Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 B.tech PH3101 Engineering Physics Unit2
Uploaded by
Nishant ShahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 B.tech PH3101 Engineering Physics Unit2
Uploaded by
Nishant ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
MFT
(1) The Coherent sources of light should have same, Time period, frequency,
wavelength and …………………….
(2) Two independent sources of light of same wavelength cannot show interference.
( True / False )
(3) Condition for constrictive interference of light is that path difference b/w two
coherent light should be ……………………..
(4) For destructive interference, path difference is
a) odd number of half wavelengths
b) even number of half wavelengths
c) whole number of wavelengths
d) even whole number of wavelengths
(5) Constructive interference happens when two waves are
a) out of phase
b) zero amplitude
c) in phase
d) in front
(6) Two waves with phase difference 180° have resultant of amplitude
a) one
b) zero
c) same as the single wave
d) doubles the single wave
(7) If two waves are in phase and have same amplitude then resultant wave has
a) half of amplitude of single wave
b) same amplitude as single wave
c) twice of amplitude of single wave
d) thrice of amplitude of single wave
(8) Fringe width in wedge shaped film is ……………………….
(9) Path difference for destructive interference is …………………..
(10) Path difference for constructive interference is……………………….
Long Answer
(11) Define coherent sources. Explain Young’s double slit experiment and find the
expression for fringe width.
(12) Discuss the formation of interference fringes due to a wedge shaped thin film seen
by normally reflected sodium light and obtain an expression for fringe width.
(13) Describe and explain the formation of Newton’s rings in reflected monochromatic
light. Find the condition of maxima and minima in terms of thickness t.
(14) Show that in Newton’s rings the diameters of bright rings are proportional to the
square roots of odd natural numbers.
(15) Show that in Newton’s rings the diameters of dark rings are proportional to the
square roots of natural numbers.
(16) Explain how Newton’s rings be used to determine refractive index of a liquid?
Derive the formula used.
(17) Newton’s rings are formed in reflected light wavelength 6000 Å with a liquid
between the plane and curved surfaces. If the diameter of the sixth bright ring be 3.1
mm and radius of curvature of the curved surface is 100 cm. Calculate refractive
index of liquid.
(18) Discuss the formation of interference fringes due to thin parallel film seen by
normally reflected light and obtain an expression for maxima and minima condition.
(19) A plane transmission grating has 1500 lines per inch. Find the resolving power of
the grating and the smallest wavelength difference that can be resolved a light of
wavelength 6000 A in the second order.
(20) In Newton’s rings experiment, the diameter of 15th ring was found to be 5900 m
and that of the 5th ring was 3360 m. If the radius of Plano-convex lens is 1 m.
calculate the wave length of lighter used.
(21) Find the expression for the maxima and minima at any point on a screen from
central point in Young’ double slit experiment.
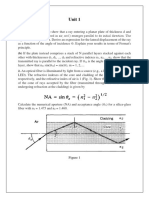
(22) Explain condition of maxima and minima condition produces due to single slit
diffraction. Draw and explain the intensity distribution graph.
(23) Find the range for zero order principle (central) maxima in diffraction grating.
Derive an expression for the minimum number of orders with diffraction grating.
(24) Explain dispersive power of a diffraction grating. Find its expression.
(25) Define resolving power. Derive an expression for the resolving power of grating.
