Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B11 - PASCUA, Ronice Christiane G.
Uploaded by
Jharelle SaronaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B11 - PASCUA, Ronice Christiane G.
Uploaded by
Jharelle SaronaCopyright:
Available Formats
B11 Pascua, Ronice Christiane G.
11-Einstein
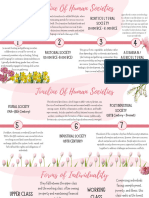
FORMS OF SOCIETY
IN HISTORY
Hunter-Gatherer Horticultural
Society Pastoral Society Society
Cooperation played a crucial role in the Settled societies raised animals for wool They cultivate crops alongside
survival of early hunting and gathering and milk, fostering trade and new gathering, maintaining mobility and
societies, where members depended on professions, distinguishing between relocating when resources are
activities like hunting, fishing, and foraging for nomadic and settled groups. Animal scarce. Occasionally, they produce
sustenance. Gender often determined the domestication drove technological surpluses, leading to the
division of labor, with men predominantly advances and social inequalities development of professions beyond
involved in hunting and women in gathering. compared to hunter-gatherer societies. basic survival in the society.
12,000 Years Ago 10,500 Years Ago 9000 Years Ago
Agricultural Industrial Post-Industrial
Society Society Society
The Industrial Revolution, starting in The rise of the computer chip has led
Cooperation was vital for early 18th-century Britain, brought to a society emphasizing information
hunting and gathering societies' mechanized factories, wealth and services. However, unequal
survival, relying on hunting, fishing, concentration, urbanization, and access to education is a concern.
and foraging. Gender often dictated conflicts between employers and People strive for a fairer society where
tasks, with men primarily hunting workers, leading to labor unions. It also everyone is supported, working
and women gathering. advanced public education, health, together to solve problems and
bureaucracy, and technology. reduce conflicts.
51 Years Ago -
5,300 Years Ago 273 Years Ago Present
B11 Pascua, Ronice Christiane G. 11-Einstein
4 FORMS OF
INDIVIDUALITY
Lower Class Working Class
They are individuals They are individuals
who have faced who have limited career
hunger, opportunities and low
unemployment, wages, such as waiters,
homelessness, and drivers, salespersons,
poverty. and cashiers.
Middle Class Upper Class
They are individuals who They are born into
face minimal material aristocratic families
difficulties and provide
and are often
professional services,
such as doctors, lawyers, involved in large
architects, engineers, and family business
others. ventures.
You might also like
- Types of Society UCSPDocument4 pagesTypes of Society UCSPMarilou MontillaNo ratings yet
- Types of SocitiesDocument34 pagesTypes of SocitiesPrincess CastanioNo ratings yet
- Bank Statement (Various Formats)Document48 pagesBank Statement (Various Formats)Araman AmruNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Learning Modules For Senior High School LearnersDocument14 pagesSupplementary Learning Modules For Senior High School LearnersAc LeeNo ratings yet
- Types of SocietiesDocument7 pagesTypes of SocietiesAnonymous JI7VsgxZanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 The Study of Human Society and CommunityDocument52 pagesChapter 13 The Study of Human Society and CommunityJoshua CruzNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 3Document9 pagesUCSP Module 3jonalyn obina100% (1)
- Types of SocietiesDocument2 pagesTypes of SocietiesTracy LewisNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module II Culture and Society 1Document11 pagesUCSP Module II Culture and Society 1Cathleen Racadio100% (1)
- Origin of SocietyDocument34 pagesOrigin of SocietyJae Unnie GileNo ratings yet
- The Study of Human SocietyDocument24 pagesThe Study of Human SocietyJM Magayanes100% (1)
- Hudbay Minerales 2016-2015Document94 pagesHudbay Minerales 2016-2015Anonymous au6UvN92kBNo ratings yet
- CS144 Autumn 2023Document20 pagesCS144 Autumn 2023dbedggoodNo ratings yet
- Procurement Manual of WapdaDocument170 pagesProcurement Manual of WapdaWaqar Ali Rana69% (13)
- AgarbattiDocument42 pagesAgarbattiDhwani Thakkar50% (2)
- Ucsp Week 4Document4 pagesUcsp Week 4Nichole John ErnietaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To ICTDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Introduction To ICTNabilah Nordin100% (2)
- Module 1. Math InvestmentDocument43 pagesModule 1. Math InvestmentManuel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Society and CultureDocument50 pagesSociety and CultureJavaraiah lgNo ratings yet
- B9 JUAN, Marc Abrielle F.Document2 pagesB9 JUAN, Marc Abrielle F.Jharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- UCSP TimelineDocument2 pagesUCSP TimelineShannel Kate NuñezNo ratings yet
- How We Got Here: Sociocultural EvolutionDocument2 pagesHow We Got Here: Sociocultural EvolutionSanja AngNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - The Human Person in SocietyDocument23 pagesModule 7 - The Human Person in SocietyRalph Ryan TooNo ratings yet
- UCSP Q3 Module 7 Cultural and Sociopolitical EvolutionDocument12 pagesUCSP Q3 Module 7 Cultural and Sociopolitical EvolutionMaria Hannahlyn Batumbakal DimakulanganNo ratings yet
- Culture and Society 1Document25 pagesCulture and Society 1Lance RoldanNo ratings yet
- Timelines of Different SocietiesDocument14 pagesTimelines of Different SocietiesJOHN MARTIN SAPANTANo ratings yet
- FCL ReviewerDocument10 pagesFCL ReviewerClara PrimaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Societies Based On The Mode of Subsistence or The Types of TechnologyDocument42 pagesClassification of Societies Based On The Mode of Subsistence or The Types of TechnologyChristian Nathaniel Ramon PalmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Personmorphine dreamNo ratings yet
- B7 GAMBA, Marc Stephen R.Document2 pagesB7 GAMBA, Marc Stephen R.Jharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Types of Society Final TruthfulDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Types of Society Final TruthfulzaballerovencentNo ratings yet
- Module 4ADocument3 pagesModule 4APaul Vincent JimenezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12Document2 pagesWorksheet 12Aira SheneNo ratings yet
- PHILODocument28 pagesPHILOsesaldochristianaameliaNo ratings yet
- (Output 041124 - 11 Einstein - B19 Tadena)Document3 pages(Output 041124 - 11 Einstein - B19 Tadena)Jharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- B15 RAMONES, Ramil J Jr. 11 Einstein TimelineDocument1 pageB15 RAMONES, Ramil J Jr. 11 Einstein TimelineJharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- Private Files UCSP MODULE-3Document8 pagesPrivate Files UCSP MODULE-3Marvin PameNo ratings yet
- Hunting and Gathering SocietiesDocument3 pagesHunting and Gathering Societiessyed abu hurairaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Society and Their CultureDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Society and Their CultureEj RoxasNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Week 4.2Document32 pagesUcsp Week 4.2Roseann EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Types of Human SocietiesDocument4 pagesTypes of Human SocietiesMwanarusi MwatondoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08 Feb 2021Document11 pagesAdobe Scan 08 Feb 2021Dakshita DubeyNo ratings yet
- 03-04-2020-1585905678-8-Ijhss-2. Ijhss - Handicrafts in Assam and Role of Mising Tribe A Study On Socio-Economic StatusDocument6 pages03-04-2020-1585905678-8-Ijhss-2. Ijhss - Handicrafts in Assam and Role of Mising Tribe A Study On Socio-Economic Statusiaset123No ratings yet
- Module 2Document26 pagesModule 2Lara Angela RigorNo ratings yet
- 4 Stages of SocietiesDocument17 pages4 Stages of SocietiesSheryl Corbe MolinaNo ratings yet
- BASIC CONCEPTS From Sociology and AnthropologyDocument20 pagesBASIC CONCEPTS From Sociology and AnthropologyKristelJaneDonaireBihagNo ratings yet
- Cultural Biodiversity Indigenous Relationships Within Their EnvironmentDocument3 pagesCultural Biodiversity Indigenous Relationships Within Their EnvironmentleoNo ratings yet
- Hunting and Gathering Societies 3-41Document21 pagesHunting and Gathering Societies 3-41Rhenz'c Tuazon MaturanNo ratings yet
- B13 - Quirante, Joshua Uriel P. - 11einsteinDocument2 pagesB13 - Quirante, Joshua Uriel P. - 11einsteinJharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- 2ND Reviewer-UcspDocument4 pages2ND Reviewer-UcspRoss SalesNo ratings yet
- CS144 Autumn 2023 4Document20 pagesCS144 Autumn 2023 4dbedggoodNo ratings yet
- Cot-Hunting and Gathering SocietyDocument6 pagesCot-Hunting and Gathering SocietyLEANNA MAE TAPANGCONo ratings yet
- Types of Societies and How Social Issues Affect Sport ActivitiesDocument12 pagesTypes of Societies and How Social Issues Affect Sport ActivitiesAdil NaseemNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Daay 1Document4 pagesWeek 2 Daay 1Jasmin BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Anthropological Foundations (Culture and Society)Document5 pagesAnthropological Foundations (Culture and Society)JOHNNY GALLANo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 1Document8 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 1rachelleann.convocarNo ratings yet
- Wholesome LivingDocument3 pagesWholesome LivingPeter BoneyNo ratings yet
- SocietyDocument13 pagesSocietyJona D'johnNo ratings yet
- Mielky Templonuevoe Soc - ScieDocument28 pagesMielky Templonuevoe Soc - ScieVinNo ratings yet
- Dhormo ClassDocument4 pagesDhormo ClassMD. JAHEDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- 6 Types and Characteristics of Societies Through HistoryDocument11 pages6 Types and Characteristics of Societies Through HistoryFranc Mike Jaryx TobiasNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Human SocietiesDocument26 pagesEvolution of Human SocietiesCresiljen BongoNo ratings yet
- History of The Organization of Work - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument20 pagesHistory of The Organization of Work - Britannica Online EncyclopediajonNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Philosophy in The Human Person HandoutsDocument3 pagesIntroduction of Philosophy in The Human Person HandoutsMaRvz Nonat Montelibano100% (1)
- The Work of Repair: Capacity after Colonialism in the Timber Plantations of South AfricaFrom EverandThe Work of Repair: Capacity after Colonialism in the Timber Plantations of South AfricaNo ratings yet
- Different Forms of Societies and IndividualismDocument1 pageDifferent Forms of Societies and IndividualismJharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- B15 RAMONES, Ramil J Jr. 11 Einstein TimelineDocument1 pageB15 RAMONES, Ramil J Jr. 11 Einstein TimelineJharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- B13 - Quirante, Joshua Uriel P. - 11einsteinDocument2 pagesB13 - Quirante, Joshua Uriel P. - 11einsteinJharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- B7 GAMBA, Marc Stephen R.Document2 pagesB7 GAMBA, Marc Stephen R.Jharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- (Output 041124 - 11 Einstein - B19 Tadena)Document3 pages(Output 041124 - 11 Einstein - B19 Tadena)Jharelle SaronaNo ratings yet
- Techno 101 LESSON 1 Week 2Document16 pagesTechno 101 LESSON 1 Week 2JaneGuinumtadNo ratings yet
- Bs. Accountancy (Aklan State University) Bs. Accountancy (Aklan State University)Document9 pagesBs. Accountancy (Aklan State University) Bs. Accountancy (Aklan State University)JANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- IA RoqueDocument52 pagesIA RoqueTrisha RafalloNo ratings yet
- Mock Test (Only Writing Session) : Deadline: 6th December 2021 ( 5pm )Document3 pagesMock Test (Only Writing Session) : Deadline: 6th December 2021 ( 5pm )Thu HàNo ratings yet
- 51 Checklist Buy BackDocument3 pages51 Checklist Buy BackvrkesavanNo ratings yet
- Acct Practice PaperDocument11 pagesAcct Practice PaperKrish BajajNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Globalization - A Comprehensive Overview and A Proposed DefinitionDocument21 pagesDefinitions of Globalization - A Comprehensive Overview and A Proposed Definitionnagendrar_2No ratings yet
- Micro Tutorial 8 - 2017Document2 pagesMicro Tutorial 8 - 2017AndyNo ratings yet
- Tonota Lephaneng Ward ReportDocument11 pagesTonota Lephaneng Ward Reportmokane.mokane1No ratings yet
- Expand/Collapsesd Expand/Collapse SD-BF Sd-Bf-AcDocument18 pagesExpand/Collapsesd Expand/Collapse SD-BF Sd-Bf-AcserradajaviNo ratings yet
- Csec Pob January 2015 p2Document15 pagesCsec Pob January 2015 p2Ikera ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Avrio PLT Corporate ProfileDocument16 pagesAvrio PLT Corporate Profilemiss anuarNo ratings yet
- CN WWF 20191021Document14 pagesCN WWF 20191021Maria Fernanda ZuluagaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A-Level Economics Paper 3 2019Document36 pagesEdexcel A-Level Economics Paper 3 2019William BackNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Essay Operations Management EssayDocument4 pagesOperations Management Essay Operations Management EssayShirley Soriano-QuintoNo ratings yet
- CIRCO Döngüsel Ekonomi 2016 PDFDocument75 pagesCIRCO Döngüsel Ekonomi 2016 PDFŞeyda DağdevirenNo ratings yet
- SCM AgreementDocument6 pagesSCM AgreementankitaprakashsinghNo ratings yet
- PAYE-GEN-01-G02 - Guide For Employers in Respect of Fringe Benefits - External GuideDocument25 pagesPAYE-GEN-01-G02 - Guide For Employers in Respect of Fringe Benefits - External Guidelixocan100% (1)
- Fixedline and Broadband Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesDocument2 pagesFixedline and Broadband Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- International TaxationDocument46 pagesInternational TaxationsridhartksNo ratings yet
- Allegro Data (Smart Sheet)Document5 pagesAllegro Data (Smart Sheet)Fathi RaufNo ratings yet
- Ortiz, John Paul HRM 1-4Document5 pagesOrtiz, John Paul HRM 1-4John Paul Aguilar OrtizNo ratings yet
- WmsDocument43 pagesWmssanthosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Abbott Laboratories Pakistan LimitedDocument15 pagesAbbott Laboratories Pakistan LimitedHibaNo ratings yet
- Swiggy Single ItemDocument2 pagesSwiggy Single ItemUsnshsnsNo ratings yet