Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Base Plate Modeling in Staad Pro
Base Plate Modeling in Staad Pro
Uploaded by
Ferdolin EbikOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Base Plate Modeling in Staad Pro
Base Plate Modeling in Staad Pro
Uploaded by
Ferdolin EbikCopyright:
Available Formats
Base Plate Modeling in
STAAD PRO V8i
By
Eng. Ali Albess
YouTube: www.youtube.com/c/alialbess
Blogger: www.ali-albess.blogspot.com
Website: www.ali-albess.weebly.com
22 March 2015
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Introduction:
In normal situations Base plates are designed using codebase procedures (e.g. AISC-ASD). But most
of the times Structural Engineers often run into situations where there are no codes available to design
a particular type of a base plate.
In these situations, an engineer may opt to do a finite element analysis on the base plate. STAAD.Pro
V8i is equipped with a lot of mesh generation and loading tools.
The purpose of this document is to demonstrate how engineers can analyze base plates using
STAAD.Pro V8i.
Exercise Problem:
Create the following base plate geometry in
STAAD.Pro.
Base plate size: 400mmX400mmX14mm
Pipe: Ø100, Wall thickness= 10mm
Stiffener: 150mmX100mm X10mm
Fig. (2): Base Plate Plan
Fig. (1): Isometric Sketch of Base Plate
Fig. (3): Base Plate Stiffener Elevation
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Work Procedure:
1- Open a new STAAD.Pro file using the space option and the units of mm and KN.
2- Name your File
3- Click on the Next button and then click on the Finish button on the following screen.
The STAAD.Pro interface will appear as shown in Fig. (5)
Fig. (5): STAAD.Pro user interface
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
4- Create a new grid. Click on the Create button in the data area. The Linear input box will
appear as shown in Fig. (6)
Fig. (6): Linear grid box
5- Input the parameters as shown in Fig. (6)
6- Click on the Ok button. You will notice the Base plate Entry in the Data Area.
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (7): Base plate Entry in the Data Area
7- Draw the outline of the base plate using beam elements. Press the Snap Node/Beam button in the Data
Area.
Fig. (8): Outline beams created using the grid system
8- Now create the pipe section base plate
9- Click on the Create button in the Data Area.
10- Select the Radial grid option and enter the input parameters as shown in Fig. (9)
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Pipe R=50
Stiffener Length = 150mm
Stiffener Limit = 150+ 50 =200mm
Fig. (9): Circular grid layout for base plate interface.
11- Click on OK button
12- Turn on the R1 grid and the radial grid will appear in the STAAD.Pro graphics window as
illustrated in Fig. (10).
Fig. (10): R1-Radial Grid for Pipe & Stiffener
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
13- Draw the Pipe Perimeters and Stiffener
- Select R1 grid,
- Click on Snap Node/Beam,
- Draw lines as show in Fig. (13)
Fig. (13): Drawing Pipe and Stiffener Base Lines
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig.(14): Drawing Stiffener Lines
14- Drawing the Pipe (Height = 300mm)
- Select the Line representing the Pipe base as shown in Fig. (14)
Fig. (14): Selecting the Lines representing the Pipe Base
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
15- Click on Transitional Repeat and fill the values as show in Fig. (15)
- Global Direction= Y
- No of Steps = 6
- Default Step Spacing = 50mm
(No of Steps X Spacing = 6 x 50 = 300mm (Pipe Height)
Fig. (15): Making Transitional repeat in the Y-direction, for the Pipe Base Plate
16- Click Ok and you get Shape Similar to what in Fig. (16)
Fig. (16): Shape after Transitional Repeat
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
17- Click on (Add beam) and Draw Pipe’s Vertical lines as shown in Fig. (17)
Fig. (17): Pipe Vertical Edge Lines
18- Drawing the Stiffener
Select the Node as Shown in Fig. (18), and click on Transitional Repeat
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (18): Selecting Nodes for Transitional Repeat
19- Fill the 3D Repeat parameters as Shown in Fig. (19)
Fig. (19): Copy Nodes in Y- Direction, Step = 1, Default step spacing = 30mm
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
20- Draw the lines as shown in Fig. (20)
Fig. (20): Adding Beams
21- Select the lines as shown in Fig. (21), and Copy them in the Y- Direction:
- No of Steps = 1
- Default Step Spacing = 100mm (Stiffener Height)
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (21): Transitional Repeat in Y-Direction, Distance = 100mm
22- To Get the Stiffener top Limit:
- Select the new copied lines,
- Click the Right Mouse Button
- Choose Inset Node
- Then Choose: New Node by Distance & Fill Distance = 30mm (as shown in Fig. (22))
Fig.(22): Inserting New Nodes @ Distance = 30mm
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
23- Now Add New Members as Shown in Fig. (23)
Fig. (23): Adding new members
24- Delete the Extra Lines/members
Fig. (24): Shape after Deleting the Extra Lines/ members
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
25- Filling the Pipe Plates:
- Select the Pipe Lines/Members as shown in Fig. (25),
- From Geometry: Select Create Infill Plates
Fig. (25): Selecting the Pipe Members
26- Click Right Mouse Button, Choose Structural Diagram,
- Under View: Choose: Fill Plates/Solids/Surface, You will see a shape similar to Fig. (26)
Fig. (26): Shape after selecting Fill Plates/solid/Surface
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
27- To fill the Stiffener Plates:
- Click on Surface Meshing
- Follow the Same Sequence Shown in Fig. (27)
3
4
2 5
Fig. (27): Sequence of Points to create Surface Meshing
Note: You can choose any other continuous sequence but you shall remember the pints sequence
when filling the Meshing parameters,
See Fig. (28) to understand how we will adjust the meshing parameters
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
No of Divisions = 1
No of Divisions = 4
No of Divisions = 2
No of Divisions = 4
No of Divisions = 1
Fig. (28): Number of division for Mesh adjusting parameters
28- Define Mesh Parameters
After following the mesh sequence shown in Fig. (27), and Keeping in mind the Numbers of
Divisions shown in Fig. (28), Adjust the meshing parameters as show in Fig. (29)
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Line 1 No of Divisions
Line 2 No of Divisions
Line 3 No of Divisions
Line 4 No of Divisions
Line 5 No of Divisions
Fig. (29): Adjusting Meshing parameters
29- Click OK, and your Stiffener Plates Fill will looks like the ones shown in Fig. (30)
Fig. (30): Stiffener’s Filled Plates
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
30- Do the reaming 3- Stiffeners plates filling (using Generate Rotate )
- Before using Generate Rotate, you need 2-Nodes on the Rotation Axis
- Add Two Members as shown in Fig. (31)
- Select the Two new Added Members, Click the Mouse Right Click and Choose Insert Node,
then Choose Add Mid-Point
Fig.(31) Adding Two Members at Bottom & top Bases of the Pipe, with Inserting a Mid-Point
- Click on Plate Cursor
- Select the Stiffener Plates as shown in Fig. (32)
- Click on (Generate – Rotate)
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (32): Selecting the Stiffener Plates
31- Create – Rotate Parameters as shown in Fig. (33), and Click OK
Fig. (33): Generate – Rotate Parameters, Selecting Node 1 & Node 2, Angle = 90, Generate Mode =
Copy
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
The New model will be as shown in Fig. (34)
Fig. (34): Model after applying Generate – Rotate
32- Keep the Plates Selected and Repeat the Generate – Rotate more two times as following
- Click on Generate – Rotate again and adjust the Angle = 180, then OK
- Click on Generate – Rotate again and adjust the Angle = -90, then OK
- The final Shape Shall be Same as shown in Fig. (35)
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (35): The Stiffeners Shape after finishing Generate - Rotate
33- Creating Mesh for the Base Plate
- Click on Generate Surface Meshing Icon
- Flow the sequence shown in Fig. (36)
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
- Number of divisions Between [1] & [2] = 4 (Same No of Stiffener’s Plates]
- Number of divisions Between [2] & [3] = 1 (Same No of Pipe Plates]
- Number of divisions Between [3] & [4] = 1 (Same No of Pipe Plates]
- Number of divisions Between [4] & [5] = 4 (Same No of Stiffener’s Plates]
- Number of Divisions Between [5] & [1] = 6
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
4
2 3
5
Divisions=4
Divisions=1
Divisions=1
Divisions=4
1
Fig.(36): Sequence of Meshing on Base Plate and Number of Divisions
Fig.(37): Generated Mesh on Part of Base Plate
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
34- Complete the Balance Part of Base plate shown in Fig. (38)
Click on Generate Surface Meshing and Follow the Sequence show in Fig. (38), and use number
of divisions as shown in Fig. (39)
1
4
Fig.(38): Sequence of Meshing on Base Plate and Number of Divisions
Fig. (39): Number of Divisions
- Number of divisions Between [1] & [2] = 6 (Same No Plates]
- Number of divisions Between [2] & [3] = 2 (Optional]
- Number of divisions Between [3] & [4] = 8 (Optional]
- Number of divisions Between [4] & [5] = 2 (Optional]
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
The New generated mesh shape will be similar to the one shown in Fig. (4)
Fig.(40): Generated Mesh on Part of Base Plate
35- Select all the plates as shown in Fig. (41),
Fig. (41): Selecting all plates on the base plate
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
36- Click on Generate Mirror Icon. The Mirror Pop menu will appear, Select Mirror Plan X-Y, and
Select a point on the Mirror Surface (Center Node of the Pipe), as shown in Fig. (42), and Click
OK, The opposite site of the plate will be generated.
Fig. (42): Mirror Parameters
Fig. (43): Plate Shape after the mirror
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
37- To do the remaining Two sides, we will use Create – Rotate, adjust the Rotate Parameters as
Shown in Fig. (44)
Fig. (44): Adjusting Mirror Parameters
38- Repeat Create- Rotate again and Use the Angle = -90, all parameters as Shown in Fig. (45)
Fig. (45): Adjusting Mirror Parameters
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (46): Rendered Shape of the Pipe with Base Plate
39- Now we Need to Assign Materials:
- From Geometry , Click on Thickness, and add 3-Plate Thickness as below:
- 14mm: will be used for the Base Plate
- 10mm: will be used for the Stiffeners
- 05mm: Will be used for the Pipe Thickness
Fig. (47): Adding Plate Thickness
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
40- Next Step is to Assing Materials as per the previous Description
- To Select the Base Plates, From Select Menu, choose Select Plates Parallel to X-Z, then
assign the 14mm Thikness
- To select the Pipe Plates, use Select by missing objects propoerties
- Assign the 5mm Plate Thickness to Pipe Plates
Fig. (48): Assigning Plate Thickness (10mm) to Stiffiner Plates
41- Next Step is to Delete unwated Lines which we use to idintify the shape edges
- Select the Beam Cursor
- Select all the shape, and then delete all lines, except the two lines in the center of the Pipe
(at top & Botton as we need to use the cente point when assigning the loads), as shown in
Fig.(49)
- Now Select the Two Center Lines Delete them but Keep the Nodes,
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (49): Selcting & Deleting all unwanted Lines
42- From Spec Tap, Choose Node Specifications, Master/Slave, and Define Node No 89 as Master
Node as shown in Fig. (50), then Click Add
Fig. (50): Define Master/Slave Nodes
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
43- Select the other Nodes as shown in Fig. (51), and Click on Assign
Fig. (51): Assigning Master/Slave Point
44- From Support, Click on Create, and then select Foundation, Define Support as shown in Fig.
(52), then Click on Add
Fig. (52): Defining Foundation Support
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
45- Pick Support 2 from the Supports List, Select the all Base Plate plates, (use Select by plates
parallel to X-Z), then Click on Assign as shown in Fig. (53),
Fig. (53): Assigning Support 2 (Foundation) to Base Plate selected Plates
Loadings:
46- Select the General->Load & Definition control tab on the left.
47- Click on Load Case Details tree item in the Data Area.
48- Click on Add
49- Define a load case and name it as: DEAD LOAD + WIND Load, as shown in Fig. (54), then Click
on Add
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (54): Defining a Load Case: Dead Load + Wind Load
50- Under the defined load case (Dead Load + Wind Load) add the below listed Load Cases
- Self-weight Y-1
- Nodal Load (as shown in Fig. (55)
Notes:
a- Self-weight: will include the base plate weight
b- Nodal Load: This represents the reaction on the support, taken from the Full Staad Model of
the whole Structure you are designing.
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (55): Defining the Nodal Load, Fy= -25 KN, Mx= 5 KNm
51- Assign the Nodal Load:
- Select the Nodal Load case, Select the master Node at top of the Pipe, and click assign, as
shown in Fig. (56)
Fig. (56): Assigning the Nodal Load to the Master Node
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
52- Now you assigned load shall be same as shown in Fig. (57)
Fig. (57): Assigned Nodal Load on Master Node
53- Select Analysis/ Print, Define Analysis type, Click on Add
54- Performa Analysis
55- Go toe Post processing
56- Check the design analysis
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
Fig. (58): Design Analysis: Node displacement (Resultant)
Note: you can do necessary modifications to your designed plate to get reasonable results, For
Example if you want to reduce the Node Displacement (Plate Deflection) increase the base Plate
Thickness
Eng. Ali Albess, www.youtube.com/c/alialbess , Email: albessali@gmail.com, www.ali-albess.weebly.com
You might also like
- Reading Questions - Science and BeautyDocument3 pagesReading Questions - Science and BeautyEllen Lam100% (1)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GroundControlforUndergroundMines PDFDocument72 pagesGroundControlforUndergroundMines PDFJannela yernaiduNo ratings yet
- Staad TutorialDocument58 pagesStaad TutorialSritoko83% (6)
- ABAQUS - Tutorial Cantilever BeamDocument24 pagesABAQUS - Tutorial Cantilever BeamShadiNo ratings yet
- Keysight ADS Example Book CH 04 - Planar Electromagnetic (EM) Simulation in ADS 5992-1479Document27 pagesKeysight ADS Example Book CH 04 - Planar Electromagnetic (EM) Simulation in ADS 5992-1479jumper_bonesNo ratings yet
- ETABS-Example-RC Building - Equivalent Special SeismicDocument83 pagesETABS-Example-RC Building - Equivalent Special Seismicdilrangi100% (17)
- Structural Steel Detailing Practices - Good and BadDocument15 pagesStructural Steel Detailing Practices - Good and Badzeek77No ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers McqsDocument56 pagesCircuit Breakers McqsEngrAneelKumarAkhani79% (14)
- MT Unit 4 LeachingDocument72 pagesMT Unit 4 Leachinglavanya thanigaiNo ratings yet
- Wave - TutorialDocument59 pagesWave - TutorialJacob Dodson100% (1)
- Orion 18 TutorialsDocument77 pagesOrion 18 TutorialsSamuel Antobam78% (9)
- Hecsalv Ship Design SoftwareDocument37 pagesHecsalv Ship Design SoftwareAhmed Elhewy100% (1)
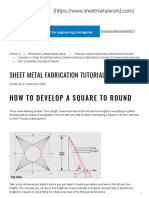
- Square To Round DuctDocument6 pagesSquare To Round DuctDtl Saroz100% (1)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Sheet Metal Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Sheet Metal Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- A Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsFrom EverandA Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsNo ratings yet
- Root Locus Design Using MATLABDocument19 pagesRoot Locus Design Using MATLABMatlabAsignmentExpertsNo ratings yet
- 3D Modelling Practice ModelsDocument19 pages3D Modelling Practice Modelsprateekg92No ratings yet
- Learn Flat Slab-Flat Slab Analysis Design and Drawing SoftwareDocument137 pagesLearn Flat Slab-Flat Slab Analysis Design and Drawing SoftwareWanda BeasleyNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2016 and AutoCAD LT 2016 No Experience Required: Autodesk Official PressFrom EverandAutoCAD 2016 and AutoCAD LT 2016 No Experience Required: Autodesk Official PressRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Base Plate Modelling Using Staad Pro 200Document28 pagesBase Plate Modelling Using Staad Pro 200Maha Moddather Hassan100% (1)
- Axially Loaded Columns - Base Plate DesignDocument2 pagesAxially Loaded Columns - Base Plate DesignaomareltayebNo ratings yet
- What Is TeaDocument12 pagesWhat Is TeaMilen PeninNo ratings yet
- Tutorial AbaqusDocument24 pagesTutorial AbaqusWalter MendezNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D - Roads Design: 2From EverandAutoCAD Civil 3D - Roads Design: 2Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Propped Cantilever Beam Tutorial Abaqus FinalDocument36 pagesPropped Cantilever Beam Tutorial Abaqus FinalINME0% (1)
- Composite OEM and Replacement ScreensDocument6 pagesComposite OEM and Replacement ScreensShamsulamri SamsirNo ratings yet
- OHG M&E Performance Specification - V2Document199 pagesOHG M&E Performance Specification - V2DONGTA123100% (1)
- Axial+Bending+Torsion+Combined+Buckling Analysis of A Beam (Abaqus Cae) JasDocument57 pagesAxial+Bending+Torsion+Combined+Buckling Analysis of A Beam (Abaqus Cae) JasWares Chancharoen67% (3)
- How To Calculate Basic Pitch TimeDocument3 pagesHow To Calculate Basic Pitch TimealaminNo ratings yet
- 7 Drawing in ExcelDocument6 pages7 Drawing in ExcelstarspleshNo ratings yet
- ABAQUS Tutorial 12 PDFDocument36 pagesABAQUS Tutorial 12 PDFkkkrajaNo ratings yet
- I Generalised BeamDocument36 pagesI Generalised BeamErnest NsabimanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 400 - OcrDocument40 pagesLesson 8 400 - Ocrapi-241156742No ratings yet
- EAGLE Introduction TutorialDocument9 pagesEAGLE Introduction Tutorialady_marinescuNo ratings yet
- Base Plate DesignDocument1 pageBase Plate DesignmadodandembeNo ratings yet
- Modeling A Mixing Elbow (2-D) : 2.1 PrerequisitesDocument34 pagesModeling A Mixing Elbow (2-D) : 2.1 Prerequisitesangusyoung1No ratings yet
- Staad TutorialDocument59 pagesStaad TutorialglbforuNo ratings yet
- Full Custom IC Design Flow NewDocument59 pagesFull Custom IC Design Flow NewAKSHAY SONARNo ratings yet
- Design of A Steel Structure SAFIDocument55 pagesDesign of A Steel Structure SAFIÉmilie RiverinNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Plate With Stress Concentrations (Abaqus)Document26 pagesAnalysis of A Plate With Stress Concentrations (Abaqus)mailtoswaroopNo ratings yet
- ACAD Tut - LinesDocument11 pagesACAD Tut - LinesJeesonAntonyNo ratings yet
- Open Flows Editor Module Manual2023Document31 pagesOpen Flows Editor Module Manual2023Vivek KasarNo ratings yet
- DM 12 CH08 Concept Modeling WS1Document16 pagesDM 12 CH08 Concept Modeling WS1Aham GtyNo ratings yet
- Full Custom Ic Design Flow UpdatedDocument60 pagesFull Custom Ic Design Flow UpdatedASHISH KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Bridge Continuous GirderDocument35 pagesBridge Continuous GirderGinald SantosNo ratings yet
- 2 - Subframe and EngineDocument20 pages2 - Subframe and EngineminhnguyenvonhatNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics Practical FileDocument21 pagesFracture Mechanics Practical Filesubashish100% (1)
- Taper Maker, Curve Maker and Stock Maker Plugins For SketchupDocument42 pagesTaper Maker, Curve Maker and Stock Maker Plugins For SketchupFernando BarrientosNo ratings yet
- ETABS - To Start OffDocument15 pagesETABS - To Start OffChai Weng KuakNo ratings yet
- Vis BeamContours Slides Abaqus611Document5 pagesVis BeamContours Slides Abaqus611anastasiosNo ratings yet
- EtabsDocument8 pagesEtabsRavi MalikNo ratings yet
- Final 5Document29 pagesFinal 5qaiserNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On SAP2000Document21 pagesTutorial On SAP2000Xet FatNo ratings yet
- Designing A SwitchbackDocument23 pagesDesigning A SwitchbackEnrique Cruz Checco100% (1)
- Making 3D Threads in Solidworks 2009Document16 pagesMaking 3D Threads in Solidworks 2009Quiqua Acosta Fonseca0% (1)
- Etabs Lecture 1Document10 pagesEtabs Lecture 1morphie_blackNo ratings yet
- F.E.M Lab Manual: Submitted By:-Qazi Samie Saeed 10-ME-120 Section - C Group - C2Document12 pagesF.E.M Lab Manual: Submitted By:-Qazi Samie Saeed 10-ME-120 Section - C Group - C2Qazi Samie SaeedNo ratings yet
- Abaqus - FEA of A Cantilevered BeamDocument23 pagesAbaqus - FEA of A Cantilevered BeamIvanadoNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks AssignmentsDocument4 pagesSolidWorks AssignmentsmukeshysNo ratings yet
