Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HGJGJ
Uploaded by
Rhodoralyn Ilagan Balhag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesxfstrhgv
Original Title
hgjgj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentxfstrhgv
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesHGJGJ
Uploaded by
Rhodoralyn Ilagan Balhagxfstrhgv
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Review April 2025 Situation 2: Resolve the force onto x, y and z
components that passes from the origin to A
Static of Rigid Bodies:
(2,3,4) in the Figure.
I. Three Dimensional Forces and Structure
Components of three-dimensional forces acting
on structure can be written as:
F = < Fx Fy Fz >
F = Fxi + Fyj + Fzk
When an object is in equilibrium, the sum of all
the forces acting on it must be zero.
(∑Fx)i + (∑Fy)j + (∑Fz)k = 0
This equation will be satisfied only when Situation 3: Determine the resultant of concurrent
system in the Figure that acts on ball and socket
∑Fx = 0; ∑Fy = 0; and ∑Fz = 0
joint at the origin.
They are valid at any point in equilibrium and allow
you to solve for up to three unknowns.
To determine the components in of three-
dimensional forces is by multiplying unit vector or
directional cosine to the force acting on structure.
Fx = Fλx = Fcosθx
Fy = Fλy = Fcosθy
Fz = Fλz = Fcosθz
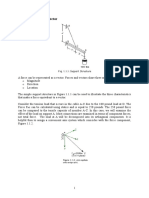
Situation 1: Determine the component of the
force shown in the figure.
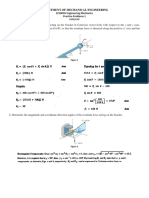
Situation 4: Determine the magnitude of F3 and
the angle it makes with the positive Axes in, so that
the resultant of F1, F2, and F3 is 30 kN directed
exactly with positive z-axis shown in the figure.
Situation 5: The ends of the three cables are
attached to a ring at A and to the edge of a uniform
150kg plate. Determine the tension AB, AC, AD.
Moment on of a Force on Space
• About a point
M=r x F
• About an Axis
M = (r x F) • λaxis
Types of Reactions on a Body
Situation 6: For the given situation, determine
a) Moments about point E b) Moment about
axis CE c) Moment about axis X
Situation 7: The gear box is subjected to three
forces as shown. Given that C1 = 200 lb-in, C2 =
250 lb – in and C3 = 150 lb – in, Determine the x,
y and z component of the resultant couple and
also the resultant couple.
Practice Problems Problem 4: From the figure shown determine
Problem 1 : The sign post shown is acted by a tension AB, AD and AC.
wind force F1 acting at the centroid of signage,
and cable AB is tightened by 12 kN. For the
condition, determine the reactions and
moments at the base of the post.
Problem 5: A derrick is shown in the figure
supporting a 1240 N load. The vertical beam
has a ball and socket connection into the
ground at D and is held by guy wires AC and
BC. Neglecting the weight of the members and
Problem 2 : Calculate the resultant couple of
guy wires. Determine tesion CE, BC and AC.
the two couple as shown in the figure.
Problem 3: Determine the magnitude of a
moment about axis AC of T = 15 kN.
Problem 6: Given the figure, determine the
force acting on member AD, BD and CD.
You might also like
- 2372 - The Bermuda TriangleDocument97 pages2372 - The Bermuda TriangleRomain SuchetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 5 - PDFFiras Abu taleb100% (1)
- Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument371 pagesEquilibrium of A ParticleChristine Torrepenida RasimoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Analysis of Pin Jointed FramesDocument19 pagesChapter 3 Analysis of Pin Jointed Framesghodghod123No ratings yet
- Ia Masonry 17Document8 pagesIa Masonry 17Alliah Jane DelfinNo ratings yet
- W3 1 EquilibriumDocument24 pagesW3 1 EquilibriumNolan ConchaNo ratings yet
- YC6L 中英文图册Document63 pagesYC6L 中英文图册api-3847557100% (2)
- Review Chapter 4-5Document29 pagesReview Chapter 4-5fannyparamitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Analysis 4th Edition Hagen Solutions Manual 1Document94 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Analysis 4th Edition Hagen Solutions Manual 1virginia100% (49)
- Alloy SteelDocument7 pagesAlloy SteelRavinJohnNo ratings yet
- CIPS Level 4 - Diploma in Procurement and Supply Module 1 - Scope and Influence of Procurement and SupplyDocument4 pagesCIPS Level 4 - Diploma in Procurement and Supply Module 1 - Scope and Influence of Procurement and SupplyJalal Quteineh100% (1)
- Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument27 pagesEquilibrium of A ParticleUmut ARSLANNo ratings yet
