100% found this document useful (4 votes)
1K views29 pagesCompetency-Based People Management
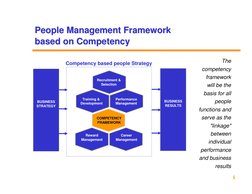
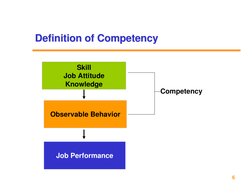
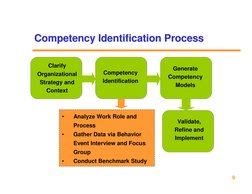
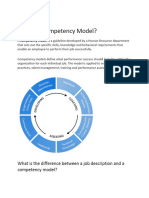
The document outlines a framework for developing a competency-based people management system. It discusses defining competencies, identifying competencies, developing a competency model, and using competencies for career planning, training, and performance management. The goal is to align all human resource functions with business strategy using an integrated competency framework.
Uploaded by
api-3823729Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (4 votes)
1K views29 pagesCompetency-Based People Management
The document outlines a framework for developing a competency-based people management system. It discusses defining competencies, identifying competencies, developing a competency model, and using competencies for career planning, training, and performance management. The goal is to align all human resource functions with business strategy using an integrated competency framework.
Uploaded by
api-3823729Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd