0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views19 pagesUnderstanding Electromagnetic Theory
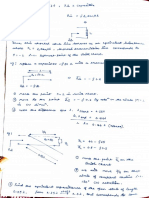
1) The document discusses Maxwell's equations, Gauss's law, Faraday's law of induction, and electromagnetic waves in vacuum.
2) It explains that Maxwell found that Gauss's law must be zero for steady currents, but is generally not zero. This led him to propose Maxwell's addition equations to resolve this issue.
3) The document also discusses how Faraday's law helps explain induction and changes in magnetic flux through a loop of wire. This relates to Lenz's law and the direction of induced currents.
Uploaded by
sharmapiyush5783Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views19 pagesUnderstanding Electromagnetic Theory
1) The document discusses Maxwell's equations, Gauss's law, Faraday's law of induction, and electromagnetic waves in vacuum.
2) It explains that Maxwell found that Gauss's law must be zero for steady currents, but is generally not zero. This led him to propose Maxwell's addition equations to resolve this issue.
3) The document also discusses how Faraday's law helps explain induction and changes in magnetic flux through a loop of wire. This relates to Lenz's law and the direction of induced currents.
Uploaded by
sharmapiyush5783Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd