Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2-DRIVING FORCES & LEVELS OF CHANGE
Unit 2-DRIVING FORCES & LEVELS OF CHANGE
Uploaded by
Yoven Comorandy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views19 pagesThe document discusses the various forces driving change at different levels, from the global arena down to individual organizations. It presents a four-tier model examining forces at the global, regional/subregional, national, and organizational levels. At the organizational level, it analyzes internal forces influencing individuals, groups/teams, and the overall organization. The document aims to provide a holistic understanding of internal and external change factors in order to effectively manage organizational development.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the various forces driving change at different levels, from the global arena down to individual organizations. It presents a four-tier model examining forces at the global, regional/subregional, national, and organizational levels. At the organizational level, it analyzes internal forces influencing individuals, groups/teams, and the overall organization. The document aims to provide a holistic understanding of internal and external change factors in order to effectively manage organizational development.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views19 pagesUnit 2-DRIVING FORCES & LEVELS OF CHANGE
Unit 2-DRIVING FORCES & LEVELS OF CHANGE
Uploaded by
Yoven ComorandyThe document discusses the various forces driving change at different levels, from the global arena down to individual organizations. It presents a four-tier model examining forces at the global, regional/subregional, national, and organizational levels. At the organizational level, it analyzes internal forces influencing individuals, groups/teams, and the overall organization. The document aims to provide a holistic understanding of internal and external change factors in order to effectively manage organizational development.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Unit 2
Driving Forces and
Levels of Change
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 1
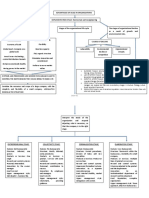
A Four-Tier Model
This model utilises a holistic view in understanding
the various internal and external forces to change.
Global arena
Regional and subregional arena
National context
Organisation: Individual, Group/ Team and
Organisation level
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 2
Globalisation
Globalisation is intertwined with the rise of
technology and the existence of permeable
boundaries,exposing countries such as South Africa
to international competition.
The global arena also brings about international
diversity, changing the nature of workand its
workforce.
Political environment has a great influence on
change of legislation and regulations
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 3
FORCES OF CHANGE – NATURE OF
WORKFORCE
Force of Change Implications
• Greater degree of cultural Effective management
diversity in Organisations of cultural diversity
• Increase in professionals Intellectual capital
management
• Many new entrants and Strategic human
many with resource management
inadequate skills
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 4
FORCE OF CHANGE – TECHNOLOGY
Force of Change Implications
Faster and cheaper Effective technology and
computers relationship Management of
TQM
Total Quality Management Effective implementation of
(TQM) the principles
• Re-engineering programmes Effective knowledge
management
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 5
FORCES OF CHANGE – ECONOMIC
Forces of Change Implications
Increased oil prices
Increased petrol prices
Volatility of the South African
Need for sustainable
rand and high inflation rates
development
Electricity shortages
Attacks in the US
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 6
FORCES OF CHANGE – COMPETITION
Forces of Change Implications
Global competitors Need for strategic
Mergers and acquisitions planning and
Management
Growth of Internet
Commerce
Need to attain Business
Excellence
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 7
FORCES OF CHANGE – SOCIAL TRENDS
Forces of Change Implications
Delayed marriages by young
people
Increased divorce rates
Smaller families
Need for early
Quality of life and increased
focus on leisure
recognition of market
opportunity
Popularity of sport utility vehicles
Attitude towards smokers
HIV/ AIDS
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 8
FORCES OF CHANGE – WORLD POLITICS
Forces of Change Implications
Opening of markets in
China Need to identify, sustain
and exploit a
competitive advantage
Post-apartheid entry into
the global arena
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 9
FORCES OF CHANGE – REGIONAL
ARENA
A marginalised political level
Poor social indicators – High levels of
malnutrition, illiteracy, unemployment, low life
expectancy, etc.