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tutorial - Wave Optics PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial - Wave Optics PDFRavi NasitNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics Pyq 2023Document10 pagesWave Optics Pyq 2023Likitha DashNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightDocument28 pagesApplied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightADARSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument12 pagesWave OpticssanjaysajivkumarNo ratings yet
- Theories of Light and Interference: Questions For PracticeDocument8 pagesTheories of Light and Interference: Questions For PracticeAthulPaiNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightDocument30 pagesApplied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightWilliam MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tabhaii and Diffraction QuestionDocument4 pagesTabhaii and Diffraction QuestionRonish SinghNo ratings yet
- QbankphyaaDocument33 pagesQbankphyaaSteven Brown100% (1)
- Engineering Physics-Physical Optics Imp. QuestionsDocument2 pagesEngineering Physics-Physical Optics Imp. QuestionsSrinivasulu Pudu100% (1)
- Assignment Diffraction 2016Document3 pagesAssignment Diffraction 2016Mankush JainNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Interference 2022Document4 pagesTutorial Interference 2022Shrishti ChordiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Interference 2016Document4 pagesAssignment Interference 2016Ritesh MeelNo ratings yet
- A) B) Xo o C) D) OEO: Malus LawDocument12 pagesA) B) Xo o C) D) OEO: Malus LawDevikaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Sixth EditionDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Physics Sixth EditionQahtan Al-zaidiNo ratings yet
- Army Public School and College Khanewal: Schedule Test 4 (chp7 & 9)Document3 pagesArmy Public School and College Khanewal: Schedule Test 4 (chp7 & 9)Muhammad sajjadNo ratings yet
- Physics ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics ProblemsDiana StavaracheNo ratings yet
- Waves&Optics Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesWaves&Optics Assignment PDFTanisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- 15-04-2022 - SR Iit Star Batch-Ii& Co SC N120, Co Spark, Nipl Super-60 - Main Model Full Test (MFT-1) QP FinalDocument10 pages15-04-2022 - SR Iit Star Batch-Ii& Co SC N120, Co Spark, Nipl Super-60 - Main Model Full Test (MFT-1) QP FinalRani SaiNo ratings yet
- CC 4: Waves and Optics: I. One MarkquestionsDocument11 pagesCC 4: Waves and Optics: I. One MarkquestionsAk CreationNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics QuestionDocument6 pagesWave Optics QuestionMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (Assignment 2)Document2 pagesWave Optics (Assignment 2)garvit1223No ratings yet
- Physics .. Interference, L BiswalDocument5 pagesPhysics .. Interference, L BiswalAnish AnuragNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics AssignmentDocument11 pagesWave Optics AssignmentRudraksh khanna 10th C 5828No ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH-10,11,12,13Document12 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH-10,11,12,13sumitsagar2405No ratings yet
- Engineering Physics Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesEngineering Physics Sample QuestionsJahedul Abedin SohelNo ratings yet
- Questions Unit 1, 2 and 3Document7 pagesQuestions Unit 1, 2 and 3Vigneshwar DhavamaniNo ratings yet
- March 04 PhysicsDocument6 pagesMarch 04 PhysicsDipesh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Physics - I (PH 1110)Document3 pagesPhysics - I (PH 1110)Kappagantu Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics - Question Bank - 3Document8 pagesPhysics - Question Bank - 3Atharv SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Ch9-10 CBSE 2023Document4 pagesCh9-10 CBSE 2023tebor93898No ratings yet
- Assignment Diffraction 2016Document3 pagesAssignment Diffraction 2016Ritesh MeelNo ratings yet
- Case Based 10 and 11 CHPDocument19 pagesCase Based 10 and 11 CHPNETRA DAMGUDENo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Adarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Pruebas IllionoisDocument37 pagesPruebas IllionoisVerito A SecasNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Fiber OpticsDocument24 pagesFundamental of Fiber Opticsramyakrishna kunalaNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics QPDocument2 pagesWave Optics QPschrujhana.jaganNo ratings yet
- Diffraction ProblemsDocument4 pagesDiffraction ProblemsRachit_Goyal25_10No ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument1 pageDiffractionBikash LohaniNo ratings yet
- WAVE OPTICS Previous Year Question (1) Class 12 ImportantDocument4 pagesWAVE OPTICS Previous Year Question (1) Class 12 ImportantYatin KumarNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz Diffraction 1Document2 pagesPractice Quiz Diffraction 1pauljkt1No ratings yet
- Partha QstnsDocument2 pagesPartha QstnsGokul thennarasuNo ratings yet
- Optics Past Paper QuestionDocument3 pagesOptics Past Paper QuestionNadir Ali ShahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 Interference-2 and DiffractionDocument2 pagesAssignment-4 Interference-2 and Diffractionysirola9410No ratings yet
- PaperDocument7 pagesPaperAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics - I: Group - A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Document4 pagesPhysics - I: Group - A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Sayan DasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-WAVES TEST-SPH4U 2023Document9 pagesUnit 4-WAVES TEST-SPH4U 2023Keval DaveNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi University: Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesMahatma Gandhi University: Model Question PaperaNo ratings yet
- Interference of LightDocument2 pagesInterference of LightSalmanNo ratings yet
- Interference of LightDocument2 pagesInterference of LightSalmanNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankSwapnil TripathiNo ratings yet
- Diffraction GratingsDocument5 pagesDiffraction GratingsJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physics - I (PH 111) 0Document3 pagesPhysics - I (PH 111) 0Kappagantu Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Xii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsDocument3 pagesXii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsMaster GamingNo ratings yet
- 9936858-Class 12 - Physics - Wave Optics - Ws With Ans - AnuDocument14 pages9936858-Class 12 - Physics - Wave Optics - Ws With Ans - AnuJoyce CarilloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial I - Interference - 28.01.2019 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial I - Interference - 28.01.2019 PDFrajeshwar ojhaNo ratings yet
- Engineering OpticsDocument2 pagesEngineering OpticshsuyabNo ratings yet
- The Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandThe Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Properties of MaterialsDocument705 pagesThe Properties of Materialsvu0007No ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0260356A1Document4 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0260356A1reynerNo ratings yet
- Translate Section 13 - Analysis of The Basic Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument69 pagesTranslate Section 13 - Analysis of The Basic Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleBeautYy PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and CoordiDocument1 pageInfrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordishiva kumarNo ratings yet
- Persian Gum and Xanthan GumDocument11 pagesPersian Gum and Xanthan GumIoana PeptănaruNo ratings yet
- CHE 10 SylDocument3 pagesCHE 10 SylConrado Galang Jr.No ratings yet
- Food Technology TrendDocument56 pagesFood Technology TrendBambang NurhadiNo ratings yet
- Adrash RaiDocument57 pagesAdrash RaiSTAR PRINTINGNo ratings yet
- UNIT TASK 2 - Fire-Flash Point of DiselDocument13 pagesUNIT TASK 2 - Fire-Flash Point of DiselEddiemar TulinNo ratings yet
- European Patent Specification C23F 11/10, C02F 5/12: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)Document11 pagesEuropean Patent Specification C23F 11/10, C02F 5/12: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)mini2018No ratings yet
- Idp 444Document2 pagesIdp 444sajad gohariNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Natural Gas Processing & ExtractionDocument9 pagesRationale of Natural Gas Processing & ExtractionUJJWALNo ratings yet
- Thermo2 MidDocument4 pagesThermo2 MidnoelNo ratings yet
- TAMOL™ 960 Tamol 731A: Scale InhibitorsDocument4 pagesTAMOL™ 960 Tamol 731A: Scale InhibitorsErick FaundezNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Steady State Conduction: By: Taz 1Document52 pagesOne Dimensional Steady State Conduction: By: Taz 1Adam AndualemNo ratings yet
- Solid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesSolid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of Ethanol On Zeolite Based MediaDocument11 pagesDehydration of Ethanol On Zeolite Based MediaHasan AbuyNo ratings yet
- DPP - 1 - Mole Concept and Redox Reactions - StudentDocument6 pagesDPP - 1 - Mole Concept and Redox Reactions - StudentAngan DeyNo ratings yet
- Lava Lamp Experiment: NAME: Trisha Joanne S. Galang DATE: November 16, 2021Document2 pagesLava Lamp Experiment: NAME: Trisha Joanne S. Galang DATE: November 16, 2021Cyrus De LeonNo ratings yet
- Answer: Q1: What Is Plasma?Document7 pagesAnswer: Q1: What Is Plasma?حنين حسن شعبانNo ratings yet
- CHEM1920 Lecture 10Document22 pagesCHEM1920 Lecture 10Kahelia CampbellNo ratings yet
- Half-Heusler Topological Insulators: A First-Principles Study With The Tran-BlahaDocument5 pagesHalf-Heusler Topological Insulators: A First-Principles Study With The Tran-Blahahumengli525No ratings yet
- Cain CogenDocument12 pagesCain Cogenbradalbi100% (1)
- NPSH CalculationDocument12 pagesNPSH CalculationKiran YadavNo ratings yet
- Cluster Chemistry Chapter 4 PDFDocument48 pagesCluster Chemistry Chapter 4 PDFGax AllebNo ratings yet
- R410a IceloongDocument6 pagesR410a IceloongMarco Ruales100% (1)
- ThermalDocument3 pagesThermalNisa NiichiNo ratings yet
- Zeolites As Sensitive Materials For Dielectric Gas SensorsDocument12 pagesZeolites As Sensitive Materials For Dielectric Gas SensorsHenry AlonsoNo ratings yet
- HW09Document2 pagesHW09Fatah Imdul UmasugiNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneDocument30 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneridwanNo ratings yet