Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HISTORY Classwork 15.03.2024
HISTORY Classwork 15.03.2024
Uploaded by
mittal.rohan2010Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HISTORY Classwork 15.03.2024
HISTORY Classwork 15.03.2024
Uploaded by
mittal.rohan2010Copyright:
Available Formats
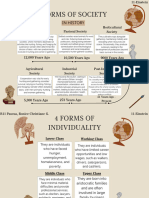
Aspect Working Class Middle Class Upper Class
Factory workers, mill
Professionals (doctors,
workers, domestic Clerks, shopkeepers,
lawyers), landowners,
servants. For example, in small business owners.
Occupations, aristocrats. For example,
1851, 2 million people in In 1851, there were about
Jobs, and the aristocracy comprised
England and Wales worked 900,000 shopkeepers
Careers less than 1% of the
in agriculture, while 1.25 and clerks in England
population but owned
million worked in textile and Wales.
about 25% of the land.
factories.
Semi-detached houses,
Cramped, back-to-back Large estates, mansions,
small apartments. By the
terraced housing. For townhouses. For example,
late 19th century,
instance, in 1851, a survey in 1851, only 3% of houses
Housing suburban housing
found that in Manchester, 1 in London were considered
developments were
in 5 houses had only one high-class, but they
emerging for the middle
room. occupied 17% of the land.
class.
Cramped and quickly built More substantial Grand, imposing
houses. Many housing, sometimes with architecture. Upper-class
working-class ornate features. residences were often
Architecture
neighborhoods lacked Middle-class homes large, elaborate structures,
proper sanitation and were often featured decorative showcasing the wealth
overcrowded. elements and were built and status of their owners.
with more durable
materials.
Some rights and
Limited rights and Extensive rights and
freedoms, participation
freedoms, little political freedoms, significant
in local government.
power. Working-class political power. The upper
Rights and Middle-class individuals
individuals had minimal class wielded considerable
Freedoms had more influence in
say in political matters and influence in national
local politics and greater
were often subject to politics and enjoyed
access to legal
exploitation by employers. various legal privileges.
protections.
Limited voting rights, often Some voting rights, Extensive voting rights,
excluded from political involvement in local participation in national
participation. For example, politics. The Reform Act politics. The
the Reform Act of 1832 of 1867 further expanded Representation of the
Political Rights
extended the franchise but suffrage, granting voting People Act of 1884 further
still excluded many rights to male extended suffrage, giving
working-class people from householders and certain many more men the right
voting. renters. to vote.
Some labor protection,
Often subject to poor Benefited from favorable
improvements in working
working conditions, lack of legislation, minimal labor
Laws, Acts, and conditions. The Factory
protective labor laws. regulation. Upper-class
Legislation Acts of the 19th century
Working-class individuals interests often influenced
introduced regulations
faced harsh working legislation, resulting in
on child labor, working
conditions and minimal hours, and workplace fewer regulations and
legal protections. safety. protections for workers.
Limited access to Access to basic Access to quality
education, children often education, emphasis on education, often private
worked instead. The literacy and numeracy. tutors or prestigious
Education Act of 1870 Middle-class children schools. Upper-class
Education established elementary had greater access to children received the best
education for formal education, often education, often through
working-class children, but attending grammar private tutors or
many still had to work to schools or private attendance at elite
support their families. academies. boarding schools.
More varied clothing, High-quality, fashionable
Basic, functional clothing.
reflecting social status. clothing. The upper class
Working-class attire was
Middle-class clothing wore expensive,
practical and affordable,
Clothing was more varied and of fashionable clothing made
often consisting of simple
better quality, reflecting from luxury materials,
garments made from
the social status and showcasing their wealth
inexpensive materials.
aspirations of the wearer. and status.
Better quality and variety, Gourmet cuisine, access
Simple, affordable fare
ability to afford luxuries. to exotic foods. The upper
such as bread and
Middle-class families class had access to the
porridge. Working-class
enjoyed a more varied finest foods and dining
Food diets were often basic and
diet, with access to a experiences, including
focused on inexpensive
wider range of foods gourmet cuisine and exotic
staples like bread, porridge,
including meat, dairy, and imports from around the
and potatoes.
imported goods. world.
You might also like
- The Gilded Age Review Flow Chart: WhenDocument6 pagesThe Gilded Age Review Flow Chart: WhenJxjxh100% (1)
- Why A Right To Housing Is Needed and Makes Sense: Editors' IntroductionDocument23 pagesWhy A Right To Housing Is Needed and Makes Sense: Editors' IntroductionMatthew WylieNo ratings yet
- The Wealth HoardersDocument56 pagesThe Wealth HoardersforbesadminNo ratings yet
- Chibi Alpaca Pattern From La PandustriaDocument4 pagesChibi Alpaca Pattern From La PandustriaCamila Eduarda100% (1)
- Knife PleatsDocument13 pagesKnife PleatsNessy Carry Fly100% (1)
- Brenda Polan, Roger Tredre-The Great Fashion Designers-Bloomsbury Academic (2009)Document273 pagesBrenda Polan, Roger Tredre-The Great Fashion Designers-Bloomsbury Academic (2009)Anonymous 6Kq79N0fo100% (5)
- Pre-Spanish GovernmentDocument15 pagesPre-Spanish GovernmentHobi Sunshine100% (3)
- 08 Social Justice in Housing and Urban Development - Prof. Ernesto M. SeroteDocument36 pages08 Social Justice in Housing and Urban Development - Prof. Ernesto M. SeroteJ. O. M. Salazar100% (1)
- Evolution of Human Resource ManagementDocument13 pagesEvolution of Human Resource Managementmsk_1407No ratings yet
- Evolution of Human Resource ManagementDocument20 pagesEvolution of Human Resource ManagementEdwin Chinel MonaresNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Reform Law ClassDocument61 pagesAgrarian Reform Law ClassVincent john Nacua100% (4)
- Training Manual ContentsDocument23 pagesTraining Manual ContentsSheena Bansal100% (4)
- Admin Law by DR Yashomati GhoshDocument245 pagesAdmin Law by DR Yashomati GhoshSanika GadgilNo ratings yet
- Victorian EnglandDocument17 pagesVictorian Englandbzlara17No ratings yet
- Living and Working Standards Classsified TableDocument4 pagesLiving and Working Standards Classsified TableJosep Prats Marín-LozanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Ancient Regime 2023 - 2024Document12 pagesUnit 1 The Ancient Regime 2023 - 2024BrumSin CMNo ratings yet
- Social Consequences of Industrialisation: 4.1.-Urbanisation ProcessDocument2 pagesSocial Consequences of Industrialisation: 4.1.-Urbanisation ProcessFatima VazquezNo ratings yet
- 1stmidtermtestHyG NardaczabanyiDocument5 pages1stmidtermtestHyG NardaczabanyiMartin CortadaNo ratings yet
- Civ-The End of The Industrial RevolutionDocument5 pagesCiv-The End of The Industrial RevolutionAmeni Ben HamoudaNo ratings yet
- How The Other Half LivesDocument5 pagesHow The Other Half Livesapi-376398096No ratings yet
- Expo HoyDocument16 pagesExpo Hoywilmer caspa carrascoNo ratings yet
- Social System in BritainDocument13 pagesSocial System in BritainOis KholisohNo ratings yet
- Living and Working Conditions Industrial RevolutionDocument3 pagesLiving and Working Conditions Industrial RevolutionJosep Prats Marín-LozanoNo ratings yet
- The History of Torts in Uganda PDFDocument14 pagesThe History of Torts in Uganda PDFAnnet MutabarukaNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument208 pagesChapterAakash BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Industralization Assignmet Mr. Francsico Cadavid Plata Isis Daniela Hernandez 11th GradeDocument4 pagesIndustralization Assignmet Mr. Francsico Cadavid Plata Isis Daniela Hernandez 11th GradeDaniela HernandezNo ratings yet
- SSM 106 Lesson 3Document53 pagesSSM 106 Lesson 3King Arnold SatsatinNo ratings yet
- Year 8 History Spring 2021 Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesYear 8 History Spring 2021 Knowledge OrganiserTanvi BujalaNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution: Old OrderDocument6 pagesThe French Revolution: Old OrderAnant Dwivedi100% (1)
