0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 views2 pagesA-Level Mechanics Homework Problems
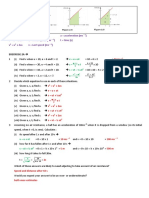
This document contains 5 mechanics problems involving SUVAT equations. Problem 1 involves calculating the velocity of a falling stone and explaining why it hits the water before a ping pong ball. Problem 2 involves drawing velocity-time and displacement-time graphs for a car that accelerates, travels at a steady speed, and then decelerates. Problem 3 involves drawing a velocity-time graph for a cyclist and car, with the car accelerating to catch up to the cyclist. Problem 4 involves calculating the time and height at which two balls colliding, one falling and one rising. Problem 5 involves calculating the time for an object with an initial velocity and acceleration to be caught by another object with an initial velocity in the opposite direction and
Uploaded by
Indervir SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 views2 pagesA-Level Mechanics Homework Problems
This document contains 5 mechanics problems involving SUVAT equations. Problem 1 involves calculating the velocity of a falling stone and explaining why it hits the water before a ping pong ball. Problem 2 involves drawing velocity-time and displacement-time graphs for a car that accelerates, travels at a steady speed, and then decelerates. Problem 3 involves drawing a velocity-time graph for a cyclist and car, with the car accelerating to catch up to the cyclist. Problem 4 involves calculating the time and height at which two balls colliding, one falling and one rising. Problem 5 involves calculating the time for an object with an initial velocity and acceleration to be caught by another object with an initial velocity in the opposite direction and
Uploaded by
Indervir SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd