Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCV4U 4.4 - Assessment
Uploaded by
laureniscapuletOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCV4U 4.4 - Assessment
Uploaded by
laureniscapuletCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
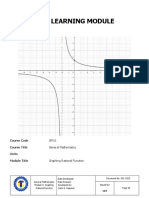
4 Concavity and Points of Inflection
Name: ______________________________ Score: / 20
Teacher: Date: Time:
Purpose of Assessment: Assessment of Learning
Method of Assessment: KTCA
Learning Goals:
● Students know how to use the second derivative to find and test points of
inflection of functions and classify intervals over which functions are concave up
and concave down.
Overall Expectations
● B. DERIVATIVES AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
● 1. make connections, graphically and algebraically, between the key features of a
function and its first and second derivatives, and use the connections in curve
sketching;
● 2. solve problems, including optimization problems, that require the use of the
concepts and procedures associated with the derivative, including problems
arising from real-world applications and involving the development of
mathematical models.
Specific Expectations
● B 1. Connecting Graphs and Equations of Functions and Their Derivatives
● B 1.1 sketch the graph of a derivative function, given the graph of a function that
is continuous over an interval, and recognize points of inflection of the given
function
● B 1.2 recognize the second derivative as the rate of change of the rate of change,
and sketch the graphs of the first and second derivatives, given the graph of a
smooth function
● B 1.3 determine algebraically the equation of the second derivative f”(x) of a
polynomial or simple rational function f(x), and make connections, through
investigation using technology, between the key features of the graph of the
function and corresponding features of the graphs of its first and second
derivatives
● B 1.4 describe key features of a polynomial function, given information about its
first and/or second derivatives, sketch two or more possible graphs of the function
that are consistent with the given information, and explain why an infinite number
of graphs is possible
● B 1.5 sketch the graph of a polynomial function, given its equation, by using a
variety of strategies to determine its key features, and verify using technology
● B 2. Solving Problems Using Mathematical Models and Derivatives
● B 2.1 makes connections between the concept of motion and the concept of the
derivative in a variety of ways.
● B 2.2 make connections between the graphical or algebraic representations of
derivatives and real-world applications
● B 2.3 solve problems, using the derivative, that involve instantaneous rates of
change, including problems arising from real-world applications, given the
equation of a function
Instructions:
1. Make a copy of this document.
2. Answer the questions.
3. Put a copy of your work in a course folder.
K: _______ / 5 T: _______ / 5 C: _______ / 5 A: _______ / 5
Knowledge & Thinking 10
For each of the following functions, determine any points of inflection.
a) y = x4 + 4x
4𝑥 2 −3
b) y = 𝑥3
Marking Scheme (10 marks)
• 4 marks for correctly answering question a)
• 6 marks for correctly answering question b)
Communication 5
For each function, state whether the value of the second derivative is positive or
negative at each of points A, B, C, and D.
c) b)
Marking Scheme (5 marks)
• 5 marks for correctly answering the questions
Application 5
Determine the critical points for each function and use the second derivative test to
decide if the point is a local maximum, a local minimum, or neither.
a) y = x3 - 6x2 - 15x + 10
25
b) y = 𝑥 2 +48
Marking Scheme (5 marks)
• 2 marks for correctly finding the critical points
• 3 marks for correctly determining local max/min
You might also like
- 048 InternationalLaw Admiralty Maritime PDFDocument228 pages048 InternationalLaw Admiralty Maritime PDF:Lawiy-Zodok:Shamu:-El100% (2)
- Tax 2 Case DigestDocument3 pagesTax 2 Case DigestBobbyNo ratings yet
- Course Notes - Calculus 1Document34 pagesCourse Notes - Calculus 1Amirah SyahirahNo ratings yet
- g8 Ms Mastering Mct2 SeDocument80 pagesg8 Ms Mastering Mct2 SeShorya Kumar100% (2)
- Modular Activities PeptDocument37 pagesModular Activities PeptJaninne Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Itch To Stitch Lindy Petal Skirt PDF Pattern Large Format - 645d68894228eDocument1 pageItch To Stitch Lindy Petal Skirt PDF Pattern Large Format - 645d68894228eDenisha McCarterNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions UbDDocument6 pagesQuadratic Functions UbDVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Red Notes Crim (Finalized)Document28 pagesRed Notes Crim (Finalized)Zoroaster Guitelen BolingetNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Advanced Mathematics Assessment 2022Document12 pagesYear 11 Advanced Mathematics Assessment 2022sumNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Add Maths Form 4-Edit1Document23 pagesYearly Plan Add Maths Form 4-Edit1Kyra LingNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quadratic FunctionsDocument15 pagesMathematics: Quadratic FunctionsDo HaNo ratings yet
