Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASSIGNMENT1
Uploaded by
harekrishnaiitkanpur2004Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT1
Uploaded by
harekrishnaiitkanpur2004Copyright:
Available Formats
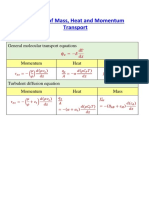
Practice problems on molecular diffusion
1. Think of atleast 2-3 examples involving (a) diffusion of A through non-diffusing B and
(b) equimolar counterdiffusion of A and B.
2. What is the stationary medium approximation? What does Fick’s second law look like?
3. In a diffusion of A in non-diffusing B though a constant cross-sectional area, from 𝑧 =
𝑧1 , 𝑝𝑎 = 𝑝𝐴1 to 𝑧 = 𝑧2 , 𝑝𝑎 = 𝑝𝐴2 (𝑝𝐴1 > 𝑝𝐴2 ), where will you find the highest
magnitude of the partial pressure gradient?
4. Explain why you can’t use the Stefan-tube experiment to measure the gas-phase
diffusivity if it is carried out very close to the boiling point of the liquid?
5. Equimolar counter-diffusion of A and B occurs between points 1 (𝑦1 = 0.3) and 2
(𝑦2 = 0.1) through a distance of 1 cm. Given 𝑃𝑡 =1atm, and 𝐷𝐴𝑏 = 0.2 𝑐𝑚2 /𝑠.What is
the diffusion velocity of A halfway in the diffusion path?
6. Example 2.14 and 2.15 from B.K. Dutta
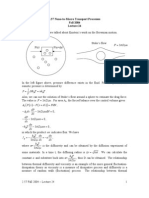
7. A spherical drop of liquid A and radius 𝑟𝑜 evaporates into a stagnant layer of gas B.
Derive an expression for the evaporation rate of species A in terms of the saturation
pressure of species A, 𝑝𝐴,𝑠𝑎𝑡 , the partial pressure of species A at an arbitrary radius r,
𝑝𝐴 (𝑟) the total pressure 𝑃𝑇 , and other necessary quantities. Assume the droplet and the
mixture are at a uniform pressure and temperature T.
8. Exercise problem 2.23, 2.24, 2.28, 2.31 in B.K.Dutta
9. Just as heat diffusion may be influenced by internal sources of energy, species transfer
by diffusion may be influenced by homogeneous chemical reactions. We restrict our
𝑑𝐶𝐴
attention to stationary media, in which case we have 𝑁𝐴 = 𝐽𝐴 = −𝐷𝐴𝐵 . Starting
𝑑𝑥
from the species conservation equation
𝜕𝐶𝐴 𝜕𝑁𝐴,𝑥 𝜕𝑁𝐴,𝑦 𝜕𝑁𝐴,𝑧
+ + + + 𝑅𝐴 = 0
𝜕𝑡 𝜕𝑥 𝜕𝑦 𝜕𝑧
and assuming steady, one-dimensional transfer in the 𝑥 direction, constant 𝐷𝐴𝐵 and
with 𝑅𝐴 = 𝑘 (zeroth order reaction), determine the concentration profile and the molar
flux as a function of 𝑥. Assume that the media is contained between the points 𝑥 = 0
𝑑𝐶𝐴
and 𝑥 = 𝐿. At 𝑥 = 0, 𝐶𝐴 = 0 and at 𝑥 = 𝐿, = 0 (The second boundary condition
𝑑𝑥
can arise if the flux at 𝑥 = 𝐿 is zero). Will 𝑁𝐴 be constant in this case? Why or why not?
10. Consider the radial diffusion of a gaseous species (A) through the wall of a plastic tube
(B) and allow for chemical reactions that provide for the depletion of A at a rate 𝑅𝐴
𝑘𝑚𝑜𝑙
( ). Derive a differential equation that governs the molar concentration of species A
𝑚3 𝑠
in the plastic.
