Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACCTY 312 - Lesson 3
Uploaded by
shsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACCTY 312 - Lesson 3
Uploaded by
shsCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 3:
THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
Learning Objectives:
At the end of the lesson, the students are expected to:
a. Differentiate normal distribution and standard normal distribution; and
b. Use the standard normal distribution table to determine area under the standard
normal curve.
Normal distribution, also known
as the Gaussian distribution, plays a
central role in psychological statistics.
This is because many psychological
variables, such as intelligence, personality
traits, and emotional states, are naturally
distributed in a way that closely follows
the normal distribution.
In psychological research, the
normal distribution is often used in
hypothesis testing, where researchers are
interested in determining whether a
sample of data is significantly different
from a known population or distribution. The normal distribution is often used as a
reference or benchmark distribution, and researchers can compare their data to this
distribution to determine whether their results are statistically significant.
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 1
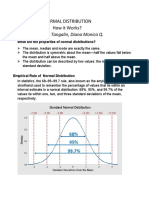
PROPERTIES OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
A normal distribution is a continuous, symmetric, bell-shaped distribution of a
variable. The known characteristics of the normal curve make it possible to estimate the
probability occurrence of any value of a normally distributed variable. The properties of
the normal distribution are as follows:
1. The distribution is bell-shaped.
2. The mean, median, and mode are equal and are located at the center of the
distribution.
3. The normal distribution is unimodal.
4. The normal distribution curve is symmetric about the mean (the shapes are same
on both sides).
5. The normal distribution is continuous.
6. The normal curve is asymptotic at x-axis.
7. The total area under the normal distribution curve is 1.00 or 100%.
8. The area under the part of a normal curve that lies within 1 standard deviation of
the mean is 68%, within 2 standard deviation is about 95%, and with 3 standard
deviation is about 99.7%.
OTHER TYPES OF DISTRIBUTION
a. Positively Skewed Distribution. In this distribution, most of the values in the data
fall to the left of the mean and group at the lower end of the distribution, the tail
is to the right. In addition, the mean is to the right of the median, and the mode is
to the left of the median.
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 2
b. Negatively Skewed Distribution. A distribution in which the mass of the data
values falls to the right of the mean and group at the upper end of the
distribution, with the tail to the left. The mean is to the left of the median, and the
mode is to the right of the median.
STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
A normal distribution can be converted into a standard normal distribution by
obtaining the z value. A z value is the signed distance between a selected value,
designated x, and the mean divided by the standard deviation. It is also called the z score,
z statistics, standard normal deviates, or the standard normal values. It is given by the
formula:
x-x
z=
σ
where: z = z value
x = the value of any particular observation
x = mean
Σ = standard deviation
Example 1: A student has a score of 56 in his midterm examination is Psychological
Statistics in which the average score of the whole class is 54 with σ = 2.31. The same
student has a score of 61 in his midterm examination in Advanced Statistics in which the
average score of the whole class is 68 with σ = 5.17. Determine which subject did the
student excel most.
Step 1. Solve for the z scores of the student in the two subjects.
56-54
Psychological Statistics: z1 = 2.31
= 0.87
61-68
Advanced Statistics: z2 = 5.17
= -1.35
Step 2. Interpret the results. Notice that the z score of the student in Psychological
Statistics is greater than his z score in Advanced Statistics. This suggests that the student
perform better in Psychological Statistics than in Advanced Statistics.
This time, we shall be using the Standard Normal Distribution table to determine
the area under the normal curve.
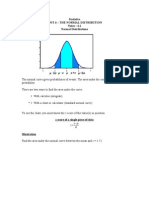
Example 2: Determine the area under the standard normal curve between z = 0 and z
= 1.85.
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 3
Step 1. Draw the figure to represent the area.
0 1.85
Step 2. Locate the area of the shaded region using the Standardized Normal Distribution
table.
z 0.00 0.01 … 0.05 …
0.0 0.0000 0.0040 … 0.0199 …
0.1 0.0398 0.0438 … 0.0596 …
0.2 0.0793 0.0832 … 0.0987 … P(0 < z < 1.85)
: : : … : …
1.8 0.4641 0.4649 … 0.4678 …
: : : … … …
P(0<z<1.85) = 0.4678
0.4678
0 1.85
Hence, the area under the normal curve from z = 0 to z = 1.85 is 0.4678.
APPLICATIONS OF THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
Example 3: To qualify for a master’s degree program in Psychology, a candidate must
score in the top of 20% on mental ability test. The test has a mean score of 180 and a
standard deviation of 25. Find the probability that an applicant will qualify in the program
if his score in mental ability test is 187.
Step 1. Solve for the z-score.
z = (187 – 180)/25 = 0.28.
This means that the score of 187 is 0.28 standard deviation above the mean score.
Step 2. Draw the figure to represent the area.
0 0.28
Step 3. Find the area under the normal curve to the right of z=0.28 which represents the
top 20% of scores. Based on the normal distribution table, a z score of 0.28 =
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 4
0.1103. Take note that the area needed to solve is at the right of 0.28. Also note
that the whole right region of the curve equals 0.50 or 50%.
This means that to solve for the shaded region, we subtract 0.1103 from 0.50.
As a result, the area of the shaded region would be 0.50 – 0.1103 = 0.39.
Hence, the probability that an applicant will quality to the master’s degree
program in Psychology, given that his score in mental ability test is 187, is 39%
only.
Example 4: In a medical examination, 300 people underwent height measurement and
was found out that the average height of all are 150 cm. If the standard deviation
is 19, find the number of people that fall under the given conditions:
a. With height less than 132 cm.
b. With height from 140 cm to 180 cm.
c. With height taller than 200 cm.
Solution (a)
Step 1. Solve for z score for a height of 132 cm: z = (132 – 150)/19 = -0.95.
Step 2. Locate the value of -0.95 in the normal distribution table. We can find in the table
that the proportion of people with a z-score less than -0.95 is 0.17.
Step 3. Compute for the total number of people with height less than 132 cm.
That is, 300 people x 0.17 = 51.33 or 51.
Therefore, there are 51 people with height less than 132 cm.
Solution (b)
Step 1. Solve for z scores for a height of 140 cm and 180 cm.
z1 = (140 – 150)/19 = -0.53
z2 = (180 – 150)/19 = 1.58
Step 2. Illustrate the normal curve for easier identification of the area.
-0.53 0 1.58
Step 3. Locate the values of z1 and z2 in the normal distribution table.
P(-0.53 < z 1.58) or
P(-0.53 < z < 0) + P(0 < z < 1.58)
0.20 + 0.46 = 0.66
Step 4. Calculate the number of people with height from 140 cm to 180 cm.
300 x 0.66 = 198
Hence, there are 198 people with height from 140 cm to 180 cm.
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 5
EXERCISES 3
Name: ______________________________________________________________________ Score: ______________
Course/Section: ____________________________________________________________ Date: _______________
1. Find the probability of each under the normal curve.
a. P(0 < z < 1.56) b. P(z < 2.23)
c. P(0.38 < z < 2.27) d. P(z < -1) + P(z > 0.84)
e. P(z < 1.73) f. P(z > 0.58
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 6
2. Solve the following:
a. The average score of employees on a mental examination is 120. The standard
deviation of the scores is 30. What is the percentage of the employees with scores
less than the 100?
b. The time needed to finish an examination is normally distributed with mean of 56
minutes and SD of 1.2 minutes. What is the probability that a randomly selected
examinee will consume more than 60 minutes in the examination?
c. A study claimed that the average weight of a depressed teenager is 83 kilograms
with SD of 2.3 kilograms. If the study is correct, what is the probability that a
randomly selected teenager with depression has a weight less than 70?
d. The amount of time that students devote to their review session in a week is
normally distributed with a mean of 6.5 hours and SD of 3.2 hours. What is the
probability that 30 randomly selected students review between 3 and 5 hours per
week?
ACCTY 312 - Statistical Analysis with Software Applications 7
You might also like
- NormalDistribution2012 PDFDocument29 pagesNormalDistribution2012 PDFElisa Dela Reyna BaladadNo ratings yet
- Module Using The Empirical RuleDocument14 pagesModule Using The Empirical RuleIzyle CabrigaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document15 pagesQuiz 3diana_762131871No ratings yet
- Module 2Document13 pagesModule 2Princess Kaye RicioNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Waliso Campus: Statistics For MGT I: Normal Distributions (Continuous Probability Distributions)Document121 pagesAmbo University Waliso Campus: Statistics For MGT I: Normal Distributions (Continuous Probability Distributions)keransotadeseNo ratings yet
- Standard Scores and The Normal Curve: Report Presentation byDocument38 pagesStandard Scores and The Normal Curve: Report Presentation byEmmanuel AbadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - T-Distribution (Module)Document26 pagesLesson 3 - T-Distribution (Module)charmaine marasigan100% (1)
- The Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesThe Normal DistributionDog VenturesNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesDocument11 pagesSaint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesJimkenneth RanesNo ratings yet
- Assignment Inferential Statistics 1Document5 pagesAssignment Inferential Statistics 1maudy octhalia d4 kepNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Z ScoreDocument32 pagesLesson 5 Z ScoreLala CkeeNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution 2012Document29 pagesNormal Distribution 2012Gabriel LloydNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M4 PDFDocument16 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M4 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Result Analysis 2bDocument60 pagesWeek 6 - Result Analysis 2bAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- High School Statistics WorksheetsDocument14 pagesHigh School Statistics WorksheetsDindo HiocoNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution and Probability Distribution FunctionDocument5 pagesNormal Distribution and Probability Distribution Functionvs6886No ratings yet
- Normal Random VariableDocument8 pagesNormal Random VariableLoraine Buen FranciscoNo ratings yet
- n$1'q5h n5) Iop) 0chDocument4 pagesn$1'q5h n5) Iop) 0chCamille RalletaNo ratings yet
- QTM Cycle 7 Session 4Document79 pagesQTM Cycle 7 Session 4OttilieNo ratings yet
- Statistics Unit 6 NotesDocument10 pagesStatistics Unit 6 NotesgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 StatProb ModuleDocument37 pagesWeek 3 StatProb Modulealex antipuestoNo ratings yet
- Standard Score and Normal distMEdDocument12 pagesStandard Score and Normal distMEdRizalyn GepilanoNo ratings yet
- Statistic Sample Question IiswbmDocument15 pagesStatistic Sample Question IiswbmMudasarSNo ratings yet
- Jurnal StatistikDocument7 pagesJurnal StatistikAry PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics You Should Know For The PMP Certification ExamDocument5 pagesBasic Statistics You Should Know For The PMP Certification ExamIan SecretariaNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution 2012Document29 pagesNormal Distribution 2012kya karegaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Z-Scores, Measuring Performance: Learning OutcomeDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Z-Scores, Measuring Performance: Learning OutcomeCheska AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 5 Z&NormalDocument33 pages5 Z&NormalRosemarie GasparNo ratings yet
- Normal 30Document2 pagesNormal 30Kerdid SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Tangalin ReportDocument3 pagesNormal Distribution Tangalin ReportVanessa LacbayanNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution LASDocument6 pagesNormal Distribution LASaljun badeNo ratings yet
- Stat-and-Prob_Q4-Week-4_Module-12-Hilario-Garcia_Document18 pagesStat-and-Prob_Q4-Week-4_Module-12-Hilario-Garcia_gabezarate071100% (1)
- The Normal Distribution PDFDocument12 pagesThe Normal Distribution PDFIsraelNo ratings yet
- STat Quiz 2Document2 pagesSTat Quiz 2Gian Carlo Gonje GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Analysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataDocument50 pagesAnalysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataJayson EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Normal CurveDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Normal CurveAdrianNo ratings yet
- Normal Curve PowerpointDocument18 pagesNormal Curve PowerpointKatherine PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1515102479569Document23 pagesOrca Share Media1515102479569Chachi QuibuyenNo ratings yet
- Statistics Assignment For IIUM PGDocument5 pagesStatistics Assignment For IIUM PGSyaza Hazirah AzieNo ratings yet
- Z - Scores: Why Is This Impor Tant?Document10 pagesZ - Scores: Why Is This Impor Tant?Anonymous hXd6PJlNo ratings yet
- List The Importance of Data Analysis in Daily LifeDocument22 pagesList The Importance of Data Analysis in Daily LifeKogilan Bama Daven100% (1)
- Handout-B-Standard-Score-And-Normal-Dist Advance StatisticsDocument13 pagesHandout-B-Standard-Score-And-Normal-Dist Advance StatisticsRichard HisanzaNo ratings yet
- 4.-Normal-Distribution - LECTUREDocument34 pages4.-Normal-Distribution - LECTURERoyce GomezNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionsDocument13 pagesSampling DistributionsRaza AnsariNo ratings yet
- 5 FIN10002 Chapter4 2015 PDFDocument40 pages5 FIN10002 Chapter4 2015 PDFAnna XiNo ratings yet