- History and Culture Britain and United StatesDocument6 pagesHistory and Culture Britain and United StatesDenisa Alexandra AdamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Evolution of Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - Evolution of Human Resource Managementchuwii wiNo ratings yet
- The History of TortsDocument8 pagesThe History of Tortsmasikafauziah100% (1)
- History of TortDocument11 pagesHistory of Tortbabirye rehemaNo ratings yet
- Urbanization PPT Pd.8-1Document30 pagesUrbanization PPT Pd.8-1Roynell BakerNo ratings yet
- Review 43 Industrial RevolutionDocument38 pagesReview 43 Industrial RevolutionAvi DasNo ratings yet
- HAYDEN - What Would A Nonsexist City Be LikeDocument10 pagesHAYDEN - What Would A Nonsexist City Be Likecaitriona leeNo ratings yet
- FEEDBACK Q1W2 CWs PDFDocument6 pagesFEEDBACK Q1W2 CWs PDFHania gamalNo ratings yet
- 06 at Myth 02Document33 pages06 at Myth 02sami text065No ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution NotesDocument8 pagesThe Industrial Revolution NoteskatieNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Practice Test 25Document11 pagesIELTS Reading Practice Test 25Nguyễn Thị Huyền Dịu 5A-20No ratings yet
- Assumptions About Human Behavior. A Historical PerspectiveDocument3 pagesAssumptions About Human Behavior. A Historical PerspectiveIsmi Fadhliati100% (1)
- History of Planning in The Year 1801-1850 Industrial Revolution Iii. Housing and Public Health ConcernsDocument3 pagesHistory of Planning in The Year 1801-1850 Industrial Revolution Iii. Housing and Public Health ConcernsTroy Kenneth AlamaresNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution - Pros Vs ConsDocument2 pagesIndustrial Revolution - Pros Vs ConsNikki DouglassNo ratings yet
- Historia (Burgesia y Trabajadores)Document2 pagesHistoria (Burgesia y Trabajadores)Merino JoneNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Urb - Imm Note Taking Guide FillableDocument3 pages3.2 Urb - Imm Note Taking Guide FillableYuliat AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Studies - Task #10 Students: Grigioni and PerezDocument8 pagesIntercultural Studies - Task #10 Students: Grigioni and PerezMariana Grigioni100% (1)
- Internal Security - Linkages Between Development and ExtremismDocument24 pagesInternal Security - Linkages Between Development and Extremismarmaan.carpediemNo ratings yet
- RizalDocument4 pagesRizalHad LiasunNo ratings yet
- Rupture Apr08 ScreenDocument4 pagesRupture Apr08 ScreenPublicacions AnarquistesNo ratings yet
- Bright Susan Land Law Themes and Perspectives Pp457 486Document29 pagesBright Susan Land Law Themes and Perspectives Pp457 486farroohaahmedNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Analysis, Reflection, and Criteria - Jullie LugongDocument3 pagesFishbone Analysis, Reflection, and Criteria - Jullie LugongJULLIE MARIE LUGONGNo ratings yet
- Industrial Sociology Chap 2Document8 pagesIndustrial Sociology Chap 2Asha RaniNo ratings yet
- B11 - PASCUA, Ronice Christiane G.Document2 pagesB11 - PASCUA, Ronice Christiane G.Jharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- Socialism in Europe and The Russian RevolutionDocument9 pagesSocialism in Europe and The Russian Revolutionarushigupta06kNo ratings yet
- Final Term ActivitiesDocument6 pagesFinal Term ActivitiesAngelo Louis MartejaNo ratings yet
