Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics - Point and Straight Line
Uploaded by
mangeshchavan980Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics - Point and Straight Line
Uploaded by
mangeshchavan980Copyright:
Available Formats
JEE-Main (Previous Year Questions)
1. Let a, b, c and d be non-zero numbers. If the point of intersection of the lines 4ax + 2ay + c =0
and 5bx + 2by + d = 0 lies in the fourth quadrant and is equidistant from the two axes then:
[JEE(Main)-2014]
(1) 2bc 3ad = 0 (2) 2bc + 3ad = 0 (3) 3bc 2ad = 0 (4) 3bc + 2ad = 0
2. Let PS be the median of the triangle with vertices P (2, 2), Q (6, 1) and R (7, 3). The equation
of the line passing through (1, 1) and parallel to PS is: [JEE(Main)-2014]
(1) 4x 7y 11 = 0 (2) 2x + 9y + 7 = 0 (3) 4x + 7y + 3 = 0 (4) 2x 9y 11 = 0
3. Locus of the image of the point (2, 3) in the line (2x 3y + 4) + k (x 2y + 3) = 0, k R, is a
[JEE(Main)-2015]
3a a 3a a
(1) circle of radius ,− (2) circle of radius − ,−
2 2 2 2
(3) straight line parallel to x-axis (4) straight line parallel to y-axis
4. Two sides of a rhombus are along the lines, x y + 1 = 0 and 7x y 5 = 0. If its diagonals
intersect at ( 1, 2), then which one of the following is a vertex of this rhombus?
[JEE(Main)-2016]
2
(1) 3 (2) ( 3, 9) (3) ( 3, 8) (4)
5 5
5. Let k be an integer such that triangle with vertices (k, 3k), (5, k) and ( k, 2) has area 28 sq.
units. Then the orthocentre of this triangle is at the point : [JEE(Main)-2017]
1− 7 3 1− 3 1+ 7 3 1+ 3 1 − 14 3 1 − 2 3 1 + 14 3 1 + 2 3
(1) , (2) , (3) , (4) ,
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
6. Let the orthocentre and centroid of a triangle be A( 3, 5) and B(3, 3) respectively. If C is the
circumcentre of this triangle, then the radius of the circle having line segment AC as diameter,
is: [JEE(Main)-2018]
3 5 5
(1) (2) 10 (3) 2 10 (4) 3
2 2
7. A straight line through a fixed point (2, 3) intersects the coordinate axes at distinct points
P and Q. If O is the origin and the rectangle OPRQ is completed, then the locus of R is:
[JEE(Main)-2018]
(1) 3x + 2y = 6xy (2) 3x + 2y = 6 (3) 2x + 3y = xy (4) 3x + 2y = xy
Point and Straight Line 47
8. Consider the set of all lines px + qy + r = 0 such that 3p + 2q + 4r = 0. Which one of the following
statements is true? [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) The lines are all parallel (2) Each line passes through the origin
3 1
(3) The lines are not concurrent (4) The lines are concurrent at the point ,
4 2
9. Let the equations of two sides of a triangle be 3x 2y + 6 = 0 and 4x + 5y 20 = 0. If the
orthocentre of this triangle is at (1,1), then the equation of its third side is : [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) 26x + 61y + 1675 = 0 (2) 26x 122y 1675 = 0
(3) 122x + 26y + 1675 = 0 (4) 122x 26y 1675 = 0
10. A point P moves on the line 2x 3y + 4 = 0. If Q(1, 4) and R(3, 2) are fixed points, then the
locus of the centroid of PQR is a line: [JEE(Main)-2019]
2 3
(1) parallel to x-axis (2) parallel to y-axis (3) with slope (4) with slope
3 2
11. If the line 3x + 4y 24 = 0 intersects the x-axis at the point A and the y-axis at the point B,
then the incentre of the triangle OAB, where O is the origin, is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) (4, 4) (2) (2, 2) (3) (4, 3) (4) (3, 4)
12. Two sides of a parallelogram are along the lines, x + y = 3 and x y + 3 = 0. If its diagonals
intersect at (2, 4), then one of its vertex is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) (2, 6) (2) (3, 5) (3) (2, 1) (4) (3, 6)
13. Two vertices of a triangle are (0, 2) and (4, 3). If its orthocentre is at the origin, then its third
vertex lies in which quadrant? [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) first (2) second (3) third (4) fourth
14. If in a parallelogram ABDC, the coordinates of A, B and C are respectively (1, 2), (3, 4) and
(2, 5), then the equation of the diagonal AD is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) 3x 5y + 7 = 0 (2) 5x 3y + 1 = 0
(3) 3x + 5y 13 = 0 (4) 5x + 3y 11 = 0
15. If the straight line, 2x 3y + 17 = 0 is perpendicular to the line passing through the points
(7, 17) and (15, ), then equals: [JEE(Main)-2019]
35 35
(1) − (2) 5 (3) (4) 5
3 3
16. If a straight line passing through the point P( 3, 4) is such that its intercepted portion between
the coordinate axes is bisected at P, then its equation is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) x y+7=0 (2) 4x 3y + 24 = 0
(3) 4x + 3y = 0 (4) 3x 4y + 25 = 0
48 Point and Straight Line
17. A point on the straight line, 3x + 5y = 15 which is equidistant from the coordinate axes will lie
only in: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) 1st and 2nd
quadrants (2) 1st, 2nd and 4th quadrants
(3) 4th quadrant (4) 1st quadrant
18. Let O(0, 0) and A(0, 1) be two fixed points, Then the locus of a point P such that the perimeter
of AOP is 4, is [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) 8x + 9y
2 2
9y = 18 (2) 9x + 8y
2 2
8y = 16
(3) 8x2 9y2 + 9y = 18 (4) 9x2 8y2 + 8y = 16
19. Suppose that the points (h, k), (1, 2) and ( 3, 4) lie on the line L1. If a line L2 passing through
k
the points (h, k) and (4, 3) is perpendicular to L1, then equals: [JEE(Main)-2019]
h
1 1
(1) − (2) (3) 0 (4) 3
7 3
20. Slope of a line passing through P(2, 3) and intersecting the line, x + y = 7 at a distance of
4 units from P, is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
1 1
x
f( 3)
(1)
125
(2)
2
(3) f(t)dt + x (4)
1 3
21. A rectangle is inscribed in a circle with a diameter lying along the line 3y = x + 7. If the two
adjacent vertices of the rectangle are ( 8, 5) and (6, 5) then the area of the rectangle
(in sq. units) is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) 72 (2) 56 (3) 98 (4) 84
3
22. Lines are drawn parallel to the line 4x 3y + 2 = 0, at a distance from the origin. Then which
5
one of the following points lies on any of these lines? [JEE(Main)-2019]
1 2 1 2 1 1 1 1
(1) − , − (2) − , (3) , − (4) ,
4 3 4 3 4 3 4 3
23. The equation y = sinx sin(x + 2) sin2 (x + 1) represents a straight line lying in:
[JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) first, third and fourth quadrants (2) third and fourth quadrants only
(3) second and third quadrants only (4) first, second and fourth quadrants
24. A triangle has a vertex at (1, 2) and the mid points of the two sides through it are ( 1, 1) and
(2, 3). Then the centroid of this triangle is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
1 1 5 1 7
(1) ,2 (2) , (3) , 1 (4) 1,
3 3 3 3 3
Point and Straight Line 49
25. A straight-line L at a distance of 4 units from the origin makes positive intercepts on the
coordinate axes and the perpendicular from the origin to this line makes an angle of 60° with
the line x + y = 0. Then an equation of the line L is: [JEE(Main)-2019]
(1) x + 3y = 8 (2) ( ) (
3−1 x+ )
3+1 y =8 2
(3) ( ) (
3+1 x+ )
3−1 y =8 2 (4) 3x + y = 8
26. The locus of the mid-points of the perpendiculars drawn form points on the line, x = 2y to the
line x = y is: [JEE(Main)-2020]