Regional economy
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 10
FORCES OF CHANGE – NATIONAL
CONTEXT
Demographic profile consists of differences in age
distribution, official languages,
education levels and unemployment rates
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 11
INTERNAL FORCES OF CHANGE
The Individual Level – Individuals differ in terms
of personality, values, interests, etc. which creates
a complex situation in understanding how each
individual behaves and operates in an
organisation.
Individuals accumulate knowledge and
experience, creating a workforce with diverse
thinking and insights.
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 12
INTERNAL FORCES OF CHANGE
Group Level – teams and groups in organisations
can be constituted in a number of ways that allows
for an array of teams and groups to exist and
function differently in the workplace.
“Task and project teams allow an organisation to
operate in a more flexible way and, as a
consequence, an organisation can be more
responsive to its business environment.
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 13
INTERNAL FORCES OF CHANGE
Organisational Level – At this level, changes at a
strategic level or changes influenced by internal or
external forces can impact on the entire system of
the organisation. Changes in this level can focus
onorganisational design, culture, structure or
operations
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 14
Contingency Approach
Considers organization and environment.
Identifies “if-then” relationships.
Suggests change directions.
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 15
Future Shock and Change
Too much change in too short a time.
Inability to adapt to accelerating rates of
change.
Management reaction to change strained.
Managers must be adaptable and flexible.
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 16
Table 2.2
Millennial Megatrends: Gateways to Twenty-first
Century
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 17
Key Words and Concepts
Client System - organization employing a
practitioner to assist them in planning
change.
Closed systems - self-contained and isolated
from environment.
Content - task of the group.
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 18
Contingency approach - attempt to determine
proper management technique to employ.
Dynamic equilibrium - steady state, reacting
with environment.
Entropy - movement toward disorder and
eventual termination.
An Experiential Approach to Organization Development 7th edition Chapter 2
Slide 19
You might also like
- Career in Insurance SectorDocument44 pagesCareer in Insurance SectorMinal Dalvi100% (1)
- DILG Nexus To Local Governance - General SupervisionDocument32 pagesDILG Nexus To Local Governance - General SupervisionAngelito CortunaNo ratings yet
- Vuca Management PDFDocument58 pagesVuca Management PDFShaikh RameezaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Designing InterventionsDocument4 pagesLecture Notes - Designing InterventionsJohn Robert YuNo ratings yet
- Change Management POMP - Pembukaan KelasDocument35 pagesChange Management POMP - Pembukaan KelasPutri KartikaNo ratings yet
- General Mihailovich The World's Verdict A Selection of Articles On The First Resistance Leader in Europe Published in The World Press, 1947Document224 pagesGeneral Mihailovich The World's Verdict A Selection of Articles On The First Resistance Leader in Europe Published in The World Press, 1947koekude100% (2)
- Leading Organizational ChangeDocument47 pagesLeading Organizational ChangeTubagus Donny Syafardan100% (2)
- Session 16 - Change ManagementDocument39 pagesSession 16 - Change Managementarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank-1Document272 pagesTest Bank-1ASUS ZENFONENo ratings yet
- Sindh Land Revenue Act 1967Document62 pagesSindh Land Revenue Act 1967Tarique Jamali100% (1)
