Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AHW QP SM-4a
Uploaded by
Indervir SinghOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AHW QP SM-4a
Uploaded by
Indervir SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessed Homework SM-4a Probability & Trigonometry
1. A school has different A-Level options for its students, and the probability of a student chosen at random
studying a particular subject now follows a probability distribution as follows:-
The probability they study Mathematics (M) is 0.6
The chance that they study Computer Science (C) is 5%, and to do so they must also study
Mathematics
It has been shown that the likelihood of a student studying Biology (B) is 1 in 5, and that
does not change whether they are a Mathematician or not.
Lastly, while Historians take up a tenth of every year group, it is impossible in the option
blocks to choose both History and Mathematics, and similarly, Biology cannot be taken
alongside Computer Science.
The chances of a student studying none of the above is 26%.
a) Draw a Venn Diagram illustrating the full distribution of probabilities
(5)
b) Hence find the value of…
i. 𝑃(𝐵 ∪ 𝐻)
ii. 𝑃(𝐵 ∩ 𝐻′)
iii. 𝑃(𝐵 ∪ 𝐻 ∪ 𝑀′)
iv. 𝑃( 𝐶 ′ ∩ (𝑀 ∪ 𝐵))
(4)
c) What is the name given (in the vocabulary of our Probability chapter) for the relationship
between
i. 𝐵 & 𝑀
ii. 𝐻 & 𝐶
iii. (𝐵 ∪ 𝐻) & (𝐵′ ∩ 𝐻′)
(3)
12 marks
2. Three events A, B and C are defined in the sample space S. The event outcome A cannot be true if B is
true, but is unaffected in its likelihood if C is true.
a) Draw a Venn diagram to illustrate the relationships between the 3 events. (1)
b) What specific words describe the relationships between
i) A and B (1)
ii) A and C (1)
Given that 𝑃(𝑨) = 0.2, 𝑃(𝑩) = 0.4 and 𝑃(𝑨 ∪ 𝑪) = 0.7, find
c) 𝑃(𝑨 ∪ 𝑩) (1)
d) 𝑃(𝑪) (2)
e) 𝑃(𝑪 | 𝑩), if 𝑃(𝐴′ ∩ 𝐵′ ∩ 𝐶 ′ ) = 0 (2)
8 marks
Page 1 of 3 KEGS Mathematics © 2018
A-Level Mathematics – Cornerstone Skills for Building Resilient Problem Solvers
1. Algebraic & numeric fluency 2. Calculator skill & IT literacy 3. Graphs & Constructions 4. Comprehension & Interpretation
Assessed Homework contd.
3. A triangle 𝐴𝐵𝐶 has lengths 𝐴𝐵 = (𝑥 − 1) cm, 𝐴𝐶 = (√3𝑥 − 1) cm, and 𝐵𝐶 = (𝑥 + 1) cm, with an angle
of ∠𝐵𝐶𝐴 = 30°.
a) Find the exact value of 𝑥, in the form 𝑎 + 𝑏√3. (5)
b) Hence, find the exact value of the triangle’s area, in the form 𝑐 + 𝑑√3. (3)
c) Find the remaining two angles, to the nearest degree. (2)
10 marks
4.
The figure shows a square PQRS. The corners of the
square have the co-ordinates:
𝑃(2,5), 𝑄(4,11), 𝑅(10,9), 𝑆(8,3).
The circle C1 circumscribes the square.
a) Find the co-ordinates of the centre of circle C1 (1)
b) Find the radius of the circle C1. (1)
The circle C2 is inscribed in the square.
c) Find the equation of the circle C2. (2)
The point M is the mid-point of RS, while N is the mid-point of PS.
d) Find the lengths QN, QM, PM and NM. (2)
Hence using the cosine rule, or otherwise, find
e) the angle 𝑃𝑀𝑄 (to the nearest degree) (2)
f) the angle NQM (to the nearest degree) (2)
g) the area of the triangle NMQ. (if possible, the exact answer is preferable) (2)
12 marks
TOTAL: 40 Marks
Page 2 of 3 KEGS Mathematics © 2018
A-Level Mathematics – Cornerstone Skills for Building Resilient Problem Solvers
1. Algebraic & numeric fluency 2. Calculator skill & IT literacy 3. Graphs & Constructions 4. Comprehension & Interpretation
Assessed Homework contd.