(1) 2x 3y = 0 (2) 5x 7y = 0 (3) 3x 2y = 0 (4) 7x 5y = 0
27. Let two points be A(1, 1) and B(0, 2). If a point P(x', y') be such that the area of PAB = 5sq.
units and it lies on the line, 3x + y 4 = 0, then a value of is : [JEE(Main)-2020]
(1) 1 (2) 4 (3) 3 (4) 3
28. The length of the perpendicular from the origin, on the normal to the curve, x2 + 2xy 3y2 = 0
at the point (2, 2) is: [JEE(Main)-2020]
(1) 2 2 (2) 2 (3) 4 2 (4) 2
29. Let C be the centroid of the triangle with vertices (3, 1), (1, 3) and (2, 4). Let P be the point of
intersection of lines x + 3y 1 = 0 and 3x y + 1 = 0. Then the line passing through the points
C and P also passes through the point. [JEE(Main)-2020]
(1) ( 9, 7) (2) ( 9, 6) (3) (9, 7) (4) (7, 6)
3
30 Let A(1, 0), B(6, 2) and C ,6 be the vertices of triangle ABC. If P is a point inside the triangle
2
ABC such that the triangle APC, APB and BPC have equal areas, then the length of the line
7 1
segment PQ, where Q is the point − , − , is .......... [JEE(Main)-2020]
6 3
31. The set of all possible values of in the interval (0, ) for which the points (1, 2) and (sin, cos)
lie on the same side of the line x + y = 1 is: [JEE(Main)-2020]
3 3
(1) 0, (2) 0, (3) , (4) 0,
4 2 4 4 4
32. If a ABC has vertices A( 1, 7), B( 7, 1) and C(5, 5), then its orthocentre has coordinates:
[JEE(Main)-2020]
3 3 3 3
(1) , − (2) (3, 3) (3) ( 3, 3) (4) − ,
5 5 5 5
50 Point and Straight Line
33. A triangle ABC lying in the first quadrant has two vertices as A(1, 2) and B(3, 1). If BAC = 90°, and
ar(ABC) = 5 5 sq. units, then the abscissa of the vertex C is: [JEE(Main)-2020]
(1) 2 + 5 (2) 2 5 1 (3) 1 + 2 5 (4) 1 + 5
34. If the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points P(l, 4) and Q(k, 3)
has y-intercept equal to 4, then a value of k is : [JEE(Main)-2020]
(1) 2 (2) 4 (3) 14 (4) 15
1 2
35. If the line, 2x y + 3 = 0 is at a distance and from the lines 4x 2y + = 0 and
5 5
6x 3y + = 0, respectively, then the sum of all possible values of and is ________.
[JEE(Main)-2020]
36. A ray of light coming from the point (2,2 3) is incident at an angle 30° on the line x=l at the
point A. The ray gets reflected on the line x = 1 and meets x-axis at the point B. Then, the line
AB passes through the point: [JEE(Main)-2020]
1 3
(1) 3, − (2) (3, − 3) (3) 4, − (4) (4, − 3)
3 2
37. Let AD and BC be two vertical poles at A and B respectively on a horizontal ground. If AD = 8
m, BC = 11 m and AB = 10 m; then the distance (in meters) of a point M on AB from the point A
such that MD2 + MC2 is minimum is. [JEE(Main)-2020]
38. Let L denote the line in the xy-plane with x and y intercepts as 3 and 1 respectively. Then the
image of the point ( 1, 4) in this line is : [JEE(Main)-2020]
8 29 29 11 11 28 29 8
(1) , (2) , (3) , (4) ,
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
39. Let a point P be such that its distance from the (5, 0) is thrice the distance of P from the point
( 5, 0). If the locus of the point P is a circle of radius r, then 4r 2 is equal to (Round off to the
nearest integer) [JEE(Main)-2021]
40. Let A ( 1, 1), B(3, 4) and C(2, 0) be given three points. A line y = mx, m > 0, intersects lines AC
and BC at point P and Q respectively. Let A1 and A2 be the areas of ABC and PQC respectively,
such that A1 = 3 A2, then the value of m is equal to: [JEE(Main)-2021]
4
(1) (2) 1 (3) 2 (4) 3
15
Point and Straight Line 51
41. Let the tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = 25 at the point R (3, 4) meet x-axis and y-axis at point P
and Q, respectively. If r is the radius of the circle passing through the origin O and having centre
at the incentre of the triangle OPQ, then r2 is equal to: [JEE(Main)-2021]
529 125 625 585
(1) (2) (3) (4)
64 72 72 66
42. Let tan , tan tan ; , ,
(2n − 1) , n N be the slopes of three-line segments OA, OB and
2
OC, respectively, where O is origin. If circumcenter of ABC coincides with origin and its
2
cos 3 + cos 3 + cos 3
orthocenter lies on y-axis, then the value of is equal to:
cos cos cos
[JEE(Main)-2021]
43. The number of integral values of m so that the abscissa of point of intersection of lines
3x + 4y = 9 and y = mx +1 is also an integer, is: [JEE(Main)-2021]
(1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 (4) 0
44. The equation of one of the straight lines which passes through the point (1, 3) and makes an
angles tan ( 2 ) with the straight line, y + 1 = 3 2 x is
1
[JEE(Main)-2021]
(1) 4 2 x + 5y − ( 15 + 4 2 ) = 0 (2) 5 2 x + 4y − ( 15 + 4 2 ) = 0
(3) 4 2 x + 5y − 4 2 = 0 (4) 4 2 x − 5y − ( 15 + 4 2 ) = 0
45. Let the centroid of an equilateral triangle ABC be at the origin. Let one of the sides of the
equilateral triangle be along the straight-line x + y = 3. If R and r be the radius of circumcircle
and incircle respectively of ABC, then (R + r) is equal to: [JEE(Main)-2021]
9
(1) (2) 7 2 (3) 2 2 (4) 3 2
2
3
46. Let A , a a 0, be a fixed point in the xy-plane. The image of A in y-axis be B and the
a,
image of B in x-axis be C. If D(3 cos, a sin) is a point in the fourth quadrant such that the
maximum area of ACD is 12 square units, then a is equal to _______. [JEE(Main)-2021]
47. The equations of the sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle ABC are 2x + y = 0, x + py = 15a and
1
x y = 3 respectively. If its orthocenter is (2, a), − < a < 2, then p is equal to
2
[JEE(Main)-2022]
52 Point and Straight Line
48. Let A(1, 1), B( 4, 3) C( 2, 5) be vertices of a triangle ABC, P be a point on side BC and 1 and
2 be the areas of triangle APB and ABC. Respectively. IF 1 : 2 = 4 : 7, then the area enclosed
by the lines AP, AC and the x-axis is: [JEE(Main)-2022]
1 3 1
(1) (2) (3) (4) 1
4 4 2
49. The equations of the sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle ABC are 2x + y = 0, x + py = 39 and
x y = 3 respectively and P(2, 3) is its circumcenter. Then which of the following is NOT true:
[JEE(Main)-2022]
(1) (AC)2 = 9p (2) (AC)2 + p2 = 136
(3) 32 < area(ABC) < 36 (4) 34 < area(ABC) < 38
50. For t (0, 2), if ABC is an equilateral triangle with vertices A(sint, cost), B(cost, sint) and
C(a, b) such that its orthocenter lies on a circle with centre 1, 1 , then (a2
b2) is equal to :
3
[JEE(Main)-2022]
8 77 80
(1) (2) 8 (3) (4)
3 9 9
51. Let the circumcentre of a triangle with vertices A(a, 3), B(b, 5) and C(a, b), ab > 0 be P(1, 1).
If the line AP intersects the line BC at the point Q(k1, k2), then k1 + k2 is equal to :
[JEE(Main)-2022]
4 2
(1) 2 (2) (3) (4) 4
7 7
52. Let m1, m2 be the slopes of two adjacent sides of a square of side a such that
( )
a2 + 11 a + 3 m22 + m21 = 220. If one vertex of the square is (10(cos sin), 10 (sin + cos)),
where a 0, and the equation of one diagonal is (cos sin)x + (sin + cos)y = 10, then
2
72 (sin4 + cos4) + a2 3a + 13 is equal to : [JEE(Main)-2022]
(1) 119 (2) 128 (3) 145 (4) 155
53. Let A (, 2), (, 6) and C , −2 be vertices of a ABC. If 5, is the circumcentre of ABC,
4 4
then which of the following is NOT correct about ABC: [JEE(Main)-2022]
(1) areas is 24 (2) perimeter is 25
(3) circumradius is 5 (4) inradius is 2
Point and Straight Line 53
ANSWER KEY
1. (3) 2. (2) 3. (1) 4. (4) 5. (1) 6. (4) 7. (4)
8. (4) 9. (2) 10. (3) 11. (2) 12. (4) 13. (2) 14. (2)
15. (2) 16. (2) 17. (1) 18. (2) 19. (2) 20. (2) 21. (4)
22. (2) 23. (2) 24. (1) 25. (3) 26. (2) 27. (4) 28. (1)
29. (2) 30. 5.00 31. (2) 32. (3) 33. (3) 34. (2) 35. 30.00
36. (2) 37. 5.00 38. (3) 39. 56.00 40. (2) 41. (3) 42. 12.00
43. (2) 44. (1) 45. (1) 46. 8.00 47. 3.00 48. (3) 49. (4)
50. (2) 51. (2) 52. (2) 53. (2)
54 Point and Straight Line
JEE-Advanced (Previous Year Questions)
1. The area bounded by the angle bisectors of the lines x2 y2+ 2y = 1 and the line x + y = 3, is
[JEE(Advanced)-2004]
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 6
2. The area of the triangle formed by the intersection of a line parallel to x-axis and passing
through P(h, k) with the lines y = x and x + y = 2 is 4h2. Find the locus of the point P.