- Managing Change & Organizational EffectivenessDocument27 pagesManaging Change & Organizational EffectivenessangelhereNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Session 1: Organization Development and Reinventing The OrganizationDocument49 pagesUnit 1 - Session 1: Organization Development and Reinventing The Organizationchemist_tma100% (1)
- Science Olympiad 17-18 Tryout Study GuideDocument2 pagesScience Olympiad 17-18 Tryout Study Guideapi-362736764No ratings yet
- Overcoming Resistance To ChangeDocument46 pagesOvercoming Resistance To Changeberitahr100% (1)
- Organizational Change and DevelopmentDocument18 pagesOrganizational Change and DevelopmentMary R. R. PanesNo ratings yet
- Innovation Governance: How Top Management Organizes and Mobilizes for InnovationFrom EverandInnovation Governance: How Top Management Organizes and Mobilizes for InnovationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Unit 5-STRATEGIC CHANGEDocument26 pagesUnit 5-STRATEGIC CHANGEYoven ComorandyNo ratings yet
- An Experiential Approach To Organization Development 7 EditionDocument35 pagesAn Experiential Approach To Organization Development 7 EditionberitahrNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Designing Interventions 10edDocument12 pagesCH 7 Designing Interventions 10edvaishnavjiNo ratings yet
- An Experiential Approach To Organization Development 7 EditionDocument46 pagesAn Experiential Approach To Organization Development 7 EditionPoonamNo ratings yet
- Leading - Managing The Revolution and Evolution in Globalization of Business Div C Group 8Document30 pagesLeading - Managing The Revolution and Evolution in Globalization of Business Div C Group 8mandar kandalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Organization Renewal: The Challenge of ChangeDocument37 pagesOrganization Renewal: The Challenge of ChangeSnehal Sunil DarjiNo ratings yet
- ANGCOS - The Challenge and The Future For OrganizationsDocument28 pagesANGCOS - The Challenge and The Future For Organizationshoney beeNo ratings yet
- Developing Managerial Leadership Skills.Document8 pagesDeveloping Managerial Leadership Skills.mahisoftsol1No ratings yet
- Syllabus: St. Michael's College College of Accountancy Iligan CityDocument10 pagesSyllabus: St. Michael's College College of Accountancy Iligan CityJohanna AdremesinNo ratings yet
- Org ChangeDocument12 pagesOrg Changekartik bharadwajNo ratings yet
- TNCT Module 4Document3 pagesTNCT Module 4Venizecarylle Alina BorretaNo ratings yet
- CL Study Volume2 WebDocument28 pagesCL Study Volume2 WebSREENo ratings yet
- HR05 - Organizational DevelopmentDocument10 pagesHR05 - Organizational DevelopmentBenny JohnNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change and Stress Management-Group Dynamics-First Group-20210702-Final - Withoud VideoDocument28 pagesOrganizational Change and Stress Management-Group Dynamics-First Group-20210702-Final - Withoud VideoNasr Ahmad NasrNo ratings yet
- Effective Training: Strategies, Systems and PracticesDocument18 pagesEffective Training: Strategies, Systems and PracticesRatneesh NijjarNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Challenges in Quality Leadership in The Public SectorDocument3 pagesStrategies and Challenges in Quality Leadership in The Public SectorijcnesNo ratings yet
- 07 Formulate Recommendations For A Change Process Facilitator SlidesDocument39 pages07 Formulate Recommendations For A Change Process Facilitator SlidesFrans RapetsoaNo ratings yet
- Annual Meeting of The New Champions 2013Document46 pagesAnnual Meeting of The New Champions 2013Anonymous WIhmu39ibwNo ratings yet
- Institutional Reform Cp5Document29 pagesInstitutional Reform Cp5NoreenNo ratings yet
- Organizational Growth, Change and Decline: Prepared By: Danny A. Hinay JRDocument19 pagesOrganizational Growth, Change and Decline: Prepared By: Danny A. Hinay JRErickson CauyaoNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders Management: Sudhir K SinhaDocument79 pagesStakeholders Management: Sudhir K Sinhaajay singh rathoreNo ratings yet
