAgricultureritikaNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument50 pagesAgricultureGauri GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cropping PatternDocument35 pagesCropping PatternShailendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Agriculture WatermarkDocument15 pagesAgriculture WatermarkS SARAVANANNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Notes Ans QaDocument30 pagesAgriculture Notes Ans QaPuja BhardwajNo ratings yet
- UctxxyxgdyxigxDocument35 pagesUctxxyxgdyxigxGyanendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Geo Agri Greenvalley 1Document10 pagesGeo Agri Greenvalley 1Abhinav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Pragati Public School, Dwarka: Revision Notes: Geography Class 12 Chapter 5: Primary Activities (Book-1)Document10 pagesPragati Public School, Dwarka: Revision Notes: Geography Class 12 Chapter 5: Primary Activities (Book-1)Surbhi RajaramaniNo ratings yet
- Geography CH 4 Agriculture G10Document6 pagesGeography CH 4 Agriculture G10SoniaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-7 & 8:: Primary Economic Activities: AgricultureDocument19 pagesLecture-7 & 8:: Primary Economic Activities: AgricultureMuktar HossainNo ratings yet
- Geog YE NotesDocument12 pagesGeog YE NotesHongkonger LoyalNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Class 10 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 4Document4 pagesAgriculture Class 10 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 4Seethala ANo ratings yet
- Crops of IndiaDocument42 pagesCrops of Indiaaftab ziyadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Geography Class 10Document7 pagesChapter 4 Geography Class 10Sawan panchalNo ratings yet
- Agriculture, VegetationDocument34 pagesAgriculture, VegetationRashin MohammedNo ratings yet
- Agriculture, Industries and Human Resources - SUBDocument23 pagesAgriculture, Industries and Human Resources - SUBsafa sahebNo ratings yet
- Agriculture YTDocument86 pagesAgriculture YTdark aaasNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument27 pagesAgricultureValery GvNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Ch-4Document12 pagesAgriculture Ch-4Debasis Mishra VI CNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - AgricultureDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - AgricultureSaravanan SaravanaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Updated CHAPTER 7Document159 pagesAgriculture Updated CHAPTER 7hassangreat2010No ratings yet
- Ashu AgricultureDocument5 pagesAshu AgriculturesanyacamaterialNo ratings yet
- Major CropsDocument5 pagesMajor Cropslayalll.yassineNo ratings yet
- Cropping Pattern in IndiaDocument38 pagesCropping Pattern in IndiaKanniha SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AgricultureDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Agriculture039Anas NazeerNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument24 pagesAgricultureArchana KujurNo ratings yet
- Major Crops - Prelims - 16-07-12 - Single ColumnDocument48 pagesMajor Crops - Prelims - 16-07-12 - Single ColumnParveen SainiNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTUREDocument37 pagesAGRICULTUREzeinab.hassanNo ratings yet
- Soils and Agriculture Part 2Document54 pagesSoils and Agriculture Part 2bking bbNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument5 pagesAgricultureYasho MadhavNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTUREDocument45 pagesAGRICULTUREabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Agriculture 22Document5 pagesChapter 4 Agriculture 22BNo ratings yet
- Agriculture NotesDocument11 pagesAgriculture NotesßläcklìsètèdTȜèNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: Class 10 - Geography - Chapter 4Document69 pagesAgriculture: Class 10 - Geography - Chapter 4Shilpa Reddy50% (2)
- Rice Crop CultivationDocument15 pagesRice Crop CultivationNuur Yusuf Sheikh OmarNo ratings yet
- DJBKF BSSDLBVDLDocument7 pagesDJBKF BSSDLBVDLiowvhvovewioNo ratings yet
- Environment 8Document16 pagesEnvironment 8soundu ranganathNo ratings yet
- 609edad55f1c0316146f6340 - AP Human Geography Unit 5Document13 pages609edad55f1c0316146f6340 - AP Human Geography Unit 5hmahnoor746No ratings yet
- Agriculture NotesDocument7 pagesAgriculture NotesBhagath K sNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 AgricultureDocument4 pagesCBSE Notes Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 AgricultureAditya VatsNo ratings yet
- 9 Main Types of Farming Systems Practices in IndiaDocument4 pages9 Main Types of Farming Systems Practices in Indiakeertigunani100% (1)
- Major CropsDocument45 pagesMajor CropsEr Anil SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Introduction To AgricultureDocument22 pages5.1 Introduction To AgricultureOh NoNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTUREDocument12 pagesAGRICULTURESadiqa ArooshNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Notes PDFDocument6 pagesClass 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Notes PDFLomas GandhiNo ratings yet
- Cropping System RevisedDocument15 pagesCropping System Revisedricellelupos25No ratings yet
- Agriculture and Crops - SST Project Base LearningDocument4 pagesAgriculture and Crops - SST Project Base LearningMohammed Ashfahan Ahmed MallickNo ratings yet
- State & Crops: Dr. Gaurav GargDocument14 pagesState & Crops: Dr. Gaurav GargRoy KrNo ratings yet
- Geography Agricalture & ClimateDocument39 pagesGeography Agricalture & Climatesami887604354No ratings yet
- 2001, 8, 1Document95 pages2001, 8, 1usuariosdelserra1727No ratings yet
- Science, Technology and Society ResearchDocument17 pagesScience, Technology and Society ResearchHungry HopeepigNo ratings yet
- Soil and Soil Water RelationshipsDocument9 pagesSoil and Soil Water RelationshipsChristian LibangNo ratings yet
- Organic Farmers and Farms of KeralaDocument16 pagesOrganic Farmers and Farms of KeralaNyah KingsleyNo ratings yet
- HAPAG QuarterlyDocument1 pageHAPAG QuarterlyIzsh LizardoNo ratings yet
- History of Extension Education PartDocument32 pagesHistory of Extension Education PartB.p. Singh100% (3)
- Chia Seed Export To Nepal Final Report AutosavedDocument14 pagesChia Seed Export To Nepal Final Report Autosavedapi-273920737No ratings yet
- The Agrarian Roots of The ConflictDocument12 pagesThe Agrarian Roots of The Conflictapi-252051055No ratings yet
- Myanmar INC Report To UNFCCC Secretariat 26-12-12 ECD-MOECAFDocument313 pagesMyanmar INC Report To UNFCCC Secretariat 26-12-12 ECD-MOECAFTechne PhobosNo ratings yet
- Organic Food and It's AdvantagesDocument6 pagesOrganic Food and It's AdvantagesIonicNo ratings yet
- Impact of Socio-Cultural Factors On Environmental DegradationDocument74 pagesImpact of Socio-Cultural Factors On Environmental DegradationChristine Mikaela AbahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 5: Watershed Management and Objectives in IndiaDocument11 pagesLecture No. 5: Watershed Management and Objectives in IndiaPankhuri SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Status and Strategy of Biodiversity Conservation For Sustainable Development in The Barrind Tracts Areas of BangladeshDocument25 pagesStatus and Strategy of Biodiversity Conservation For Sustainable Development in The Barrind Tracts Areas of Bangladesharahman1984No ratings yet
- CFC News February 2014Document22 pagesCFC News February 2014Srivatsan SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- When Alabama Was Called The Cotton StateDocument2 pagesWhen Alabama Was Called The Cotton StateElton CampNo ratings yet
- Swades Tractors Case Study - Prof - Anirban DasDocument16 pagesSwades Tractors Case Study - Prof - Anirban DasRose RanjanNo ratings yet
- Iswarya.H: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesIswarya.H: ObjectivelooserNo ratings yet
- What Is Asexual Reproduction?Document5 pagesWhat Is Asexual Reproduction?Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Deindustrialization in 18th and 19th Century India: Mughal Decline, Climate Shocks and British Industrial AscentDocument26 pagesDeindustrialization in 18th and 19th Century India: Mughal Decline, Climate Shocks and British Industrial AscentKim LeNo ratings yet
- Organic Fertilizers: Types, Production and Environmental ImpactDocument290 pagesOrganic Fertilizers: Types, Production and Environmental ImpactBarsha ThakurNo ratings yet
- TurmericDocument17 pagesTurmericRaja GopalNo ratings yet
- Pop PauDocument82 pagesPop PauRakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week1 Day2Document7 pagesQ2 Week1 Day2LAARNI DE LA SANTANo ratings yet
- Sugar Crisis in Pakistan Research PaperDocument10 pagesSugar Crisis in Pakistan Research Paperrehan9891No ratings yet
- Agricultue in Ancient EgyptDocument32 pagesAgricultue in Ancient EgyptShaimaa AbouzeidNo ratings yet
- LBP SorsogonDocument124 pagesLBP SorsogonMichael Rivera100% (2)
- Lesson A: Exploring The Food System: © 2020 Johns Hopkins UniversityDocument7 pagesLesson A: Exploring The Food System: © 2020 Johns Hopkins Universitymyriam pilar gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Handbook On Pig Production - English Layout-Vietanm-DraftDocument86 pagesHandbook On Pig Production - English Layout-Vietanm-Draftsambrefo100% (3)
- Upaya Meminimalisir Dampak Lingkungan Dari Penggunaan Pestisida Dalam Pertanian (Dampak Lingkungan Dan Penanggulangannya)Document9 pagesUpaya Meminimalisir Dampak Lingkungan Dari Penggunaan Pestisida Dalam Pertanian (Dampak Lingkungan Dan Penanggulangannya)HafizNo ratings yet
- NVC in Agricuture - NBTEDocument211 pagesNVC in Agricuture - NBTEsimsotuquyNo ratings yet