Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 PL Lect NCM105NDT Introduction
Uploaded by
Ma Ellen Lumauag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
1_PL_LECT_NCM105NDT_INTRODUCTION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pages1 PL Lect NCM105NDT Introduction
Uploaded by
Ma Ellen LumauagCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Nutrition and Dietetics Nutrition
is the study of food and how the body makes
Introduction (Lecture) use of it.
INTRODUCTION: “The way people eat” Function of Nutrition:
Factors Influencing Food Habits Is to maintain life by allowing one to grow
and be in a state of optimum health.
1. Biological determinants
The following are reasons why nutritional
2. Economic determinants
science is applied to nursing care:
3. Physical determinants
The recognition of the role of nutrition in
4. Social determinants
preventing diseases and illnesses.
5. Psychological determinants
The concern of adapting food patterns of
6. Attitudes, beliefs, and knowledge about food.
individuals to their nutritional needs within
the framework of their cultural, economic
Why do we prefer certain foods? and psychological situation and style.
The awareness of the need in specified
Positive: disease states to modify nutritional factors for
therapeutic purpose.
Because we associate it with happiness.
Family gatherings
Eat out with friends
As kids we always ask for “pasalubong” Definition of Terms:
Negative: Good Nutrition: [optimum] body has adequate
supply of essential nutrients for growth and
We associate it with punishment. maintenance of body functions.
Forcing us food we don’t like Poor Nutrition: a state of inadequate or excess
Allergic rxn nutritional intake. [common to people living in
Stomachache/diarrhea poverty]
When we are ill Nutrition: are chemical substances found in food
performing diverse roles in the body namely, to
provide heat and energy, to build and repair body
tissues, and to regulate body processes.
Food Opinion vs Food Preference
What is food opinion?
Classification of Nutrients:
Are set of ideas or concepts held by a person
regarding a certain food. As to Function: nutrients from tissues in the body
These are afflicted or influenced by culture and and body building. These furnish heat and energy
vary from region to region. such as fats, carbohydrates, and protein.
As to Chemical Properties: nutrients are classified
as either organic or inorganic.
Example of Food opinion:
Organic: protein, lipids, carbohydrates,
and vitamins.
Inorganic: water and minerals.
As to Essentiality: this refers to the significant
distribution to the body’s physiological
functioning.
As to Concentration: some nutrients are needed
in large amounts than others.
What is food preference?
Are evaluative attitudes that people express
towards food.
highly influenced by taste.
Food
FOOD is anything which when taken and digested
nourishes the body.
1|ME LUMAUAG
It is a vital need without which man cannot live. Poverty
Foods are also culturally acceptable substances that Ignorance
supply heat and energy, repair body tissues and Poor food habits
regulate body processes. Limited food supply
Distribution of food
Cultural taboos
Qualities of a Good Food:
Nourishing Secondary Factor:
Has satiety value Include all conditions within the body that reduce
Prepared safely. the ultimate supply of nutrients to the cells after the
Palatable food goes beyond the mouth.
Within economic contact
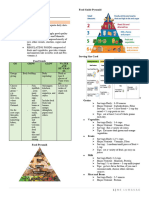
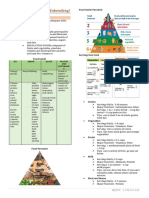
Classification of food: Three Parts of Prevention
Whole Food – fresh foods; unprocessed. Primary Prevention:
Processed Food – manufactured foods; ready to Focus on health promotion.
cook. 1. Conducting nutrition classes
Convenience Food – those that have been prepared 2. Modifying menus and offering low fat
partly or largely by the manufacturer to save us alternatives
from making it. 3. Offering veggies and fresh fruits in
Fast Food – those that are prepared quickly on a cafeterias.
large scale and retail outlets and specializes on a
Secondary Prevention:
few foods instead of larger menu.
Junk Foods – ready made foods in vending Focuses on risk reduction.
machines. 1. Screening on potential diseases
Frozen Foods – food subjected to freezing process. 2. Nutritional counselling for people at risk
[0°F or -18* C] for cardiovascular diseases and diabetes
3. immunizations
Basic Concepts of Nutrition: Tertiary Prevention:
Focus on disease treatment and rehabilitation.
1. Adequate nutrition is essential to good health. 1. Physical rehabilitation for the stroke
2. The nutrient in our body is in dynamic equilibrium. patient
3. Dietary intake and nutrient need should be 2. Cardiac rehabilitation for cardiac patient
individualized. 3. Diabetes education classes for patient with
4. Human requirements are known for some and have newly diagnosed type 1 or type2 DM
to be determined as yet for others.