- Solid Edge - Tund8Document30 pagesSolid Edge - Tund8Edmund Laugasson100% (4)
- Tutorial PypeDocument10 pagesTutorial PypeEnrique BlancoNo ratings yet
- Getting Started Abaqus Appendix CDocument63 pagesGetting Started Abaqus Appendix Ckrongdak100% (1)
- AutoCAD 2015 and AutoCAD LT 2015: No Experience Required: Autodesk Official PressFrom EverandAutoCAD 2015 and AutoCAD LT 2015: No Experience Required: Autodesk Official PressNo ratings yet
- Autodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressFrom EverandAutodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Modeling and Simulation of Logistics Flows 3: Discrete and Continuous Flows in 2D/3DFrom EverandModeling and Simulation of Logistics Flows 3: Discrete and Continuous Flows in 2D/3DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Operation ManagementDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Operation ManagementAnn BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Finance Project On WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENTDocument82 pagesSummer Training Finance Project On WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENTPravin chavda100% (2)
- PublicationDocument56 pagesPublicationAlvarin CsboyNo ratings yet
- Months Deman D 3-Month MA WMA (0.6, 0.3, 0.1) ES (Alpha 0.2)Document7 pagesMonths Deman D 3-Month MA WMA (0.6, 0.3, 0.1) ES (Alpha 0.2)ABHIRUP DATTANo ratings yet
- GroundhogDay ReflectionDocument2 pagesGroundhogDay ReflectionRenelie FarangaoNo ratings yet
- Snap Vocab - Compiled From PyqsDocument17 pagesSnap Vocab - Compiled From PyqsNair SajithNo ratings yet
- Guidelines ProbioDocument1 pageGuidelines Probiomisbah ijazNo ratings yet
- TICO Pipe SupportsDocument8 pagesTICO Pipe SupportsEjeantengNo ratings yet
- The Changing Profile of Social DeathDocument26 pagesThe Changing Profile of Social DeathCrystal LegionairesNo ratings yet
- Steelwork in Action 11Document11 pagesSteelwork in Action 11bachNo ratings yet
- OPS12 - Operational ReportDocument5 pagesOPS12 - Operational ReportEmre AlgülNo ratings yet
- Rig To Reef and Rig To Fish Farm CourseDocument20 pagesRig To Reef and Rig To Fish Farm Coursesaefulloh misbahudinNo ratings yet
- NP 2.0 LabsDocument7 pagesNP 2.0 Labsajei xiaoNo ratings yet
- Service and Maintenance Instructions: Residential Fan Coil UnitsDocument32 pagesService and Maintenance Instructions: Residential Fan Coil UnitsBrayandPachNo ratings yet
- Users Manual For Oslo, Bremen and Turboaire.: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsDocument40 pagesUsers Manual For Oslo, Bremen and Turboaire.: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructionsbuttler25No ratings yet
- Biju Patnaik University of Technology: Mechanical EngineeringDocument37 pagesBiju Patnaik University of Technology: Mechanical EngineeringBhagaban Das100% (1)
- Manual de Serviço TV LG 15LS1RA MK Chassis LN71A PDFDocument24 pagesManual de Serviço TV LG 15LS1RA MK Chassis LN71A PDFanon_942038258100% (1)
- Download full chapter The First Institutional Spheres In Human Societies Evolutionary Analysis In The Social Sciences 1St Edition Abrutyn pdf docxDocument54 pagesDownload full chapter The First Institutional Spheres In Human Societies Evolutionary Analysis In The Social Sciences 1St Edition Abrutyn pdf docxmarcus.stassinos948No ratings yet
- AngulDocument167 pagesAngulPartha Pratim BiswasNo ratings yet
- Tourism Management: Liguo Wang, Yukio Yotsumoto TDocument13 pagesTourism Management: Liguo Wang, Yukio Yotsumoto TRezza Bagus Afif AmanaNo ratings yet
- ETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ACI 318-11 Beam Section DesignDocument1 pageETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ACI 318-11 Beam Section DesignstatikaNo ratings yet
- 2 Measures, Perimeter and Area: For Key Stage 3Document4 pages2 Measures, Perimeter and Area: For Key Stage 3Sheena ThorneycroftNo ratings yet
- CDSCO Daily Today Letter 06 - 04 - 2015Document5 pagesCDSCO Daily Today Letter 06 - 04 - 2015Meghal MistryNo ratings yet