Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seminar Lecture
Uploaded by
Edzel JosonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Seminar Lecture
Uploaded by
Edzel JosonCopyright:
Available Formats
Test - instrument, tool, method, or procedure used to measure a behavior.
Measurement - the qualification of the level of knowledge or skills.
Evaluation - judgement of the quality or worth.
Assessment - all activities teachers and students undertake.
Assessment FOR LEARNING - (Formative) KWL, Pre-test
Assessment AS LEARNING - metacognition
Assessment OF LEARNING - (Summative) Periodical test
Why Test?
* It assesses what students have learned.
* Identifies student's strengths and weaknesses.
Stages in Test Creation
1. Define the purpose
2. Determine item format
3. Determine what is to be tested
4. Write the items
5. Review the items
6. Prepare scoring key
7. Write directions
8. Evaluate
Types of Tests
Diagnostic Tests - measures that the students already know and not yet know
Formative Tests - simple test quiz or a recitation
Summative Tests - given at the end of the quarter and graded
Standardized Tests - standard for all
Types of Tests based on format/
* Multiple-choice questions
* True or false
* Matching
* Short answer (identification, fill-in-the-blank)
* Enumeration
* Esssay
* Oral
Construct - what do you want to measure
Example(s) reading comprehension, english proficiency, confidence
NEW BLOOM'S TAXONOMY (verb)
LOTS (lower order thinking skills) and HOTS (higher order thinking skills)
Remember - rote learning or memorization
Understand - explaining using own words
Apply - application
Analyze - breaking down into components
Evaluate - criticizing
Create - make something
Question Words
- who, what, where, when, why and how
Questio Phrases
- in what way, how often, to what extent, and how far
OBJECTIVES (Grade 1 - Tastes and Textures)
At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to:
QUESTIONS
1. Define tastes and textures;
1. What is taste and texture?
2. Explain the different types of tastes and textures;
2. What are the difference between the different tastes and textures?
3. Give the different types of tastes and textures and examples of it;
3. What are the different tastes and textures? Give examples.
4. Classify the different types of tastes and textures;
4. What were the tastes and textures for the given set of pictures?
5. Evaluate which is not an example of taste and texture; and,
5. How will you know if it has a tastes or a textures?
6. Construct a chart or graph giving the different types of tastes and textures.
6. What chart or graph can you use to create or show the similarities and
differences of each types of tastes and textures?
What is taste and texture? (REMEMBER)
1. What do you call the sensation of flavors?
a. color b. taste c. tongue d. texture
What are the difference between the different tastes and textures? (UNDERSTAND)
2. contains sugar: sweet :: contains salt: _________
What are the different tastes and textures? Give examples. (APPLY)
3 - 10. Enumerate the different tastes and texture. Give 1 example of each tastes
and textures.
What were the tastes and textures for the given set of pictures? (ANALYZE)
Directions: Look at the pictures. Write the correct taste or texture of each
picture.
11. (Picture of a mirror)
12. (Picture of a coffee)
How will you know if it has a tastes or a textures? (EVALUATE)
Directions: Look at the picture. Do you think it has a taste or a texture. Why? (3
points)
13 - 15. (Picture of a pineapple)
What chart or graph can you use to create or show the similarities and differences
of each types of tastes and textures? (CREATE)
Directions: Make a venn diagram. Write the similarities and differences of each
tastes and textures. (5 points)
16 - 20. Venn diagram
Considerations
* number of items
* phrasing of the questions
* answerability
* sequence of questions
* grade weights
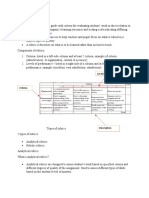
Rubrics
Holistic Rubric - assess as a whole (Score with description)
Analytical Rubric - based on certain criteria ( Criteria, ratings and descriptors)
Single Point Rubric - provides ideal standard and allows for feedback (Criteria
with areas of improvement and evidence)
Common Pitfalls in Test Construction
* writing confusing questions
* including trick or false questions
* multiple choice with different lenghts
* creating page-flipping tests
* not arranging questios in logical order
* giving away answers elsewhere on the test
* writing unclear directions
* writing unimportant questions
FORMS OF VALIDITY
* face validity (looking out of it)
