Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 2 Struc Set 2 Watermark
Chap 2 Struc Set 2 Watermark
Uploaded by
Alvin Dang Zhi BinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 2 Struc Set 2 Watermark
Chap 2 Struc Set 2 Watermark
Uploaded by
Alvin Dang Zhi BinCopyright:
Available Formats
(d) Is the collision between the bullet and the wooden block elastic?
3 Figure shows a cart of mass
PUSAT TUISYEN ALPHA DINAMIK Use relevant figures to prove your answer. 30 kg travelling at a velocity of
4 m s-1 along a straight line.
Form 4 Revision S2B Prepared by Alfred Lim
An impulse of 90 N s is
supplied to the cart in the direction of motion of the cart.
1 Figure shows a bullet
of 20 g mass being (a) What is the change in (c) What is the final velocity
fired from a pistol. The (e) What would be the (f) What is the frictional force that momentum of the cart? of the cart?
bullet, travelling with a acceleration of the bullet if it stops the bullet in the wooden
velocity of 200 m s-1, enters the wooden block block?
strike a wooden target in 0.2 s?
of 0.48 kg mass and
is embedded in it.
(a) (i) What happens to the pistol when the bullet is fired?
Explain how it can happen.
(b) What is the final momentum
of the cart?
2 Figure shows a man
standing on a stationary
trolley. He then jumps
out of the trolley onto
a platform.
(ii) Name the principle involved. (a) State the physics principle that is involved in the movement of
the trolley as the man jumps on to platform.
4 A car of total mass 900 kg travelling at 20 m s-1 collides with a truck
of mass 1500 kg which is initially at rest. The car stuck to the
truck after the collision and they move together
(b) Explain why the trolley moves away from the platform as the
(b) Before the bullet strikes the wooden block, calculate: man jumps. (a) Determine the velocity of (c) If the collision time is 0.75 s,
(i) the momentum of the (ii) the kinetic energy of the bullet. the combined vehicles calculate the impulsive force
bullet. after the collision. on the car during the collision.
(c) The mass of the man is 60 kg
and he jumps at a velocity of
(c) After the bullet is embedded inside the wooden block, calculate: 3 m s-1. The mass of the trolley
(i) the common velocity of (ii) the kinetic energy of the bullet is 20 kg. Calculate the velocity
the bullet and the and the wooden block. of the trolley as the man jumps. (b) Determine the impulse
wooden block to the truck during the
(d) Name one application of the physics principle stated in (a) in collision.
an exploration of outer space.
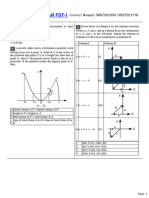
5 Figure (a) shows a feather and 6 In one of the activities at the National Service Camp, a participant of 7 Figure shows how the speed
a small plasticine ball are 55 kg is to climb up 2.5 m wall from ground level and jump down as of a car varied from the time
released from the same height. shown in the figure. driver saw an obstacle on the
The mass of the feather and (b) Based on the jump of the road to the time the car stopped.
plasticine ball are the same. participant, calculate (i) How long does it take the
The velocity-time graph for the two object are shown in figure below i. the speed of the participant driver to begin applying the
just before his legs touch brakes after seeing the
the ground. obstacle?
(a) (i) What is the potential
energy of the participant (ii) What is the time taken for the car to stop
before the jump? while the brakes were being applied?
(iii) Determine the retardation (iv) Calculate the total distance
(a) Name two forces acting on the the change in momentum of the of the car. travelled by car
feather and the plasticine ball. participant at this moment.
(b) Using figure (a), compare the surface area of the feather and
the plasticine ball.
ii. Calculate the power of
the participant if he
climb up the wall in 8 A customer pushes a 15 kg shopping cart,accelerating it from
(c) Using the graph in figure (b), compare the changes in the 14 seconds. rest to a speed of about 5m s-1 in 2 s.
velocity of the feather and the plasticine ball. iii. the impulse of the force a) Find the force exerted by b) How far does it move in 2 s?
on the participant if the the customer on the cart.
time of action between
his legs and the ground
is 0.03 seconds.
