Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditional Sentence and Conditional Conjunctions
Uploaded by
NCD NAWADA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesConditional Sentence and Conditional Conjunctions
Uploaded by
NCD NAWADACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Conditional Sentences &
Conditional Conjunctions
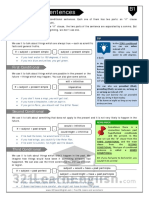
What is a Conditional Sentence?
A conditional sentence is a sentence that denotes a
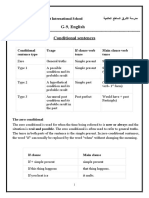
condition. Like, “If you want to succeed, work hard.” Conditionals If-Clause/ Principal Clause
0th (zeroth) Present Present Indefinite
In the sentence above, you can see that it expresses a Indefinite (V1) (V1)
condition for succeeding. 1st Present Future Indefinite
And what is that condition? Yes, it’s working hard. Indefinite (V1) (Will + V1)
2nd Past Indefinite Would + V1
(V2)
Structure of a Conditional Sentence:
3rd Past perfect (had Would have + V3
All the conditional sentences have two clauses –
+ V3)
i. The principal clause.
ii. A subordinate clause (the If-clause),
Zeroth Conditional Sentences:
E.g. – 0th conditional sentences express general truths. It
• If I had an extra umbrella, I would lend it to means if one thing happen, the other thing also
you. happens as a result of the first.
In the sentence above, the first part “If I had an extra
Look at the following examples –
umbrella” is the subordinate clause, while the
second part “I would lend it to you” is the principal
• If you boil water to 100°C, it gets vapoured.
clause. • If I don’t drink water, my body becomes
dehydrated.
Moreover, both the clauses are joined by a • If you cut the branches of a tree, they grow again.
conjunction called conditional conjunction. In the • If we don’t make noise, our teachers don’t
above instance, the conjunction is If. scold us.
• The price increases, if the demand increases.
What are Conditional Conjunctions?
Conditional conjunctions are the conjunctions used to Syntax:
join two clauses to form a conditional sentence. The We have learnt that the verb of the principal clause is
most commonly used conditional conjunction usually in future tense. But, to express habitual action
is If. However, there are many of them, such and result, the verb of the principal clause is used in
as, unless, until since, lest etc. other than that. present tense.
1st Conditional Sentences:
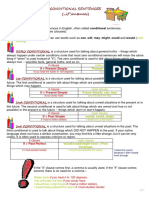
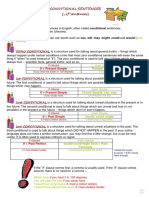
Types of Conditional Sentences: The 1st Conditional Sentences express possible /
How many types of conditional sentences are there? realistic imaginations in the future.
There are mainly 4 types of conditional sentences. E.g. – If she comes, John will tell her everything.
Zero 1st 2nd 3rd Syntax:
Conditional Conditional Conditional Conditional If clause with a verb in present tense. And the main
Expresses Expresses Expresses Expresses clause with a verb in the future (shall/will + V1).
general realistic Unrealistic Unrealistic
truth imaginations imaginations imaginations
in the future. in the future. in the past. If + subject + verb (present tense) + object + , +
subject 2 + will/shall + verb + object.
Let’s explain one by one – More examples –
• If it rains, I’ll use an umbrella.
• I shall not buy you chocolates if you don’t listen
to me.
2nd Conditional Sentences: 3rd Conditional Sentences:
The 2nd Conditional Sentences express impossible 3rd conditional sentences are used to express that the
unrealistic imagination in the future. present circumstances would have been different if
E.g. – If I had a pen I would give it to you something different had happened in the past.
For example–
Structure – • If you had worked hard, you would have
If + subject + Verb 2 + object + , + subject + would + succeeded.
verb 1 + object.
The sentence states a condition that if someone had
worked hard, he would have succeeded. But in reality
Remember this conditional sentence expresses
he did not do that and so he didn’t succeed.
unrealistic imagination of the future, though the past
More such examples are as follows. –
form of the verb (verb 2) is used in the if-clause.
• If I had known the answer, I would have told you.
(But I didn’t know the answer.)
Other examples – • If she had been present here, she would have
• If I won a lottery, I would buy a new car. helped us. (But she was not present there).
• If John worked hard, he would pass the exam. • His father would have been upset if he had found
• If we played the first round well, we would you there. (But his father didn’t find him there.)
qualify for the final.
• If the man got the job, he would be very
Exception:
happy.
When the verb of the main clause is in past
use subject + had + V3 after if, if only, as if, as
Exception: though, I wish, we wish etc.
Sometimes, 2nd conditional also express unrealistic For example,
imagination of the present. • The man talked as if he had known everything.
In the sentence above you can see that the verb used
For this, the subordinate clause starts with some in the main clause, in in past tense (talked). For this
phrases like if only, as though, as if, I reason, the verb of the subordinate clause is in past
wish ('if' too) etc. is followed by (subject + perfect.
V2) or (subject + were), then the verb used in the
main clause, should be in the past. Other examples:
• She acted as though she had drunk.
E.g. – • I wish, I had been a bird.
• If I had been the president, I put all of them
• Her father talks as though he knew everything. behind bars.
If you analyse the sentence above, you can find that
the subordinate clause is starting with 'as though' one
of the phrases.
Inversions of the 3rd conditional
And the verb used after the phrase, is un past (knew), sentences:
unlike the 2nd Conditional rule where would + V1 is Now here comes tricky part. We, as students, are
used. often confused when they come across sentences
starting with auxiliary verbs like had, were etc.
Structures: Actually they all are 3rd conditional sentences with
Main clause + one of the phrases + subject + verb 2 + inversions of the structures.
object.
Or, Let's look at the table below and see how they are
One of the phrases + subject + verb 2 + object + Main inverted.
clause. 3rd Conditional Its Inversions
(Mainly these two structures are followed. There are Structures
several variations of it.) If + subject + had + V3, Had + subject + V3, ...
...
More examples: If + subject + had been + Had + subject + been +
object object
If + subject + were + Were + subject + object
• I wish I went to a hill-station.
object.
• If I were a horse, I would run to my mother.
• She acts as if she were the president.
• The people will raise their voices only if their
Examples: personal interests are involved.
• If I were the President – Were I the president.
• If you were I – Were you I.
• If I had been a bird – Had I been a bird. Even if:
Meaning: Despite of anything to the contrary.
Sentences:
• Even if john doesn’t join us, we’ll still visit
that place.
• She gives her best even if the most difficult
Conditional conjunctions: task is assigned to her.
• Even if you apologise, I won’t talk to you.
Conditional conjunctions are the conjunctions used to
join two clauses to form a conditional sentence. The
most commonly used conditional conjunction Unless:
is If. However, there are many of them, such Meaning: Unless = If + not
as, unless, until since, lest etc. other than that. Sentences:
Unless you work hard, you won’t get success.
We can divide them into two Unless you work hard = If you don’t work hard.
- affirmative and negative. • I won’t give you chocolates unless you finish
your homework.
Affirmative conditional conjunctions include if, since, • Emma will not stay here unless she gets a
only if, when etc., while the negative conditional room of her choice.
conjunctions include until, unless (if + not), lest and
so on.
Until:
Use of some Conditional Conjunctions: Meaning: Up to, before the time.
Sentences:
• We shall wait until the train arrives.
If: • Sleep until it gets light.
Meaning: In case • We don’t know what is good until we lose it.
Sentences:
• If you practise well, you can perform well.
• I will go to the college if I can afford it.
Lest:
• If she has come tell her to take her book.
Meaning: In order to prevent, for fear that.
Sentences:
• He tiptoed lest his mother should hear her.
If only: • I ran fast lest I should be caught.
Meaning: Never except when... • Dayna hurried lest she should be late again.
• Lest I forget I note everything taught in the
Sentences:
class.
• I would have cleared the exam if only I had
studied smartly.
• If only you listened to my words, you would
perform well. Whether:
• She will come here again if only you ask her Meaning: Expressing doubt or choice between
to come alternatives.
Sentences:
• She spent all her money on her car whether it
Only if: was smart or not.
Meaning: Never except when... • I doubt whether John will pass or not.
Sentences: • I will go to the party whether you like it or
not.
• Call me only if you face difficulties solving
this math problem.
• Only if you came here, you would see what
was going on. Once:
Meaning: As soon as / when
Sentences: But for:
• Once it stops raining, you will go out to play. Meaning: without
• I will put off my hills once I reach home. Sentences:
• We will go for a trip once my examination is • You would have been be ruined but for your
over. brother’s help.
• But for your notes I would fail.
After: • But for her advice I would not get the job.
Meaning: In the following period o time.
Sentences:
• We all went home after the match had been Therefore:
finished. Meaning: Consequently
• Bella would start reading the news paper after Sentences:
she finished her breakfast. • You did not attend the class, therefore you
• The soldiers began to march after the sun could not understand this chapter.
rose. • It was raining in the afternoon therefore we
could not play.
• She contributed a lot in the field of
Since: Radioactivity therefore she was honoured
Meaning: On account of / for the reason that with Nobel Prize.
Sentences:
• Since you’re my friend, I shall not leave you
in adversity. Provided:
• You have to stay home since its raining.
Meaning: On condition that
• Since it's Sunday our school will remain
Sentences:
closed.
• I shall go provided I can wear what I like.
• You will get the job provided You will work
honestly.
As:
• She will lead you provided you will be
Meaning: on account of / for the reason that.
respectful to her.
Sentences:
• As you didn’t repay your previous loan, you
won’t get another.
• Hardly anybody could see the old man as he Providing:
was sitting in the darkest corner of the room. Meaning: On condition that / only if
• As she was ill she could not attend the Sentences:
meeting. • We will take you in our team providing you
will respect the captain.
Yet: • It is easier to get good marks on a short
Meaning: in spite of it answer, providing you do it well.
Sentences: • People have every right to lead their lives in a
way they want, providing they ate not hurting
• Emma waited for you so long, yet you call her
someone else.
selfish.
• She was cheated, yet she loves him as before.
• I could not go out of the room all the day, yet
I had a very good time alone. Given that:
Meaning: Although / assuming that
Sentences:
Because : • John didn't selected for the post given that
Meaning: On account of / for the reason that (although) he was preparing hard for that.
• You can get the loan, given that you can
Sentences:
repay it within six months.
• Because the employee worked very hard for
the company, she was promoted.
• Jack could not come last Sunday because he
was not well.
• Because he accused of murdering someone,
he was arrested.
You might also like
- STIHL TS410, TS420 Spare PartsDocument11 pagesSTIHL TS410, TS420 Spare PartsMarinko PetrovićNo ratings yet
- Risk Response PlanDocument8 pagesRisk Response Planapi-639207174No ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsPetra StefanescuNo ratings yet
- VDA Volume Assessment of Quality Management Methods Guideline 1st Edition November 2017 Online-DocumentDocument36 pagesVDA Volume Assessment of Quality Management Methods Guideline 1st Edition November 2017 Online-DocumentR JNo ratings yet
- Conditional TensesDocument3 pagesConditional TensesMuhammad yousafNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsDocument28 pagesHydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsFelipe Pisklevits LaubeNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechDocument22 pagesActive and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechTrịnh Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- Conditionals PDFDocument10 pagesConditionals PDFMARNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Zero FirstDocument21 pagesConditional Sentences Zero FirstJosé Henrique Tobias PereiraNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ProjectDocument7 pagesConditionals ProjectIon PopescuNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsКоля МогильниковNo ratings yet
- Modul Pre IntermediateDocument40 pagesModul Pre IntermediateSomad BotNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Type Patterns DescriptionDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences: Type Patterns DescriptionYoga PramudanaNo ratings yet
- Conditionalsclass MethodDocument11 pagesConditionalsclass MethodAlejandro J Oquendo MNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONAL Sentences All TypesDocument9 pagesCONDITIONAL Sentences All TypesMaríaEstelaVinellaNo ratings yet
- Conditionalsandwishes 160420081955Document47 pagesConditionalsandwishes 160420081955Ali Chahin100% (1)
- CONDITIONALSDocument23 pagesCONDITIONALSherz eliNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseDocument8 pages2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseArmeliaNo ratings yet
- Materi - Conditional Sentence + Exercises (1-3)Document11 pagesMateri - Conditional Sentence + Exercises (1-3)bae chuNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesConditional Sentencesabdellah dandoumNo ratings yet
- Tiene Error Ejemplo Final 321LearnEnglish Com Grammar Conditional Sentences Intermediate b1Document1 pageTiene Error Ejemplo Final 321LearnEnglish Com Grammar Conditional Sentences Intermediate b1Malory LizarazoNo ratings yet
- L6 Grammar - ConditionalsDocument7 pagesL6 Grammar - ConditionalsLaury CarrollNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsJaunius AugustisNo ratings yet
- Future Events or Situations (That Will Happen, or Are Likely To Happen) and Their Possible or Likely ResultsDocument7 pagesFuture Events or Situations (That Will Happen, or Are Likely To Happen) and Their Possible or Likely ResultsbelbachirNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsentenseDocument9 pagesConditionalsentenseyahaha.hayyun1No ratings yet
- Generally True, Especially For Laws and Rules: (Propoziția Principală)Document1 pageGenerally True, Especially For Laws and Rules: (Propoziția Principală)Ioana LipanNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence 0 and 1Document17 pagesConditional Sentence 0 and 1exuuu698No ratings yet
- Tugas Makalah B InggrisDocument12 pagesTugas Makalah B InggrisLuthfiana KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Docente:Mg María Luz Murguía FloresDocument8 pagesDocente:Mg María Luz Murguía Floresjuan padillaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document1 pageConditional Sentences 1Bozhidara KaragyozovaNo ratings yet
- First ConditionalDocument1 pageFirst ConditionalNataly CimeNo ratings yet
- Conditional Type 1,2,3: Group 4Document21 pagesConditional Type 1,2,3: Group 4Starting For FOLLOWNo ratings yet
- If Clause Group 5Document24 pagesIf Clause Group 5FauzanNo ratings yet
- Conditional-Easy ExplanationDocument1 pageConditional-Easy ExplanationFernanda Shine SantosNo ratings yet
- If Clause Type 0,1,2,3Document26 pagesIf Clause Type 0,1,2,3Jenn LNo ratings yet
- GrammaR LessonDocument24 pagesGrammaR LessonLettie MilesNo ratings yet
- A'la Faradisil Jannah Rangkuman Sasing Bab 1-5Document13 pagesA'la Faradisil Jannah Rangkuman Sasing Bab 1-5A'la Faradisil Jannah XI MIPA 3No ratings yet
- Lecture 1st QuarterDocument43 pagesLecture 1st QuarteremailqsacignalplayNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clauses: Type ConditionDocument12 pagesConditional Clauses: Type ConditionFranz ThereNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument17 pagesConditional SentencesQyuBeeNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureDocument7 pagesType 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Group5 - 22HcbDocument73 pagesEnglish Grammar: Group5 - 22HcbThiện HoàngNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggri 1Document15 pagesBahasa Inggri 1masayususanti62No ratings yet
- Conditional and WishesDocument7 pagesConditional and WishesInesa SadlauskaiteNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Group 4Document8 pagesConditional Sentences Group 4Dwi RahmaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConditional SentencesAdelia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument12 pagesConditional Sentencesniko_blue55No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Reading Comprehension English Smart Book BBA - 103 Courseware PatronusDocument1 pageChapter 12 Reading Comprehension English Smart Book BBA - 103 Courseware PatronusRashed RomanNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences in Englis Fix 112027Document3 pagesConditional Sentences in Englis Fix 112027adittyapratamaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFDocument15 pagesConditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFUmu NeroNo ratings yet
- PEL 130 Lecture 2Document19 pagesPEL 130 Lecture 2soumyosishpal.108No ratings yet
- Zero SuperstitionDocument2 pagesZero SuperstitionLUCIANO RIVERANo ratings yet
- Grammar PartsDocument8 pagesGrammar Partsfirewyimer921No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGrace Gesto RubillosNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 - ConditionalDocument7 pagesMeeting 3 - ConditionalIkram Wahyu PratamaNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- 07 CONDITIONAL - RevDocument20 pages07 CONDITIONAL - RevBima Dwi Priya SNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliNo ratings yet
- Conditionalsentencesif 100413210036 Phpapp01Document15 pagesConditionalsentencesif 100413210036 Phpapp01ChristineNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument8 pagesConditional SentenceTamiê PagesNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConjunction and Conditional SentencesRahmatia Candra DewiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Using ConditionalsDocument19 pagesLesson 4 Using ConditionalsZaren James D. RacaNo ratings yet
- Framing Questions Yes-No and WHDocument10 pagesFraming Questions Yes-No and WHNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- Composition Levy SchemeDocument2 pagesComposition Levy SchemeKumariNo ratings yet
- AkbarpurDocument7 pagesAkbarpurNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- Kawako LDocument7 pagesKawako LNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- Kawako LDocument7 pagesKawako LNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Current and Resistance: 5.1 The Motion of Electric ChargeDocument11 pagesChapter 5: Current and Resistance: 5.1 The Motion of Electric Chargeayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- Pyle 4ch Marine BTDocument4 pagesPyle 4ch Marine BTRafael VieiraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62EffNo ratings yet
- Hasan Bin Ekram: Career ObjectiveDocument3 pagesHasan Bin Ekram: Career ObjectiveHasan SarikNo ratings yet
- Porifera and CnidariaDocument16 pagesPorifera and CnidariaMichaelNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Online Games To The AcademicDocument20 pagesThe Impact of Online Games To The AcademicJessica BacaniNo ratings yet
- Second Language Learning in The Classroom PDFDocument2 pagesSecond Language Learning in The Classroom PDFThanh Phương VõNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics of SoilDocument26 pagesPhysical Characteristics of SoillfpachecoNo ratings yet
- Norm ANSI PDFDocument1 pageNorm ANSI PDFAbdul Quddus Mat IsaNo ratings yet
- What Role Does Imagination Play in Producing Knowledge About The WorldDocument1 pageWhat Role Does Imagination Play in Producing Knowledge About The WorldNathanael Samuel KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Assignment OSDocument11 pagesAssignment OSJunaidArshadNo ratings yet
- The Two Diode Bipolar Junction Transistor ModelDocument3 pagesThe Two Diode Bipolar Junction Transistor ModelAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Btech CertificatesDocument6 pagesBtech CertificatesSuresh VadlamudiNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Thermal Pre-Hydrolysis For Operational Performance of Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocument7 pagesBenefits and Drawbacks of Thermal Pre-Hydrolysis For Operational Performance of Wastewater Treatment PlantsmartafhNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Course Syllabus (2023) - SignedDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability Course Syllabus (2023) - SignedDarence Fujihoshi De AngelNo ratings yet
- The Elder Scrolls V Skyrim - New Lands Mod TutorialDocument1,175 pagesThe Elder Scrolls V Skyrim - New Lands Mod TutorialJonx0rNo ratings yet
- 555 TimerDocument25 pages555 TimerDr-Muhammad Aqeel AslamNo ratings yet
- Hssive-Xi-Chem-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Q & ADocument11 pagesHssive-Xi-Chem-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Q & AArties MNo ratings yet
- Splash25 Winner InstructionsDocument8 pagesSplash25 Winner InstructionsRamkrishna PaulNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers DSPs S10Document16 pagesMicrocontrollers DSPs S10Suom YnonaNo ratings yet
- Cooperative LinuxDocument39 pagesCooperative Linuxrajesh_124No ratings yet
- Mge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFDocument38 pagesMge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFRafa TejedaNo ratings yet
- Dosificación Gac007-008 Sem2Document2 pagesDosificación Gac007-008 Sem2Ohm EgaNo ratings yet
- Emulsion LectureDocument30 pagesEmulsion LectureRay YangNo ratings yet
- Outbound Idocs Code Error Event Severity Sap MeaningDocument2 pagesOutbound Idocs Code Error Event Severity Sap MeaningSummit YerawarNo ratings yet
- Vialyn Group ResearchDocument17 pagesVialyn Group ResearchVial LynNo ratings yet