Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ans To wb3
Uploaded by
zitingxia60Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ans To wb3
Uploaded by
zitingxia60Copyright:
Available Formats
bbcbd badad cbccd bdbca addca
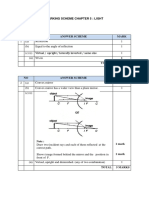
Question Answer Marks
4(a)(i) (Molecules) vibrate 1
4(a)(ii) random/haphazard/in all directions 1
Any one of: 1
with high speed
freely
zig-zag
in straight lines
4(b) (Molecules) collide with walls (of box) OR (Molecules) rebound from walls (of box) 1
Change of momentum (occurs) 1
force (on walls) = (total) change of momentum per second 1
Pressure = (total) force ÷ (total) area (of walls) 1
© UCLES 2018 Page 5 of 9
0625/41 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
5(a)(i) Refraction OR reflection 1
5(a)(ii) If refraction in (i) 1
Change or increase or decrease in speed of wave OR change of refractive index OR
If reflection in (i) (1)
Mention of surface or boundary
5(b)(i) 2 points both labelled F at 3.5 cm either side of optical centre of lens 1
5(b)(ii) Any two of: 2
Paraxial ray from tip of O refracted through farther F/3.5 cm
Undeviated ray from tip of O through optical centre of lens
Ray from tip of O through nearer F refracted paraxially
Image/I drawn from intersection of rays to principal axis with indication that image is inverted 1
5(b)(iii) In range 3.6 to 4.1 cm 1
5(b)(iv) (Image is) real and light passes through it OR can be projected/seen on a screen OR refracted rays cross/meet 1
© UCLES 2018 Page 6 of 9
0625/41 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
6(a)(i) At least 3 circular wavefronts centred on gap extending to at least half of semicircle 1
Same spacing as incident wavefronts 1
6(a)(ii) At least 3 straight, parallel, wavefronts, approximately same length as width of gap 1
Ends of straight lines curving towards but not reaching barrier 1
6(b) Any four of: 4
Diagram to show: labelled barrier, incident straight or curved waves
Diagram shows appropriately reflected waves
Water surface e.g. tank of water/ripple tank/pond/acceptable alternative
How waves are produced: e.g., moving end or length of solid rod dipping into surface OR small solid object thrown in.
Detail of barrier: made of metal, glass or wood fixed in position
How observed: by eye, video, film, stroboscope
Question Answer Marks
7(a) (Metals) contain free/mobile electrons/delocalised electrons 1
7(b)(i) R α L and R α 1 ÷ A OR R α L ÷ A OR R = 16 × ½ ÷ 2 OR R = 16 ÷ 4 1
4.0 Ω 1
7(b)(ii) 1 ÷ R = (1 ÷ R1) + (1 ÷ R2) OR R = (R1 × R2) ÷ (R1 + R2) OR (1 ÷ R) = (1 ÷ 4) + (1 ÷ 16) OR (4 × 16) ÷ (4 + 16) 1
3.2 Ω 1
7(c)(i) 3E or 3 × E 1
7(c)(ii) IB > I2 > I1 (6th box ticked) 1
© UCLES 2018 Page 7 of 9
0625/41 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
8(a) (Q =) mc∆θ OR 200 × 4.2 × 22 1
18000 J 1
8(b) Q = m × L OR (L =) Q ÷ m OR 18 480 ÷ 60 1
310 J / g 1
8(c) (Thermal) energy/heat transfers from surroundings OR into water 1
Question Answer Marks
9(a) Would not be effective OR No 1
With current on OR the (alternating) current should not be switched off 1
Magnet should be withdrawn from the coil 1
OR Magnet would be alternately magnetised in different directions (1)
Would remain magnetised in the direction occurring at the moment of switching off (1)
9(b)(i) Coil turns 1
Clockwise/continuously 1
Current (in coil) reverses every half turn/when coil is in vertical position OR force on current in a magnetic field 1
9(b)(ii) 1 × (4 × T) 1
2 × (2 × T) 1
3 × (T ÷ 2) 1
© UCLES 2018 Page 8 of 9
0625/41 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
10(a) To produce an alternating/changing magnetic field 1
so that current/voltage is induced (continuously) in the secondary coil OR secondary circuit 1
10(b)(i) Ns ÷ Np = Vs ÷ Vp in any form OR (Ns =) Np × Vs ÷ Vp OR 8000 × 6 ÷ 240 1
200 1
10(b)(ii) IpVp = IsVs in any form OR (Ip =) Is × Vs ÷ Vp OR 2.0 × 6 ÷ 240 1
0.050 A 1
10(b)(iii) (Number of lamps =) 2 ÷ 0.05 = 40 1
Question Answer Marks
11(a) Number of protons = 86 and number of electrons = 86 1
Number of neutrons = 136 1
11(b) 218 1
84 Po
4 1
+2 α
11(c) 7.6 days = 2 half-lives or evidence of two halvings 1
(number of Rn atoms left = 6.4 × 106 ÷ 4 =) 1.6 × 106 1
number of α-particles emitted = (6.4 × 106 – 1.6 × 106 =) 4.8 × 106 1
© UCLES 2018 Page 9 of 9
0625/61 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
2(a)(i) EITHER V1 = 2.2 OR I = 0.46 correct 1
Both values correct and correct units V and A 1
2(a)(ii) R1 = 4.78 (Ω) (allow ecf from 2(a)(i)) 1
2(b) Statement matches readings (Expect YES) 1
Expect justification to include the idea of within the limits of experimental accuracy (but accept beyond limits, if ecf allowed for 1
statement matching readings)