- Applications of Normal DistributionDocument13 pagesApplications of Normal DistributionMohammed Demssie MohammedNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoresDocument26 pagesStandard ScoresJennie Mendoza0% (1)
- NormalWS1 PDFDocument4 pagesNormalWS1 PDFRizza Jane BautistaNo ratings yet
- MMM SD NDDocument41 pagesMMM SD NDEj VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 MMWDocument26 pagesModule 4 MMWClash Of clanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference: Prepared By: Antonio E. Chan, M.DDocument227 pagesStatistical Inference: Prepared By: Antonio E. Chan, M.Dश्रीकांत शरमाNo ratings yet
- A. The Standard Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesA. The Standard Normal DistributionAlexa LeeNo ratings yet
- WIN SEM (2020-21) CSE4029 ETH AP2020215000156 Reference Material I 27-Jan-2021 DistibutionDocument7 pagesWIN SEM (2020-21) CSE4029 ETH AP2020215000156 Reference Material I 27-Jan-2021 DistibutionmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- Data Organization and Standardized TestingDocument7 pagesData Organization and Standardized TestingJohn LamNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module 2 Key ConceptsDocument37 pagesStatistics and Probability Module 2 Key ConceptsMara M. LabanderoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Practical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsFrom EverandPractical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Testing and Assessment A Practical Guide For Counselors Social Workers and Psychologists 3Rd Edition Neukrug Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesEssentials of Testing and Assessment A Practical Guide For Counselors Social Workers and Psychologists 3Rd Edition Neukrug Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJerryMitchellkegq100% (12)
- Penting 2Document22 pagesPenting 2Raihatul Jannah Raihatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Real Statistics Examples Correlation ReliabilityDocument404 pagesReal Statistics Examples Correlation ReliabilityMetalurgista SosNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 3Document24 pagesChapter No. 3Anonymous GirlNo ratings yet
- Expectation and VarianceDocument16 pagesExpectation and VarianceWahab HassanNo ratings yet
- Deliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationDocument5 pagesDeliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationAdroit WriterNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10Document3 pagesMathematics 10Katelyn Mae SungcangNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument49 pagesDescriptive StatisticsTheGimhan123No ratings yet
- Merryland High School - Entebbe S5 Term 2020 Holiday Break Mathematics P1 Pure Maths Instructions: Answer ALL QuestionsDocument4 pagesMerryland High School - Entebbe S5 Term 2020 Holiday Break Mathematics P1 Pure Maths Instructions: Answer ALL QuestionsVictor Lusiba100% (1)
- Skew Ness Kurtosis and MomentsDocument31 pagesSkew Ness Kurtosis and MomentsDr. POONAM KAUSHALNo ratings yet
- Correlation Analysis MethodsDocument11 pagesCorrelation Analysis MethodsIlovedocumintNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Establishing Test Validity and Reliability Activity 7 - January, 2022Document4 pagesModule 7: Establishing Test Validity and Reliability Activity 7 - January, 2022Michael AgustinNo ratings yet
- HW 03 220Document5 pagesHW 03 220zhang JayantNo ratings yet
- MBR Lab Week 10-12-1Document65 pagesMBR Lab Week 10-12-1Sadaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical PresentationsDocument26 pagesDescriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical PresentationsRavichandran SekarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 SolutionDocument12 pagesProblem Set 6 SolutionTACN-2T?-19ACN Nguyen Dieu Huong LyNo ratings yet
- Contoh Analisis DistribusiDocument5 pagesContoh Analisis Distribusiartsy artNo ratings yet
- S1 - Chapter Review 2Document5 pagesS1 - Chapter Review 2Mweene Ruth MatongoNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics (HS167) Lab Manual: # Variable Name Variable Label Codes and Parameters (Dots Represent Missing Data)Document15 pagesBiostatistics (HS167) Lab Manual: # Variable Name Variable Label Codes and Parameters (Dots Represent Missing Data)Raj Kumar SoniNo ratings yet
- Measures and GraphsDocument3 pagesMeasures and GraphsBernard BanalNo ratings yet
- Tema1 EjerciciosDocument21 pagesTema1 EjerciciosJust SomebodyNo ratings yet
- Whoqol-100 Item QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesWhoqol-100 Item QuestionnaireAna Keila Carvalho Vieira KeilaNo ratings yet
- Gsya 76 WGSGDocument4 pagesGsya 76 WGSGwirda zuljannahNo ratings yet
- T Test and ANOVA - Test: (Use Demo Discriptive - Sav Data File)Document5 pagesT Test and ANOVA - Test: (Use Demo Discriptive - Sav Data File)ishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution: Postgraduate CornerDocument3 pagesFrequency Distribution: Postgraduate CornerPranay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Module5 Measures of Central Tendency Grouped Data Business 1Document13 pagesModule5 Measures of Central Tendency Grouped Data Business 1Donna Mia CanlomNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics QuestionsDocument33 pagesDescriptive Statistics QuestionsPARUL SINGH MBA 2019-21 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Measures of VariabilityDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Measures of VariabilityAdrianNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document12 pagesWeek 2Nisal KarunathilakeNo ratings yet
- Regression: NotesDocument5 pagesRegression: NotesBENNY WAHYUDINo ratings yet