Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PWA-RPD-HSS-ALRT-067 Mobile Scaffolding Safety
Uploaded by
Sonesh SethumadhavanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PWA-RPD-HSS-ALRT-067 Mobile Scaffolding Safety
Uploaded by
Sonesh SethumadhavanCopyright:
Available Formats
Roads Projects Department
SAFETY ALERT
Mobile Scaffolding Safety
Background: A recent incident in one of the RPD
projects involving a mobile scaffold resulted in a
work injury due to a worker falling from a height.
While the mobile scaffold was being relocated by
pushing it with workers on the scaffold's top
working platform, one of the scaffold's caster
wheels broke off, leading to the scaffold's tilting and
subsequent fall of the personnel from height.
Mobile scaffold: Also known as movable scaffolding, this scaffold is designed for easy mobility. It consists of a stable
platform supported by wheels or casters, which allow workers to move the scaffold to different locations without
disassembly and reassembly. However, moving the scaffold with personnel onboard shall not be permitted.
Here are the main types of mobile scaffolding:
Single-Width Scaffold: Double-Width Mobile Scaffold: Folding Mobile Scaffold:
Compact with a single platform, Broader platform with two single- Easily collapsible for transport and
ideal for indoor tasks in tight width platforms, offering more space storage, convenient for limited
spaces. and stability for larger projects. spaces or frequent movement.
Podium Steps: Stairway Mobile Scaffolds: Adjustable Mobile Scaffolds:
Specifically for low-level access tasks, Incorporate stair units for safe access Allows height adjustment with
featuring a single platform with to multiple levels, common in telescopic legs or adjustable frames,
guardrails, commonly used in retail construction and events. versatile for various job
and warehouses. requirements.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the appropriate mobile scaffolding for safety and efficiency at heights.
Choosing the right mobile scaffolding!
❑ Assess Requirements: Start by understanding specific project needs. Consider the height and size of the structures
needing access and any unique site conditions that may affect the operation. Also, determine the maximum weight the
scaffolding needs to support. Consider the combined weight of workers, tools, equipment, and materials that will be
present on the platform. Choose a mobile scaffold with a weight capacity that exceeds the estimated requirements to
provide a safety margin.
❑ Compliance With Regulations and Standards: Ensure the mobile scaffolding chosen complies with local safety
regulations, industry standards, and codes. Always follow the manufacturer’s or supplier’s instruction manual.
❑ Mobility And Stability: Look for scaffolding with sturdy wheels and locking mechanisms, allowing easy movement and
stability. Consider the construction site's terrain and surface conditions to ensure the wheels suit the environment.
❑ Ease Of Assembly And Disassembly: Choose mobile scaffolding that is easy to assemble and disassemble, allowing for
efficient use of time and resources. Look for systems with quick-lock mechanisms or modular designs that facilitate
rapid setup and takedown.
❑ Durability And Material Quality: The materials used to design the scaffolding determine its longevity and resistance to
wear and tear. Look for options made from robust materials like steel or aluminium, which offer strength and stability.
PWA-RPD-HSS-ALRT-067 PAGE 1/2 Issue Date: 22 February 2024
Roads Projects Department
SAFETY ALERT
Mobile Scaffolding Safety
❑ Safety Features: Prioritise the safety features incorporated into the scaffolding design. This may include
guardrails, non-slip surfaces, secure locking mechanisms, and stability braces. These features enhance worker
safety and reduce the risk of accidents.
Safety Measures
❑ Stability: Mobile scaffolds rely on a stable base to provide a secure and safe working platform. The uneven or
unstable ground can lead to an imbalance in the scaffold, increasing the risk of tipping or collapsing. It is
essential to assess the ground conditions where the scaffold will be placed and ensure it is firm and level.
❑ Ground Inspection: Before setting up the mobile scaffold, inspect the ground for any irregularities, such as
holes, loose soil, debris, or slopes, and clear away any obstacles that could affect the stability or cause tripping
hazards. If significant irregularities exist, level the ground or use appropriate levelling equipment, such as base
plates or adjustable legs, to ensure stable footing.
❑ Weight Distribution: Mobile scaffolds have weight limits specified by the manufacturer. Even on level ground,
exceeding the recommended load capacity can compromise the scaffold’s stability. Be mindful of the weight of
workers, tools, and equipment on the scaffold, ensuring it does not exceed the maximum allowed load.
❑ Level Adjustments: Mobile scaffolds often have adjustable legs or mechanisms to compensate for uneven
ground. Take the time to adjust the scaffold’s levelling components properly to ensure that all four sides have
equal support and eliminate any tilting or rocking motion.