* content validity (content corresponds with the objective)
* construct validity (items should reflect)
* predictive validity (chances of predicting the learner what to learn)
You might also like
- Master the Essentials of Assessment and Evaluation: Pedagogy of English, #4From EverandMaster the Essentials of Assessment and Evaluation: Pedagogy of English, #4No ratings yet
- Sensory Evaluation 1Document9 pagesSensory Evaluation 1Sachin TondarkarNo ratings yet
- Lessonplan Writing MenusDocument2 pagesLessonplan Writing Menusapi-134423826No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Final 2Document6 pagesLesson Plan Final 2api-282314189No ratings yet
- Generalization Lesson Plan Edu505Document10 pagesGeneralization Lesson Plan Edu505api-284836900No ratings yet
- 2 - Preparing TOS. FinalDocument17 pages2 - Preparing TOS. FinalEy VincentNo ratings yet
- Classroom Tests.: Prof. Verónica Pérez Ifd Rocha, Feb, 2011Document15 pagesClassroom Tests.: Prof. Verónica Pérez Ifd Rocha, Feb, 2011Veronica PerezNo ratings yet
- Fruit Operation Lesson Plan: Bloom's TaxonomyDocument3 pagesFruit Operation Lesson Plan: Bloom's Taxonomyapi-340127619No ratings yet
- Tpa 3 - Assessing Student LearningDocument49 pagesTpa 3 - Assessing Student Learningapi-317738807100% (9)
- Problem Pictures C StrempelDocument9 pagesProblem Pictures C Strempelapi-293923613No ratings yet
- Table of Specification TOS With An OvervDocument46 pagesTable of Specification TOS With An OvervNorman T. RegalNo ratings yet
- Marking and TUTDocument26 pagesMarking and TUTgholden12No ratings yet
- Finalproject Assessmentplan AudreyhamillDocument14 pagesFinalproject Assessmentplan Audreyhamillapi-334281741No ratings yet
- Cognitive Process Dimension - Jen&Ryan's ReportDocument48 pagesCognitive Process Dimension - Jen&Ryan's ReportJen NI FerNo ratings yet
- Revision Book For Senior BiologyDocument85 pagesRevision Book For Senior Biologyapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Chocolate Chip Cookies Rubric MakingDocument4 pagesChocolate Chip Cookies Rubric Makingapi-299736788No ratings yet
- Comic How ToDocument8 pagesComic How Toapi-264115497No ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation For Improved Student LearningDocument44 pagesAssessment and Evaluation For Improved Student LearningFebrianiNo ratings yet
- Using Appropriate Assessment Tools Target Competency: Observation ChecklistDocument13 pagesUsing Appropriate Assessment Tools Target Competency: Observation Checklistalmari_11405No ratings yet
- Interview Sheet #4Document17 pagesInterview Sheet #4Louis Knoll BrionesNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationsDocument45 pagesTable of SpecificationsAloha Rodriguez Dael100% (2)
- Math2-Pr AssessmentDocument9 pagesMath2-Pr Assessmentapi-267356151No ratings yet
- Balud Municipal College: (Observations of Teaching-Learning in Actual School Environment)Document9 pagesBalud Municipal College: (Observations of Teaching-Learning in Actual School Environment)Hadji ArmezaNo ratings yet
- Assesment 5 DecDocument10 pagesAssesment 5 DecNed NilNo ratings yet
- Fractions Math 3 RDDocument10 pagesFractions Math 3 RDMeyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Math Shapes Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesMath Shapes Lesson Planapi-506315455No ratings yet
- Critique 2frubricDocument2 pagesCritique 2frubricapi-373754262No ratings yet
- Name: Polycarp C. Nieves Date: October 25, 2020 Subject: Educ 6 - Assessment of Learning Reflection #3Document1 pageName: Polycarp C. Nieves Date: October 25, 2020 Subject: Educ 6 - Assessment of Learning Reflection #3poyNo ratings yet
- L23lesson Plan Final 2Document6 pagesL23lesson Plan Final 2api-282314189No ratings yet
- Michael Grego Social/Emotional Health Unit Plan Dates of Instruction: 9/29, 10/6, 10/13 Grade Level: 5 Munger Hill Elementary SchoolDocument30 pagesMichael Grego Social/Emotional Health Unit Plan Dates of Instruction: 9/29, 10/6, 10/13 Grade Level: 5 Munger Hill Elementary Schoolapi-340420535No ratings yet
- Assessment Cognitive, Psychomotor and AffectiveDocument8 pagesAssessment Cognitive, Psychomotor and Affectivetondutosuau100% (2)
- Audio Report ScriptDocument6 pagesAudio Report ScriptKristine Mae Morillo PalacioNo ratings yet
- 3.3 - Formative Assessment in MathematicsDocument74 pages3.3 - Formative Assessment in MathematicsRiza GusteNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Writing: (Assessment in The Primary School Curriculum, Guidelines For School. NCCA, 2007, P. 4)Document17 pagesAssessment of Writing: (Assessment in The Primary School Curriculum, Guidelines For School. NCCA, 2007, P. 4)khaterine nabongNo ratings yet