- Newchapter 2 CstaticsofparticleDocument24 pagesNewchapter 2 Cstaticsofparticlehamizanafiq0809No ratings yet
- LN 5 & 6 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsDocument32 pagesLN 5 & 6 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsSakibNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Module I: Force SystemsDocument12 pagesMechanics: Module I: Force Systemsdevendra044No ratings yet
- Week 3 PDFDocument109 pagesWeek 3 PDFSaid AlzamarehNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Particle (Important Notes)Document36 pagesEquilibrium of Particle (Important Notes)Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- CE311-01 Statics of Rigid Bodies Practice Problems 1Document3 pagesCE311-01 Statics of Rigid Bodies Practice Problems 1Rhiza AtienzaNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Analysis of Simple StructureDocument32 pagesCH-4 Analysis of Simple StructureHaftamu HilufNo ratings yet
- Lec1pt1-Force Analysis-IntroductionDocument36 pagesLec1pt1-Force Analysis-IntroductionEman AhmedNo ratings yet
- 03 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument60 pages03 Equilibrium of A ParticleBaran KirazNo ratings yet
- Task 2Document7 pagesTask 2JOSE ANDRES DE LA A AGUILARNo ratings yet
- For Finals Practice ProblemsDocument13 pagesFor Finals Practice Problemsengr marcialawNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document16 pagesLecture 8Lester JohnNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument128 pagesThermodynamicskushagra singhNo ratings yet
- Principles of StaticsDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Staticsblue nnnNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- L05 - EquilibriumDocument25 pagesL05 - EquilibriumHassanAhmed124No ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument39 pagesEquilibrium of A ParticleTayabaNo ratings yet
- Es 61 - Statics of Rigid Bodies: A B C RDocument3 pagesEs 61 - Statics of Rigid Bodies: A B C RRuel CedeñoNo ratings yet
- QB-em-1 - Mem202Document19 pagesQB-em-1 - Mem202rahuljaiswal1931No ratings yet
- S - Kuliah04 - 2 MARCH - FORCE IN 3DDocument23 pagesS - Kuliah04 - 2 MARCH - FORCE IN 3DFahmi FauziNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document8 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2Jeffrey CachoNo ratings yet
- Forces in Space, Equilibrium of Particles in 3D, Free-Body DiagramsDocument28 pagesForces in Space, Equilibrium of Particles in 3D, Free-Body DiagramsIzay OcenaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Force VectorDocument56 pagesTopic 2 Force VectorhmzhwryajNo ratings yet
- 6 Forces in 3DDocument43 pages6 Forces in 3DKiel JohnNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics-002Document36 pagesEngineering Mechanics-002Oshane So-confidential SawyersNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - 3 - 3D Forces PDFDocument19 pagesCh3 - 3 - 3D Forces PDFislaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - 3 - 3D ForcesDocument19 pagesCh3 - 3 - 3D ForcesXocolynJade ZooValles100% (1)
- Example Problems On Static EquilibriumDocument5 pagesExample Problems On Static Equilibrium-Manvendra Pratap Singh-No ratings yet
- Module1 - Set 1c - SolnDocument6 pagesModule1 - Set 1c - Solnindhubalab200413chNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Strength of Materials - 1Document93 pagesLecture Notes in Strength of Materials - 1Rhea MambaNo ratings yet
- L3-1 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument31 pagesL3-1 Equilibrium of A Particlekalahanmoonga82No ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Analysis 4Th Edition Hagen Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Analysis 4Th Edition Hagen Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmargaret.clark112100% (13)
- 4 Kuliah Kesetimbangan PartikelDocument18 pages4 Kuliah Kesetimbangan PartikelIntan Devi NataliasariNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Section 3 - 4Document17 pagesLecture Notes For Section 3 - 4McFinnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-1 Solutions 2023 - F1Document9 pagesTutorial-1 Solutions 2023 - F1Vaibhav Raman PratapNo ratings yet
- S Kuliah03 Equin2dDocument31 pagesS Kuliah03 Equin2dMuhammad Fekrie Bin SarudinNo ratings yet
- 4 Kuliah Kesetimbangan PartikelDocument18 pages4 Kuliah Kesetimbangan PartikelAra FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- S Kuliah04 Forcein3d 281 29Document24 pagesS Kuliah04 Forcein3d 281 29Muhammad Fekrie Bin SarudinNo ratings yet