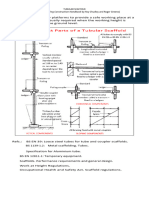
Height to Base Ratio
The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) recommends explicitly not using a The Construction Industry Training Board
safety harness and lanyard when working on mobile towers. If the guardrails (CITB) recommends a ratio of 1:3.5 for
have been correctly installed, the tower has collective fall protection, so scaffolds used inside buildings and 1:3 for
personal fall protection is unnecessary. ones used outside buildings. No tower
In the event of an arrest fall on a mobile tower, one is likely to cause the tower should be built with a least base
to overturn, increasing the risk of injury to oneself and others in the vicinity. dimension of less than 1.2 m.
❑ Locking Wheels: Most mobile scaffolds are equipped with wheels or
casters for easy mobility. However, it is crucial to ensure the wheels
stay in place once the scaffold is in position. Lock the wheels securely
to prevent unintended movement or shifting, providing stability during
work activities.
❑ Regular Inspections: Throughout scaffold “…A mobile working platform (such
use, periodically check the stability and as a mobile scaffold tower or a
levelness of the scaffold’s footing. mobile elevating work platform)
Conduct routine inspections for signs of must have been inspected within the
ground settling or other factors affecting previous seven days…”
stability. Promptly address issued QCS 2014 Section 11 Part 1.2.1.17
detected before continuing work.
❑ Erection of mobile scaffold? *Competent person: A person who has practical and theoretical
Mobile scaffolds must only be erected, knowledge and actual experience of the work activities that they are
altered or dismantled by, or under the direct required to do. A person's competence will, be tangibly demonstrated by
supervision of, a *competent person. the award of a qualification or other recognition of training received.
Legal requirements: QCS 2014 Section 11Part 1.3.4 System Scaffolds and Mobile
Towers, 1.01 (78), Part 1.3.5 Tube and Fitting Scaffolds (and any other relevant
sections).
The Supervision Consultants and the Construction Contractors hold a
shared responsibility in communicating and ensuring the ‘Control
Measures’ in this Alert.
PWA-RPD-HSS-ALRT-067 PAGE 2/2 Issue Date: 22 February 2024
You might also like
- Scaffold Training 2023Document98 pagesScaffold Training 2023HILAL ALSAMA100% (1)
- Mobile Scaffold Training: Safe Work PracticesDocument41 pagesMobile Scaffold Training: Safe Work PracticesEHS AcefireNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding: Submitted By, Akhilesh.A Production Operator (TR), Forbes Bumiarmada LimitedDocument42 pagesScaffolding: Submitted By, Akhilesh.A Production Operator (TR), Forbes Bumiarmada LimitedHamzaNoumanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding: Submittedby, Akhilesh. A Productionoperator (TR), Forbesbu MiarmadalimitedDocument42 pagesScaffolding: Submittedby, Akhilesh. A Productionoperator (TR), Forbesbu MiarmadalimitedChandan Kumar Singh100% (1)
- UNIT 5 Scaffolds and LaddersDocument87 pagesUNIT 5 Scaffolds and Laddersmohsin khanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolds and BarricadesDocument22 pagesScaffolds and BarricadesMikaella Manzano100% (3)
- Osha3722 PDFDocument2 pagesOsha3722 PDFTharaka Perera100% (1)
- 28 - Scaffolding ProceduresDocument17 pages28 - Scaffolding ProceduresLalit Tomar100% (1)
- Presentation Lifting Equipment SafetyDocument17 pagesPresentation Lifting Equipment SafetyTahir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Mobile ScaffoldDocument41 pagesMobile ScaffoldEka Candra SuryadiNo ratings yet
- Safety Standards ScaffoldDocument9 pagesSafety Standards ScaffoldhassanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety Instruction (498 A)Document5 pagesScaffolding Safety Instruction (498 A)Mythri Metallizing Pvt Ltd ProjectsNo ratings yet
- TATA Power Scaffold Safety StandardDocument7 pagesTATA Power Scaffold Safety StandardDSG100% (1)
- Scaffolds 3slidesDocument13 pagesScaffolds 3slidesCharles MitchellNo ratings yet
- PREVENTING LIFTING POINT FAILURES IN CONSTRUCTIONv2Document3 pagesPREVENTING LIFTING POINT FAILURES IN CONSTRUCTIONv2Sandra FildesNo ratings yet
- Guide Scaffolds ScaffoldingDocument5 pagesGuide Scaffolds ScaffoldingCoolaboo22No ratings yet