Page 3 of 3 KEGS Mathematics © 2018
A-Level Mathematics – Cornerstone Skills for Building Resilient Problem Solvers
1. Algebraic & numeric fluency 2. Calculator skill & IT literacy 3. Graphs & Constructions 4. Comprehension & Interpretation
You might also like
- (D Iagram Not To Scale) : IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Document2 pages(D Iagram Not To Scale) : IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Alinda Nurul BadriyahNo ratings yet
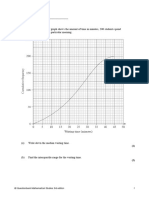
- The Cumulative Frequency Graph Shows The Amount of Time in Minutes, 200 Students Spend Waiting For Their Train On A Particular MorningDocument8 pagesThe Cumulative Frequency Graph Shows The Amount of Time in Minutes, 200 Students Spend Waiting For Their Train On A Particular MorningJonathanNo ratings yet
- HL Vectors Old QBDocument19 pagesHL Vectors Old QBmavelNo ratings yet
- Cce RF Cce RR: SubjectDocument8 pagesCce RF Cce RR: SubjectHackerzz ArenaNo ratings yet
- X Math Sample Paper 23-24-2Document6 pagesX Math Sample Paper 23-24-2mandalankan2No ratings yet
- December MathsDocument5 pagesDecember MathsNamraNo ratings yet
- Math 1011 - 2023 - Worksheet - IIIDocument2 pagesMath 1011 - 2023 - Worksheet - IIIAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Question Paper MathsDocument9 pagesQuestion Paper MathsPrachi SinghNo ratings yet
- 42 Circle Geometry With Answers Apr2020Document17 pages42 Circle Geometry With Answers Apr2020Kyle kNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Sample Paper 1: General InstructionsDocument21 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Sample Paper 1: General InstructionsAyush YadavNo ratings yet
- GP PaperDocument2 pagesGP Paperpankajchauhaan02No ratings yet
- Class Ix Maths QP Sample Paper 2023-24Document6 pagesClass Ix Maths QP Sample Paper 2023-24sanketyadav1108No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityNIRAV GOHELNo ratings yet
- Class-X Mathematics-Basic (241) Sample Question Paper 2020-21Document11 pagesClass-X Mathematics-Basic (241) Sample Question Paper 2020-21madhav haibateNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper With Solutions 2020 2021Document27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper With Solutions 2020 2021Shankar ji guptaNo ratings yet
- MME Test 8 Full Course XDocument4 pagesMME Test 8 Full Course Xjyotisahni13No ratings yet
- G10 Standard - Iii Preboard 2022-23 - QP (Set B)Document7 pagesG10 Standard - Iii Preboard 2022-23 - QP (Set B)sahanaaarunNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationDocument8 pagesCambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- SIDqp UEAIRWf IQji T4 PNDocument12 pagesSIDqp UEAIRWf IQji T4 PNJyoti MundaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Maths Paper 1 (QP)Document5 pagesCBSE Maths Paper 1 (QP)Acharya Dronacharya Foundation CenterNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Question Paper by KSTA (Eng Med)Document13 pagesSSLC MATHS Question Paper by KSTA (Eng Med)Nitin BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper IX Mathematics Annual Exams 2022-23Document4 pagesSample Paper IX Mathematics Annual Exams 2022-23Kriday MisriNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Apr 13 Standard Sample Paper 2023 24Document9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Apr 13 Standard Sample Paper 2023 24RAKESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Annual 7TH Math QP 4Document5 pagesAnnual 7TH Math QP 4Biswaswarup pandaNo ratings yet
- $maths Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pages$maths Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024Prerna JainNo ratings yet
- 10 23 24sp MathsstandardDocument18 pages10 23 24sp Mathsstandardrajmocci69No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class X Session 2023-24: Mathematics Standard (Code No.041)Document9 pagesSample Question Paper Class X Session 2023-24: Mathematics Standard (Code No.041)रिद्धम वर्माNo ratings yet
- Cbiemapu 05Document10 pagesCbiemapu 05Nikita JainNo ratings yet
- Cbjemasu 02Document5 pagesCbjemasu 02AnshuNo ratings yet
- F.1 LSC Math UT2 17-18Document6 pagesF.1 LSC Math UT2 17-18Ching Yan CheungNo ratings yet
- KV Class 10 Pre Board Sample Question Paper MATHS 7Document7 pagesKV Class 10 Pre Board Sample Question Paper MATHS 7sreejaps45No ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths SA2Document5 pagesClass 10 Maths SA2Priyank GuptaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Sample Paper 3 Time: 2 Hrs Total Marks: 80Document5 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Sample Paper 3 Time: 2 Hrs Total Marks: 80MdNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 AM WA3 Mock Exam 2023Document10 pagesSec 3 AM WA3 Mock Exam 2023Jayden Chua Qi Ze (Amkss)No ratings yet
- Secondary 3 A Math WA3 Mock Exam Paradigm MathDocument9 pagesSecondary 3 A Math WA3 Mock Exam Paradigm MathrohNo ratings yet
- SBHS 2011 Yr 9 Yearly PDFDocument17 pagesSBHS 2011 Yr 9 Yearly PDFKevin QuachNo ratings yet
- Imo Sample Paper Class-10Document2 pagesImo Sample Paper Class-10sai kuberNo ratings yet
- P1-Trigonometry: Past Papers QuestionsDocument37 pagesP1-Trigonometry: Past Papers QuestionsJumanaAsimNo ratings yet
- FN - 10 - Maths Test-01 - 10-11-23 - QuestionDocument3 pagesFN - 10 - Maths Test-01 - 10-11-23 - QuestionlwhmrvavrodrljeuwoNo ratings yet
- 81-E Cce PF - PRDocument9 pages81-E Cce PF - PRGuruprasad SNo ratings yet
- Solomon C QP - C2 Edexcel PDFDocument4 pagesSolomon C QP - C2 Edexcel PDFHappy AyichNo ratings yet
- Maths Revision SheetDocument8 pagesMaths Revision Sheetanubhavonwork60No ratings yet
- Solomon J QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon J QP - C1 EdexcelMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - RetestDocument8 pagesGrade 9 - RetestvissrisaifrNo ratings yet
- Adv Mathematics 2-1Document5 pagesAdv Mathematics 2-1rajabumahalalaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IIDocument5 pagesMathematics IIitsmeshimrithNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10B Paper 2Document16 pagesMaths Year 10B Paper 2Krishan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: PAPER 1 Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Document8 pagesMathematics: PAPER 1 Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Private of ScienceNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Sample Question Paper 2021-22Document11 pagesMathematics Sample Question Paper 2021-22suhailNo ratings yet
- Q1: Encircle The Correct Answer For The Following Multiple Choice Questions. (10) 1. 1. 2. 3Document1 pageQ1: Encircle The Correct Answer For The Following Multiple Choice Questions. (10) 1. 1. 2. 3Irfan AliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Maths Paper 2 (QP)Document6 pagesCBSE Maths Paper 2 (QP)Acharya Dronacharya Foundation CenterNo ratings yet
- 2067 SLC For 2072 Kins SchoolDocument2 pages2067 SLC For 2072 Kins SchoolSantosh AryalNo ratings yet
- 20.01.24. X (Cbse) Maths Prelim PaperDocument6 pages20.01.24. X (Cbse) Maths Prelim PaperMr.Saksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Solomon B QP - C2 Edexcel PDFDocument4 pagesSolomon B QP - C2 Edexcel PDFmangerahNo ratings yet
- Cce PR: - Moêfi) - Msê¿Document9 pagesCce PR: - Moêfi) - Msê¿AjithNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Millard Care Home PresentationDocument5 pagesMillard Care Home PresentationIndervir SinghNo ratings yet
- Internet AwarenessDocument3 pagesInternet AwarenessIndervir SinghNo ratings yet
- ComponentsDocument1 pageComponentsIndervir SinghNo ratings yet
- Economics OCR Microeconomics1 Workbook AnswersDocument44 pagesEconomics OCR Microeconomics1 Workbook AnswersIndervir SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesMechanics Exam QuestionsIndervir SinghNo ratings yet
- GCSE Geography Checklist For Jan MockDocument43 pagesGCSE Geography Checklist For Jan MockIndervir SinghNo ratings yet
- A Drill-Book in Trigonometry 1000172770 PDFDocument214 pagesA Drill-Book in Trigonometry 1000172770 PDFGautam Dutta100% (1)
- GCSE-Mathematics -504-Summer2022-Higher Tier, M7 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) -PaperDocument21 pagesGCSE-Mathematics -504-Summer2022-Higher Tier, M7 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) -Paperhifine8429No ratings yet
- SIM GeometryDocument11 pagesSIM GeometryJashey Dee83% (6)
- Startup Math Book 1 Solution of Selected QuestionsDocument20 pagesStartup Math Book 1 Solution of Selected QuestionsZoya Ashwaq Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Maths CGL 2019 Mains SpecialDocument54 pagesAdvanced Maths CGL 2019 Mains Specialdeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Igcse Paper 4h June 2014Document20 pagesIgcse Paper 4h June 2014Sanidu AbeywickramaNo ratings yet
- L7 Distance Measurement Nautical MileDocument9 pagesL7 Distance Measurement Nautical MileMoamen AbdienNo ratings yet
- Dec 2014 & Jan 2015 NCTM Calendar For StudentsDocument2 pagesDec 2014 & Jan 2015 NCTM Calendar For StudentsBLSantosch0% (1)
- 2014 Intermediate Relay Solutions (English) PDFDocument4 pages2014 Intermediate Relay Solutions (English) PDFalex jobogNo ratings yet
- School Geometry by Hall and Stevens PDFDocument296 pagesSchool Geometry by Hall and Stevens PDFAnonymous IwqK1Nl0% (1)
- 09 # ASSINGEMENT N Straight Line TOPS & TNPS StudentDocument14 pages09 # ASSINGEMENT N Straight Line TOPS & TNPS StudentParthMaluNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) Grade 8 - MathematicsDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheets (LAS) Grade 8 - MathematicsThe BeastNo ratings yet
- Circles and Cylinders Part 1Document6 pagesCircles and Cylinders Part 1shadowosNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Programacion Tema 01Document3 pagesEjercicios de Programacion Tema 01Sayed NúñezNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument9 pagesTrigonometrybenjoeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-3 Trigonometric Functions of AnglesDocument4 pagesLesson 4-3 Trigonometric Functions of AnglesCPK HKNo ratings yet
- Soalan Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Ting 1 Kertas 1Document11 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Ting 1 Kertas 1Cikgu Faizal100% (5)
- 2002 GR 0708Document4 pages2002 GR 0708Pei JingNo ratings yet
- Handbook of GeometryDocument82 pagesHandbook of GeometryHRCNo ratings yet
- SMOPS 2016 SolutionDocument13 pagesSMOPS 2016 SolutionMarilyn CitadelNo ratings yet
- GR 4 Unit 6 Extra PracticeDocument5 pagesGR 4 Unit 6 Extra PracticeAnnie NNo ratings yet
- Geometry!!!Document19 pagesGeometry!!!Jane AnonasNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocument17 pagesPlane and Solid GeometryAdc ClamorNo ratings yet
- American Math ProblemsDocument6 pagesAmerican Math ProblemsKumar MkNo ratings yet
- 1 3 1 1 3Document13 pages1 3 1 1 3Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- LAS 3rd Q Math 7Document59 pagesLAS 3rd Q Math 7Maryfrance FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Missing Data Sample ProblemDocument10 pagesMissing Data Sample ProblemKenn ValNo ratings yet
- Manim RelationsDocument1 pageManim RelationsnayNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Activity Sheet: Quarter 4 - MELC 5bDocument9 pagesMathematics Activity Sheet: Quarter 4 - MELC 5bPrilyn Sultan Alb100% (2)
- Math 7 - Quarter 3 - Module 5Document17 pagesMath 7 - Quarter 3 - Module 5arlyn.ferolinNo ratings yet