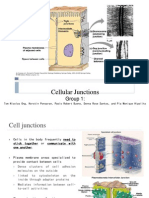
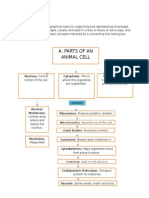
Cell Junctions
Cell Junctions
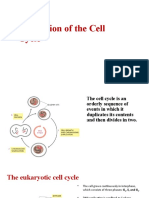
Specialized structures called cell junctions link cells to the extracellular matrix
(which is network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals) or to one
other. In fact, Cell junctions are protein structures.
They serve a variety of purposes, including sensing, sealing, anchoring, and
communicating.
There are 3 main types of Cell Junctions. They include:
1) Tight Junctions
2) Gap Junctions in animal cells
3) Plasmodesmata in plant cells
4) Desmosomes
*There are more cell junctions, but only these are covered in this report.
* The Gap junctions and Plasmodesmata have the same function, but one is found in animal cell, the other
in plant cell.
1) Tight Junctions
Tight junctions are multiprotein junctional complexes that have several different functions. Their
most important functions are to:
• Help cells form a barrier that prevents molecules from getting through.
• Stop proteins in the cell membrane from moving around.
Tight junctions are often found in the Bladder and Intestine.
They are only found in vertebrates, animals with a backbone and
skeleton; invertebrates have septate junctions instead.
They also keep the correct proteins on the correct sides of the cell in order for these functions to
occur. This also helps maintain the polarity of cells.
� 2) Gap Junctions in animal cells
Gap junctions join cells to allow chemicals to flow between
them, which is their primary purpose. This increases
communication between cells and permits chemicals to reach
nearby cells directly, avoiding the extracellular fluid that
surrounds them.
They are particularly important in heart muscle.
In fact, the human body has about 200 types of gap junction
Channels.
3) Plasmodesmata in plant cells
Plasmodesmata join cells to allow the movement of RNA, ions,
pigments, water, and any other substance to flow between them.
Plasmodesmata usually form during the cell division process
when the cell wall is not fully developed.
4) Desmosomes
Desmosomes are specialized junctions that connect cells in tissues that
undergo mechanical stress, such as skin and heart. They help hold cells strongly together
with the help of cytoskeleton
• provide structural stability and strength to the tissues by
distributing the mechanical force across the cell layer.
• They also play a role in signaling pathways that regulate
cell differentiation.
Desmosomes can be affected by various diseases, such as
pemphigus, which is an autoimmune disorder that causes blisters
and erosions on the skin and mucous membranes.
They are essential for maintaining the integrity and function of many organs
and tissues in the human body.
Quick Recap
� 1) The ____ surrounds the cell like a belt, preventing the passage of substances between the
cells.
A) gap junctions
B) desmosome
C) tight junctions
D) light junctions
2) Cell junctions that prevent small molecules from passing in between two cells are called_____
A) gap junctions
B) tight junctions
C) adhesions
D) plasmodesmata
3) _____ join cells to allow chemicals to flow between them.
A) Trap Junctions
B) Map Junctions
C) Gap Junctions
4) Plasmodesmata occur in __________.
A) bacterial cells
B) all eukaryotic cells
C) plant cells
D) animal cells
E) the nucleus of the cell
Thank You For Paying Attention!