Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAE101
MAE101
Uploaded by
Đặng Đình Đức0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesMAE101
MAE101
Uploaded by
Đặng Đình ĐứcCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chapter 2 : DERIVATIVES
đây là hàm liên tục -> x tiến đến x0
y phải tiến đến y0
lim delta y khi delta x tiến đến 0 phải bằng 0
PHẦN 1 : Defining the Dẻivatives
I) The Tangent line ( bài toán về tiếp tuyến )
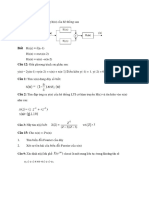
Example: Find tangent line of y = x^2 at P(1,1)
- Lấy Q nằm trên đồ thị y = x^2
- Slope of PQ ( hệ số góc của PQ )
m(PQ) = ( x^2 - 1 ) / ( x - 1 )
- Slope of tangent line at P ( hệ số góc của đường tiếp tuyến tại P )
m = lim m(PQ) khi Q tiến tới P
= lim (x^2-1)/(x-1) khi x-> 1
= 2
=> The tangent line at P(1,1) is y= 2x -1
=> hệ số góc của đường tiếp tuyến là delta y chia cho delta x
=== The tangent line to the curve y = f(x) at the point P(a,f(a)) is the line
through P with slope
m = lim [f(x)-f(a)] / (x-a)
x->a
provided that this limit exists
=== In general, (x^n)' = n.x^(n-1)
***If f is differentiable at a, then f is continuous at a
=> This theorem states that, if f is not continuous at a, then f is not
differentiable at a
2.1 4 va` 5
2.2 9,11,39
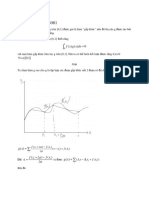
Chapter 5 : Intergration ( tích phân )
II) Definite Integeral ( tích phân xác định )
Theorem ( Fundamental theorem of calculus )
5.2: 17,18,44
5.3: 11,17,22,62,66
You might also like
- Chuong 4 - Giáo trình Matlab, BK Đà NẵngDocument31 pagesChuong 4 - Giáo trình Matlab, BK Đà Nẵngtienanh_0867% (3)
- ĐSTTDocument2 pagesĐSTTTrần Đình KhangNo ratings yet
- Chuong3 Phan1Document7 pagesChuong3 Phan1Đình Anh HồNo ratings yet
- TNH PTVP Cap 1Document7 pagesTNH PTVP Cap 1Trung Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - 1a - Derivatives and Applications of DifferentiationDocument26 pagesChapter - 1 - 1a - Derivatives and Applications of DifferentiationHà TrungNo ratings yet
- - Nguyễn Đào Lan Anh - AMA303 - 211 - D02Document14 pages- Nguyễn Đào Lan Anh - AMA303 - 211 - D02Sa SaNo ratings yet
- Bai Giang GT2 (Chuong 1)Document53 pagesBai Giang GT2 (Chuong 1)Huy HoangNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Giai Tich 1 Chuong 1 Gioi Han Ham SoDocument67 pages(123doc) Giai Tich 1 Chuong 1 Gioi Han Ham SoloanqnqlnNo ratings yet
- Bang Cong Thuc BDocument5 pagesBang Cong Thuc BHƯNG LÊ KHÁNHNo ratings yet
- Toan Ung Dung Chuong 5Document55 pagesToan Ung Dung Chuong 5Nguyễn Như ÝNo ratings yet
- Giai Tich 2. Chuong 1 Bai Giang Bai Tap Dap AnDocument87 pagesGiai Tich 2. Chuong 1 Bai Giang Bai Tap Dap An21020795No ratings yet
- CHƯƠNG III - HAMSO cả chươngDocument44 pagesCHƯƠNG III - HAMSO cả chươngNguyễn MinhNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet XSTKDocument3 pagesCheatsheet XSTKNguyễn HiềnNo ratings yet
- Bang Cong Thuc BDocument4 pagesBang Cong Thuc BHaroshi TatsuyaNo ratings yet
- BTL gt1Document25 pagesBTL gt1binh.nguyen2310302No ratings yet
- 4.3. Một Số Phân Phối Thông DụngDocument24 pages4.3. Một Số Phân Phối Thông DụngTrí HoàngNo ratings yet
- Chuong 2Document28 pagesChuong 2Lãnh Vực Vô HạnNo ratings yet
- Công thức xác suấtDocument3 pagesCông thức xác suấtLINH HOÀNG NHẬTNo ratings yet
- Bai giảng Giai tich 2. Chuong 1 PDFDocument58 pagesBai giảng Giai tich 2. Chuong 1 PDFNguyễn NamNo ratings yet
- Bai Giang Giai Tich 2. Chuong 1Document57 pagesBai Giang Giai Tich 2. Chuong 1lequang100805No ratings yet
- Toán đt quốc giaDocument10 pagesToán đt quốc giaHải Quân LC NguyễnNo ratings yet
- I Love You More Than I Can SayDocument32 pagesI Love You More Than I Can Sayapi-19749449No ratings yet