5. An adequate diet is the foundation of good
nutrition.
6. The physiological function of foods is from
nutrients.
7. Malnutrition is brought about by faulty diets and/or
by conditioning factors like hereditary, infections,
ingestion of certain drugs and parasitism.
8. Need for Nutrition education.
Factors influencing Food habits:
Primary Factor:
Faulty diet - lacking nutrient intake in
quantity and quality.
Factors of a Faulty Diet:
2|ME LUMAUAG
You might also like
- Train Like Bane Workouts InkSaverDocument24 pagesTrain Like Bane Workouts InkSaveruzair ul hasan100% (1)
- Proofed - Final - Clinical Evaluation 4020-21-22 - 1Document11 pagesProofed - Final - Clinical Evaluation 4020-21-22 - 1api-313199824No ratings yet
- 1 PL Lect NCM105NDT IntroductionDocument2 pages1 PL Lect NCM105NDT IntroductionMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- Hmpe 00 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHmpe 00 ReviewerRichmae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Theraphy LabDocument6 pagesNutrition and Diet Theraphy LabCrystal MiranaNo ratings yet
- Nudiet LecDocument5 pagesNudiet LecLeilah DelilahNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition - Lesson 1Document2 pagesFood and Nutrition - Lesson 1donny pangilinanNo ratings yet
- PHEDN01G - Transes in Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 1Document13 pagesPHEDN01G - Transes in Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 1Mikhaella GwenckyNo ratings yet
- Nutri NotesDocument5 pagesNutri NotesMary Anthonyth SereñoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Diet TherapyDocument70 pagesNutrition Diet TherapyMay Rodeo100% (1)
- Food Nutrution XIDocument152 pagesFood Nutrution XITrupti PatilNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec&labDocument18 pagesNCM 105 Lec&labmary navalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy ReviewerDocument10 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy ReviewerNicole CastillaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Why Is Nutrition ImportantDocument6 pagesMODULE 1 - Why Is Nutrition ImportantDonna MarieNo ratings yet
- Basic of Nutrition: Acute Vs ChronicDocument1 pageBasic of Nutrition: Acute Vs ChronicCYRELLE ANNE MALLARINo ratings yet
- Nutrition Introduction - NotesDocument5 pagesNutrition Introduction - NotesLudymae BulahanNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 (Nutrition and Diet Therapy)Document3 pagesNCM 105 (Nutrition and Diet Therapy)Clint Mikael EulatrizNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ch1Document37 pagesNutrition ch1Quang VĩNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Introduction - NotesDocument5 pagesNutrition Introduction - NotesLudymae BulahanNo ratings yet
- NCM105 (Lec) - Prelim ReviewerDocument3 pagesNCM105 (Lec) - Prelim ReviewerAlthea ManarpiisNo ratings yet
- LP 1 - Nutritional AssessmentDocument11 pagesLP 1 - Nutritional AssessmentDacuma Rey JohnNo ratings yet
- TLE 302 ReportDocument9 pagesTLE 302 ReportShiela Amor PequerroNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument4 pagesNUTRITIONaira michaella libiran0% (1)
- Nutridiet-Meaning and Importance of NutrientsDocument2 pagesNutridiet-Meaning and Importance of NutrientsBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument9 pagesLecture - Nutrition and Diet TherapyLalaine Marie BianzonNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 321-E-Lesson-4 PDFDocument21 pagesNutrition 321-E-Lesson-4 PDFteshome teklehaimanotNo ratings yet
- 321 E Lesson 4Document21 pages321 E Lesson 4Novia eka PutriNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument21 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyMrz Alz100% (2)
- Introduction To NutritionDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Nutritionseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Formerly: Notre Dame Hospital and School of MidwiferyDocument14 pagesFormerly: Notre Dame Hospital and School of MidwiferyMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition LectureDocument2 pagesNutrition LectureIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- Basic Food and Nutrition Concepts and TerminologiesDocument29 pagesBasic Food and Nutrition Concepts and TerminologiesDianna MadejaNo ratings yet
- Block I: Healthy Nutrition and Functional Foods: Juliana González Gabriel LadinoDocument38 pagesBlock I: Healthy Nutrition and Functional Foods: Juliana González Gabriel LadinoGabo LadinoNo ratings yet
