Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Excess Fluid Volume Related To Sodium Intake
Uploaded by
Nil Gyi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Excess fluid volume related to sodium intake
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Related To Sodium Intake
Uploaded by
Nil GyiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
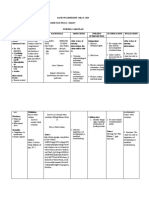
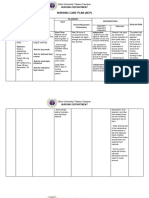
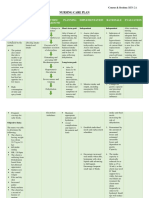
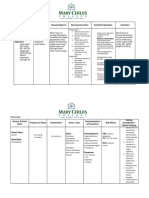
COR JESU COLLEGE, INC.
,
College of Health Sciences
Sto. Rosario, Tres De Mayo, Digos City
NURSING CARE PLAN NO. 1
DATE/ CUES/ DATA NURSING SCIENTIFIC GOALS/ NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
TIME DIAGNOSIS BASIS OBJECTUVE/ INTERVENTION
CRITERIA
11/20/23 Objective: Excess fluid volume Heart failure results Within 8 hours of 1. Regularly monitor vital 1. Regularly monitor vital Within 8 hours of nursing
8AM-3PM - Edema in both related to sodium in poor perfusion nursing intervention the signs, signs of fluid signs, signs of fluid intervention the patient was
overload (edema, overload (edema,
lower extremities intake as evidence by of the kidneys. If patient will be able to: able to:
distended neck veins, distended neck veins,
- weakness edema in both lower the kidneys cannot 1. demonstrate a shortness of breath), shortness of breath), 1. demonstrated a reduction
- activity extremities excrete sodium, reduction of edema, and and accurate intake and and accurate intake and of edema, and exhibit a
output. output.
intolerance water retention will exhibit a reduce in reduce in swelling.
2. Collaborate with the 2. Restricting fluid intake
- type II Diabetes occur and swelling. healthcare team to helps prevent further 2. achieved balance fluid
Mellitus accumulate in establish and fluid accumulation,
2. maintain cardiac implement a fluid reducing the workload intake and output.
-weight 50 kg tissues leading to
output. restriction plan; educate on the heart and
- cardiac output fluid overload. 3. verbalized dietary
the patient and family improving overall fluid
3.58 L/min 3. achieve balance fluid about adherence. balance. recommendations and fluid
intake and output. 3. Administer diuretics as 3. Diuretics increase urine restrictions to maintain.
prescribed to promote output, reducing excess
(Maegan Wagner, 4. verbalize dietary diuresis and fluid fluid. Monitoring for
BSN, RN, CCM, recommendations and elimination; monitor side effects ensures
for side effects. patient safety during PARTIALLY MET
2023) fluid restrictions to
4. Weigh the patient daily pharmacological
maintain. and report significant interventions.
weight gains promptly. 4. Daily weights are an
5. Elevate the legs to effective way to
reduce dependent monitor fluid balance.
edema; encourage Sudden weight gains
frequent position may indicate fluid
changes. retention and require
prompt attention.
5. Elevation of the legs
promotes venous return
and reduces edema.
Position changes
prevent pressure ulcers
and enhance overall
comfort.
You might also like
- Supercharging Autophagy - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Eric Berg: Unleashing Its Full PotentialFrom EverandSupercharging Autophagy - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Eric Berg: Unleashing Its Full PotentialNo ratings yet
- NCS Cuba LiverDocument3 pagesNCS Cuba LiverMeryl EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument21 pagesLiver Cirrhosis NCPJeco Valdez100% (4)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Liver Cirrhosis - NCPDocument18 pagesLiver Cirrhosis - NCPIshmael Solamillo83% (6)
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Ncp-Retdem Torio Grp6Document6 pagesNcp-Retdem Torio Grp6pinkgirljojiNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document2 pagesNCP 3Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisChe SalveronNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- CHOLELITHIASISDocument4 pagesCHOLELITHIASISKate ValdesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument22 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSampada GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 3Document6 pagesNCP 1 3Allyzah Faith BernalesNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- Group 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaAngel Joyce MontezaNo ratings yet
- Plan of Care Patient Independent-2 PDFDocument1 pagePlan of Care Patient Independent-2 PDFHilary AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume Related Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Renal Failure) (Acute Renal Failure)Document3 pagesNCP - Excess Fluid Volume Related Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Renal Failure) (Acute Renal Failure)Kian Herrera100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Kiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Document2 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- NCP BeeaDocument3 pagesNCP BeeaKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Prio NCP NG Dka ByeDocument5 pagesPrio NCP NG Dka ByeMARIA HILARY TABLANTENo ratings yet
- Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Margaret Macasaet0% (1)
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Volume 1Document2 pagesVolume 1roxybiscanteNo ratings yet