- Câu 7: Tìm đáp ứng xung h (n) của hệ thống sau: (n) = δ (n-1) H (n) = rect (n-2) H (n) = u (n) -u (n-2)Document1 pageCâu 7: Tìm đáp ứng xung h (n) của hệ thống sau: (n) = δ (n-1) H (n) = rect (n-2) H (n) = u (n) -u (n-2)NeemoNo ratings yet
- Phương trình vi phân cấp 1Document39 pagesPhương trình vi phân cấp 1NhưHoaMạcNo ratings yet
- Math Chap 2 4Document37 pagesMath Chap 2 4Lâm PhụngNo ratings yet
- Bang Cong Thuc ADocument2 pagesBang Cong Thuc Asinhvoz24No ratings yet
- Chuong 3Document26 pagesChuong 3huynhthithanhhong1001No ratings yet
- Lý Thuyết Ôn Tập Xác Suất Thống KêDocument5 pagesLý Thuyết Ôn Tập Xác Suất Thống KêPhuong AnhNo ratings yet
- PP Giai GT4Document15 pagesPP Giai GT4tranthituquynh0523No ratings yet
- Review TheoreticalDocument9 pagesReview TheoreticalMinh ĐăngNo ratings yet
- Btl Xác Xác Suất Thống Kê - Mat5234.17 - Mai Ngọc Anh - 193134103220Document18 pagesBtl Xác Xác Suất Thống Kê - Mat5234.17 - Mai Ngọc Anh - 193134103220Mai Ng AnhNo ratings yet
- Chui Fourier Va Tich Phan FourierDocument29 pagesChui Fourier Va Tich Phan FourierThiên Nguyễn TấtNo ratings yet
- 2. Định nghĩa đạo hàm tại một điểmDocument15 pages2. Định nghĩa đạo hàm tại một điểmTrần Thiên HươngNo ratings yet
- Bai Giảng Giai Tich 2. Chuong 1 (1.1. Và 1.2.)Document13 pagesBai Giảng Giai Tich 2. Chuong 1 (1.1. Và 1.2.)Phạm NhậtNo ratings yet
- Bài giảng PTH các lớp hàm liên tụcDocument23 pagesBài giảng PTH các lớp hàm liên tụcLê BảoNo ratings yet
- Chương III. Biến ngẫu nhiên liên tụcDocument5 pagesChương III. Biến ngẫu nhiên liên tụcTuan Nguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Bang Dao HamDocument4 pagesBang Dao HamHiền ThanhNo ratings yet
- WinterSchool2022 TranNamDungDocument7 pagesWinterSchool2022 TranNamDungMinh Toàn LêNo ratings yet
- ChuongIV DANGTOANPHUONGDocument28 pagesChuongIV DANGTOANPHUONGCẩm Ly NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bang Cong Thuc BDocument2 pagesBang Cong Thuc BCao Đức HuyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document33 pagesLecture 4Hill HillNo ratings yet
- Task 2Document4 pagesTask 2vonhattan43No ratings yet
- Chương 1Document3 pagesChương 1Uyên PhạmNo ratings yet
- DSP VN FFT SlidesDocument34 pagesDSP VN FFT SlidesLangKhoaiNo ratings yet
- bài tập lớn giải tíchDocument8 pagesbài tập lớn giải tíchTrần PhươngNo ratings yet
- Tim Tap Xac Dinh Cua Ham SoDocument29 pagesTim Tap Xac Dinh Cua Ham SoHong LeNo ratings yet
- Hàm số liên tục Nhóm 3Document16 pagesHàm số liên tục Nhóm 3Trym DatNo ratings yet
- Thống Kê Tính Toán 1Document12 pagesThống Kê Tính Toán 1Trần Hoàng DanhNo ratings yet
- 11.6 DaoHamTheoHuong GradientDocument24 pages11.6 DaoHamTheoHuong GradientLuong Tuan TungNo ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề. Ứng Dụng Tích Phân, Đạo Hàm Trong Bài Toán Vật LýDocument45 pagesChuyên Đề. Ứng Dụng Tích Phân, Đạo Hàm Trong Bài Toán Vật LýSheng Bill LinNo ratings yet
- biến đổi KLDocument26 pagesbiến đổi KLNguyễn Ngọc HiếuNo ratings yet
- Slide5 PDFDocument45 pagesSlide5 PDFNguyễn Trọng ThườngNo ratings yet
- (Thuvientoan.net) - Chuyên Đề Hàm Số Bậc Nhất Và Hàm Số Bậc 2 - Đại Số 10Document81 pages(Thuvientoan.net) - Chuyên Đề Hàm Số Bậc Nhất Và Hàm Số Bậc 2 - Đại Số 10thu pnaNo ratings yet
- btl giải tích 2 phần 3,4Document13 pagesbtl giải tích 2 phần 3,4Đạt ĐặngNo ratings yet
- GT3 04Document60 pagesGT3 04An PhạmNo ratings yet
- Báo Cáo: Bộ Giáo Dục Và Đào Tạo Trường Đại Học Bách Khoa Tp.Hcm - Đh Quốc Gia Tp Hồ Chí Minh Bộ Môn Toán Ứng DụngDocument20 pagesBáo Cáo: Bộ Giáo Dục Và Đào Tạo Trường Đại Học Bách Khoa Tp.Hcm - Đh Quốc Gia Tp Hồ Chí Minh Bộ Môn Toán Ứng Dụngkhai.to0707No ratings yet
- Bồi dưỡng HSG về Đa thứcDocument21 pagesBồi dưỡng HSG về Đa thứchatkienxuong9509No ratings yet
- lý thuyết rút gọn XSTKDocument9 pageslý thuyết rút gọn XSTKTú KhểnhNo ratings yet