- 02 - Guidance - Ladders and PlatformsDocument30 pages02 - Guidance - Ladders and PlatformsAmjad Wael Yahia FayedNo ratings yet
- vYMeuoP5WRyc8NIv - Jltnw0O1UgbBz9sp-OSHA 10 Construction - Module 11 - Study GuideDocument7 pagesvYMeuoP5WRyc8NIv - Jltnw0O1UgbBz9sp-OSHA 10 Construction - Module 11 - Study GuideBelkacem BouazzaNo ratings yet
- Tower Mobile Scaffolds Information SheetDocument2 pagesTower Mobile Scaffolds Information SheetthecrowdedhouseNo ratings yet
- Aerial LiftDocument10 pagesAerial LiftARULSELVAN MURUGESANNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding: Safe Erection and USE: Jerus V. Lucine 5-BSCE-BDocument103 pagesScaffolding: Safe Erection and USE: Jerus V. Lucine 5-BSCE-Bjerus lucineNo ratings yet
- Flat Feet Barricade Bridge Feet Barricade Swing GatesDocument24 pagesFlat Feet Barricade Bridge Feet Barricade Swing GatesTristan Paul Guerra OrodioNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldDocument8 pagesScaffoldSAYED100% (1)
- Mobile ScaffoldDocument41 pagesMobile ScaffoldcherrylcalabiaNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Safety GuideDocument17 pagesScaffold Safety Guideuserr29990100% (2)
- COSH 413 2022 - Module 5 - Scaffolding Safety, DO 128 - 13 As Amended Rule 1414Document12 pagesCOSH 413 2022 - Module 5 - Scaffolding Safety, DO 128 - 13 As Amended Rule 1414Xandra Patricia BarreraNo ratings yet
- SMRsDocument194 pagesSMRsRichu PaliNo ratings yet
- ST 7016 PfsDocument57 pagesST 7016 Pfsg.rajaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix and Pour Safety Program - Construction - ProgramDocument7 pagesConcrete Mix and Pour Safety Program - Construction - ProgramSaleem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Scaffold SafetyDocument1 pageMobile Scaffold SafetyDhiraj ThukralNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding ProcedureDocument22 pagesScaffolding ProcedureMuhammad Saqib Asif100% (2)
- Guide Suspending (Swing Stage) ScaffoldsDocument14 pagesGuide Suspending (Swing Stage) ScaffoldsthecrowdedhouseNo ratings yet
- Scaffold LT PDFDocument23 pagesScaffold LT PDFparamarthasom1974100% (2)
- X Structures Tag and Grating Removal r1Document58 pagesX Structures Tag and Grating Removal r1Tharun100% (4)
- UK Construction - Scaffold Checklist - HSEDocument10 pagesUK Construction - Scaffold Checklist - HSEderdushaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesMobile Scaffold Inspection ChecklistjohainaNo ratings yet
- 016 Procedure ScaffoldingDocument13 pages016 Procedure ScaffoldingHSE CERINo ratings yet
- Healt and SafetyDocument14 pagesHealt and SafetyJefry SandyNo ratings yet
- Man Basket Operation Guideline - 1Document8 pagesMan Basket Operation Guideline - 1Raju100% (3)
- Guide Falsework AustraliaDocument4 pagesGuide Falsework AustraliaHafizah MohdNo ratings yet
- Tubular ScaffoldingDocument17 pagesTubular Scaffoldingfoxsins226100% (1)
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection Checklist: Scaffold Location / Number: Complies? Y Yes N No N/A Not ApplicableDocument2 pagesMobile Scaffold Inspection Checklist: Scaffold Location / Number: Complies? Y Yes N No N/A Not ApplicableMarulitua100% (1)
- Al-Jazeera Scaffolding Company: Method Statement / Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesAl-Jazeera Scaffolding Company: Method Statement / Risk AssessmentHany Farouk100% (2)
- Mobile Gantries SI 20.3Document2 pagesMobile Gantries SI 20.3reda mesbahNo ratings yet
- Safety in Erection and Dismantling of Constructions: Submitted by Saravana Kumar Saravanan ShilpaDocument13 pagesSafety in Erection and Dismantling of Constructions: Submitted by Saravana Kumar Saravanan ShilpaMageshwarNo ratings yet
- Safe Lifting Operations: What Do You Know About Lifting Safety?Document14 pagesSafe Lifting Operations: What Do You Know About Lifting Safety?nincatNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety TrainingDocument25 pagesScaffolding Safety Trainingmt_powers100% (1)
- Construction Machineries Mobile Equipment 2021 Pax PDFDocument56 pagesConstruction Machineries Mobile Equipment 2021 Pax PDFErvin ManchusNo ratings yet
- Sample Swms Heights Mobile ScaffoldDocument7 pagesSample Swms Heights Mobile Scaffoldmani narayananNo ratings yet
- Working at Heights ProcedureDocument11 pagesWorking at Heights ProcedureMo AboukhzamNo ratings yet
- Slinger Signaller Study Guide 19-07-22Document36 pagesSlinger Signaller Study Guide 19-07-22Dominican MontanoNo ratings yet
- Work InstructionsDocument32 pagesWork InstructionshainguyenbkvhvNo ratings yet
- NA - Engineering Catalogue V 8-17 PDFDocument40 pagesNA - Engineering Catalogue V 8-17 PDFehsan ahmad khan100% (1)
- Icorr BookDocument984 pagesIcorr BookSuraj M SethuNo ratings yet
- CT-CST-L8-Scaffolds Shoring and Underpinning - 2 PDFDocument45 pagesCT-CST-L8-Scaffolds Shoring and Underpinning - 2 PDFSanthush KavishaNo ratings yet
- SOP 10 - Safe Lifting Operations PDFDocument5 pagesSOP 10 - Safe Lifting Operations PDFMohammedJunaid100% (1)
- CS E11:2014: Guidelines on Design for Safety of Skyrise GreeneryFrom EverandCS E11:2014: Guidelines on Design for Safety of Skyrise GreeneryNo ratings yet
- NRA - Liability Letter To GovernorDocument2 pagesNRA - Liability Letter To GovernorRiley SnyderNo ratings yet
- Building The Performance You Need: A Guide To State-of-the-Art Tools For Seismic Design and AssessmentDocument28 pagesBuilding The Performance You Need: A Guide To State-of-the-Art Tools For Seismic Design and AssessmentMarkito SantosNo ratings yet
- MaintenanceDocument67 pagesMaintenanceBala M100% (1)
- Abbreviations: Kuwait National Petroleum CompanyDocument4 pagesAbbreviations: Kuwait National Petroleum CompanybabjihanumanthuNo ratings yet
- DLL DRRR Docx FireDocument3 pagesDLL DRRR Docx FireRoseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- MalhotraDocument98 pagesMalhotraFlorin CarageaNo ratings yet
- TWM50FBM User ManualDocument28 pagesTWM50FBM User ManualhamorcomNo ratings yet
- CTRL-70 Ui ConDocument20 pagesCTRL-70 Ui Conسکریپ بوائےNo ratings yet
- Komposisi Msds Gluco p20Document3 pagesKomposisi Msds Gluco p20warrior 81No ratings yet
- Sigma Guard CoatingDocument6 pagesSigma Guard CoatingAnonymous YcAZv5qF67No ratings yet
- Psychological Attitude Towards SafetyDocument17 pagesPsychological Attitude Towards SafetyAMOL RASTOGI 19BCM0012No ratings yet
- Serie X50M PDFDocument244 pagesSerie X50M PDFAndrei MihaiNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Installation of Thread Rod Support and Cable Tray Using Boomscissor LiftDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Thread Rod Support and Cable Tray Using Boomscissor LiftNaveenNo ratings yet
- Defensive Driving - 1Document17 pagesDefensive Driving - 1İlyas FeyziyevNo ratings yet
- Permatex Fast MSDSDocument7 pagesPermatex Fast MSDSSangita ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Smoke Ventilation Solutions BrochureDocument48 pagesSmoke Ventilation Solutions BrochureThanh Nguyen NgocNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Environmental ManagementakistanDocument40 pagesHealth and Safety Environmental ManagementakistanAminullah01No ratings yet
- Sampling and Preparation of Wet Blue and Wet White For Physical and Chemical TestsDocument3 pagesSampling and Preparation of Wet Blue and Wet White For Physical and Chemical Testsmohammed karasnehNo ratings yet
- Calculation SheetDocument8 pagesCalculation SheetViết Thành HồNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law, Health & SafetyDocument22 pagesEnvironmental Law, Health & SafetyfieqaNo ratings yet
- DNV-RP-H102 Marine Operations During Removal of Offshore Installations April 2004Document22 pagesDNV-RP-H102 Marine Operations During Removal of Offshore Installations April 2004TroyNo ratings yet
- Gulf Synthetic Gear Oil 320 PDFDocument6 pagesGulf Synthetic Gear Oil 320 PDFAnshuman AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Apollo Fire Detectors UL 268 7th Edition HandoutDocument2 pagesApollo Fire Detectors UL 268 7th Edition HandoutnaveedfndNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant MaintenanceDocument7 pagesTypes of Plant MaintenanceTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNo ratings yet
- Tappi T403Document6 pagesTappi T403Hà Trần MạnhNo ratings yet
- From ETFO PDFDocument3 pagesFrom ETFO PDFToronto StarNo ratings yet
- RS 485 CommunicationDocument50 pagesRS 485 CommunicationJavier Rodriguez100% (2)
- Ipc2012 90580Document7 pagesIpc2012 90580Marcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- Sodium Lauryl SulphateDocument6 pagesSodium Lauryl SulphateIbrahim MoNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Nueva Ecija SDO Guimba East Annex: Annex V. I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesSchools Division of Nueva Ecija SDO Guimba East Annex: Annex V. I. ObjectivesNatividad Jo Ann CuadroNo ratings yet