[JEE(Advanced)-2005]
3. (a) Let O(0, 0), P(3, 4), Q(6, 0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point R inside the triangle
OPQ is such that the triangles OPR, PQR, OQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are
(A) (4/3, 3) (B) (3, 2/3) (C) (3, 4/3) (D) (4/3, 2/3)
(b) Lines L1: y x = 0 and L2: 2x + y = 0 intersect the line L3: y + 2 = 0 at P and Q, respectively.
The bisector of the acute angle between L1and L2intersects L3at R.
1 1
Statement-1 : The ratio PR : RQ equals 2 :
8 4
because
Statement-2 : In any triangle, bisector of an angle divides the triangle into two similar triangles.
(A) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true; statement-2 is a correct explanation for statement-1
(B) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true; statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for
statement-1.
(C) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false.
(D) Statement-1 is false, statement-2 is true. [JEE(Advanced)-2007]
4. Consider the lines given by
L1= x + 3y 5=0
L2= 3x ky 1=0
L3= 5x + 2y 12 = 0
Match the statements/Expression in Column-I with the statements/Expressions in Column-II
and indicate your answer by darkening the appropriate bubbles in the 4 × 4 matrix given in OMR.
[JEE(Advanced)-2008]
Column-I Column-II
(A) L1, L2, L3are concurrent, if (P) k = 9
5
(B) One of L1, L2, L3 is parallel to at least one of the other two, if (Q) k =
8
3
(C) L1, L2, L3form a triangle, if (R) k =
8
(D) L1, L2, L3do not form a triangle, if (S) k = 5
Point and Straight Line 55
10 ˆj , 13
5. Let P, Q, R and S be the points on the plane with position vectors 2 4 ,
3 3
11 2
3 +3 3 4 + 2 10 respectively. The quadrilateral PQRS must be a
3 3
[JEE(Advanced)-2010]
(A) parallelogram, which is neither a rhombus nor a rectangle
(B) square
(C) rectangle, but not a square
(D) rhombus, but not a square
6. A straight-line L through the point (3, 2) is inclined at an angle 60° to the line 20 x + y =1.
If L also intersect the x-axis, then the equation of L is: [JEE(Advanced)-2011]
32 16 3 3
(A) y + 50 x +2 3 =0 (B) y x +2 +3 =0
3 3 2
3 3 3 2 2 3
(C) y x +3 +2 =0 (D) y +x 3 +2 3, 2 = 0
4 2 4
7. For a > b > c > 0, the distance between (1, 1) and the point of intersection of the lines
ax + by + c = 0 and bx + ay + c = 0 is less than 2 3 . Then [JEE(Advanced)-2013]
(A) a + b c>0 (B) a b+c<0 (C) a b+c>0 (D) a + b c<0
8. For a point P in the plane, let d1 (P) and d2 (P) be the distances of the point P from the lines
x y = 0 and x + y = 0 respectively. The area of the region R consisting of all points P lying in
the first quadrant of the plane and satisfying 2 d1(P) + d2 (P) 4, is: [JEE(Advanced)-2014]
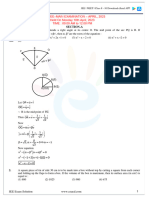
9. Consider a triangle whose two sides lie on the x -axis and the line x + y + 1 = 0 . If the
orthocenter of is (1, 1) , then the equation of the circle passing through the vertices of the
triangle is: [JEE(Advanced)-2021]
(A) x2 + y2 − 3x + y = 0 (B) x2 + y2 + x + 3y = 0
(C) x2 + y2 + 2y − 1 = 0 (D) x2 + y2 + x + y = 0
Consider the lines L1 and L2 defined by
L1 : x 2 + y − 1 = 0 andL2 : x 2 − y + 1 = 0
For a fixed constant , let C be the locus of a point P such that the product of the distance of
P from L1 and the distance of P from L2 is 2 . The line y = 2x + 1 meets C at two points R and
S, where the distance between R and S is 270
Let the perpendicular bisector of RS meet C at two distinct points R' and S' Let D be the square
of the distance between R' and S'.
56 Point and Straight Line
10. The value of 2 is ___. [JEE(Advanced)-2021]
11. The value of D is ___ . [JEE(Advanced)-2021]
9
12. The area of the region ( x, y ) : 0 x , 0 y 1, x 3y, x + y 2 is [JEE(Advanced)-2021]
4
11 35 37 13
(A) (B) (C) (D)
32 96 96 32
ANSWER KEY
1. (A) 2. y = 2x + 1, y = 2x + 1 3. (a)-C; (b)-C
4. (A)-S; (B)-P, Q; (C)-R ; (D)-P,Q,S 5. (A) 6. (B)
7. (A) or (C) or (AC) 8. 6 9. (B)
10. 9 11. 77.14 12. (A)
Point and Straight Line 57
You might also like
- Introduction To MatricesDocument54 pagesIntroduction To MatricesChongMYNo ratings yet
- Scoring Sat Practice Test 2 DigitalDocument5 pagesScoring Sat Practice Test 2 DigitalDabeer AfzalNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions:: Sat Subject Test Math Level 1Document7 pagesSample Questions:: Sat Subject Test Math Level 1Shiv PatelNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Normalization of Database TablesDocument16 pagesNormalization of Database TablesJaya MalathyNo ratings yet
- Maths Straight Line CPP-1-10Document13 pagesMaths Straight Line CPP-1-10raghavendra jNo ratings yet
- Command in AutocadDocument9 pagesCommand in AutocadRichard VenturinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 Dan 1.4 EnglishDocument12 pagesChapter 1.2 Dan 1.4 EnglishAnonymous t5pFAF0% (1)
- Human CapitalDocument31 pagesHuman CapitalAmit Sharma100% (1)
- UT General ExamDocument25 pagesUT General ExamMohamed Ibrahim100% (1)
- M - Ch-10 - Straight LinesDocument8 pagesM - Ch-10 - Straight LinesjdhdufhdieoNo ratings yet
- 08 P PyqmDocument18 pages08 P PyqmkislaysmithschoolNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CircleDocument9 pagesMathematics Circlesonidaksh1812No ratings yet
- MATHS Revision DPP No 2Document8 pagesMATHS Revision DPP No 2ashutosh100% (2)
- Straight Line - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - (Prayas 2.0 2023 PW Star)Document3 pagesStraight Line - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - (Prayas 2.0 2023 PW Star)Deep SarkarNo ratings yet
- Ex. (JM) VectorDocument30 pagesEx. (JM) VectorShreyam VermaNo ratings yet
- Circle: Aakash Educational Services Limited - Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456Document4 pagesCircle: Aakash Educational Services Limited - Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Dpp-2 English PC BwyryeuDocument7 pagesDpp-2 English PC Bwyryeum2595jn9d9No ratings yet
- 3D GeometryDocument47 pages3D Geometrykrishnagamer565No ratings yet
- M - Ch-26 - Three Dimensional Geometry PDFDocument15 pagesM - Ch-26 - Three Dimensional Geometry PDFBlake RichardsonNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Question DPP - Straight LinesDocument7 pages(PDF) Question DPP - Straight LinesArham BothraNo ratings yet
- 2-Quadratic Equation JEE (Main) PDFDocument15 pages2-Quadratic Equation JEE (Main) PDFRajarajeshwari venkateshNo ratings yet
- M - Ch-02 - Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesM - Ch-02 - Quadratic EquationsraghuNo ratings yet
- 05 - Coordinate Geometry Practice WS - 2Document2 pages05 - Coordinate Geometry Practice WS - 2Saraf santhosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Classnote 573598c38d689Document14 pagesClassnote 573598c38d689HarshitShuklaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesQuadratic EquationsShivansh SudhaNo ratings yet
- Xercise: Jee ProblemsDocument2 pagesXercise: Jee ProblemspandaNo ratings yet
- Assignment PointDocument6 pagesAssignment PointAyan RazaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Online Exam 2019: (Memory Based Paper)Document5 pagesJEE Main Online Exam 2019: (Memory Based Paper)Deepak SainiNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry FinalDocument4 pages3D Geometry FinalUtkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- CLASS TEST-2 (Straight Line) Maths RC SirDocument2 pagesCLASS TEST-2 (Straight Line) Maths RC Sircaptainprice351100No ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-5 Level-2 Chapter-15 PDFDocument14 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-5 Level-2 Chapter-15 PDFManisha JindalNo ratings yet
- Straight Line & Circle Only QuestionDocument15 pagesStraight Line & Circle Only QuestionShikhar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 05 - Coordinate Geometry Practice WS - 3Document2 pages05 - Coordinate Geometry Practice WS - 3Saraf santhosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Maths 05 Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesMaths 05 Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Practice Questionssamarth mishraNo ratings yet
- New Doc Oct 31, 2023 20.23Document3 pagesNew Doc Oct 31, 2023 20.23tasveenm5No ratings yet
- IB 01 Coordinate System (1 5)Document3 pagesIB 01 Coordinate System (1 5)eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Straight Line GB Sir ModuleDocument15 pagesStraight Line GB Sir ModuleSaptarshiNo ratings yet
- Icse 2011 Maths Solution 1aDocument5 pagesIcse 2011 Maths Solution 1aSanjayNo ratings yet
- 07march MainsDocument38 pages07march Mainsprakash karnaNo ratings yet
- DPP# Straight LinesDocument3 pagesDPP# Straight Linessarvesh goyalNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Jeemain - GuruDocument3 pagesExercise 5 Jeemain - GuruUnknown UnknownNo ratings yet
- Level-Iv: Circles Jee-Adv-Sr-Maths Vol-IvDocument37 pagesLevel-Iv: Circles Jee-Adv-Sr-Maths Vol-IvSurya teja cvNo ratings yet
- AREA UNDER CURVE JEE MAIN Previous Year Q Bank Till 2017Document5 pagesAREA UNDER CURVE JEE MAIN Previous Year Q Bank Till 2017Arnav SinghalNo ratings yet
- CLASS TEST-3 (Straight Line) Maths RC SirDocument2 pagesCLASS TEST-3 (Straight Line) Maths RC Sircaptainprice351100No ratings yet
- (Maths) - (10-4-2023) Shift 1Document20 pages(Maths) - (10-4-2023) Shift 1p10piyushNo ratings yet
- TEST-5: JEE MainDocument22 pagesTEST-5: JEE MainRdNo ratings yet
- DETERMINANTS - Practice Sheet Notes - Manzil Legends-JEEDocument4 pagesDETERMINANTS - Practice Sheet Notes - Manzil Legends-JEEArya PatelNo ratings yet
- Mathongo Question Straight Line Jee Main 2021 February chapterwiseiEwGHx1VYvrNB6umk4aFDocument3 pagesMathongo Question Straight Line Jee Main 2021 February chapterwiseiEwGHx1VYvrNB6umk4aFHARSHIT RAJ PRATAP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines PYQSDocument3 pagesStraight Lines PYQSHrushikesh BarikNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 10th Maths Book Back 1 Mark Questions With Answers emDocument11 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th Maths Book Back 1 Mark Questions With Answers emJAYARAJALAKSHMI IlangoNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Manoj Chauhan Sir: Mathematics byDocument30 pagesManoj Chauhan Sir: Mathematics byRaval sagarNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee Maths Coordinate Geometry DPPDocument2 pagesIit Jee Maths Coordinate Geometry DPPPrince ChauhanNo ratings yet
- TB Wow CG 01Document2 pagesTB Wow CG 01darshan4141.kaspaNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines 2Document3 pagesStraight Lines 2Priywrat HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument4 pagesStraight LinesPriywrat HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Matrices - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06)Document2 pagesMatrices - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06)Shambhavi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Tty 5 K FM Sa 9 VAPi NN 0 U 3 LDocument2 pagesTty 5 K FM Sa 9 VAPi NN 0 U 3 LWahab HasanNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Conic+Sections+ (Parabola,+Ellipse, Hyperbola)Document17 pagesJee Advanced Conic+Sections+ (Parabola,+Ellipse, Hyperbola)avneetsinghtoaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Top 25 QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Top 25 QuestionssinghejouraaritNo ratings yet
- G Gpe B 4 QuadrilateralsintheCoordinatePlane2Document15 pagesG Gpe B 4 QuadrilateralsintheCoordinatePlane2maddiekurtaNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics DPP 06 (Of Lecture 08)Document3 pagesBasic Mathematics DPP 06 (Of Lecture 08)munimunendra00No ratings yet
- Point (Co-Ordinate Geometry)Document2 pagesPoint (Co-Ordinate Geometry)Deepanshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesMaths Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01veeNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Sample Paper 01 For Sessing Ending Exam (2017-18)Document5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Sample Paper 01 For Sessing Ending Exam (2017-18)SanjayNo ratings yet
- IB 04 Straight Lines (11 16)Document3 pagesIB 04 Straight Lines (11 16)eamcetmaterials100% (1)
- Quadratic Equation JEE MAINDocument6 pagesQuadratic Equation JEE MAINAnshNo ratings yet
- DPP Functions 1 1692544858305Document12 pagesDPP Functions 1 1692544858305mangeshchavan980No ratings yet
- 13 DPP 09a-09d Halk & Harn EvolveDocument17 pages13 DPP 09a-09d Halk & Harn Evolvemangeshchavan980No ratings yet
- Physics - Newtons Laws of Motion and FrictionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Newtons Laws of Motion and Frictionmangeshchavan980No ratings yet
- F-Block and Doubt Clearing Session With Anno 1697946668295Document12 pagesF-Block and Doubt Clearing Session With Anno 1697946668295mangeshchavan980No ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Tutorial Sheets 1Document11 pagesLinear Algebra Tutorial Sheets 1Vidushi VinodNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Design and Analysis PDFDocument14 pagesSupply Chain Design and Analysis PDFTropic Thunder100% (1)
- Kvpc++materialfor12 Xii PDFDocument149 pagesKvpc++materialfor12 Xii PDFRavichandra PallaNo ratings yet
- MAT 2101 Complex Variables, Laplace and Z Transform COURSE OUTLINE Fall 23-24Document7 pagesMAT 2101 Complex Variables, Laplace and Z Transform COURSE OUTLINE Fall 23-24jop23343No ratings yet
- Base ExcitationDocument51 pagesBase ExcitationPuneet BahriNo ratings yet
- Management ConceptsDocument85 pagesManagement ConceptsArvind RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 The Mathematics of GraphsDocument64 pagesLesson 9 The Mathematics of GraphsiganNo ratings yet
- Classification Error: Training Errors Generalization ErrorsDocument39 pagesClassification Error: Training Errors Generalization ErrorsOscar WongNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Engineering Mathematics Final ExamDocument3 pagesFundamental of Engineering Mathematics Final ExamrowelNo ratings yet
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Document7 pagesLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Equilibrium of Force SystemsDocument55 pagesChapter 3 - Equilibrium of Force Systemsforojaypee2002No ratings yet
- Pages From SAS - A00-240Document15 pagesPages From SAS - A00-240Chirag SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Mathematics First Term Paper Practice PaperDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Mathematics First Term Paper Practice PaperSiddhi Gupta100% (1)
- Prediction and Analysis of Gear Rattle: Development TransmissionsDocument5 pagesPrediction and Analysis of Gear Rattle: Development TransmissionssmsnvhNo ratings yet
- Calculating Empirical FormulasDocument3 pagesCalculating Empirical FormulasThe BluemanNo ratings yet
- Neural Adaptive Control by State Space System UPFC (SSNN) For Compensation of Active and Reactive PowerDocument7 pagesNeural Adaptive Control by State Space System UPFC (SSNN) For Compensation of Active and Reactive PowerKrimo de SaidaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document32 pagesCH 02TahaNo ratings yet
- The ParthenonDocument8 pagesThe ParthenonAbhishek GandhiNo ratings yet
- Types of Loading ME 311 - 4Document15 pagesTypes of Loading ME 311 - 4Nakshatra Patil 4-Year B.Tech. Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 8 - Module 4Document22 pagesQ2 Mathematics 8 - Module 4Jose Carlos FernandezNo ratings yet
- Linear and Non-Linear Dynamic AnalysisDocument9 pagesLinear and Non-Linear Dynamic AnalysisvempadareddyNo ratings yet
- AHP IRPAnIntegratedApprochforDecisionMakingDocument9 pagesAHP IRPAnIntegratedApprochforDecisionMakingFun Toosh345No ratings yet