- Enduring Ideas and Art CompositionDocument10 pagesEnduring Ideas and Art CompositionJames V. SantoNo ratings yet
- Tosandtcdo 160606120705 PDFDocument45 pagesTosandtcdo 160606120705 PDFstorosarionhs starosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6Ruvy Caroro Legara DenilaNo ratings yet
- Revision Package TSL 3112 Sem 2 2013Document12 pagesRevision Package TSL 3112 Sem 2 2013Wan Amir Iskandar IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument9 pagesTable of Specificationruclito morataNo ratings yet
- Stats Survey ProjectDocument3 pagesStats Survey Projectapi-211552617No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice (2 Points Each)Document9 pagesMultiple Choice (2 Points Each)api-302991474No ratings yet
- СымбатDocument7 pagesСымбатКамила ЖумагулNo ratings yet
- Fs 5 Episode 1Document7 pagesFs 5 Episode 1api-30769713450% (2)
- RUBRICSDocument17 pagesRUBRICSYsmael Villarba CabansagNo ratings yet
- Episode 1 Field 1 PDFDocument20 pagesEpisode 1 Field 1 PDFnikoru nikoNo ratings yet
- Assessment As A Way To Learning. (Session3)Document3 pagesAssessment As A Way To Learning. (Session3)marcaicedo100% (1)
- Cur 528 Assessment PurposesDocument13 pagesCur 528 Assessment Purposesapi-327198421No ratings yet
- Capstone 1 Lesson Plan NourheneDocument3 pagesCapstone 1 Lesson Plan NourheneNGuyễn HuyNo ratings yet
- Marketing Lesson Plan For Branding Taste TestDocument3 pagesMarketing Lesson Plan For Branding Taste TestSusan100% (1)
- Scoring RubricsDocument42 pagesScoring RubricsMuhd Sabrie Ali100% (3)
- Study SkillsDocument16 pagesStudy Skillsganiasma758No ratings yet
- L24lesson Plan Final 2Document6 pagesL24lesson Plan Final 2api-282314189No ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument26 pagesGroup 1 ReportAvergonzado Roquez AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson 1 2nd GradeDocument5 pagesMath Lesson 1 2nd Gradeapi-247228121No ratings yet
- Informal Assessment Buts Report SundayDocument25 pagesInformal Assessment Buts Report SundayDennis Millares YapeNo ratings yet
- Lars LindtsromDocument6 pagesLars LindtsromDila JaafarNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan: ColorDocument37 pagesUnit Plan: Color100001418No ratings yet
- Millicent Atkins School of Education: Common Lesson Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesMillicent Atkins School of Education: Common Lesson Plan Templateapi-489134454No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5 - TasteDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 5 - Tasteapi-253744633No ratings yet
- School Year 2023 2024Document2 pagesSchool Year 2023 2024Edzel JosonNo ratings yet
- OperationswithdecimalsDocument8 pagesOperationswithdecimalsEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Hallways DecorDocument10 pagesHallways DecorEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon PoDocument4 pagesGood Afternoon PoEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- OperationswithdecimalsDocument5 pagesOperationswithdecimalsEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Using Building Up Learning Comprehension Kit (BULCK) Towards An Improved Reading Comprehension SkillDocument20 pagesUsing Building Up Learning Comprehension Kit (BULCK) Towards An Improved Reading Comprehension SkillEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Importance of Soil To AgricultureDocument2 pagesImportance of Soil To AgricultureAqib UmarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Socio-Cultural Outcomes of Mass Communication Objective/SDocument21 pagesLesson 2: Socio-Cultural Outcomes of Mass Communication Objective/SEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Importance of Soil To AgricultureDocument2 pagesImportance of Soil To AgricultureAqib UmarNo ratings yet
- Sample FormatDocument7 pagesSample FormatEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Using Building Up Learning Comprehension Kit (BULCK) Towards An Improved Reading Comprehension SkillDocument34 pagesUsing Building Up Learning Comprehension Kit (BULCK) Towards An Improved Reading Comprehension SkillEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Enhancing The Pupils' Problem Solving Skills Involving Time Through Mobile Learning Approach (Mlearning)Document6 pagesEnhancing The Pupils' Problem Solving Skills Involving Time Through Mobile Learning Approach (Mlearning)Edzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Statement of The ProblemDocument4 pagesStatement of The ProblemEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- PEH MidtermsDocument5 pagesPEH MidtermsEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Bulacan Agricultural State College Pinaod, San Ildefonso, Bulacan PhilippinesDocument3 pagesBulacan Agricultural State College Pinaod, San Ildefonso, Bulacan PhilippinesEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Panitikan Sa Isang Klaseng PangwikaDocument49 pagesPanitikan Sa Isang Klaseng PangwikaEdzel Joson0% (1)