- StateOfAgileCulture2020 1Document26 pagesStateOfAgileCulture2020 1Othmane ChadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 OD Intervention StrategiesDocument30 pagesChapter 8 OD Intervention Strategiesrivaaz88100% (3)
- 21st Century Leadership Michael LorzDocument16 pages21st Century Leadership Michael LorzRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dasgupta 2009Document22 pagesDasgupta 2009TauseefAhmadNo ratings yet
- Lectura Sesión 14 - Singh & Ramdeo - Leading Organizational Development and ChangeDocument27 pagesLectura Sesión 14 - Singh & Ramdeo - Leading Organizational Development and ChangeLinette Vera100% (1)
- Unit04 Managing Change NewDocument37 pagesUnit04 Managing Change NewThảo PhạmNo ratings yet
- Mapa Conceptual Activity 7Document2 pagesMapa Conceptual Activity 7Gabriel Betalleluz FernandezNo ratings yet
- Organizational RenewalDocument28 pagesOrganizational RenewalMahalia SultanNo ratings yet
- Article 3 - Org Learning Knowledge Management - Xid-1202319 - 1Document23 pagesArticle 3 - Org Learning Knowledge Management - Xid-1202319 - 1Cat JoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Busines Stratergy For Digital OrganisationsDocument16 pagesLecture 1 Busines Stratergy For Digital OrganisationsKatongo ChisakutaNo ratings yet
- Strategy SafariDocument42 pagesStrategy SafariGr8 zaibiNo ratings yet
- 1-Leadership, Globalization, Change Management GlobalizationDocument9 pages1-Leadership, Globalization, Change Management Globalizationabdelaziz.tolan2014No ratings yet
- RV CH 7changeDocument37 pagesRV CH 7changekassahunNo ratings yet
- Ijsred V2i1p19Document6 pagesIjsred V2i1p19IJSREDNo ratings yet
- Influencing Factors On Knowledge Management For Organizational SustainabilityDocument18 pagesInfluencing Factors On Knowledge Management For Organizational SustainabilityGabrielaNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Perubahan Dan Pengembangan OrganisasiDocument22 pagesManajemen Perubahan Dan Pengembangan OrganisasiNand2115No ratings yet
- Scaling Up-From Vision To Large Scale Change: A Management Framework For PractitionersDocument61 pagesScaling Up-From Vision To Large Scale Change: A Management Framework For PractitionersYuji EnriquezNo ratings yet
- The People Side of ChangeDocument36 pagesThe People Side of ChangeYasmeen RehmanNo ratings yet
- BPR Presentation (MWU)Document153 pagesBPR Presentation (MWU)zelalem kumiNo ratings yet
- What Is An OrganizationDocument14 pagesWhat Is An OrganizationShipra AnandNo ratings yet
- Achieving and Maintaining Strategic Competitivenes PDFDocument17 pagesAchieving and Maintaining Strategic Competitivenes PDFNnamdi NwosuNo ratings yet
- Achieving and Maintaining Strategic Competitivenes PDFDocument17 pagesAchieving and Maintaining Strategic Competitivenes PDFNnamdi NwosuNo ratings yet
- Strategic ChangeDocument6 pagesStrategic ChangeLohan Strategic Investment limitedNo ratings yet
- Lecciones para Construir Mentalidades ÁgilesDocument7 pagesLecciones para Construir Mentalidades ÁgilesTProyecta: Emprendimiento Cultural de VanguardiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer EthicsDocument13 pagesReviewer EthicsRiccel lanticseNo ratings yet
- Presentation 8Document10 pagesPresentation 8Garima SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Sixteen: Organization Change and DevelopmentDocument17 pagesChapter Sixteen: Organization Change and DevelopmentjananinirNo ratings yet
- E.O.Q CalculationsDocument3 pagesE.O.Q CalculationsYoven ComorandyNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma ProcessDocument41 pagesSix Sigma ProcessYoven ComorandyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Total Quality MGTDocument15 pagesUnit 3 - Total Quality MGTYoven ComorandyNo ratings yet
- Operations MGT - FULL NOTESDocument297 pagesOperations MGT - FULL NOTESYoven ComorandyNo ratings yet