- Chap. 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument32 pagesChap. 3 Equilibrium of A ParticlesasasasasNo ratings yet
- Forces and EquilibriumDocument57 pagesForces and EquilibriumUnknown_unknown_unknownNo ratings yet
- S - Kuliah03 - 28 Feb - Equ in 2d - 2Document23 pagesS - Kuliah03 - 28 Feb - Equ in 2d - 2Fahmi FauziNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #1Document3 pagesProblem Set #1AshTzy OfficialNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids by Crandall, Dahl, Lardner, 2nd ChapterDocument118 pagesMechanics of Solids by Crandall, Dahl, Lardner, 2nd Chapterpurijatin100% (2)
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Document22 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Fredy Arana Rodríguez100% (1)
- Vectors and Force System (Lec 5-6) ME 122Document34 pagesVectors and Force System (Lec 5-6) ME 122Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Worksheet FEMDocument4 pagesWorksheet FEMwondimuNo ratings yet
- IE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument8 pagesIE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleBernadeth MontardeNo ratings yet
- Md. Musfiqur Rahman Milton: Lecturer, CSE BaiustDocument15 pagesMd. Musfiqur Rahman Milton: Lecturer, CSE Baiustadiba adibNo ratings yet
- Bda 10203 - Statics: Statics of Particle Lecture 3 - Equilibrium in Plane (2D)Document26 pagesBda 10203 - Statics: Statics of Particle Lecture 3 - Equilibrium in Plane (2D)Norsahira Binti MaslazimNo ratings yet
- Today's Objectives: We Are Able ToDocument26 pagesToday's Objectives: We Are Able ToMohamaadNo ratings yet
- Safety Management Manual: Seafarer's Briefing and FamiliarizationDocument1 pageSafety Management Manual: Seafarer's Briefing and FamiliarizationPoulNo ratings yet
- Direct Vs Indirect Fire SupportDocument1 pageDirect Vs Indirect Fire Support水傲南100% (1)
- CS209Document6 pagesCS209RicardoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibily Guide Galvanized SteelDocument1 pageChemical Compatibily Guide Galvanized Steelralina milyaniNo ratings yet
- DGDocument7,652 pagesDGNaga NitheshNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body Dynamics & RotationDocument45 pagesRigid Body Dynamics & RotationAshlesh Sonje100% (1)
- Ergonomics For Product DesignDocument45 pagesErgonomics For Product DesignNORASHIKEN BINTI OTHMANNo ratings yet
- 12 Pipes and CisternDocument40 pages12 Pipes and Cisternhemanth kumarNo ratings yet
- 295SA NozzleDocument1 page295SA NozzleAmoy AliciaNo ratings yet
- Lima Et Al. 2018Document9 pagesLima Et Al. 2018JOSE ROBERTO DA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Applications of NanotechnologyDocument24 pagesApplications of NanotechnologyVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Krezo 2016 Field Investigation and Parametric Study of Greenhouse GasDocument14 pagesKrezo 2016 Field Investigation and Parametric Study of Greenhouse GasAbhiram shuklaNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metals - Environmental Contaminants and Their Occurrence in Different Types of MilkDocument10 pagesHeavy Metals - Environmental Contaminants and Their Occurrence in Different Types of MilkAdeel ZafarNo ratings yet
- IMSA GTD Spec Scrutineering Manual v0.3Document42 pagesIMSA GTD Spec Scrutineering Manual v0.3emanuelNo ratings yet
- TP - RTT Calculation UMTSDocument11 pagesTP - RTT Calculation UMTSShahnawaz AnjumNo ratings yet
- Project Documentation Part 2Document42 pagesProject Documentation Part 2Lorena LanchoNo ratings yet
- Atlantis Bulletin (No. 3 March 1948)Document2 pagesAtlantis Bulletin (No. 3 March 1948)tjmigoto@hotmail.com100% (1)
- Additol-Xw-330 en LetterDocument2 pagesAdditol-Xw-330 en Letternicolas chNo ratings yet
- A.kishore Journal PaperDocument34 pagesA.kishore Journal PaperA KishoreNo ratings yet
- PSLVDocument14 pagesPSLVVinod SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- The Correlation of Central Corneal Thickness (CCT) To Degree of Myopia and Compare It With EmmetropesDocument4 pagesThe Correlation of Central Corneal Thickness (CCT) To Degree of Myopia and Compare It With EmmetropesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Typical NotesDocument13 pagesTypical NotesDevang TripathiNo ratings yet
- Englisch LK MediationDocument1 pageEnglisch LK Mediation5m2yjn778sNo ratings yet
- Work 2dos - Indigenous and Piñata-6 NovDocument1 pageWork 2dos - Indigenous and Piñata-6 NovDoris50% (2)
- RM50HG 12SDocument3 pagesRM50HG 12SAbu Bakr M. SaeedNo ratings yet