Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMP Formula Pocket Guide
Uploaded by
nanaba06Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP Formula Pocket Guide
Uploaded by
nanaba06Copyright:
Available Formats
PMP® Formula Pocket Guide
Print it - Fold it - Study wherever you go.
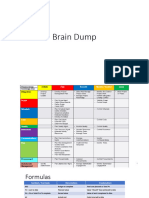
Earned Value Mathematical Basics
CV = EV - AC Average (Mean) = Sum of all members divided by the number of items.
CPI = EV / AC Median = Arrange values from lowest value to highest. Pick the middle
SV = EV - PV one. If there is an even number of values, calculate the mean of the
SPI = EV / PV two middle values.
EAC ‘no variances’ = BAC / CPI Mode = Find the value in a data set that occurs most often.
EAC ‘fundamentally flawed’ = AC + ETC
EAC ‘atypical’ = AC + BAC - EV Values
EAC ‘typical’ = AC + ((BAC - EV) / CPI) 1 sigma = 68.26%
ETC = EAC - AC 2 sigma = 95.46%
ETC ‘atypical’ = BAC - EV
ETC ‘typical’ = (BAC - EV) / CPI 3 sigma = 99.73%
ETC ‘flawed’ = new estimate 6 sigma = 99.99%
Percent Complete = EV / BAC * 100 Control Limits = 3 sigma from mean
VAC = BAC - EAC Control Specifications = Defined by customer; looser than
EV = % complete * BAC the control limits
PERT Order of Magnitude estimate = -25% to +75%
PERT 3-point = (Pessimistic+(4*Most Likely)+Optimistic)/6 Preliminary estimate = -15% to + 50%
PERT = (Pessimistic - Optimistic) / 6 Budget estimate = -10% to +25%
PERT Activity Variance = ((Pessimistic - Optimistic) / 6)^2 Definitive estimate = -5% to +10%
PERT Variance all activities = sum((Pessimistic - Optimistic) / 6)^2 Final estimate = 0%
Float on the critical path = 0 days
Network Diagram
Activity Duration = EF - ES + 1 or Activity Duration = LF - LS + 1 Pareto Diagram = 80/20
Total Float = LS - ES or Total Float = LF – EF Time a PM spends communicating = 90%
Free Float = ES of Following - ES of Present - DUR of Present Crashing a project = Crash least expensive tasks on critical
EF = ES + duration - 1 path.
ES = EF of predecessor + 1 JIT inventory = 0% (or very close to 0%.)
LF = LS of successor - 1
LS = LF - duration + 1
Minus 100 = (100) or -100
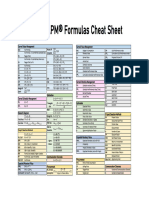
Acronyms
Project Selection AC Actual Cost
PV = FV / (1+r)^n BAC Budget at Completion
FV = PV * (1+r)^n BCR Benefit Cost Ratio
NPV = Formula not required. Select biggest number. CBR Cost Benefit Ratio
ROI = Formula not required. Select biggest number.
IRR = Formula not required. Select biggest number. CPI Cost Performance Index
Payback Period = Add up the projected cash inflow minus expenses CV Cost Variance
until you reach the initial investment. DUR Duration
BCR = Benefit / Cost EAC Estimate at Completion
CBR = Cost / Benefit EF Early Finish
Opportunity Cost = The value of the project not chosen.
EMV Expected Monetary Value
Communications ES Early Start
Communication Channels = n * (n-1) / 2 ETC Estimate to Complete
EV Earned Value
Probability FV Future Value
EMV = Probability * Impact in currency IRR Internal Rate of Return
Procurement LF Late Finish
PTA = ((Ceiling Price - Target Price) / Buyer's Share Ratio) + Target LS Late Start
Cost NPV Net Present Value
PERT Program Evaluation and Review Technique
Depreciation PTA Point of Total Assumption
Straight-line Depreciation:
Depr. Expense = Asset Cost / Useful Life
PV Planned Value
Depr. Rate = 100% / Useful Life PV Present Value
Double Declining Balance Method: ROI Return on Investment
Depr. Rate = 2 * (100% / Useful Life) SPI Schedule Performance Index
Depr. Expense = Depreciation Rate * Book Value at Beginning of Year SV Schedule Variance
Book Value = Book Value at beginning of year - Depreciation Expense
VAC Variance at Completion
Sum-of-Years' Digits Method:
Sum of digits = Useful Life + (Useful Life - 1) + (Useful Life - 2) + etc. Sigma / Standard Deviation
Depr. rate = fraction of years left and sum of the digits (i.e. 4/15th) ^ “To the power of” (2^3 = 2*2*2 = 8)
Visit www.pmprepcast.com for more PMP resources. Please see disclaimer on the PMP Formula Study Guide.
© 2008 ScopeCreep Project Management Consultants. All rights reserved. Version 1.1
You might also like
- VI VI - PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pageVI VI - PMP Formula Pocket GuideSMAKNo ratings yet
- Visit For Exam Resources For Disclaimer See PMP® Formula Study GuideDocument2 pagesVisit For Exam Resources For Disclaimer See PMP® Formula Study GuideNeeraj ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidesunil_v5No ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidejindalyash1234100% (2)
- PMP FormulasDocument3 pagesPMP Formulasleonel ruizNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Waleed El-Naggar,: Earned Value ManagementDocument3 pagesPrepared By: Waleed El-Naggar,: Earned Value Managementsalem saberNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas: PMBOK - PMI: Cod. Nombre Descripción EVDocument4 pagesFórmulas: PMBOK - PMI: Cod. Nombre Descripción EVWilliam Rojas MoralesNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Pocket Guidesantiroes pmp80% (5)
- PMP Formulas: Earned ValueDocument3 pagesPMP Formulas: Earned ValuefraspaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Professional (PMP) - Sample ExamDocument1 pageProject Management Professional (PMP) - Sample ExamAlish ChelackalNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Pocket Guiderambalajir100% (2)
- PMP Formulas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Cheat SheetAn Nguyen100% (12)
- PMP Formula CompilationDocument3 pagesPMP Formula CompilationJRNo ratings yet
- 17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideDocument14 pages17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideStéphane SmetsNo ratings yet
- Answer: Initiating: Identify Stakeholders Process GroupDocument6 pagesAnswer: Initiating: Identify Stakeholders Process GroupJonathan BrenesNo ratings yet
- KH-Formula-Sheet - PMP ExamDocument1 pageKH-Formula-Sheet - PMP Examjalejandropinedag100% (1)
- PMP Formulas EnglishDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas EnglishArash SadeghipourNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Know For ExamDocument5 pagesFormulas To Know For ExamMohsin RazaNo ratings yet
- Brain DumpDocument4 pagesBrain DumpDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- Formulas Math For PMPDocument3 pagesFormulas Math For PMPramorclNo ratings yet
- Formulas CAPMDocument1 pageFormulas CAPMrrreNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulaDocument3 pagesPMP FormulaCarmen SalazarNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Pass CAPM ExamDocument3 pagesFormulas To Pass CAPM ExamPhu Anh Nguyen75% (4)
- FORMULASDocument4 pagesFORMULASGaneshNo ratings yet
- PMP - Formula Sheet - Project Academy PDFDocument5 pagesPMP - Formula Sheet - Project Academy PDFYelamanchi Vivek ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Pass PMP Exam PDFDocument3 pagesFormulas To Pass PMP Exam PDFGalal MohamedNo ratings yet
- PMP Quick Reference GuideDocument20 pagesPMP Quick Reference Guidevivek100% (2)
- PMP FormulasDocument3 pagesPMP FormulasMohyuddin A MaroofNo ratings yet
- Formulas PMP V01Document1 pageFormulas PMP V01Eric AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Know For EXAM: Activity & Project Duration FormulasDocument5 pagesFormulas To Know For EXAM: Activity & Project Duration FormulasMMNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Know For EXAM: Activity & Project Duration FormulasDocument5 pagesFormulas To Know For EXAM: Activity & Project Duration FormulasbhavikaNo ratings yet
- PMP Exam FormulasDocument1 pagePMP Exam FormulasupendrasNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas PMBOK6 PDFDocument3 pagesPMP Formulas PMBOK6 PDFMirek GodzwonNo ratings yet
- Key Concept and Formulas For PMP ExamDocument4 pagesKey Concept and Formulas For PMP ExamaaranganathNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Week5Document5 pagesPMP Formulas Week5Oscar DoreyNo ratings yet
- Project Management Professional PMP FormulasDocument4 pagesProject Management Professional PMP FormulassachingandhiNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasSuranjan Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management Terms & Definitions Abbr. PV EV AC BAC EAC ETC VACDocument1 pageEarned Value Management Terms & Definitions Abbr. PV EV AC BAC EAC ETC VACcNo ratings yet
- CMQ-OE FormulasDocument2 pagesCMQ-OE FormulasMusman SattarNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument3 pagesPMP Formulasravikumar_sqaNo ratings yet
- PmpformulasDocument2 pagesPmpformulasDurga Prasad CuddapahNo ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisDocument3 pagesMy Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisshanmugaNo ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesMy Notes On PMP Formulasshakeelkhn18No ratings yet
