Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fishbone Diagram
Uploaded by
陳品Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fishbone Diagram
Uploaded by
陳品Copyright:
Available Formats
Fishbone Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa diagram or Cause-
and-Effect diagram, is a visual tool used for identifying and organizing potential
causes of a problem or effect. Developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, the
Fishbone Diagram helps teams systematically analyze complex issues by breaking
them down into categories and subcategories of possible causes.
Key Components:
1. Problem Statement: Begin by clearly defining the problem or effect that
needs to be addressed. This provides focus and ensures that the analysis
remains relevant to the desired outcome.
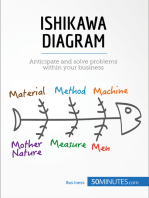
2. Main Cause Categories: The main horizontal line of the Fishbone Diagram
represents the backbone of the fish. Along this line, draw branches or "bones"
to represent different categories of potential causes. Common categories
include:
• People: Human factors such as knowledge, skills, and training.
• Process: Operational procedures, methods, and workflows.
• Machines: Equipment, tools, and technology.
• Materials: Raw materials, supplies, and resources.
• Measurement: Metrics, data collection methods, and performance
indicators.
• Environment: Physical surroundings, conditions, and external factors.
3. Subcauses: Beneath each main cause category, identify and list specific factors
or subcauses that may contribute to the problem. Use brainstorming
techniques or data analysis to generate ideas and hypotheses.
4. Analysis: Once all potential causes are identified, analyze each one to
determine its relevance and impact on the problem. Consider using tools such
as the 5 Whys technique to delve deeper into root causes.
5. Prioritization: Evaluate the significance of each cause based on factors such
as frequency of occurrence, severity of impact, and feasibility of control.
Prioritize causes that are most likely to be addressed effectively and have the
greatest impact on resolving the problem.
Benefits of Fishbone Diagram:
• Structured Problem Solving: The Fishbone Diagram provides a systematic
approach to problem analysis, helping teams organize their thoughts and
identify potential causes in a logical manner.
• Visualization: By visually mapping out the relationships between causes and
effects, the Fishbone Diagram enhances understanding and communication
among team members, facilitating collaboration and consensus-building.
• Root Cause Identification: The Fishbone Diagram helps teams uncover root
causes of problems rather than just addressing symptoms, leading to more
effective and sustainable solutions.
• Continuous Improvement: By identifying areas for improvement and
implementing corrective actions, organizations can drive continuous
improvement and enhance overall performance.
Conclusion: The Fishbone Diagram is a valuable tool for problem-solving and root
cause analysis in various industries and contexts. By providing a structured framework
for identifying and organizing potential causes, the Fishbone Diagram empowers
teams to effectively address complex issues and drive continuous improvement.
You might also like
- The Young Entrepreneur How To Start A Business While You'Re Still A StudentDocument241 pagesThe Young Entrepreneur How To Start A Business While You'Re Still A StudentJivitesh NjNo ratings yet
- Fishbone DiagramDocument7 pagesFishbone DiagramAnik Das67% (3)
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument34 pagesRoot Cause Analysishgciso80% (5)
- Ishikawa Diagram: Anticipate and solve problems within your businessFrom EverandIshikawa Diagram: Anticipate and solve problems within your businessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Quality Tools WorkshopDocument45 pagesQuality Tools WorkshopAhmed Hassan ShehataNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Problem Solving - Fishbone DiagramDocument9 pagesRoot Cause Problem Solving - Fishbone DiagramNigthstalker100% (1)
- Cause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolDocument21 pagesCause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolVivek V NairNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolDocument21 pagesCause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolAditya JainNo ratings yet
- Fish BoneDocument23 pagesFish BoneAnonymous So5qPSnNo ratings yet
- Fish Bone AnalysisDocument21 pagesFish Bone AnalysisDeeksha RainaNo ratings yet
- Case On Fishbone DiagramDocument6 pagesCase On Fishbone DiagramIsmail shaikhNo ratings yet
- The New Quality ToolsDocument42 pagesThe New Quality ToolsRavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Fish Bone DiagramDocument2 pagesFish Bone DiagramDeepankar ShrigyanNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolDocument21 pagesCause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolYashini BhuguthNo ratings yet
- Resume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 5Document3 pagesResume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 5Dani YustiardiNo ratings yet
- A Problem-Analysis Tool: Fishbone DiagramDocument2 pagesA Problem-Analysis Tool: Fishbone DiagramAbhimanyu JhaNo ratings yet
- Fast Food Nation by Eric Schlosser - Discussion QuestionsDocument8 pagesFast Food Nation by Eric Schlosser - Discussion QuestionsHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument5 pagesRoot Cause AnalysisNishabharatNo ratings yet
- Ishikawa Diagram FinalDocument9 pagesIshikawa Diagram Finalpurvangi_r5661No ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolDocument21 pagesCause and Effect Diagram: CA/PA-RCA: Basic Toolsiddiquiee74100% (1)
- Fishbone Analysis-My ReportDocument14 pagesFishbone Analysis-My ReportKathleen LimNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Analysis (Fishbone Diagram) : CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolDocument23 pagesCause and Effect Analysis (Fishbone Diagram) : CA/PA-RCA: Basic ToolDipraj KayasthaNo ratings yet
- Logical Framework Analysis/Approach (LFA)Document61 pagesLogical Framework Analysis/Approach (LFA)Kaelel BilangNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation (Principles of Taxation) : Fritz A. Perez, Cpa, CTT, Mritax, Mba (O.G)Document40 pagesIncome Taxation (Principles of Taxation) : Fritz A. Perez, Cpa, CTT, Mritax, Mba (O.G)JessaNo ratings yet
- Metal Mayhem How To Niche Nail Scale With Metal 1Document18 pagesMetal Mayhem How To Niche Nail Scale With Metal 1Bilal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Control of Ductile Iron Pipelines - Dipra PDFDocument10 pagesCorrosion Control of Ductile Iron Pipelines - Dipra PDFAnonymous gr5Pr9AVNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument39 pagesAnswerALMACHIUS RWERENGELA86% (7)
- 12-Project Procurement Management-2019!06!13 13-23-21Document79 pages12-Project Procurement Management-2019!06!13 13-23-21AhmadKkawaldeh100% (1)
- SWPPS 104 Reviewer 1 PDFDocument11 pagesSWPPS 104 Reviewer 1 PDFSean C.A.ENo ratings yet
- Analisis Tulang Ikan PDFDocument5 pagesAnalisis Tulang Ikan PDFJebtaNo ratings yet
- Fish ReloadedDocument6 pagesFish Reloadedqueenmutheu01No ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis Using Fishbone DiagramDocument6 pagesRoot Cause Analysis Using Fishbone DiagramRose Mae TecsonNo ratings yet
- Itec70 - Principles of Systems ThinkingDocument22 pagesItec70 - Principles of Systems ThinkingKim DomingoNo ratings yet
- Problem Identification MethodologyDocument4 pagesProblem Identification Methodologyprasangi.wijeweeraNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Fishbone DiagramDocument3 pagesExploring The Fishbone DiagramamirophobiaNo ratings yet
- Presentación Diagrama IshikawaDocument13 pagesPresentación Diagrama IshikawaAgustin GalvanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Quality AssuranceDocument80 pagesLec 2 Quality AssurancePhilip WagihNo ratings yet
- Pdsa FishboneDocument2 pagesPdsa FishboneChetan KusramNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Note D SSQMDocument20 pagesModule 4 Note D SSQMSaszzNo ratings yet
- Agile TermDocument13 pagesAgile TermAbdulla MamunNo ratings yet
- .... Importance of Quality Circles - HDFCDocument87 pages.... Importance of Quality Circles - HDFCnawazNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Problem Solving Tools and TechniquesDocument74 pagesGroup 7 Problem Solving Tools and TechniquesMonica GavinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Root Cause AnalysisDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Root Cause AnalysisAlo, Monique Marie A.No ratings yet
- CAUSAL ANALYSIS - Recognition of Root CauseDocument5 pagesCAUSAL ANALYSIS - Recognition of Root CauseLuna KimNo ratings yet
- Quality CirclesDocument6 pagesQuality CirclesAyswarya MuthNo ratings yet
- Project Management Tools Fishbone DiagramDocument3 pagesProject Management Tools Fishbone DiagramHrvoje MatezovicNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Tools of TQMDocument61 pagesUnit-2 Tools of TQMFarshan SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Understanding RC AnalysisDocument3 pagesUnderstanding RC AnalysisamirophobiaNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment-4Document17 pagesTQM Assignment-4api-546637261No ratings yet
- Module 2 TOSDocument74 pagesModule 2 TOSDr. Leela M HNo ratings yet
- Presentation Kaizen BaDocument87 pagesPresentation Kaizen BaAbela DrrsNo ratings yet
- SMP5 Group 2 ReportDocument33 pagesSMP5 Group 2 ReportHazelyn delcoNo ratings yet
- Fishbone DiagramDocument3 pagesFishbone DiagramMuhammad ArhamNo ratings yet
- Sysdesi-09-Problem DetectionDocument8 pagesSysdesi-09-Problem DetectionGabriel M. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Name. Hajira Rahman. REG - NO. 0000465163. Course Code. 8611. Level. B.Ed. Semester. 2nd (Autumn) 2023Document23 pagesName. Hajira Rahman. REG - NO. 0000465163. Course Code. 8611. Level. B.Ed. Semester. 2nd (Autumn) 2023Hajra RahmanNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument14 pagesRoot Cause AnalysisAmal GhroozNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Tools Used in Product DevelopmentDocument4 pagesProblem Solving Tools Used in Product Developmentshivam chauhanNo ratings yet
- Fish Bone DiagramDocument17 pagesFish Bone Diagramp ganeshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 ESSAYDocument4 pagesLesson 8 ESSAYKaren CasaulNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document43 pagesUnit 3SandeepNo ratings yet
- TQM 3Document11 pagesTQM 3Bibin K SNo ratings yet
- Creating-Analysis-Plan PW Final 09242013Document45 pagesCreating-Analysis-Plan PW Final 09242013Hien DinhthithuNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis FindingsDocument11 pagesData Analysis FindingsMulya Fajar RahmawanNo ratings yet
- My Notes On Conducting A Root Cause Analysis in Project ManagementDocument16 pagesMy Notes On Conducting A Root Cause Analysis in Project ManagementjcarantoNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesProblem SolvingTun Lin NaingNo ratings yet
- Shigeru Mizuno: - Philosopher of Quality - Born in JapanDocument15 pagesShigeru Mizuno: - Philosopher of Quality - Born in JapanhannahNo ratings yet
- Confirmative Evaluation: Practical Strategies for Valuing Continuous ImprovementFrom EverandConfirmative Evaluation: Practical Strategies for Valuing Continuous ImprovementNo ratings yet
- Stradcom Philippines RFID Project FAQDocument9 pagesStradcom Philippines RFID Project FAQTan_Wei_Chan_3670No ratings yet
- Introduction To FinacleDocument17 pagesIntroduction To FinaclemvsarmaNo ratings yet
- What's New in Windows 10 (Windows 10)Document56 pagesWhat's New in Windows 10 (Windows 10)NirNo ratings yet
- MGO 660 Syllabus - Spring 2023Document7 pagesMGO 660 Syllabus - Spring 2023Jasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- #2 ITTO - Report and EvaluationDocument60 pages#2 ITTO - Report and EvaluationyogiezulnipratamaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain - The Solution For Enhancing Brands of Vietnamese Agricultural Products - WOWTRACE PDFDocument5 pagesBlockchain - The Solution For Enhancing Brands of Vietnamese Agricultural Products - WOWTRACE PDFjunemrsNo ratings yet
- Nokia 5620 SAM - DatasheetDocument13 pagesNokia 5620 SAM - DatasheetNguyễnDuyKiênNo ratings yet
- The Major Types of Retailers Existing in Vietnam Market:: Group 3Document2 pagesThe Major Types of Retailers Existing in Vietnam Market:: Group 3Nguyen Duong Tu Quynh (K17 HCM)No ratings yet
- MKT-340 Creating Shared ValueDocument10 pagesMKT-340 Creating Shared ValueStuti SinghalNo ratings yet
- BSC Template: Instructions & CautionsDocument5 pagesBSC Template: Instructions & CautionsAllan VillagonzaloNo ratings yet
- Streetscape GuidanceDocument337 pagesStreetscape GuidanceQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bititci, 1997 Integrated Performance PDFDocument13 pagesBititci, 1997 Integrated Performance PDFEdson KogachiNo ratings yet
- Summary Report (4799)Document7 pagesSummary Report (4799)Mahusay Neil DominicNo ratings yet
- Anti-Money Laundering Regulation of Cryptocurrency: U.S. and Global ApproachesDocument14 pagesAnti-Money Laundering Regulation of Cryptocurrency: U.S. and Global ApproachesFiorella VásquezNo ratings yet
- YogeshPatil AnalyticsDocument3 pagesYogeshPatil AnalyticsNaga Ravi Thej KasibhatlaNo ratings yet
- CA3 - Application Report - Nur HidayahDocument8 pagesCA3 - Application Report - Nur HidayahNur HidayahNo ratings yet
- Going Rate PricingDocument3 pagesGoing Rate PricingHarshitha RNo ratings yet
- YieldDocument15 pagesYieldcrisNo ratings yet
- FMCFDocument12 pagesFMCFprashant TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 - Assignment - DTUTDocument7 pagesChap 12 - Assignment - DTUTĐặng Trần Minh QuânNo ratings yet
- Together We Fight Society Vs AppleDocument20 pagesTogether We Fight Society Vs AppleLia JoseNo ratings yet
- CORE/Prayagraj,: CLW/Chittaranjan, RCF/Kapurthala, MCF/Raebareli, DLW/Varanasi, RWF/Bangalore Railway/KolkataDocument2 pagesCORE/Prayagraj,: CLW/Chittaranjan, RCF/Kapurthala, MCF/Raebareli, DLW/Varanasi, RWF/Bangalore Railway/KolkataGopalakrishnanNo ratings yet