Professional Documents
Culture Documents
If Clause
Uploaded by
VLADUTZZU0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document summarizes the different types of conditional clauses in English grammar:
I) Type I conditional clauses discuss possible or likely present or future situations, and use the present tense in the if-clause.
II) Type II conditional clauses discuss unlikely or hypothetical present or future situations, and use the past tense ("would" + verb) in the main clause.
III) Type III conditional clauses discuss hypothetical past situations, and use "would have" + past participle in the main clause.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the different types of conditional clauses in English grammar:
I) Type I conditional clauses discuss possible or likely present or future situations, and use the present tense in the if-clause.
II) Type II conditional clauses discuss unlikely or hypothetical present or future situations, and use the past tense ("would" + verb) in the main clause.
III) Type III conditional clauses discuss hypothetical past situations, and use "would have" + past participle in the main clause.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesIf Clause
Uploaded by
VLADUTZZUThis document summarizes the different types of conditional clauses in English grammar:
I) Type I conditional clauses discuss possible or likely present or future situations, and use the present tense in the if-clause.
II) Type II conditional clauses discuss unlikely or hypothetical present or future situations, and use the past tense ("would" + verb) in the main clause.
III) Type III conditional clauses discuss hypothetical past situations, and use "would have" + past participle in the main clause.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
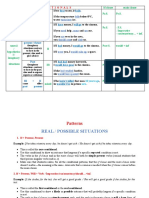
If Clause (Conditional Clauses)
Type Main Clause If Clause
I FutureTense/Present Tense/Imperative Present Tense
II Present Conditional Past Tense
(Would + Short Infinitive)
III Perfect Conditional Past perfect
(would + have + vbIII/vb-ed)
Examples:
1. Jamie won’t get the part if ……………………………………………..
2. If I had understood the situation ……………………………………….
3. If Fiona is leaving now …………………………………………………
4. They would see each other more often if ……………………………….
5. Tom would have won the dance competition if ………………………..
6. If Iris earned more money ………………………………………………
7. If I were you …………………………………………………………….
8. Tell me if ………………………………………………………………..
9. I always take my umbrella if ……………………………………………
Notes:
1. Unless = If Not
2. Should in if clause means “by chance” (types I and II)
3. Were to in if clause means “by chance” (type II)
4. If it weren’t for sb/sth (II) = But for sb/sth
If it hadn’t been for sb/sth (III) = But for sb/sth
5. Omission of “if” + inversion:
e.g. If he should call you, let me know!
Should he call you, let me know!
Type I – Should
Type II – Should or Were to
Type III – Had
6. Mixed types:
e.g. If Mary hadn’t been so rude with him, he would help her with the application now.
If Tom were an honest person, his boss wouldn’t have fired him.
7. Alternatives for “IF”
- Provided/providing (that)
- Suppose/supposing (that)
- Imagine
- As long as
- On condition that
You might also like
- Enis 1St Year Engineering: Remedial Structural Work: The Real and Unreal Conditional 1-Structure of If-ClausesDocument3 pagesEnis 1St Year Engineering: Remedial Structural Work: The Real and Unreal Conditional 1-Structure of If-ClausesChokri GhzaielNo ratings yet
- If Clause - Type 2 and 3Document12 pagesIf Clause - Type 2 and 3Natalie StasenkoNo ratings yet
- Conditionals PatternsDocument6 pagesConditionals PatternsOleseaNo ratings yet
- Untuk Bahasa Inggris Conditional SentenceDocument4 pagesUntuk Bahasa Inggris Conditional SentenceAnnisaIstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Conditional Class Full NotesDocument13 pagesConditional Class Full NotesThangavel Raj JNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesTrang Nguyễn Thị VânNo ratings yet
- If Clauses Conditional With QuestionsDocument22 pagesIf Clauses Conditional With QuestionsAroshani LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type 1Document2 pagesConditional Sentence Type 1Vicky NiSaNo ratings yet
- IF ClausesDocument5 pagesIF ClausesSimonaNo ratings yet
- Reprhrasing Conditional and TheoryDocument7 pagesReprhrasing Conditional and TheoryAngelSevillaCortesNo ratings yet
- Lectia 05Document4 pagesLectia 05cristiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences, If-Clauses Type I, Ii, IiiDocument8 pagesConditional Sentences, If-Clauses Type I, Ii, IiiYaumil Agus AkhirNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleDocument13 pagesConditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleAurelia Mihaela SoleaNo ratings yet
- If Conditional (Group 2)Document21 pagesIf Conditional (Group 2)Franc Ronaldo Galunk'sNo ratings yet
- 2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Document10 pages2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Alba Fortuny HueteNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clauses: Type ConditionDocument12 pagesConditional Clauses: Type ConditionFranz ThereNo ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument4 pagesIf Clausesadriandobre2014No ratings yet
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument5 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseRatnaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals BAC2 G PDocument4 pagesConditionals BAC2 G PAndreia Simões0% (1)
- Conditionals V 2Document49 pagesConditionals V 2dorayNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument7 pagesConditionalserdakovaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals/If Sentences: The Condition, EtcDocument2 pagesConditionals/If Sentences: The Condition, Etcoussama achouriNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesDavid MoraisNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument6 pagesConditional SentenceJuniErikaNo ratings yet
- If Clauses EnglishDocument13 pagesIf Clauses EnglishMaiden DiNo ratings yet
- Type 0, Type 1, Type 2 and Type 3.: Conditionals ConditionalsDocument6 pagesType 0, Type 1, Type 2 and Type 3.: Conditionals ConditionalsAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument2 pagesConditionalSylvie ChamberlandNo ratings yet
- Lectia 05Document4 pagesLectia 05Lillee LilutzaNo ratings yet
- Iffy The IfilantDocument1 pageIffy The IfilantJoe BenegasNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument4 pagesConditional SentenceAmelia SaphiraNo ratings yet
- First, Second, Third ConditionalDocument12 pagesFirst, Second, Third ConditionalGünel BayramovaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument49 pagesConditionalsapi-252190418100% (1)
- Conditional Sentences Fraza CondiționalăDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences Fraza CondiționalăSimonaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences (Kalimat Pengandaian)Document4 pagesConditional Sentences (Kalimat Pengandaian)gn_X00No ratings yet
- Câu điều kiện P2Document5 pagesCâu điều kiện P2laduc03hnNo ratings yet
- Ud4 Comunicacion Prof InglesDocument19 pagesUd4 Comunicacion Prof InglesJose Miguel Ortega AndresNo ratings yet
- 7A Q2 L2 LÝ THUYẾT CONDITIONALS 3, MIXED, INVERTED (GV)Document2 pages7A Q2 L2 LÝ THUYẾT CONDITIONALS 3, MIXED, INVERTED (GV)Minh Phạm NgọcNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesConditional Sentencesnghiemtrang159No ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument13 pagesIf ClausesYunanda Alya MustikaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalstamaraNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument20 pagesConditionalsFátimaNo ratings yet
- Gapol - Ro 11 IF Clauses PDFDocument10 pagesGapol - Ro 11 IF Clauses PDFDerek12121No ratings yet
- Conditionals Zsófi MódraDocument3 pagesConditionals Zsófi MódraBácskay Balázsné ZsófiaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument7 pagesConditional SentencesdevyNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument22 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseTita RashidaNo ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument16 pagesIf ClausesFaLeNNo ratings yet
- IF + PRESENT ............................. WILL + INFINITIVE: I Conditional SentencesDocument1 pageIF + PRESENT ............................. WILL + INFINITIVE: I Conditional SentencesmariaNo ratings yet
- Engleski Jezik 4: 1. Tenses 2. Conditionals 3. TranslationDocument17 pagesEngleski Jezik 4: 1. Tenses 2. Conditionals 3. TranslationMohaci IstvanNo ratings yet
- IF Clauses. Cauzalele in EnglezaDocument7 pagesIF Clauses. Cauzalele in EnglezaAngela FaurNo ratings yet
- Grammar On Unit8:: Second Conditional Because ofDocument2 pagesGrammar On Unit8:: Second Conditional Because ofjenaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Unit 6 2º BachilleratoDocument49 pagesConditional Sentences: Unit 6 2º BachilleratoOmar hopperNo ratings yet
- Frases Condicionales 1Document3 pagesFrases Condicionales 1EdwinGomezNo ratings yet
- General Truths, Laws of Nature, Things Which Are Always TrueDocument6 pagesGeneral Truths, Laws of Nature, Things Which Are Always TrueDaniela InczeNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Conditional Sentences - Updated 26 09 2021Document13 pagesUnit 8 Conditional Sentences - Updated 26 09 2021Khang PhạmNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesConditional SentencesAlice ClaraNo ratings yet
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.From EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllFrom EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (83)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonFrom EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageFrom EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (916)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideFrom EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideNo ratings yet
- The Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandThe Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageFrom EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (429)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (136)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsFrom EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Everything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfFrom EverandEverything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- Win Every Argument: The Art of Debating, Persuading, and Public SpeakingFrom EverandWin Every Argument: The Art of Debating, Persuading, and Public SpeakingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (78)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesFrom EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Messages: The Communication Skills BookFrom EverandMessages: The Communication Skills BookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (151)