Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 21
Uploaded by
Carlos LourençoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 21
Uploaded by
Carlos LourençoCopyright:
Available Formats
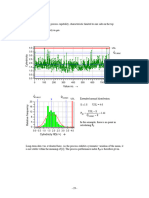
9.
Methods for Calculating Capability Indices
In this chapter, all values are called C p or C pk to make things easier.
In concrete applications, it is the statistical distribution (process model) which determines
whether the capability indices C p or C pk , or the process performance indices P p or P pk are
specified. The calculation method has no effect on this.
9.1 Method M1
This method can only be used for normal distribution.
USL LSL USL LSL
Cp C pk = minimum value of ;
6 3 3
Estimating the process average:
m
1
x xj Total mean (mean of the sample means)
m j 1
n
1
xj xi Mean of a sample with size n (e.g. n = 5)
n i 1
Estimating the standard deviation of the process
m
1
s2 where s2 s 2j
m j 1 1 n
2
where sj xij xj
s 1 m n 1 i 1
where s sj
an m j 1
m
R 1
where R Rj
dn m j 1
m n
1
s total where s total ( x ij x)2
m n 1 j 1 i 1
n 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
an 0.798 0.886 0.921 0.940 0.952 0.959 0.965 0.969 0.973
dn 1.128 1.693 2.059 2.326 2.534 2.704 2.847 2.970 3.078
PA 99 %
Advantages:
C pk can also be calculated manually.
Disadvantages
The value of the calculated index varies slightly with the formula used to estimate the
standard deviation.
- 21 -
You might also like
- Test Bank For Stat2 2nd Edition Ann Cannon George W Cobb Bradley A Hartlaub Julie M Legler Robin H Lock Thomas L Moore Allan J Rossman Jeffrey A WitmerDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Stat2 2nd Edition Ann Cannon George W Cobb Bradley A Hartlaub Julie M Legler Robin H Lock Thomas L Moore Allan J Rossman Jeffrey A Witmerbrianmcgeeprkscgnjiw100% (22)
- Case Analysis Pilgrim BankDocument3 pagesCase Analysis Pilgrim Bankpreetosh1No ratings yet
- 03 Summation NotationDocument7 pages03 Summation NotationChristian Dominic OnaNo ratings yet
- Psp-Unit-6 Estimation Theory PDFDocument38 pagesPsp-Unit-6 Estimation Theory PDFDHAIRYA KALAMBENo ratings yet
- Journal of Statistical SoftwareDocument14 pagesJournal of Statistical SoftwaresoniaNo ratings yet
- Vogel's 2Document12 pagesVogel's 2CahMbelingNo ratings yet
- Physics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document15 pagesPhysics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020EdumaaNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Via Maximization of The LikelihoodDocument6 pagesLinear Regression Via Maximization of The LikelihoodAkansha KalraNo ratings yet
- Net Protection GuideP21 30Document10 pagesNet Protection GuideP21 30Emmanuel ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- 1552649205E textofChapter3Module1Document8 pages1552649205E textofChapter3Module1Ashish TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Banking Efficiency in China: Application of DEA and Tobit AnalysisDocument5 pagesBanking Efficiency in China: Application of DEA and Tobit AnalysisBereket Zerai GebremichaelNo ratings yet
- Dihedral GroupDocument2 pagesDihedral GroupGoranHuyghNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Properties of The Z-TransformDocument13 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Properties of The Z-TransformJulie ThorNo ratings yet
- 1s. RMS DisplacementDocument3 pages1s. RMS DisplacementMsc JmcNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis Mean and Standard DeviationsDocument3 pagesStatistical Analysis Mean and Standard Deviationskostas.sierros9374100% (1)
- Two Stage Cluster 1Document2 pagesTwo Stage Cluster 1Dhofirur RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 1B40 Practical Skills: Weighted MeanDocument7 pages1B40 Practical Skills: Weighted MeanRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- CS-311 Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument23 pagesCS-311 Design and Analysis of Algorithmsabdullah noorNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document6 pagesCH 4ByhiswillNo ratings yet
- STA 342-TH9-Correlation and RegressionDocument13 pagesSTA 342-TH9-Correlation and Regressionsolomon mwatiNo ratings yet
- Binomial BSconvergenceDocument10 pagesBinomial BSconvergenceVeeken ChaglassianNo ratings yet
- Two-Variable Regression Model - The Problem of EstimationDocument35 pagesTwo-Variable Regression Model - The Problem of EstimationAyesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Image Segmentation Using Gaussian Mixture ModelsDocument9 pagesImage Segmentation Using Gaussian Mixture ModelsullisrinuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7b - Analysis of SimulationDocument34 pagesLecture 7b - Analysis of SimulationBrian GnorldanNo ratings yet
- Mohr-Coulomb Failure Condition and The Direct Shear Test RevisitedDocument4 pagesMohr-Coulomb Failure Condition and The Direct Shear Test Revisitedpaul pratimaNo ratings yet
- MTH401 - Assignment No.2 Solution Spring 2021Document5 pagesMTH401 - Assignment No.2 Solution Spring 2021wasiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ANOVADocument11 pagesIntroduction To ANOVAFernando Josafath AñorveNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 6 Data Description PDFDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 6 Data Description PDFPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Entropy-Based Inference Using R and The NP Package: A PrimerDocument11 pagesEntropy-Based Inference Using R and The NP Package: A PrimerMilkha SinghNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 52Document1 pageStat Mining 52Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Parametric MethodsDocument28 pagesCh4 Parametric MethodsRikiNo ratings yet
- e-BookJEE CenterofMass EnglishDocument29 pagese-BookJEE CenterofMass EnglishSoham KejriwalNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - Descriptive Multivariate StatisticsDocument9 pagesSection 2 - Descriptive Multivariate StatisticsTwinomugisha MorrisNo ratings yet
- Markowitz Models and CAPMDocument17 pagesMarkowitz Models and CAPMVinay DuttaNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralDocument17 pagesMultiple IntegralSurajit DasNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareDocument26 pagesX-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareukavathekarNo ratings yet
- Doe Rls TeoríaDocument52 pagesDoe Rls TeoríaFroylan FrancoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10: Recursive Least Squares EstimationDocument20 pagesLecture 10: Recursive Least Squares Estimationaang998No ratings yet
- ECMT1010 Final FormulaDocument2 pagesECMT1010 Final FormulaAbdulla ShaheedNo ratings yet
- The Lognormal Random Multivariate Leigh J. Halliwell, FCAS, MAAADocument5 pagesThe Lognormal Random Multivariate Leigh J. Halliwell, FCAS, MAAADiego Castañeda LeónNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Design and Analysis of Experiments 6th Edition 9780471487357Document11 pagesSolutions Manual To Accompany Design and Analysis of Experiments 6th Edition 9780471487357Caroline Battle100% (28)
- Formula List and Stats TablesDocument11 pagesFormula List and Stats TablessulistyokuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document21 pagesTutorial 1ChunmingChanNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R ChartsDocument26 pagesX-Bar and R ChartsscjofyWFawlroa2r06YFVabfbajNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareDocument18 pagesX-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareAldrige LuisNo ratings yet
- N-Dimensional Cyclic SystemDocument6 pagesN-Dimensional Cyclic SystemRojo JohnNo ratings yet
- Sample Size For Estimating MeanDocument5 pagesSample Size For Estimating MeanmurniNo ratings yet
- QB CombinatoricsDocument7 pagesQB Combinatoricscrazyfirefly7No ratings yet
- A Study of Weibull Mixture ROC Curve With Constant Shape Parameter PDFDocument10 pagesA Study of Weibull Mixture ROC Curve With Constant Shape Parameter PDFAzhar UddinNo ratings yet
- Polymer Physics NewDocument22 pagesPolymer Physics NewShubhamGupta100% (1)
- RMSD and MSDDocument4 pagesRMSD and MSDJorge SanchezNo ratings yet
- 4 Curve Fitting Least Square Regression and InterpolationDocument59 pages4 Curve Fitting Least Square Regression and InterpolationEyu KalebNo ratings yet
- Two Sample T-TestDocument95 pagesTwo Sample T-TestJOMALYN J. NUEVONo ratings yet
- Chap2 Lec5 Unconstrained Geometric ProgrammingDocument5 pagesChap2 Lec5 Unconstrained Geometric ProgrammingUzair AslamNo ratings yet
- Periodograms and Blackman-Tukey Spectral Estimation: - ObjectivesDocument11 pagesPeriodograms and Blackman-Tukey Spectral Estimation: - ObjectivesrakeshNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 42Document1 pageStat Mining 42Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Life-, Health-And Pension-MathematicsDocument5 pagesExercises in Life-, Health-And Pension-MathematicsDipen PandyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Binomial TheoremDocument39 pages6 Binomial TheoremHimanshu GoyalNo ratings yet
- Estimation For The Discretely Observed Cox-IngersoDocument14 pagesEstimation For The Discretely Observed Cox-IngersoLý Nguyễn Kỳ DuyênNo ratings yet
- X-Bar Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareDocument14 pagesX-Bar Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareDeepKanwarNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 36Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 36Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 26Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 26Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 31Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 31Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 33Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 33Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 29Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 29Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 16Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 16Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 1Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 1Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Transportadores WAMDocument202 pagesCatalogo Transportadores WAMCarlos Lourenço100% (1)
- Machine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 14Document1 pageMachine and Process Capability Booklet 9 - 14Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Manual - K-Ducer SeriesDocument64 pagesManual - K-Ducer SeriesCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- 5 Guidelines For Gear Unit Selection: 5.1 Additional DocumentationDocument21 pages5 Guidelines For Gear Unit Selection: 5.1 Additional DocumentationCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Pi Halotherm GBDocument2 pagesPi Halotherm GBCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Tubular Screw ConveyorsDocument4 pagesStainless Steel Tubular Screw ConveyorsCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- JP4 PDFDocument50 pagesJP4 PDFCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Learning About FA Sensors and Displacement Sensors: Beginner's GuideDocument12 pagesLearning About FA Sensors and Displacement Sensors: Beginner's GuideCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Pantógrafo BA12-ACXDocument8 pagesPantógrafo BA12-ACXCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- CP Stands-D53+D57+D58Document10 pagesCP Stands-D53+D57+D58Carlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- MFMEA Workshop Class Overhead 04Document43 pagesMFMEA Workshop Class Overhead 04Carlos Lourenço100% (2)
- Paint Mix RoomsDocument4 pagesPaint Mix RoomsCarlos LourençoNo ratings yet
- Statistics&probability11 q3 Week7 v4Document13 pagesStatistics&probability11 q3 Week7 v4juliusNo ratings yet
- STAT 606 - Some Empirical Methods Slides - 2019 - 2020Document39 pagesSTAT 606 - Some Empirical Methods Slides - 2019 - 2020TennysonNo ratings yet
- Data PenjualanDocument8 pagesData PenjualanK PNo ratings yet
- Anova Table in Research PaperDocument5 pagesAnova Table in Research Paperfyr90d7mNo ratings yet
- MC Multiple RegressionDocument7 pagesMC Multiple Regressionnhat hoang ducNo ratings yet
- Take HomeDocument4 pagesTake HomeZieyZANo ratings yet
- 1-Z-Test For Mean PDFDocument20 pages1-Z-Test For Mean PDFKhanal Nilambar0% (1)
- Book: Advanced Statistical Methods and Applications: Statistica March 2018Document10 pagesBook: Advanced Statistical Methods and Applications: Statistica March 2018DEVAKI NNo ratings yet
- Mathematical-Economics Solved MCQs (Set-3)Document8 pagesMathematical-Economics Solved MCQs (Set-3)MiressaBeJi100% (1)
- Syllabus Applied Microeconometrics 23fallDocument5 pagesSyllabus Applied Microeconometrics 23fallestifNo ratings yet
- Evans Analytics2e PPT 08Document73 pagesEvans Analytics2e PPT 08qunNo ratings yet
- M. Amir Hossain PHD: Course No: Emba 502: Business Mathematics and StatisticsDocument31 pagesM. Amir Hossain PHD: Course No: Emba 502: Business Mathematics and StatisticsSP VetNo ratings yet
- Optimization Methods of EWMA Statistics: Petar ČisarDocument15 pagesOptimization Methods of EWMA Statistics: Petar ČisarLiban Ali MohamudNo ratings yet
- MA121-1 3 4-hwDocument19 pagesMA121-1 3 4-hwMsKhan0078No ratings yet
- MODULE 4-Dr - GMDocument23 pagesMODULE 4-Dr - GMgeetha megharajNo ratings yet
- Measures of Relative PositionDocument18 pagesMeasures of Relative PositionEdesa Jarabejo100% (1)
- Hypothesis TestingDocument82 pagesHypothesis TestingNawzi kagimboNo ratings yet
- What Can Numxl Do For Me?: 1. General StatisticsDocument5 pagesWhat Can Numxl Do For Me?: 1. General StatisticsNumXL ProNo ratings yet
- Module 6A Estimating RelationshipsDocument104 pagesModule 6A Estimating Relationshipscarolinelouise.bagsik.acctNo ratings yet
- Factory Overhead Variance AnalysisDocument3 pagesFactory Overhead Variance AnalysisKabobo HanNo ratings yet
- CAT 2 Study Materials MAT 2001 PDFDocument12 pagesCAT 2 Study Materials MAT 2001 PDFsashidhar avuthuNo ratings yet
- Hasil Olah Data Penelitian SPSSDocument7 pagesHasil Olah Data Penelitian SPSSputrinurulNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical AnalysesDocument7 pagesBasic Statistical AnalysesHannah LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Regression and Correlation NotesDocument6 pagesRegression and Correlation NotesJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Kualitas Produk Kartuhalo Terhadap Kepuasan Pengguna (Studi Pada Grapari Telkomsel MTC Bandung)Document16 pagesPengaruh Kualitas Produk Kartuhalo Terhadap Kepuasan Pengguna (Studi Pada Grapari Telkomsel MTC Bandung)IrawanNo ratings yet
- Cronbacs Real StatDocument72 pagesCronbacs Real StatSer GiboNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 KNNDocument16 pagesUnit 3 KNNAman PrasadNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument69 pagesHypothesis TestingGaurav SonkarNo ratings yet