- NEWLY IMPROVED BUCK (BEEd III-A)Document10 pagesNEWLY IMPROVED BUCK (BEEd III-A)Edzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Maam JosefinaDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Maam JosefinaEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report For The Month of March 2021Document1 pageAccomplishment Report For The Month of March 2021Edzel JosonNo ratings yet
- MBTI - Validity and ReliabilityDocument28 pagesMBTI - Validity and Reliabilitypalak duttNo ratings yet
- Educ. 201 Bsed 2bDocument6 pagesEduc. 201 Bsed 2bDaryl EspinoNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Definitions of Group Dynamics - ImportanceDocument3 pagesMeaning and Definitions of Group Dynamics - ImportanceanjicieflNo ratings yet
- Sining Silabus AgricultureDocument11 pagesSining Silabus AgricultureJudemarife RicoroyoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For IYOW SkillsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For IYOW SkillsVictoria GalvezNo ratings yet
- 2021 Myp Personal Project Guide enDocument45 pages2021 Myp Personal Project Guide enSupergirl09No ratings yet
- Grammar Exercises Book 1-5th EditionDocument131 pagesGrammar Exercises Book 1-5th EditionDAVID LEONARDO ROJAS OROZCONo ratings yet
- Cordova Beverlene L. - Practicum PortfolioDocument12 pagesCordova Beverlene L. - Practicum PortfolioBeverlene Enso Lesoy-CordovaNo ratings yet
- HCI Chapter 1Document23 pagesHCI Chapter 1AschenakiNo ratings yet
- English of Oral Communication (September 2020)Document10 pagesEnglish of Oral Communication (September 2020)ESTRADANo ratings yet
- DLL-Mam SionyDocument4 pagesDLL-Mam SionyCherryl SiquigNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Conceptual Framework: Mandatory Ingredients of A Quality ResearchDocument5 pagesTheoretical and Conceptual Framework: Mandatory Ingredients of A Quality ResearchMalkOo AnjumNo ratings yet
- Ej 1077791Document8 pagesEj 1077791Ferreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument1 pageMachine LearningSuman GhoshNo ratings yet
- GRADE 6-Peace and Val Ed Catch-Up PlanDocument2 pagesGRADE 6-Peace and Val Ed Catch-Up PlanDenica BebitNo ratings yet
- Script For Possible QuestionsDocument1 pageScript For Possible QuestionsConrad Zapanta ObrialNo ratings yet
- Isbn: 978-607-8356-17-1Document6 pagesIsbn: 978-607-8356-17-1N SNo ratings yet
- Project Planning and SchedulingDocument205 pagesProject Planning and SchedulingYosef Daniel100% (1)
- Lesson 6 - Principles of Graphics and Design PDFDocument8 pagesLesson 6 - Principles of Graphics and Design PDFGheoff RicareNo ratings yet
- One-Pagers: Trying To Deliberately Increase The Chances of LearningDocument15 pagesOne-Pagers: Trying To Deliberately Increase The Chances of Learningyong enNo ratings yet
- Socialization and Personality DevelopmentDocument17 pagesSocialization and Personality Developmentmeck josephNo ratings yet
- Useful Strategies For Improving Your Spoken English by Griffin LeadabrandDocument1 pageUseful Strategies For Improving Your Spoken English by Griffin LeadabrandRydha ValendaNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesReflection Paperapi-531489457No ratings yet
- Earning Units Exam Principles of TeachingDocument1 pageEarning Units Exam Principles of TeachingJane SantiagoNo ratings yet
- COT First Quarter in English 10Document4 pagesCOT First Quarter in English 10Donzlyf Penedilla-Mojica83% (6)
- HNC U7 Film Practices Assignment KWLMCDocument5 pagesHNC U7 Film Practices Assignment KWLMCapi-425190825No ratings yet
- Orgl 3322 Behavior Ethics L Miranda Acevedo RevisedDocument5 pagesOrgl 3322 Behavior Ethics L Miranda Acevedo Revisedapi-531995233No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper-Administration and SupervisionDocument3 pagesReflection Paper-Administration and SupervisionAding SamNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks For BeginnersDocument72 pagesNeural Networks For BeginnersJonathas Kennedy86% (7)
- Questionnaire On Employee MotivationDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire On Employee MotivationKharim Beine0% (1)