- HL PAPER 3 Que-How To Prepare. For AA and AI Students 2022 Ver 2.0ibDocument10 pagesHL PAPER 3 Que-How To Prepare. For AA and AI Students 2022 Ver 2.0ibsriramaniyerNo ratings yet
- REaction On IPCRFDocument2 pagesREaction On IPCRFBauder Touchsky100% (3)
- Connecticut Appellate Court BriefDocument18 pagesConnecticut Appellate Court BriefJosephine Miller100% (1)
- Effect of Culture On Global Marketing Bangladesh PerspectiveDocument10 pagesEffect of Culture On Global Marketing Bangladesh PerspectiveTahsin AzadNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Septic Tank Systems in TheDocument57 pagesEvaluation of Septic Tank Systems in TheNesru HamidNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Gen. Math Modules W1-3Document19 pagesGrade 11 Gen. Math Modules W1-3Encluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet
- MCV4U 3.3 - AssessmentDocument4 pagesMCV4U 3.3 - AssessmentlaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- MCV4U 4.1 - AssessmentDocument5 pagesMCV4U 4.1 - AssessmentlaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- MCV4U 3.1 - AssessmentDocument5 pagesMCV4U 3.1 - AssessmentlaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- (C) Calculus PracticalDocument72 pages(C) Calculus Practicaljimmychief05No ratings yet
- MATH HS Algebra II - Unit 05 Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesMATH HS Algebra II - Unit 05 Exponential and Logarithmic Functionsnawafhassan187No ratings yet
- (Q) MCV4U Chapter 1-3 SummativeDocument4 pages(Q) MCV4U Chapter 1-3 SummativelaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- Math 95 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMath 95 Syllabusapi-327140356No ratings yet
- (Q) MHF4U Chapter 1 Summative V1 QDocument3 pages(Q) MHF4U Chapter 1 Summative V1 QlaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document4 pagesAlgebra 2api-15888876No ratings yet
- 2008 Form 5 Am Teaching SchemeDocument11 pages2008 Form 5 Am Teaching SchemeSujairi AmhariNo ratings yet
- RPT Add MT F5 2012Document20 pagesRPT Add MT F5 2012Haswa ShazwatiNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Enrichment Packet - Answer KeyDocument36 pagesAlgebra 2 Enrichment Packet - Answer KeyMarylene Montoya100% (1)
- Tutorial Kit (Mathematics-400 L) - Vol. 2Document68 pagesTutorial Kit (Mathematics-400 L) - Vol. 2Gebra TogunNo ratings yet
- Inverse Variation Summative AssessmentDocument5 pagesInverse Variation Summative Assessmentapi-249037964No ratings yet
- Functions11 Sec1 7Document10 pagesFunctions11 Sec1 7Andre YunusNo ratings yet
- Course Content Form: MAT 220 Calculus IDocument3 pagesCourse Content Form: MAT 220 Calculus IMyriam ValanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan ADD MATHS Form 4 (2012)Document17 pagesYearly Plan ADD MATHS Form 4 (2012)丽娜钱霙No ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Add Math f4 2013Document17 pagesYearly Plan Add Math f4 2013Ayu Lil'princessNo ratings yet
- HSAlgebra IIBCurriculum 2024Document32 pagesHSAlgebra IIBCurriculum 2024tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- Ap Calculus BC SyllabusDocument15 pagesAp Calculus BC Syllabusapi-306402864No ratings yet
- Gen - Math Week3 - LM3Document10 pagesGen - Math Week3 - LM3Daryll FabrosNo ratings yet
- HL Portfolio WorkDocument76 pagesHL Portfolio WorkFadi AyyoubNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Course of StudyDocument12 pagesAP Calculus BC Course of Studydanvelezz100% (1)
- Tut - FinalDocument146 pagesTut - FinalShaikh rehan Shaikh rehanNo ratings yet
- Objective ReportDocument3 pagesObjective ReportAjeng Cempaka lestariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Polynomial Functions CalendarDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Polynomial Functions Calendarapi-327821202No ratings yet
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument8 pagesImplicit Differentiationjake8837No ratings yet
- Calculus - Theme 1Document7 pagesCalculus - Theme 1GwarraNo ratings yet
- Unit - Unit 4 - Quadratic Equations and Functions - 20200503161254Document5 pagesUnit - Unit 4 - Quadratic Equations and Functions - 20200503161254Alex WellmanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterJoanne Mae LuceroNo ratings yet
- AMaths 4 (NA) 4039 Syllabus 2011Document13 pagesAMaths 4 (NA) 4039 Syllabus 2011Winson ChuaNo ratings yet