- HIS 522 Study GuideDocument14 pagesHIS 522 Study GuideAmanda HolbrookNo ratings yet
- Medieval SocietyDocument5 pagesMedieval SocietyGauravNo ratings yet
- Historical William Development of The Law of Torts in UgandaDocument17 pagesHistorical William Development of The Law of Torts in UgandaEcungu George williamNo ratings yet
- UCSP TimelineDocument2 pagesUCSP TimelineShannel Kate NuñezNo ratings yet
- GE 6 WEEK 2.ppsDocument10 pagesGE 6 WEEK 2.ppshazee0724No ratings yet
- Sujet English 2bacDocument2 pagesSujet English 2bacIzem AtlasNo ratings yet
- Applied EconomicsDocument4 pagesApplied EconomicsMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- How Property and Civil Rights Help Forest Tribes Modernize and Prosper: Lessons From IndiaDocument12 pagesHow Property and Civil Rights Help Forest Tribes Modernize and Prosper: Lessons From IndiaCato InstituteNo ratings yet
- Placemat From Millionaire Vines (Cissus Verticillata)Document39 pagesPlacemat From Millionaire Vines (Cissus Verticillata)rhea parajesNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Strategies Buyers Briefing A W 19 20Document8 pagesTop 5 Strategies Buyers Briefing A W 19 20Mikhel AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Baby Garments FinalDocument29 pagesBaby Garments FinalSheraz ImtiazNo ratings yet
- The United Colors of Benetton Collections Are Marked by Swing Tags That Identify Which Product Group Each Item Belongs ToDocument7 pagesThe United Colors of Benetton Collections Are Marked by Swing Tags That Identify Which Product Group Each Item Belongs ToGaurav BassiNo ratings yet
- Urban Dictionary SaggingDocument2 pagesUrban Dictionary SaggingedNo ratings yet
- VTT Btuo45-041224Document58 pagesVTT Btuo45-041224Khrystenn Mesias SerapioNo ratings yet
- MDF270 Cadia PatternDocument17 pagesMDF270 Cadia PatternRegina BarreiraNo ratings yet
- Application of Contemporary Fibres in Apparels - Hibiscus FIBREDocument3 pagesApplication of Contemporary Fibres in Apparels - Hibiscus FIBREVasant KothariNo ratings yet
- Cassandra Shawl Crocheted Pattern (1) - 1Document8 pagesCassandra Shawl Crocheted Pattern (1) - 1Gabriella JózsaNo ratings yet
- Blaisdell Rehearsalbreak 2018Document9 pagesBlaisdell Rehearsalbreak 2018api-729511265No ratings yet
- America GreatnessDocument44 pagesAmerica GreatnessLT ExtraNo ratings yet
- Arts7 q1Document32 pagesArts7 q1Marecel CatantanNo ratings yet
- 100 PromptsDocument8 pages100 Promptsharishprithika01No ratings yet
- Describe A ClassmateDocument2 pagesDescribe A ClassmatetastyNo ratings yet
- Case Diesel 2007 Corrected-WDocument24 pagesCase Diesel 2007 Corrected-WJuan FerrandezNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Defect - MFTDocument33 pagesInspection and Defect - MFTMudra SinghNo ratings yet
- Irina Shayk: 1 Early YearsDocument4 pagesIrina Shayk: 1 Early YearsgilNo ratings yet
- Garden ViewDocument6 pagesGarden ViewBruna SilvaNo ratings yet
- Health PersonalDocument19 pagesHealth PersonalShe's TushaNo ratings yet
- Gym RulesDocument4 pagesGym RuleshanafinurrahmadNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 2022 TshirtsDocument53 pagesCatalogue 2022 TshirtsNikunj SatraNo ratings yet
- TLKT English Ao Somi NamDocument3 pagesTLKT English Ao Somi NamNgọc Minh100% (1)
- Final InspectionDocument20 pagesFinal InspectionP. Lakshmanakanth100% (2)
- GBSB - Sleeveless Collared BlouseDocument21 pagesGBSB - Sleeveless Collared BlouseEmiliaNo ratings yet
- IJRHS 2015 Vol03 Issue 04 06Document4 pagesIJRHS 2015 Vol03 Issue 04 06aqsa imranNo ratings yet