(d) Using your answers in (b) and (c), state the relationship
between the surface area and the final velocity. (c) i. The participant bends his
legs when he reaches the 9 Aaron receives a ball of mass 0.2 kg, decelerating from an
ground and stops in 0.08s. initial speed of 90 km/h to a stop in 0.5 m.
Determine the impulse of a) What force does the ball exert on him?
the force acting on the participant.
(e) The feather and the
plasticine ball are now ii. Why do long jump athletes bend their knees on landing on
dropped in a vacuum. the sand pit?
Sketch a velocity-time
graph in graph to show
the motion of both objects.
You might also like
- Resnick & Halliday Part - 1Document737 pagesResnick & Halliday Part - 1Debarun Patra80% (5)
- Laws of Motion Advanced Level Problems For IIT-JEEDocument5 pagesLaws of Motion Advanced Level Problems For IIT-JEEEr. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)89% (9)
- TEST-07 (Impulse and Momentum)Document2 pagesTEST-07 (Impulse and Momentum)abdullah naseerNo ratings yet
- AC DrivesDocument120 pagesAC DrivesVenkata GanesanNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PROBLEM SET 1 Work, Power, and EnergyDocument5 pagesPROBLEM SET 1 Work, Power, and EnergyHan HanNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics Motion Past Paper Solutions Cheat SheetDocument23 pagesCsec Physics Motion Past Paper Solutions Cheat Sheetchelsea Alexandria100% (1)
- DC MotorsDocument31 pagesDC MotorsRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic GuideDocument884 pagesMnemonic GuideDaniloNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics-AeroEngineering-MODULE NO. 3Document33 pagesAerodynamics-AeroEngineering-MODULE NO. 3GADDI Noel Jr. N.100% (1)
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsDocument43 pagesCh1 - Steam Power PlantsShiau Fen100% (1)
- Gravitational Mass Carried by Sound WavesDocument6 pagesGravitational Mass Carried by Sound WavesJohnNo ratings yet
- New Study On Earth RodsDocument7 pagesNew Study On Earth RodsVineeth BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.3 Motion Along A Straight LineDocument83 pages3.4.1.3 Motion Along A Straight Linestudent.riya.palsinghNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Lakhmir SinghDocument4 pagesCH 2 Lakhmir SinghYashika SinghNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Pelan Taktikal Bahasa ArabDocument8 pagesDokumen - Tips Pelan Taktikal Bahasa ArabRadziah MohamedNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56Document2 pagesCH 3 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56rb8q9sz8hrNo ratings yet
- Forces, Movement, Shape and Momentum 1 QPDocument14 pagesForces, Movement, Shape and Momentum 1 QPJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Momentum & Turning Effects of ForcesDocument10 pagesMomentum & Turning Effects of ForcesSuperBrainy SuperkidsNo ratings yet
- S.3Physics Revision Exercise (24 JUNE 2020) : Assume Where Necessary Acceleration Due To Gravity, G 10ms 1. 2Document3 pagesS.3Physics Revision Exercise (24 JUNE 2020) : Assume Where Necessary Acceleration Due To Gravity, G 10ms 1. 2jerome jeromeNo ratings yet
- Take Home Assig-Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesTake Home Assig-Wps OfficeMakame AliNo ratings yet
- G Be The Gravitational Constant and M: EarthDocument2 pagesG Be The Gravitational Constant and M: EarthHAFEELNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CH9Document4 pagesTutorial CH9WinxTynix 8000No ratings yet
- FLMDocument1 pageFLMTanishq AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Questions Newton's Law of MotionDocument2 pagesQuestions Newton's Law of MotionHrishikesh BhatNo ratings yet
- Hookes Work EnergyDocument4 pagesHookes Work EnergykatieNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion QuestionDocument4 pagesLaws of Motion QuestionJoyabrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam Style 1 PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Exam Style 1 PDFMd Eizhan Shafiz SofianNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems Involving Resultant Force, Mass and Acceleration of An ObjectDocument2 pagesSolving Problems Involving Resultant Force, Mass and Acceleration of An ObjectShirlyn HeeNo ratings yet
- Booklet Momentum BWFDocument22 pagesBooklet Momentum BWFReem AshrafNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion Udaan DPP: A A A A A+ A A A A+ A ADocument33 pagesLaw of Motion Udaan DPP: A A A A A+ A A A A+ A Asona babuNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer The Following Questions by Groups of 3, On Long Bond PaperDocument2 pagesInstruction: Answer The Following Questions by Groups of 3, On Long Bond PaperDember PaulNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Work, Energy, Power & Efficiency Ms As Shown in The Figure BelowDocument1 page2.10 Work, Energy, Power & Efficiency Ms As Shown in The Figure BelowBid HassanNo ratings yet
- Newtonlaw Past PapersDocument5 pagesNewtonlaw Past PapersThisandara JayasenaNo ratings yet
- Problema Ligjet e NjutonitDocument9 pagesProblema Ligjet e NjutonitMentor KushoNo ratings yet
- M1 Monthly Test 1Document4 pagesM1 Monthly Test 1Kevin RayNo ratings yet
- Exemplar FST-1Document10 pagesExemplar FST-1susankmadiNo ratings yet
- Work To Momentum (Pear) Set 1 (Answer)Document8 pagesWork To Momentum (Pear) Set 1 (Answer)6C09 FUNG CHI LAMNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document1 pageWa0000.Kaushik MohantaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2.2Document2 pagesTutorial 2.2nixleonNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56Document2 pagesCH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56rb8q9sz8hrNo ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument3 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Work Energy Power and MachineDocument28 pages3.3 Work Energy Power and MachineGladys KNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 ForcesDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 Forcesapi-382735450% (4)
- Impulse and Momentum WS 2Document5 pagesImpulse and Momentum WS 2etbhrdyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2.2 ForcesDocument4 pagesAssignment 2.2 Forcespanghua tanNo ratings yet
- Race # 01 Newton's Laws of Motion PhysicsDocument21 pagesRace # 01 Newton's Laws of Motion PhysicsAayushman Sahu BroanyXNo ratings yet
- Momentum Assignment Class 9Document4 pagesMomentum Assignment Class 9Apex Institute0% (1)
- 02 Momentum & Energy Extra Study QuestionsDocument141 pages02 Momentum & Energy Extra Study QuestionsTheBigbrains Aceo50% (2)
- S.6 Physics Trial Questions: Figure 6.23)Document6 pagesS.6 Physics Trial Questions: Figure 6.23)Mubiru IvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Momentum and ImpulseDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Momentum and ImpulsePriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- G11 ASSIGNMENT Law of MotionDocument1 pageG11 ASSIGNMENT Law of MotionDeepti PrarupNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Collisions Explosions ImpulseDocument6 pages1.3 Collisions Explosions ImpulseOliver AbakahNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Force and Law of Motion - TestDocument2 pagesClass 9 Force and Law of Motion - TestGaurav SethiNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document157 pagesChap 5Keerthana CheboluNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- NTSE Question Bank: ForceDocument4 pagesNTSE Question Bank: ForceAnonymous G5MnzqM2WvNo ratings yet
- Physics Y11 Term 1 - Revision BookletDocument7 pagesPhysics Y11 Term 1 - Revision BookletVictor MartinezNo ratings yet
- 05 - Laws of MotionDocument3 pages05 - Laws of MotionMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4Ryan KoNo ratings yet
- 06 - Work Power Energyfor ScribdDocument3 pages06 - Work Power Energyfor ScribdvikasNo ratings yet
- PH600 CH 9 Problems PDFDocument3 pagesPH600 CH 9 Problems PDFMike GaoNo ratings yet
- Superb Academy: (A) Kinetic EnergyDocument5 pagesSuperb Academy: (A) Kinetic EnergyKamran AliNo ratings yet
- 06 - Work Energy and PowerDocument5 pages06 - Work Energy and PowerMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument8 pagesQuestionHimanshuTripathiNo ratings yet
- 3 4 1 8-Conservation-Of-EnergyDocument90 pages3 4 1 8-Conservation-Of-EnergyIts AxstroZzz-No ratings yet
- Transition MetalDocument17 pagesTransition MetalAlvin Dang Zhi BinNo ratings yet
- Definition2022 WatermarkDocument1 pageDefinition2022 WatermarkAlvin Dang Zhi BinNo ratings yet
- 2022-04-15 22-40Document9 pages2022-04-15 22-40Alvin Dang Zhi BinNo ratings yet
- Revision For Gravity WatermarkDocument5 pagesRevision For Gravity WatermarkAlvin Dang Zhi BinNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Coulomb's Law Sample ProblemsDocument7 pages7.2 Coulomb's Law Sample ProblemsMeeriya NewtonNo ratings yet
- Analisis Sistem Tenaga Listrik (C11041409)Document51 pagesAnalisis Sistem Tenaga Listrik (C11041409)moenica cabrinyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery ProblemsDocument37 pagesFluid Machinery Problemskimlouie petateNo ratings yet
- Unisonic Technologies Co., LTD: 14.7A, 100V (D-S) N-CHANNEL Power MosfetDocument5 pagesUnisonic Technologies Co., LTD: 14.7A, 100V (D-S) N-CHANNEL Power MosfetEnrique LandraNo ratings yet
- Service Manual U CROWNDocument136 pagesService Manual U CROWNopodecanoNo ratings yet
- SR-DH Series: Intelligent Wireless LED Dimming Type All-In-One Constant Current Solar Street Light ControllerDocument4 pagesSR-DH Series: Intelligent Wireless LED Dimming Type All-In-One Constant Current Solar Street Light ControllerAgus Hadi WijayaNo ratings yet
- TWH N Torque Pressure Conversion ChartS PDF273201694527Document10 pagesTWH N Torque Pressure Conversion ChartS PDF273201694527Ciprian BalcanNo ratings yet
- Partineh 57hsxxd HQMDocument4 pagesPartineh 57hsxxd HQMMelihcan ÇiltaşNo ratings yet
- ZS4VSD - A1: Performance at Operating PointDocument5 pagesZS4VSD - A1: Performance at Operating PointMarllon Boamorte LobatoNo ratings yet
- Schema Cemont125-130A PDFDocument10 pagesSchema Cemont125-130A PDFIron MaskNo ratings yet
- Understanding Parallel Generation Net Metering Pilot BillDocument1 pageUnderstanding Parallel Generation Net Metering Pilot BillJoseph BeitelspacherNo ratings yet
- FE1073-C1 Resultants and Equilibrium of Forces - May 2014 PDFDocument13 pagesFE1073-C1 Resultants and Equilibrium of Forces - May 2014 PDFDicky DjayadiNo ratings yet
- NFM1 PDFDocument2 pagesNFM1 PDFCristian MarchisNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DiodesDocument22 pagesPower Semiconductor Diodesazkasheikh19No ratings yet
- Tesys Essential GuideDocument54 pagesTesys Essential Guidewidy133No ratings yet
- Martini L1 IntroductionDocument12 pagesMartini L1 IntroductionphdcaoNo ratings yet
- BC 9080Document2 pagesBC 9080Naresh Ch MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Kvar Required: For Distribution / Industrial NetworksDocument3 pagesCalculation of Kvar Required: For Distribution / Industrial NetworksShah Raj100% (1)
- Analysis of 3D Stall Models For Wind Turbine Blades Using Data From The MEXICO ExperimentDocument8 pagesAnalysis of 3D Stall Models For Wind Turbine Blades Using Data From The MEXICO ExperimentSrinivas GunturNo ratings yet
- Fluid PropertiesDocument37 pagesFluid PropertiesdeusleanNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2PoonthalirNo ratings yet
- C100 CatalogDocument20 pagesC100 CatalogMarcela RoneNo ratings yet