2(c) R = 14.3 OR 14.4; 2 or 3 significant figures required 1
Unit Ω 1
2(d) 3V1 1
2(e) 3 resistors in parallel 1
Correct variable resistor symbol 1
Voltmeter symbol correct and circuit correct 1
© UCLES 2018 Page 5 of 7
0625/61 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
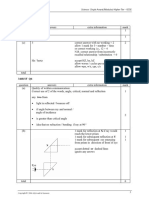
3(a) uv values 1065, 1128, 1200, 1283, 1353 1
3(b) Graph: 1
(all marks are still available if uv values are wrong)
Axes correctly labelled and right way round
Suitable scales 1
All plots correct to ½ small square 1
Good line judgement, thin, continuous line 1
3(c) Triangle method clearly shown on graph 1
Triangle using at least half of candidate’s line 1
3(d) G in range 14.0 to 16.0 1
f = G to 2 or 3 significant figures 1
3(e) Any two from: 2
Finding exact position that gives clearest image
Measuring to centre of lens
Room too bright/lamp too dim/image too faint
© UCLES 2018 Page 6 of 7
0625/61 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
4 Method to include: 1
(Hot) water in copper can, time taken for temperature to drop
Correct use of at least 3 larger outer containers, separately 1
Some indication that size of air gap is measured 1
Any two from: 2
Use of something to cover air gap
Use of lid on copper can
Same starting temperature
Same room temperature
Same volume of hot water
Use of ‘control’ with no outer container
Inner container standing on an insulator
Uniform air gap all round
Table with clear columns for temperature and/or time (to match method) and air-gap, with appropriate units 1
Conclusion: Least temperature drop OR longest time for temperature to drop shows lowest cooling rate OR best insulation 1
OR plot temperature against time and least gradient shows lowest cooling rate (ora)
© UCLES 2018 Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Lectures on Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandLectures on Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Modulation, Resolution and Signal Processing in Radar, Sonar and Related Systems: International Series of Monographs in Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandModulation, Resolution and Signal Processing in Radar, Sonar and Related Systems: International Series of Monographs in Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Testpapaer Neet - 2017 Ray & Wave Optics, Modern Physics, Electronics & Semiconductor DevicesDocument4 pagesTestpapaer Neet - 2017 Ray & Wave Optics, Modern Physics, Electronics & Semiconductor Devicesumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Document8 pagesPeperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Lee Li JieNo ratings yet
- Mka2 Ap2 FZ t5 PHG 2016Document8 pagesMka2 Ap2 FZ t5 PHG 2016renuNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik K2 Trial SPM Selangor 2019Document8 pagesSkema Fizik K2 Trial SPM Selangor 2019Nikki KimiNo ratings yet
- 4531-Skema2 FIZ Trial SPM 2015Document9 pages4531-Skema2 FIZ Trial SPM 2015Rmlyzan YahayaNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Nov1999 PhysicsDocument4 pagesPaper 2 Nov1999 Physicssolarixe100% (1)
- Ms Chem Xii PB 2020 SiDocument7 pagesMs Chem Xii PB 2020 SiRupsa MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersDocument14 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersChinWynn.com80% (5)
- Answer Scheme Module Waves 2019Document8 pagesAnswer Scheme Module Waves 2019Cart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Skema Permarkahan Kertas 3 No. 1 Answer MarkDocument5 pagesSkema Permarkahan Kertas 3 No. 1 Answer MarkHajar Aja NurNo ratings yet
- JOHORSkema P3 Trial 2008Document5 pagesJOHORSkema P3 Trial 2008toowex100% (2)
- Marking Scheme Chapter 5: Light: StructureDocument9 pagesMarking Scheme Chapter 5: Light: StructureCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Perak-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2007Document16 pagesPerak-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Trial SBP 2010 March - Marking SchemeDocument14 pagesSPM Physics Trial SBP 2010 March - Marking SchemeYudhisthiraNo ratings yet
- KS3 Physics Baseline Test - Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesKS3 Physics Baseline Test - Mark Schemefadua barakatNo ratings yet
- Physics Answer N9 08Document15 pagesPhysics Answer N9 08Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (3)
- Jawapan Latih Tubi Fizik k2Document3 pagesJawapan Latih Tubi Fizik k2ahsohaNo ratings yet
- Physics Ans SBP Trial 2008 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document14 pagesPhysics Ans SBP Trial 2008 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)NUR AQILAH AUNI BINTI SUHAIMI MoeNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Physics Paper 2 Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesSPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Physics Paper 2 Marking SchemeChinWynn.com100% (2)
- Published Answer Marks 1 1 1 1 1 1 OR D M ÷ V 4.8 ÷ (0.12Document1 pagePublished Answer Marks 1 1 1 1 1 1 OR D M ÷ V 4.8 ÷ (0.12Sanjeev NNo ratings yet
- 2020 Melaka Physics K2 JawapanDocument16 pages2020 Melaka Physics K2 JawapanLincoln LawNo ratings yet
- (A) (I) Random Distribution of Circles in The Box With at Least 50 % ofDocument7 pages(A) (I) Random Distribution of Circles in The Box With at Least 50 % ofRosy D'souzaNo ratings yet
- SPM Phy Ans (Kelantan)Document15 pagesSPM Phy Ans (Kelantan)SimPor100% (1)
- Waves - Behaviour - Test (36 Marks) Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesWaves - Behaviour - Test (36 Marks) Mark SchemeReginald SSLC Mathematics Video LecturesNo ratings yet
- Light 2 MSDocument4 pagesLight 2 MSahmedNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesMark SchemeDua LatifNo ratings yet
- Science 2023-24 MSDocument7 pagesScience 2023-24 MSIndrajit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Physics Waves in Communication May 2019 MSDocument11 pagesUnit 1 Physics Waves in Communication May 2019 MSDanushke KarunarathneNo ratings yet
- Ans Phy P2 Terengganu SPM 2009Document8 pagesAns Phy P2 Terengganu SPM 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (1)
- 0652 w06 Ms 3Document5 pages0652 w06 Ms 3rilangoNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2016Document16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2016Hollow WeenNo ratings yet
- Ece, Ee, Bme Ph201 Physics - I r18Document5 pagesEce, Ee, Bme Ph201 Physics - I r18dsreNo ratings yet
- January 2016 MS - Paper 1P Edexcel Physics IGCSEDocument16 pagesJanuary 2016 MS - Paper 1P Edexcel Physics IGCSEZ JazzNo ratings yet
- Kedah Fizik Modul 1 T5 P2 2014 SkemaDocument5 pagesKedah Fizik Modul 1 T5 P2 2014 SkemaHelmi TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On WebsiteDocument4 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On WebsiteHrinmoy HusiyarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science April25 Marking Scheme 2023 24Document7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science April25 Marking Scheme 2023 24NAVEEN GOLHANINo ratings yet
- 4PH0 - 1P - MSC - 20160302 (1) 2 PDFDocument16 pages4PH0 - 1P - MSC - 20160302 (1) 2 PDFsumaiya shahidNo ratings yet
- Selangor-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007Document7 pagesSelangor-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Orthogonal Polynomials. (AM-164): Asymptotics and Applications (AM-164)From EverandDiscrete Orthogonal Polynomials. (AM-164): Asymptotics and Applications (AM-164)No ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth Metabolism in Adult Man: A Report Prepared by a Task Group of Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiological ProtectionFrom EverandAlkaline Earth Metabolism in Adult Man: A Report Prepared by a Task Group of Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiological ProtectionNo ratings yet
- Binary Digital Image Processing: A Discrete ApproachFrom EverandBinary Digital Image Processing: A Discrete ApproachNo ratings yet
- Seeing the Light: Optics in Nature, Photography, Color, Vision, and Holography (Updated Edition)From EverandSeeing the Light: Optics in Nature, Photography, Color, Vision, and Holography (Updated Edition)No ratings yet
- The Study of Metal Structures and Their Mechanical Properties: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesFrom EverandThe Study of Metal Structures and Their Mechanical Properties: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Probability and StatisticsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Probability and StatisticsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Renormalization and 3-Manifolds Which Fiber over the Circle (AM-142), Volume 142From EverandRenormalization and 3-Manifolds Which Fiber over the Circle (AM-142), Volume 142No ratings yet
- Theory of Experiments in Paramagnetic Resonance: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandTheory of Experiments in Paramagnetic Resonance: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyNo ratings yet
- Distributions and Their Applications in Physics: International Series in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandDistributions and Their Applications in Physics: International Series in Natural PhilosophyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing from the Beginning: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandEngineering Drawing from the Beginning: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Multiple Light Scattering: Tables, Formulas, and ApplicationsFrom EverandMultiple Light Scattering: Tables, Formulas, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry and Its ApplicationsFrom EverandQuadrupole Mass Spectrometry and Its ApplicationsPeter H. DawsonNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory of the Solid State: Volume 2From EverandQuantum Theory of the Solid State: Volume 2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Relative Clause PracticeDocument1 pageRelative Clause Practicezitingxia60No ratings yet
- ESL Worksheet 2Document2 pagesESL Worksheet 2zitingxia60No ratings yet
- from the late 20th century digital technology has both created new jobs and has changed the way we work it continues to do so the demand for app developers has increased since the arrival of smartphonesDocument2 pagesfrom the late 20th century digital technology has both created new jobs and has changed the way we work it continues to do so the demand for app developers has increased since the arrival of smartphoneszitingxia60No ratings yet
- A Speech From MalalaDocument4 pagesA Speech From Malalazitingxia60No ratings yet
- G10 Physics CompendiumDocument41 pagesG10 Physics CompendiumJhin CortezNo ratings yet
- Lecture-34-35-Wave Guide and Radiation PDFDocument19 pagesLecture-34-35-Wave Guide and Radiation PDFAMAL. A ANo ratings yet
- 45 700 ManualDocument68 pages45 700 ManualZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 1,2,3 ProblemsDocument25 pages1,2,3 ProblemsWild BotNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Astronomy and AstrophysicsDocument5,306 pagesEncyclopedia of Astronomy and AstrophysicsJohnnieKyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Water Waves: Selected Papers o F Michael Longuet-HigginsDocument940 pagesDynamics of Water Waves: Selected Papers o F Michael Longuet-Higginsmfgobbi4515No ratings yet
- Opt Comn 2 Mark Ques With AnswersDocument5 pagesOpt Comn 2 Mark Ques With Answersprinceram123No ratings yet
- Radiation Pollution: A Case Study and Concluding ReportDocument10 pagesRadiation Pollution: A Case Study and Concluding ReportSwastik AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Principles of LightDocument14 pagesPrinciples of LightStuti ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Solar Simulator ReportDocument9 pagesSolar Simulator ReportAditi Khandelwal100% (1)
- Propagation of LightDocument16 pagesPropagation of LightCiara ManangoNo ratings yet
- RD Handbook PDFDocument48 pagesRD Handbook PDFManuelNo ratings yet
- Application To Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (Aerb) For Safety Status ReportDocument4 pagesApplication To Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (Aerb) For Safety Status ReportFundary ShopNo ratings yet
- Forced VibrationDocument9 pagesForced VibrationPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Fletcher Auditory PatternsDocument20 pagesFletcher Auditory Patternsantibombe100% (1)
- Combined - Physics AssignmentDocument25 pagesCombined - Physics Assignment387 OORJA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Synoptic Meteorology-IMTC PDFDocument80 pagesSynoptic Meteorology-IMTC PDFRadison sierraNo ratings yet
- Topic QuestionDocument119 pagesTopic QuestionMazen Yasser100% (2)
- Refraction of LightDocument12 pagesRefraction of LightLiza Nova DewiNo ratings yet
- Reynolds AnalogyDocument1 pageReynolds AnalogymojexNo ratings yet
- Blade Element Momentum TheoryDocument11 pagesBlade Element Momentum TheoryAnonymous qRe192No ratings yet
- SCRAPBOOKDocument37 pagesSCRAPBOOKHaru YuutoNo ratings yet
- The Design and Simulation of An S-Band Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna ArrayDocument5 pagesThe Design and Simulation of An S-Band Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna ArrayNgoc MinhNo ratings yet
- Science 3sses q3 Week 3 25revised 1Document25 pagesScience 3sses q3 Week 3 25revised 1Noah James C. EsparagozaNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2 - Intro To Lumerical and DVD Tutorial, Cont'dDocument42 pagesDiscussion 2 - Intro To Lumerical and DVD Tutorial, Cont'dBích Đỗ DanhNo ratings yet
- NLO PresentationDocument12 pagesNLO PresentationTahreem TahirNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Poster BrochureDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Poster Brochureapi-503006368No ratings yet
- Performance Measurements On A Thermoacoustic Refrigerator Driven at High AmplitudesDocument7 pagesPerformance Measurements On A Thermoacoustic Refrigerator Driven at High AmplitudessaekNo ratings yet
- JHKJHKJDocument20 pagesJHKJHKJShayanNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Week 1Document2 pagesSummative Test Week 1Lelanie PalomarNo ratings yet