Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Domain Name
Uploaded by
RosalieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Domain Name
Uploaded by
RosalieCopyright:
Available Formats
Domain name
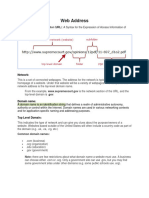
Simply put, a domain name (or just "domain") is the name of a website. It's what comes after "@" in an
email address, or after "www." in a web address. If someone asks how to find you online, what you tell
them is usually your domain name.
Examples of domain names are:
google.com
wikipedia.org
youtube.com
The first step in creating an online presence is purchasing a domain name. Anyone can purchase a
domain name by going to a domain host or registrar like Google Domains, finding a name no one else is
using, and paying an annual fee to own and register it. You can also choose from various domain name
endings (or "TLDs"), like .com, .coffee or .photography.
URL
A URL (Universal Resource Locator) is a complete web address used to find a particular web page. While
the domain is the name of the website, a URL will lead to any one of the pages within the website. Every
URL contains a domain name, as well as other components needed to locate the specific page or piece
of content.
Examples of URLs:
http://www.google.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/umami
https://www.youtube.com/feed/trending
Website
Though one leads to the other, buying a domain name doesn't mean you have a website. A domain is
the name of a website, a URL is how to find a website, and a website is what people see and interact
with when they get there. In other words, when you buy a domain, you purchase the name for your site,
but you still need to build the website itself.
In digital terms, a website is a collection of content, often on multiple pages, that's grouped together
under the same domain. You can think of it like a store, where the domain is the store name, the URL is
the store address and the website is the actual store, with shelves full of products and a cash register.
You might also like
- How To Create A Website in 3 Steps - Beginners GuideDocument21 pagesHow To Create A Website in 3 Steps - Beginners GuideBrand IT AgencyNo ratings yet
- Domain Name Handbook v4Document32 pagesDomain Name Handbook v4Paul FlyerNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Tapping Into The Billion Dollar Domain Industry: A ProductionDocument9 pagesSecrets To Tapping Into The Billion Dollar Domain Industry: A ProductionHaris MelezNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Website Using Wordpress: Create the website you've always wanted - TodayFrom EverandHow To Build A Website Using Wordpress: Create the website you've always wanted - TodayNo ratings yet
- An Intelligent Man's Guide to Domain Investing: An Intelligent Man's Guide, #1From EverandAn Intelligent Man's Guide to Domain Investing: An Intelligent Man's Guide, #1No ratings yet
- Choose A Url Step 2 Web PresenceDocument1 pageChoose A Url Step 2 Web PresenceMadame MoseilleNo ratings yet
- Ch6 - Domain Names and CybersquattingDocument47 pagesCh6 - Domain Names and CybersquattingAlhussain DarbiNo ratings yet
- Are Premium Domain Names Worth ItDocument6 pagesAre Premium Domain Names Worth ItBuk MarkzNo ratings yet
- URLDocument4 pagesURLEmmerNo ratings yet
- Search in The WebDocument1 pageSearch in The WebelectromnicsaascNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Domain NameDocument8 pagesChoosing A Domain NameInstituto DigitalizateNo ratings yet
- Masterclass 1 Assessing The Quality of A Website WorkbookDocument17 pagesMasterclass 1 Assessing The Quality of A Website WorkbookIndah Wira PutriNo ratings yet
- How The Web WorksDocument4 pagesHow The Web WorksAritraNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Domain NameDocument2 pagesChoosing A Domain NameMikhailNo ratings yet
- Web AddressesDocument1 pageWeb Addressesapi-275290022No ratings yet
- Toby WEB Site PageDocument9 pagesToby WEB Site PageBerhanu GebremichaelNo ratings yet
- Trademark Protection of Internet Domain NamesDocument3 pagesTrademark Protection of Internet Domain NamesMedha PatelNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Laws: Submitted ToDocument12 pagesIntellectual Property Laws: Submitted ToMohit BansalNo ratings yet
- Web AddressDocument2 pagesWeb AddressSifat Faridi (221051043)No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Web SystemDocument30 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Web SystemMr. EpiphanyNo ratings yet
- 2D-URL Parts - Understand The Structure of Web Address-1-1Document9 pages2D-URL Parts - Understand The Structure of Web Address-1-1Destor, Justin AndreNo ratings yet
- Mod 4Document24 pagesMod 4WorkaholicNo ratings yet
- What Is A WebsiteDocument9 pagesWhat Is A WebsitemullahNo ratings yet
- DLP Tve-Tle Css q1 Act 24-1Document4 pagesDLP Tve-Tle Css q1 Act 24-1Marivic Omosura ItongNo ratings yet
- Web Publishing Lesson PlanDocument33 pagesWeb Publishing Lesson PlanNaima IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chương 1 Giới thiệuDocument5 pagesChương 1 Giới thiệuphuckhang33203No ratings yet
- Normal Superior Lácides Iriarte Web Page 11°CDocument8 pagesNormal Superior Lácides Iriarte Web Page 11°CjuanNo ratings yet
- Web Hosting BasicDocument33 pagesWeb Hosting Basicpravesh sharma100% (1)
- Building Website Using CmsDocument19 pagesBuilding Website Using Cmswahyu edy handokoNo ratings yet
- How To Browse Websites and Files. REBANALDocument45 pagesHow To Browse Websites and Files. REBANALAirah Nicole V. RebanalNo ratings yet
- Static and DynamicDocument2 pagesStatic and DynamicAli Asaad ButtNo ratings yet
- Dent Info m1-4Document27 pagesDent Info m1-4Milca ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ict Unit1Document10 pagesIct Unit1Naveen SimmaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose of HTTP? - : An Application ProtocolDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of HTTP? - : An Application ProtocolJessa Marie Perez DaugNo ratings yet
- What Is Linking ?explain Surface Linking and Deep Linking?: HypertextDocument9 pagesWhat Is Linking ?explain Surface Linking and Deep Linking?: HypertextShreyas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept Web DesigingDocument12 pagesBasic Concept Web Desigingpalvi kapurNo ratings yet
- What Is A URLDocument4 pagesWhat Is A URLEmmerNo ratings yet
- His Article Is About Websites in General. For The Internet Domain .Website, See - Not To Be Confused WithDocument1 pageHis Article Is About Websites in General. For The Internet Domain .Website, See - Not To Be Confused WithnizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Internet CoverageDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Internet CoverageMeredith GreyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To InternetDocument8 pagesIntroduction To InternetJayChristy TarayNo ratings yet
- Ipr ProjectDocument25 pagesIpr ProjectMahima ChauhanNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Website3Document1 pageHow To Create A Website3Rachel HarrisNo ratings yet
- Web PublishingDocument3 pagesWeb PublishingjairaldodominguezNo ratings yet
- I.T AssignmentDocument3 pagesI.T AssignmentTristanNo ratings yet
- Absolute and Relative UrlDocument3 pagesAbsolute and Relative UrlJyoti BhanotNo ratings yet
- Definition of Website, 1903Document14 pagesDefinition of Website, 1903Yemima HanniNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document27 pagesUnit 4Gautham SajuNo ratings yet
- The Internet and The WebDocument10 pagesThe Internet and The WebStephanie Joy LucatenNo ratings yet
- The Components of A URLDocument3 pagesThe Components of A URLSWATINo ratings yet
- Tips To Help You Get The Best Domain Name and HostingDocument11 pagesTips To Help You Get The Best Domain Name and HostingRobert HarrisNo ratings yet
- Internet Vs World Wide WebDocument10 pagesInternet Vs World Wide WebkuvarabhishekNo ratings yet
- © 2012 Sedo, Gmbh. All Rights Reserved - 2Document4 pages© 2012 Sedo, Gmbh. All Rights Reserved - 2A2ANo ratings yet
- WWW Primer: Information Communication TechnologyDocument19 pagesWWW Primer: Information Communication Technologynjk19No ratings yet
- Adsense Email 2Document22 pagesAdsense Email 2mukund gurujiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To WebDocument53 pagesAn Introduction To WebalnasehNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Measurement PlanDocument2 pagesHow To Create A Measurement PlanRosalieNo ratings yet
- Transforming Data Using Configuration RulesDocument3 pagesTransforming Data Using Configuration RulesRosalieNo ratings yet
- Storing Data To Generate Reports QuicklyDocument3 pagesStoring Data To Generate Reports QuicklyRosalieNo ratings yet
- How Google Analytics Collects DataDocument3 pagesHow Google Analytics Collects DataRosalieNo ratings yet