- Sports and NutritionDocument13 pagesSports and NutritionBhuvi BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Sports and Nutrition Physical Educatin Class 12Document11 pagesSports and Nutrition Physical Educatin Class 12Srushti BhagitNo ratings yet
- Nutrition (Unit 1) : Mohana Priya 1Document4 pagesNutrition (Unit 1) : Mohana Priya 1thakshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument59 pagesChapter 1 - Nutrition and Diet TherapySami Ingles100% (1)
- Lesson 02 Introduction To Basic Concept in Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument4 pagesLesson 02 Introduction To Basic Concept in Nutrition and Diet TherapyMickey MouseNo ratings yet
- NDT 1-4-MergedDocument239 pagesNDT 1-4-Mergedpaula dacaymatNo ratings yet
- Basis Nutrition and Nutritional TherapyDocument9 pagesBasis Nutrition and Nutritional TherapyPrincess CaidoNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lec PrelimDocument33 pagesNutri Lec PrelimEdrea Sten LumangaNo ratings yet
- Diet and Nutrition ReviewerDocument46 pagesDiet and Nutrition ReviewerCassandra Faye JarabejoNo ratings yet
- Physical Chapter 2Document18 pagesPhysical Chapter 2ritikchilwalNo ratings yet
- Health Disparities: Introduction To Food and Nutrition Definition of Terms: 1Document12 pagesHealth Disparities: Introduction To Food and Nutrition Definition of Terms: 1anette katrinNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument5 pagesDefinition of TermsCassandra NicoleNo ratings yet
- Food, Nutrition, Health and Fitness: Earning BjectivesDocument19 pagesFood, Nutrition, Health and Fitness: Earning BjectivesAbd El Kader AshrafNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument24 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyKimberly Marie BayangNo ratings yet
- Module 1 4 PrelimDocument27 pagesModule 1 4 PrelimChezka MendozaNo ratings yet
- Comida en La Vida Saludable.Document3 pagesComida en La Vida Saludable.Martin BastiasNo ratings yet
- NT101 Pamphlet Introduction To NutritionDocument2 pagesNT101 Pamphlet Introduction To NutritionHellie WintourNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer 1711036796Document20 pagesNutrition in Pancreatic Cancer 1711036796Azakari1993No ratings yet
- Nutrition and Your HealthDocument53 pagesNutrition and Your HealthParvinder McCartneyNo ratings yet
- The Meaning and Importance of NutritionDocument3 pagesThe Meaning and Importance of NutritionMignonette PaculabaNo ratings yet
- Health & NutritionDocument35 pagesHealth & Nutritionelle leeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basic AspectsDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Basic AspectsRamkrishna JanaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Clinical Biochemistry-NotesDocument420 pagesNutritional and Clinical Biochemistry-NotesvanishivshettyNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument4 pagesPhysical EducationScythe RyuNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument3 pagesPharmacologyShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- "To Eat Is A Necessity, But To Eat Intelligently Is An Art." La RochefoucauldDocument9 pages"To Eat Is A Necessity, But To Eat Intelligently Is An Art." La RochefoucauldChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec 1Document2 pagesNCM 105 Lec 1Rizaga, Carlos BenedictNo ratings yet
- Harmony from Within: Nurturing Gut Health and Digestive Vitality NaturallyFrom EverandHarmony from Within: Nurturing Gut Health and Digestive Vitality NaturallyNo ratings yet
- 6 - Et - Lect - Basic Concepts and Principles of Diet TheraphyDocument4 pages6 - Et - Lect - Basic Concepts and Principles of Diet TheraphyMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 6 - Et - Basic Concepts and Principles of Diet TheraphyDocument4 pages6 - Et - Basic Concepts and Principles of Diet TheraphyMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 5 - MT - Nutrition in ElderlyDocument4 pages5 - MT - Nutrition in ElderlyMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 7 - ET - LECT - Dietary ManagementDocument3 pages7 - ET - LECT - Dietary ManagementMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 3 - MT - LECT - Nutrition During Pregnancy & LactationDocument3 pages3 - MT - LECT - Nutrition During Pregnancy & LactationMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 3 - MT - LECT - Nutrition During Pregnancy & LactationDocument4 pages3 - MT - LECT - Nutrition During Pregnancy & LactationMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 4 MT LAB Physiologic-Value-of-FoodDocument2 pages4 MT LAB Physiologic-Value-of-FoodMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 1 - PL - LAB - NCM105NDT - Basic Tools in NutritionDocument4 pages1 - PL - LAB - NCM105NDT - Basic Tools in NutritionMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 4 - MT - LECT - Nutrition in Infancy - Children - Adolescent-AdulthoodDocument6 pages4 - MT - LECT - Nutrition in Infancy - Children - Adolescent-AdulthoodMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 4 MT LAB Physiologic-Value-of-FoodDocument2 pages4 MT LAB Physiologic-Value-of-FoodMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 1 - PL - LAB - NCM105NDT - Basic Tools in NutritionDocument4 pages1 - PL - LAB - NCM105NDT - Basic Tools in NutritionMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- 2 PL Lab Energy-WaterDocument6 pages2 PL Lab Energy-WaterMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- The Healthy Lifestyle and Personal Control QuestionnaireDocument23 pagesThe Healthy Lifestyle and Personal Control QuestionnaireDon Chiaw ManongdoNo ratings yet
- Food Nutrition and Health Study GuideDocument14 pagesFood Nutrition and Health Study Guidelonique maximeNo ratings yet
- Virtual Diabetes and EatingDocument72 pagesVirtual Diabetes and EatingShabnam beeNo ratings yet
- Health 7 Q3 M4Document18 pagesHealth 7 Q3 M4edel dearce IIINo ratings yet
- Calisthenics On Posture, Strength and CompositionDocument9 pagesCalisthenics On Posture, Strength and CompositionMaleja ContrerasNo ratings yet
- PE Pre-AssessmentDocument2 pagesPE Pre-AssessmentRayian Mactal100% (1)
- Atu Kenechukwu FINAL YEAR PROJECT 222 (ALPHA) (AutoRecovered)Document21 pagesAtu Kenechukwu FINAL YEAR PROJECT 222 (ALPHA) (AutoRecovered)Kenny AtuNo ratings yet
- Stress Reduction ActivityDocument4 pagesStress Reduction ActivityBramwel Muse (Gazgan bram)No ratings yet
- New Year Fitness Challenge 2020Document51 pagesNew Year Fitness Challenge 2020Foxy BravoNo ratings yet
- Lydiardiowa 99Document33 pagesLydiardiowa 99Milomir JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Physical FitnessDocument38 pagesPhysical FitnessRomel john JamitoNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health 3 Grade 12 Module 1Document25 pagesPhysical Education and Health 3 Grade 12 Module 1Gellian WeeNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Covid 19: 1. Recognize That Your Anxiety Is Completely NormalDocument4 pagesSymptoms of Covid 19: 1. Recognize That Your Anxiety Is Completely NormalArsalan ZuberiNo ratings yet
- Strength and Conditioning For Adolescent Endurance RunnersDocument20 pagesStrength and Conditioning For Adolescent Endurance RunnersDelfín Contreras LendínezNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 PetaDocument1 pagePe 1 PetaAinsley Martin VidadNo ratings yet
- SPEAR 3 - CE 2A Donato A.Document5 pagesSPEAR 3 - CE 2A Donato A.Shesa Lou Suan ViñasNo ratings yet
- Marathon Half: 12-Week Training PlanDocument10 pagesMarathon Half: 12-Week Training PlanJames RetkuNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Concurrent Strength and Endurance.26 PDFDocument9 pagesEffects of A Concurrent Strength and Endurance.26 PDFLucas MatheusNo ratings yet
- Vitabiotics Jointace Max Capsules OcadoDocument1 pageVitabiotics Jointace Max Capsules OcadoShafay Jawed ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Practice Assigment The Personalised Care Operating ModelsDocument11 pagesPractice Assigment The Personalised Care Operating ModelsBrother FamilyNo ratings yet
- Risk For Constipation Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Independent: Goal MetDocument10 pagesRisk For Constipation Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Independent: Goal MetHydie Mae AlcabedosNo ratings yet
- Commerce Scheme Form 1 Term 2 - 2017-1Document17 pagesCommerce Scheme Form 1 Term 2 - 2017-1methembe dubeNo ratings yet
- 5 - 3 - 1 Building The Monolith (LB + KG)Document10 pages5 - 3 - 1 Building The Monolith (LB + KG)Wen YNo ratings yet
- OPT 2019 - Wasting - All LGUsDocument51 pagesOPT 2019 - Wasting - All LGUsRANDY BAOGBOGNo ratings yet
- Ketogenic Diet PDFDocument37 pagesKetogenic Diet PDFVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- ESL With Alice Assessment PackageDocument10 pagesESL With Alice Assessment PackageKai CabactulanNo ratings yet
- PFT Pacer TablesDocument1 pagePFT Pacer Tablesruben yair vargas moraNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness & Longevity TestsDocument17 pagesPhysical Fitness & Longevity TestsmrludiNo ratings yet