- PMP Exam Formulas Summary: Earned Value Management Name Abbr. Formula NoteDocument6 pagesPMP Exam Formulas Summary: Earned Value Management Name Abbr. Formula NoteTrương ĐịnhNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Cheat Sheet StatementDocument1 pagePMP Formulas Cheat Sheet StatementdercoconsultoresNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP Formulasvnethi9317100% (2)
- PRM101B Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPRM101B Cheat Sheetmarlize viviersNo ratings yet
- Praizion Media PMP Exam Student'S Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPraizion Media PMP Exam Student'S Cheat SheetAbhijeet BhatNo ratings yet
- Qvive PMP Formulas PMBOK6 v1bDocument1 pageQvive PMP Formulas PMBOK6 v1bObi A AgusioboNo ratings yet
- Evm 1703180224Document4 pagesEvm 1703180224ghv9cxgzjxNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 - MN Conference Plan Brief V2.0620Document3 pagesAppendix 1 - MN Conference Plan Brief V2.0620Oscar Perez YaraNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulae: 5. Estimate To CompletionDocument6 pagesPMP Formulae: 5. Estimate To CompletionSathish KannaiyanNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas v4 PDFDocument1 pagePMP Formulas v4 PDFsh1n0b1klNo ratings yet
- Advanced C++ Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandAdvanced C++ Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- IFFCO at A Glance 2012-13Document148 pagesIFFCO at A Glance 2012-13Sangram PandaNo ratings yet
- Ar 15Document324 pagesAr 15ed bookerNo ratings yet
- Blackbook FinalDocument61 pagesBlackbook FinalSanjali MukadamNo ratings yet
- Inder PPT FinalDocument38 pagesInder PPT FinalInderjeet Singh ToorNo ratings yet
- Mid Exam ReviewDocument26 pagesMid Exam Reviewmora0% (1)
- Abbreviations and AcronymsDocument5 pagesAbbreviations and AcronymsTania GalitchiNo ratings yet
- Manitou Group's Annual Report 2012Document200 pagesManitou Group's Annual Report 2012Manitou GroupNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: - 11 - Answer - Key - Chapter - 1 - and - Chapter - 2 - QuizpdfDocument70 pagesQuiz 1: - 11 - Answer - Key - Chapter - 1 - and - Chapter - 2 - QuizpdfRosebel La Bella EjaraNo ratings yet
- The Pigments Market - Coatings WorldDocument3 pagesThe Pigments Market - Coatings Worldrksp99999No ratings yet
- Boeing PresentationDocument6 pagesBoeing Presentationcbzbz711No ratings yet
- Stock Market Risk Management 2Document2 pagesStock Market Risk Management 2vimivijayNo ratings yet
- Arthur AndersenDocument5 pagesArthur AndersenWill KaneNo ratings yet
- What..? How..? and What Nextǥ?Document19 pagesWhat..? How..? and What Nextǥ?Amit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- NISM Series VIII - Equity Derivatives Certification ExaminationDocument12 pagesNISM Series VIII - Equity Derivatives Certification Examinationsaraswathi asndnzNo ratings yet
- Guideline To Install Expert Advisor's Metatrader - v1.41Document19 pagesGuideline To Install Expert Advisor's Metatrader - v1.41Widiyanto WidiyantiNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand Analysis A HistoryDocument44 pagesAggregate Supply Aggregate Demand Analysis A HistoryIoproprioioNo ratings yet
- Articipants 3 PDFDocument21 pagesArticipants 3 PDFAnonymous wUhLBS0% (1)
- BANKINGDocument1 pageBANKINGAswinNo ratings yet
- Valuation Concepts and Methods Sample ProblemsDocument2 pagesValuation Concepts and Methods Sample Problemswednesday addams100% (1)
- Real Estate Taxation - 12.11.15 (Wo Answers)Document7 pagesReal Estate Taxation - 12.11.15 (Wo Answers)Juan FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- Starbucks Case AnalysisDocument45 pagesStarbucks Case AnalysisShoaibNo ratings yet
- Tax Free Retirement WebinarDocument28 pagesTax Free Retirement Webinarphillies1111No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationkrisha milloNo ratings yet
- African Journalof Auditing Accountingand FinanceDocument13 pagesAfrican Journalof Auditing Accountingand FinanceTryl TsNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds: Rajkumar PR Aju JohnDocument12 pagesMutual Funds: Rajkumar PR Aju Johnanon_113615062No ratings yet
- Foxconn Yuanta ReportDocument12 pagesFoxconn Yuanta ReportjtbocianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Property Plant and Equipment 2023 8 24 9 48 25Document12 pagesChapter 3 Property Plant and Equipment 2023 8 24 9 48 25vchandy22No ratings yet
- Investment Banking KnowledgeDocument7 pagesInvestment Banking Knowledge1raju1234100% (1)
- Data For Giving His Heart More Room: Bruce Springsteen's Private FoundationsDocument63 pagesData For Giving His Heart More Room: Bruce Springsteen's Private FoundationsDavid WilsonNo ratings yet
- International Forex Investment Doc. 4Document10 pagesInternational Forex Investment Doc. 4solomwan100% (2)