You might also like
- Introduction To Energy PowerpointDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Energy PowerpointAgha Zeeshan Khan Soomro100% (1)
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Air Handling UnitDocument27 pagesAir Handling Unitobaidur_rehman_3No ratings yet
- Seismic Reservoir CharacterizationDocument17 pagesSeismic Reservoir CharacterizationRajdeep BuragohainNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Hydraulic ArmDocument68 pagesSynopsis Hydraulic ArmRajat Thakur100% (7)
- Falco UAV AirfoilDocument25 pagesFalco UAV Airfoiltomay777100% (1)
- The Ultimate Uplift Capacity of FoundationsDocument20 pagesThe Ultimate Uplift Capacity of FoundationsFrancisco Gonzalez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Facade Toggle CalculationDocument11 pagesFacade Toggle CalculationSudhakar KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Interstellar and Intergalactic Medium - ProblemsDocument57 pagesPhysics of The Interstellar and Intergalactic Medium - ProblemsjonasrichelieuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 - Mass Trasnfer 1-1Document14 pagesLecture Notes 2 - Mass Trasnfer 1-1Agyei MichaelNo ratings yet
- On The Global Well-Posedness For The Boussinesq System With Horizontal DissipationDocument32 pagesOn The Global Well-Posedness For The Boussinesq System With Horizontal DissipationOussama MelkemiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-MassDocument16 pagesLecture 3-Mass501238196002No ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 - Eqn of Continuity - UPDATED PDFDocument10 pagesLecture - 1 - Eqn of Continuity - UPDATED PDFShanmukShannuNo ratings yet
- Chaotic Dynamics and Oxygen Transport in Thin Films of Aerotactic BacteriaDocument8 pagesChaotic Dynamics and Oxygen Transport in Thin Films of Aerotactic BacteriaJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Governing EquationsDocument2 pagesGoverning EquationsThauan GomesNo ratings yet
- Gravity ModulationDocument4 pagesGravity ModulationArun kumar.NNo ratings yet
- Che318 Part1 Gas-Diffusion Rev1aDocument28 pagesChe318 Part1 Gas-Diffusion Rev1apiusNo ratings yet
- CH 27 PDFDocument41 pagesCH 27 PDFنزار الدهاميNo ratings yet
- Rarefied Gas Flow Past A Flat Plate at Zero Angle of AttackDocument11 pagesRarefied Gas Flow Past A Flat Plate at Zero Angle of AttackNam LeNo ratings yet
- Dong 等 - 2023 - Convergence to Nonlinear Diffusion Waves for SolutDocument37 pagesDong 等 - 2023 - Convergence to Nonlinear Diffusion Waves for Solutzinnia.romyeeNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Magnetic Field With Heat and Mass Transfer in Free Convection Flow of A Walters'-B FluidDocument15 pagesInteraction of Magnetic Field With Heat and Mass Transfer in Free Convection Flow of A Walters'-B FluidMuhammad ZafarullahNo ratings yet
- Exact Solution Tank DrainageDocument8 pagesExact Solution Tank DrainageFelipe CastNo ratings yet
- Entropy: Stochastic Thermodynamics of Brownian MotionDocument17 pagesEntropy: Stochastic Thermodynamics of Brownian MotionPhieta Fairusy FitriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Stochastic Processes: 3.1 Brownian MotionDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Stochastic Processes: 3.1 Brownian MotionAndxp51No ratings yet
- 9 Dam Break PDFDocument13 pages9 Dam Break PDFBrandon ArmeroNo ratings yet
- Jeans InstabilityDocument6 pagesJeans InstabilityClaudio Cofré MansillaNo ratings yet
- Scattering of Long Acoustic Waves in Porous Media: C. Boutin & M. BazailleDocument6 pagesScattering of Long Acoustic Waves in Porous Media: C. Boutin & M. BazailleUmed Abd-alsatarNo ratings yet
- A Solution of The Burger's Equation Arising in The Longitudinal Dispersion Phenomena in Fluid Flow Through Porous Media by Sumudu Transform Homotopy Perturbation MethodDocument4 pagesA Solution of The Burger's Equation Arising in The Longitudinal Dispersion Phenomena in Fluid Flow Through Porous Media by Sumudu Transform Homotopy Perturbation MethodInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Microchannel Cell: Solved With COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3Document18 pagesMicrochannel Cell: Solved With COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3Juan Carlos Montes CalaNo ratings yet
- Kjs 33 Aliattia 15Document9 pagesKjs 33 Aliattia 15RoberticoZeaNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: Ongitudinal Vortices in Granular FlowsDocument6 pagesAbstract:: Ongitudinal Vortices in Granular FlowsHendarNo ratings yet
- EJP35Document8 pagesEJP35kakitroll0No ratings yet
- QSP Examples1Document8 pagesQSP Examples1Utilities CoNo ratings yet
- Exam Theory Q1 EnglishDocument6 pagesExam Theory Q1 EnglishKanishk JainNo ratings yet
- Homotopy Solution For The Channel Flow of A Third Grade FluidDocument10 pagesHomotopy Solution For The Channel Flow of A Third Grade FluidMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- VIS enDocument10 pagesVIS enاحمد عبد المحسن ناجيNo ratings yet
- Population Dynamics and Phase Effects in Periodic Level CrossingsDocument35 pagesPopulation Dynamics and Phase Effects in Periodic Level CrossingsKay WhiteNo ratings yet
- 3 Steady State DiffusionDocument25 pages3 Steady State DiffusionShahadat AwanNo ratings yet
- Helge Holden and Xavier Raynaud - Global Conservative Solutions of The Generalized Hyperelastic-Rod Wave EquationDocument28 pagesHelge Holden and Xavier Raynaud - Global Conservative Solutions of The Generalized Hyperelastic-Rod Wave EquationQMDhidnwNo ratings yet
- RK Ask Chaotic RheologyDocument6 pagesRK Ask Chaotic RheologyrkailashNo ratings yet
- Schofield Et Al JEM 2020Document22 pagesSchofield Et Al JEM 2020vpcNo ratings yet
- State-Of-The-Art of Research On Seismic Pounding Between Buildings With Aligned SlabsDocument24 pagesState-Of-The-Art of Research On Seismic Pounding Between Buildings With Aligned SlabsRui CbNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document11 pagesExperiment 6CarlosLorenzoSaninNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Steady and Unsteady Mass and Heat Diffusion in Solids and Stagnant LiquidsDocument8 pagesModule 2: Steady and Unsteady Mass and Heat Diffusion in Solids and Stagnant LiquidskasvikrajNo ratings yet
- Non-Newtonian Flow in Annuli: of ofDocument6 pagesNon-Newtonian Flow in Annuli: of ofJames GarciaNo ratings yet
- Gasdynamics 2023 2024 Task1Document13 pagesGasdynamics 2023 2024 Task1sanj2498No ratings yet
- 14 Mathematical ModelsDocument8 pages14 Mathematical ModelsKaye EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 2 Jmcms 2009040 Numerical Solution of Unsteady Noushima Humera Ghouri RevisedDocument14 pages2 Jmcms 2009040 Numerical Solution of Unsteady Noushima Humera Ghouri Revisedrafiuddin2008No ratings yet
- A4........ ACoupled Vibration of A Cantilever Micro-Beam SubmergedDocument10 pagesA4........ ACoupled Vibration of A Cantilever Micro-Beam SubmergedyohannesNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- Soal Fisika StatistikDocument16 pagesSoal Fisika StatistikNingsihNo ratings yet
- Numer Sol Benjamin Eqn-Dougalis Et AlDocument37 pagesNumer Sol Benjamin Eqn-Dougalis Et Alcecilia calleNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 2Document2 pagesPractice Problems 2pm020202pmNo ratings yet
- NOE0415380416 ch042Document7 pagesNOE0415380416 ch042Umed Abd-alsatarNo ratings yet
- Sastry 2013Document7 pagesSastry 2013marco_doniseteNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9Document6 pagesExperiment 9Muzammil Iqbal100% (1)
- I. Perturbations After InflationDocument25 pagesI. Perturbations After InflationGaby TapiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Mass Transfer Rate LawsDocument53 pages3 Mass Transfer Rate LawsbalatholsNo ratings yet
- Start Up Couette Flow Second Order Fluid Analytical Solution Viscoelastic FlowsDocument23 pagesStart Up Couette Flow Second Order Fluid Analytical Solution Viscoelastic Flowsswapnil_dalalNo ratings yet
- Helge Holden and Xavier Raynaud - Periodic Conservative Solutions of The Camassa-Holm EquationDocument31 pagesHelge Holden and Xavier Raynaud - Periodic Conservative Solutions of The Camassa-Holm EquationQMDhidnwNo ratings yet
- Navier-Stokes Equation: March 2004Document4 pagesNavier-Stokes Equation: March 2004FREDY PALINGGINo ratings yet
- Ion Association in Proton Transfer Reactions: Use of ESR for the Quantitative Determination of Gas Phase Atom and Radical ConcentrationsFrom EverandIon Association in Proton Transfer Reactions: Use of ESR for the Quantitative Determination of Gas Phase Atom and Radical ConcentrationsNo ratings yet
- Macromolecular Microsymposium — 16: Main Lectures Presented at the Sixteenth Microsymposium on Macromolecules (Advances in Scattering Methods), Prague, 12 - 16 July 1976From EverandMacromolecular Microsymposium — 16: Main Lectures Presented at the Sixteenth Microsymposium on Macromolecules (Advances in Scattering Methods), Prague, 12 - 16 July 1976B. SedláčekNo ratings yet
- Me6502 Apr May 2017 PDFDocument4 pagesMe6502 Apr May 2017 PDFKannan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv 11Document16 pagesUnit-Iv 11RAGULNo ratings yet
- Two Phase Flow and Heat Transfer - Assignment 3Document11 pagesTwo Phase Flow and Heat Transfer - Assignment 3Joel Jr Rudinas (Remodulator)No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - HeuristicsDocument40 pagesChapter 11 - HeuristicsAmeerRashidNo ratings yet
- Bending Lab Report FinalDocument21 pagesBending Lab Report FinalNasri JamaludinNo ratings yet
- G9 Matter in Our Surroundings Q.bank 1Document21 pagesG9 Matter in Our Surroundings Q.bank 111Yeshwanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- IEEETransPaperJan1996Neher McGrathDocument20 pagesIEEETransPaperJan1996Neher McGrathparallax1957No ratings yet
- Loading and Buckling Ex-02 PDFDocument6 pagesLoading and Buckling Ex-02 PDFNewton ShikderNo ratings yet
- SPE-111286 Advances in Measuring Porosity and Permeability From Drill CuttingsDocument9 pagesSPE-111286 Advances in Measuring Porosity and Permeability From Drill CuttingsBruceNo ratings yet
- Cementing MechanicsDocument2 pagesCementing MechanicszapspazNo ratings yet
- Thermal Comfort and The Heat Stress IndicesDocument11 pagesThermal Comfort and The Heat Stress IndicestemterNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Beam METHODDocument13 pagesConjugate Beam METHODAdam Ahmed100% (1)
- Lab Manual For Tensile TestDocument7 pagesLab Manual For Tensile TestJIA PERN TANNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lecture - 2-ThermodynamicsDocument81 pagesVirtual Lecture - 2-ThermodynamicsRukmani DeviNo ratings yet
- Surface TensionDocument15 pagesSurface TensionkNo ratings yet
- 18CV54Document4 pages18CV54yaligarumashankar89No ratings yet
- Gao-Cfd RefrigeratorDocument13 pagesGao-Cfd RefrigeratorMonowarul IslamNo ratings yet
- Tee (T) Section Properties - Calculator - CALC RESOURCEDocument9 pagesTee (T) Section Properties - Calculator - CALC RESOURCEsreekanth6959646No ratings yet
- Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument20 pagesHydraulics and Pneumaticsharishme028100% (2)
- Calflo Heat Transfer FluidDocument4 pagesCalflo Heat Transfer FluidderekfisherNo ratings yet
- S9 Q4 Hybrid Module 5 Week 6 How Heat Transfer and Energy Transformation Make Heat EngineDocument16 pagesS9 Q4 Hybrid Module 5 Week 6 How Heat Transfer and Energy Transformation Make Heat EngineSally CustodioNo ratings yet
- Slopes Stability Analysis Using The Plaxis 2D Program and Taylor's Stability EquationDocument5 pagesSlopes Stability Analysis Using The Plaxis 2D Program and Taylor's Stability EquationJuwitaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 Mechanic StructureDocument5 pagesTOPIC 3 Mechanic StructureAininNo ratings yet