- Heizer01-Operations & ProductivityDocument32 pagesHeizer01-Operations & ProductivityYoven ComorandyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.1.9 Comparing Flowering Plants: 1 Parts of The Flowering PlantDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.1.9 Comparing Flowering Plants: 1 Parts of The Flowering PlantGadgetGlitchKillNo ratings yet
- Be 100% Sure 1 - Group 2Document13 pagesBe 100% Sure 1 - Group 2sunila2310No ratings yet
- EO No. 076 Guidelines On The Provision of Quarters Privilege For Reassigned and Transferred EmployeesDocument5 pagesEO No. 076 Guidelines On The Provision of Quarters Privilege For Reassigned and Transferred EmployeesHarvey Harry SiribanNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence: Realism Theory of Law and SkepticismDocument12 pagesJurisprudence: Realism Theory of Law and SkepticismKhairun NisaazwaniNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument7 pagesKinematicsOrlee Villafañe JrNo ratings yet
- Employment Background Verification FormDocument7 pagesEmployment Background Verification FormAnchit Aggarwal0% (2)
- Economics of Pakistan ECO 211Document2 pagesEconomics of Pakistan ECO 211M ASIFNo ratings yet
- Ach145Document23 pagesAch145prettypetNo ratings yet
- Macaw SweaterDocument2 pagesMacaw SweaternyawNo ratings yet
- The Motives of Oedipus RexDocument3 pagesThe Motives of Oedipus RexKhaya PaladaNo ratings yet
- As 1528.3-2001 Tubes (Stainless Steel) and Tube Fittings For The Food Industry Butt Weld Tube FittingsDocument7 pagesAs 1528.3-2001 Tubes (Stainless Steel) and Tube Fittings For The Food Industry Butt Weld Tube FittingsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- LastthreemonthPayslip 11Document7 pagesLastthreemonthPayslip 11delicata.benNo ratings yet
- Study Habit of The Grade 12 StudentsDocument45 pagesStudy Habit of The Grade 12 StudentsLORENA AMATIAGANo ratings yet
- Can You Find All The Hidden Words in This Word Search? Words Can Go in The Following DirectionsDocument3 pagesCan You Find All The Hidden Words in This Word Search? Words Can Go in The Following Directionspj501No ratings yet
- JointsDocument9 pagesJointsParthasarathy NanjappnNo ratings yet
- Dok 120Document3 pagesDok 120Anonymous EqDOLjk6No ratings yet
- Oakland Area League of Women Voters Voting GuideDocument76 pagesOakland Area League of Women Voters Voting GuideTheOaklandPressNo ratings yet
- Fix Any Usb, SD, Mini, Micro ''No Format Needed''Document48 pagesFix Any Usb, SD, Mini, Micro ''No Format Needed''sebastienNo ratings yet
- Talent Management Training and DevelopmentnotesDocument43 pagesTalent Management Training and DevelopmentnotesKunal SehgalNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Synopsis of Dermatology and Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument1 pageIllustrated Synopsis of Dermatology and Sexually Transmitted DiseasesManoj PavanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Viscous Dampers General Guidelines For Engineers IncludingDocument327 pagesFluid Viscous Dampers General Guidelines For Engineers IncludingAngusNo ratings yet
- San Luis vs. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 80160. June 26, 1989 (Res Judicata Applicable To Quasi-Judicial Decisions)Document13 pagesSan Luis vs. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 80160. June 26, 1989 (Res Judicata Applicable To Quasi-Judicial Decisions)Law SchoolNo ratings yet
- Developing An Evaluation Scale For Assessing The Effective Implementation of Matatag Curriculum in Philippine Public Schools Exploratory SequDocument18 pagesDeveloping An Evaluation Scale For Assessing The Effective Implementation of Matatag Curriculum in Philippine Public Schools Exploratory SequJournal of Interdisciplinary Perspectives100% (1)
- Assessment Presentation - High Quality Classroom AssessmentDocument11 pagesAssessment Presentation - High Quality Classroom AssessmentFajar AminullahNo ratings yet
- IC Auto Invoice 9174Document2 pagesIC Auto Invoice 9174larisaNo ratings yet