- Major Assignment 1A Limits and DerivativesDocument3 pagesMajor Assignment 1A Limits and DerivativesnbentzNo ratings yet
- C - Documents and Settings - Administrator - Local Settings - Application Data - Mozilla - Firefox - Profiles - GhcvulkxDocument13 pagesC - Documents and Settings - Administrator - Local Settings - Application Data - Mozilla - Firefox - Profiles - Ghcvulkxavci_16_metinNo ratings yet
- MHF4U Unit 3 ExamplerDocument8 pagesMHF4U Unit 3 ExamplerGaganpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- DLL 7Document4 pagesDLL 7REALIZA B. BELCHEZNo ratings yet
- N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 1.variables and ExpressionsDocument4 pagesN Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 1.variables and Expressionsarg456No ratings yet
- Add Maths Form 4 Yearly PlanDocument10 pagesAdd Maths Form 4 Yearly PlanTANG PEI PEI100% (9)
- Hsp-Add Math-F5Document28 pagesHsp-Add Math-F5Azreen DaudNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test 14 9 2023 1Document2 pagesMCQ Test 14 9 2023 1satyam skNo ratings yet
- 2017 A Level 9758 H2 Math Paper 1 Solution and Paper 2 Likely QuestionsDocument20 pages2017 A Level 9758 H2 Math Paper 1 Solution and Paper 2 Likely QuestionsKeiran Tan100% (1)
- Unit 3 Maths Methods - Application Task SAC - Notification FormDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Maths Methods - Application Task SAC - Notification Formjmh22504No ratings yet
- AS2 MathDocument4 pagesAS2 MathSwam Pyae Maung MaungNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algebra/Trigonometry: 2.1. Numbers, Number Systems and Number RelationshipsDocument5 pagesAdvanced Algebra/Trigonometry: 2.1. Numbers, Number Systems and Number RelationshipsAustin ChiversNo ratings yet
- Unit 103 Further Mathematics For Engineering TechniciansDocument13 pagesUnit 103 Further Mathematics For Engineering TechniciansasmonovNo ratings yet
- KMJ PDFDocument11 pagesKMJ PDFKhairul Hafizh FirdausNo ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Sample Syllabus 2Document7 pagesCalculus Ab Sample Syllabus 2api-456991000No ratings yet
- Term 4 Maths GR 12Document11 pagesTerm 4 Maths GR 12Simphiwe ShabalalaNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument19 pagesSolving Quadratic EquationsKareen Faith MendeNo ratings yet
- Las Circular Functions 2Document4 pagesLas Circular Functions 2JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- GRG 4Document1 pageGRG 4egalNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure DXDocument7 pagesAcute Renal Failure DXfarid akbarNo ratings yet
- 0610 w14 QP 13Document16 pages0610 w14 QP 13Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Le Meridien IT ReportDocument34 pagesLe Meridien IT ReportSagarMishra88% (8)
- Tales of Animals in War 2023Document4 pagesTales of Animals in War 2023Brijesh Chera - Sir Isaac Brock PS (1417)No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Suheil PDFDocument9 pagesLesson 8 Suheil PDFrusilawati sallehNo ratings yet
- 22-23rd AihraDocument4 pages22-23rd Aihragaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Car CareDocument2 pagesCar Caresuharsh koreNo ratings yet
- Haryana Government Gazette: Published by AuthorityDocument8 pagesHaryana Government Gazette: Published by AuthorityEr navneet jassiNo ratings yet
- CESMM3Document120 pagesCESMM3amiruser100% (2)
- Family ReunionDocument40 pagesFamily ReunionSham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Chemical Constituents From Eclipta Alba L. For Achieving StandardizationDocument62 pagesIsolation of Chemical Constituents From Eclipta Alba L. For Achieving StandardizationMithun NymthiNo ratings yet
- Peel Health Study GuideDocument162 pagesPeel Health Study Guideemo_bmoNo ratings yet
- Archetypes - Aboreal, Dragon, PlagueDocument5 pagesArchetypes - Aboreal, Dragon, PlagueTal Shimshon DekelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 325 "Stop Bullying": Name: Farah Mardiani Putri NIM: 2013170797Document17 pagesAssignment 325 "Stop Bullying": Name: Farah Mardiani Putri NIM: 2013170797FarahfzzNo ratings yet
- Telangana (TS) Liquor Price List 2023-24 PDF Download - PDF ListDocument36 pagesTelangana (TS) Liquor Price List 2023-24 PDF Download - PDF ListManvith ZerardNo ratings yet
- Clinical Relevance of ECGDocument4 pagesClinical Relevance of ECGdrfelixNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument4 pagesStainless SteelMARUCOT ALEXIS P.No ratings yet
- Hall Ticket.Document1 pageHall Ticket.Manisha MishraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Java ScriptDocument130 pagesAdvanced Java Scriptdinesh9866119219No ratings yet
- JUAREZ FLS 1-Training Activity MatrixDocument5 pagesJUAREZ FLS 1-Training Activity MatrixClaireSobredilla-JuarezNo ratings yet