Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISO Requirement
Uploaded by
nathansta61Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ISO Requirement
Uploaded by
nathansta61Copyright:
Available Formats
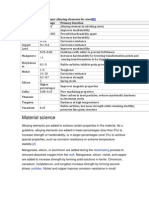
SG Iron (Ductile Iron) Composition:
Iron (Fe): Constitutes the majority of the alloy.
Carbon (C): Typically in the range of 3.2% to 3.9%. Controlled levels of carbon contribute to the formation of
nodular graphite.
Silicon (Si): Usually in the range of 2.2% to 2.8%. Silicon promotes the nodularization of graphite.
Manganese (Mn): Typically in the range of 0.1% to 0.4%. Manganese aids in the nodularization process.
Magnesium (Mg): Added intentionally to promote the formation of nodular graphite.
Cast Iron Composition:
Iron (Fe): The primary constituent.
Carbon (C): Generally in the range of 2% to 4%. Higher carbon content contributes to the brittleness of cast
iron.
Silicon (Si): Typically in the range of 1% to 3%. Silicon influences the formation of graphite.
Manganese (Mn): Present in varying amounts, typically in the range of 0.1% to 1%.
Phosphorus (P): Present in trace amounts, usually less than 0.1%.
Sulfur (S): Present in trace amounts, usually less than 0.1%.
Trace Elements: Small amounts of other elements may be present, depending on the specific grade and
application.
It's important to note that these compositions are general guidelines, and actual compositions can vary
based on the specific grade of the alloy and the manufacturing process. Additionally, there are various
standards (such as ASTM and ISO) that specify the requirements for different grades of SG Iron and Cast Iron.
Mild Steel (MS) and SG Iron (Spheroidal Graphite Iron), also known as ductile iron, are two distinct materials
with different compositions, microstructures, and properties. Here are the key differences between MS and
SG Iron:
Mild Steel (MS):
Composition:
Iron (Fe): Constitutes the majority of the alloy.
Carbon (C): Generally in the range of 0.05% to 0.25%. MS is low in carbon compared to cast iron.
Manganese (Mn): Present in varying amounts, typically in the range of 0.3% to 0.6%.
Other Elements: Trace amounts of other elements.
Microstructure:
MS has a ferritic microstructure, which consists of a body-centered cubic crystal lattice. It does not contain
the distinctive graphite structures found in cast iron.
Properties:
MS is characterized by its malleability, ductility, and weldability.
It has a relatively low tensile strength compared to cast iron and ductile iron.
MS is commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and general engineering applications.
SG Iron (Ductile Iron):
You might also like
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AccountingDocument20 pagesAccountingjanlaan0% (1)
- 2 Engineering MaterialsDocument14 pages2 Engineering MaterialsPRASAD326100% (1)
- Tree Plantations in The Caribbean Lowlands of Costa Rica: The Beginnings and EARTH UniversityDocument85 pagesTree Plantations in The Caribbean Lowlands of Costa Rica: The Beginnings and EARTH UniversityRicardo RussoNo ratings yet
- Sulphur in SteelsDocument3 pagesSulphur in Steelsnarayan kaushikNo ratings yet
- S.G IronDocument6 pagesS.G IronQasim BarkatNo ratings yet
- Tolentino Vs Commission On Elections Case DigestDocument3 pagesTolentino Vs Commission On Elections Case DigestDaf MarianoNo ratings yet
- Anatmical TermsDocument40 pagesAnatmical TermsMRS DR NIDHI SHARMA VISHWAKARMANo ratings yet
- LESSON Building A Content Cretion Framework SCRIPT PDFDocument8 pagesLESSON Building A Content Cretion Framework SCRIPT PDFJohn WilkinsNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument110 pagesEngineering MaterialsAthith D100% (1)
- Fisher v. Yangco SteamshipDocument2 pagesFisher v. Yangco SteamshipNoreenesse SantosNo ratings yet
- Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless SteelsDocument6 pagesWelding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless SteelsoifhiudsnfNo ratings yet
- Classification of MetalsDocument26 pagesClassification of MetalsNomi Wahla100% (1)
- Die Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsFrom EverandDie Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- DiassDocument7 pagesDiassDianne MirandaNo ratings yet
- Leeer para RepasarrrrrDocument21 pagesLeeer para RepasarrrrrAriana MeliánNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument91 pagesAlloysNiccoloNo ratings yet
- RaciDocument42 pagesRaciSugavanan Thangavel100% (1)
- Gray Cast Iron Metallurgy and InoculationDocument21 pagesGray Cast Iron Metallurgy and InoculationArjyajyoti Goswami100% (1)
- Tratamientos Térmicos: Carlos Bohórquez 2010Document61 pagesTratamientos Térmicos: Carlos Bohórquez 2010procesosun2010No ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5nathansta61No ratings yet
- Carbon Content Vol. 1Document1 pageCarbon Content Vol. 1nathansta61No ratings yet
- Fig 1 Typical Micro Structure of White Cast IronDocument1 pageFig 1 Typical Micro Structure of White Cast IronPRASHANTHNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of SteelDocument7 pagesChemical Composition of SteelArslan RaoNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument20 pagesSteelShashank SaxenaNo ratings yet
- SANDVIK What Is Stainless SteelDocument7 pagesSANDVIK What Is Stainless Steelpipedown456No ratings yet
- Chemical Composition SteelDocument6 pagesChemical Composition SteelSahil JhambNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Ferrous and Non-Ferrous AlloysDocument14 pagesChapter 7. Ferrous and Non-Ferrous AlloysVishal ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Alloy SteelDocument5 pagesAlloy SteelKun Hadipati Kusuma NegaraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MaterialsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Materialsabhinavgiri17No ratings yet
- To Be EditedDocument6 pagesTo Be EditedSasaleleNo ratings yet
- All DataDocument121 pagesAll DataShashank SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of Structural SteelDocument2 pagesChemical Composition of Structural SteelSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Chromium:-: 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical PropertiesDocument8 pagesChromium:-: 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Propertiesdhoni03No ratings yet
- Classification of Engineering Materials: by - A.R. GiriDocument20 pagesClassification of Engineering Materials: by - A.R. Giriabhinavgiri17No ratings yet
- Engg. Materials DMEDocument11 pagesEngg. Materials DMESudhansubhusan PaniNo ratings yet
- Alloy SteelDocument6 pagesAlloy SteelSiva BhaskarNo ratings yet
- General Information About SteelsDocument20 pagesGeneral Information About SteelsilkinNo ratings yet
- Zavarivanje Nehrđajućih ČelikaDocument50 pagesZavarivanje Nehrđajućih ČelikaTenkre TenNo ratings yet
- Effect of Impurities On Cast Iron Impurities:: SiliconDocument16 pagesEffect of Impurities On Cast Iron Impurities:: SiliconMD. ZUBAIR ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Gray IronDocument4 pagesGray IronLaboratorio CalidadNo ratings yet
- Fig 1 Fe-Mn Phase DiagramDocument3 pagesFig 1 Fe-Mn Phase DiagramAlok NayakNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter 1.1 Engineering Materilas (Metals,... )Document39 pages1 Chapter 1.1 Engineering Materilas (Metals,... )KidusNo ratings yet
- 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical PropertiesDocument12 pages21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Propertieshaidv254100% (1)
- Carbon Steel - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesCarbon Steel - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRashid SarfrazNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Graphite Nucleation Mechanism in Gray IronsDocument12 pagesA New Approach To Graphite Nucleation Mechanism in Gray IronskarahandevrimNo ratings yet
- Iron Man of SteelDocument32 pagesIron Man of SteelDeepak jose vargheseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Ferrous AlloysDocument31 pagesLecture 9 - Ferrous Alloysmahmoud foudaNo ratings yet
- An Overview: MetalsDocument61 pagesAn Overview: MetalsjswldeepNo ratings yet
- 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Properties - Jeremy HDocument7 pages21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Properties - Jeremy HxnitinxNo ratings yet
- Alloy SteelDocument9 pagesAlloy Steelamr_scorpion_engNo ratings yet
- Failure in Structural Steels and Overview of I 35W Bridge Collapse PDFDocument24 pagesFailure in Structural Steels and Overview of I 35W Bridge Collapse PDFUnknownNo ratings yet
- Name: Lia Fitri Fujiarsi NIM: 061330400319 Class: 3KBDocument1 pageName: Lia Fitri Fujiarsi NIM: 061330400319 Class: 3KBLia Fitri FujiarsiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-31 at 7.45.47 PM PDFDocument73 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-31 at 7.45.47 PM PDFHardi HedayatNo ratings yet
- IronDocument7 pagesIronShujai KrishNo ratings yet
- Alloy SteelsDocument2 pagesAlloy Steelswhi7efea7herNo ratings yet
- 7steel and Heat TreatmentDocument19 pages7steel and Heat TreatmentManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Clean Steel: Part Two: AbstractDocument4 pagesClean Steel: Part Two: AbstractdonkalonkNo ratings yet
- ESDEP Vol0302Document124 pagesESDEP Vol0302aladinmf1No ratings yet
- Ch13 Materials ApplicationsDocument69 pagesCh13 Materials ApplicationsRhanganath ArivudainambiNo ratings yet
- Alloys: SMK Methodist (Acs) KamparDocument13 pagesAlloys: SMK Methodist (Acs) KamparAvian ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Steel: Iron AlloyDocument18 pagesSteel: Iron AlloySameer ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Fe Si MGDocument34 pagesFe Si MGamitkkambleNo ratings yet
- Failure in Structural Steels and Overview of I 35W Bridge CollapseDocument24 pagesFailure in Structural Steels and Overview of I 35W Bridge CollapseopulitheNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Spectra of Organometallics: Theoretical and Experimental DataFrom EverandVibrational Spectra of Organometallics: Theoretical and Experimental DataNo ratings yet
- Symbols 128Document1 pageSymbols 128nathansta61No ratings yet
- Mechanical Testing Vol 1Document1 pageMechanical Testing Vol 1nathansta61No ratings yet
- Heat Treatment BSA1681Document1 pageHeat Treatment BSA1681nathansta61No ratings yet
- Autoamted Intelligent Coating Concept For Ferrous FoundariesDocument6 pagesAutoamted Intelligent Coating Concept For Ferrous Foundariesnathansta61No ratings yet
- Costing FormatDocument1 pageCosting Formatnathansta61No ratings yet
- JK Excel 85 GSMDocument1 pageJK Excel 85 GSMnathansta61No ratings yet
- BSL Casting PVT LTD Quotation 19.07.23Document1 pageBSL Casting PVT LTD Quotation 19.07.23nathansta61No ratings yet
- 6FC5303-0AF35-0AA0 Datasheet enDocument1 page6FC5303-0AF35-0AA0 Datasheet ennathansta61No ratings yet
- BSL Casting PVT LTD Revised 27.09.2023Document1 pageBSL Casting PVT LTD Revised 27.09.2023nathansta61No ratings yet
- Zodiac o 1237Document1 pageZodiac o 1237Libertad de Expresión YucatánNo ratings yet
- Brasso MSDSDocument4 pagesBrasso MSDSSartika SapuletteNo ratings yet
- Solved Marcy Tucker Received The Following Items This Year Determine ToDocument1 pageSolved Marcy Tucker Received The Following Items This Year Determine ToAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- The Future of Humanity Ogl340 8oct2020 John DoerschukDocument7 pagesThe Future of Humanity Ogl340 8oct2020 John Doerschukapi-454540037No ratings yet
- Linux MCQ Fot InterviewDocument2 pagesLinux MCQ Fot InterviewHromit ProdigyNo ratings yet
- Rahim2017 Article ImprovingSocialResponsibilityI PDFDocument20 pagesRahim2017 Article ImprovingSocialResponsibilityI PDFMd DidarNo ratings yet
- R5176b PDFDocument53 pagesR5176b PDFAnum ZahraNo ratings yet
- Faasos 140326132649 Phpapp01Document15 pagesFaasos 140326132649 Phpapp01Arun100% (1)
- Colours in CultureDocument9 pagesColours in CultureMeriam KasraouiNo ratings yet
- 25 Greatest Films by YearDocument196 pages25 Greatest Films by YearDimaas LöpesNo ratings yet
- Samoan Culture Profile: An Initiative of Community Partners ProgramDocument17 pagesSamoan Culture Profile: An Initiative of Community Partners ProgramDevan BhallaNo ratings yet
- CSE 08PE605 Digital Image ProcessingDocument252 pagesCSE 08PE605 Digital Image ProcessingTrilochan PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Western Political Thought - An IntroductionDocument13 pagesWestern Political Thought - An IntroductionDimas RickyNo ratings yet
- Example Prompt Formative Assessment Examples 2 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesExample Prompt Formative Assessment Examples 2 Answer Keyapi-544797221No ratings yet
- Elden Ring Guide To EverythingDocument29 pagesElden Ring Guide To Everythingip200724No ratings yet
- NGENE/NGONO - Jogja Hip Hop FoundationDocument3 pagesNGENE/NGONO - Jogja Hip Hop FoundationIT RSU Universitas Ahmad DahlanNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument13 pagesInternational BusinessShifna MohamedNo ratings yet
- Restoring The AR-3a: Roy Champagne, Ken Kantor, Minh Luong, John O'Hanlon (Ed.), Bret Thiel, and Tom TysonDocument33 pagesRestoring The AR-3a: Roy Champagne, Ken Kantor, Minh Luong, John O'Hanlon (Ed.), Bret Thiel, and Tom Tysonronald allan liviocoNo ratings yet
- Is Your Information Secure?: Sichere Und Zuverlässige IctDocument11 pagesIs Your Information Secure?: Sichere Und Zuverlässige Icthulikul22No ratings yet
- Frederick Taylor and Scientific ManagementDocument8 pagesFrederick Taylor and Scientific ManagementPavel BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - NikeDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - NikeKinjal KeyaNo ratings yet