- NCP AkdDocument3 pagesNCP AkdJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaCzarina AeriNo ratings yet
- Risk For Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageRisk For Fluid VolumeMariella BadongenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ckd-Janry FinalDocument6 pagesNcp-Ckd-Janry Finalcjpalapuz07No ratings yet
- NCP EsrdDocument9 pagesNCP EsrdMarisol Dizon100% (1)
- المستند (7) Document3 pagesالمستند (7) Mawadh AlsbhiNo ratings yet
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid VolumeALEKS MONTECINO JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage NCPDocument4 pagesHemorrhage NCPElishaNo ratings yet
- NCP (BPH)Document8 pagesNCP (BPH)NataCo50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDan MandigNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Plannin G Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plannin G Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NMarineth O. LasicNo ratings yet
- TrimetazidineDocument2 pagesTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationEula ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP of PTBDocument8 pagesNCP of PTBdisenueve_jhOanneNo ratings yet
- F and E ReviewerDocument9 pagesF and E Revieweralifah.macabagoNo ratings yet
- NCP CKDDocument5 pagesNCP CKDDbktNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument3 pagesConstipationmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome (Nephrosis) Assessment: Pressure MedicationsDocument6 pagesNephrotic Syndrome (Nephrosis) Assessment: Pressure MedicationsArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- PTB WARD Case Study (CJC-CHS) 2023Document62 pagesPTB WARD Case Study (CJC-CHS) 2023Nil GyiNo ratings yet
- Factors Modifying The Drug ActionDocument6 pagesFactors Modifying The Drug ActionNil GyiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of GI MedicationsDocument2 pagesNursing Management of GI MedicationsNil GyiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Concepts of Health and WellnessDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Concepts of Health and WellnessNil GyiNo ratings yet
- Phototherapy: Prepared By: DR/ Lamiaa Ahmed ElsayedDocument36 pagesPhototherapy: Prepared By: DR/ Lamiaa Ahmed Elsayedngocbienk56No ratings yet
- Non Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarDocument32 pagesNon Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarkrupalithakkerNo ratings yet
- Pneumonitis 2Document12 pagesPneumonitis 2Ina SahakNo ratings yet
- Pawanmuktasana Series (Part 2)Document20 pagesPawanmuktasana Series (Part 2)bhavna M100% (1)
- HHDDocument41 pagesHHDDiana IswardhaniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Understanding Pathophysiology 7th Edition Sue Huether Kathryn MccanceDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Understanding Pathophysiology 7th Edition Sue Huether Kathryn Mccancekimberlymatthewsddsqocjewyibg91% (11)
- Postoperative CareDocument9 pagesPostoperative CareJannah Marie A. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Hematopathology (Lecture II)Document45 pagesHematopathology (Lecture II)Carlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- Nitazoxanide, A New Thiazolide Antiparasitic AgentDocument8 pagesNitazoxanide, A New Thiazolide Antiparasitic AgentHenry CollazosNo ratings yet
- Laporan GiziDocument11 pagesLaporan GiziEfrata MadridistaNo ratings yet
- Water Deprivation TestDocument7 pagesWater Deprivation Testsanham100% (2)
- PM - Materi 1 HIV AIDS RevDocument72 pagesPM - Materi 1 HIV AIDS RevSaly AlatasNo ratings yet
- HMO Proposal For Individual F-1Document10 pagesHMO Proposal For Individual F-1DesNo ratings yet
- How We Conquered SmallpoxDocument4 pagesHow We Conquered SmallpoxNadir BaghdadNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice NCLEX Questions HandoutDocument6 pagesGenetics Practice NCLEX Questions HandoutAlvin L. Rozier100% (3)
- Treatment For Gangrene A. DryDocument2 pagesTreatment For Gangrene A. DryKey LomonovNo ratings yet
- Dissociative BehaviorDocument5 pagesDissociative BehaviorDump AccNo ratings yet
- Review 02Document2 pagesReview 02Vicki KimNo ratings yet
- Applications of Next Generation SequencinginhematologyDocument6 pagesApplications of Next Generation SequencinginhematologyAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Functional Limb Weakness and ParalysisDocument16 pagesFunctional Limb Weakness and Paralysis955g7sxb8pNo ratings yet
- MINOR DISORDER IN PREGNANCY MaterialDocument8 pagesMINOR DISORDER IN PREGNANCY MaterialAnuradha MauryaNo ratings yet
- 2015parathyroid Carcinoma Challenges in Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pages2015parathyroid Carcinoma Challenges in Diagnosis and TreatmentCharley WangNo ratings yet
- Waiver For Blood DonationDocument4 pagesWaiver For Blood Donationeleazar_magsino08No ratings yet
- XXXXXX 121Document11 pagesXXXXXX 121AndriantkNo ratings yet
- SciaticaDocument35 pagesSciaticaRahmadanii RahmadaniiNo ratings yet
- Stroke Due To HypertensionDocument10 pagesStroke Due To HypertensionEnrique LuNo ratings yet
- Mouth Paste-Kenalog OrabaseDocument3 pagesMouth Paste-Kenalog OrabaseKashif2008No ratings yet
- Cause and Effect EssayDocument10 pagesCause and Effect EssayМолдабекова АйсулуNo ratings yet
- Management of Upper Airway DisorderDocument46 pagesManagement of Upper Airway DisorderSahana Rangarajan100% (1)