0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views5 pagesNotes On Queue
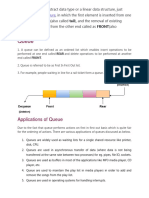
A queue is a linear data structure that follows first-in, first-out (FIFO) principles. Elements are added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front. Common operations include enqueue, which inserts an element to the rear, and dequeue, which removes an element from the front. Queues have many applications where ordering or processing is required, such as job scheduling, network packet transmission, and printing/resource sharing.
Uploaded by
sheetal85076Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views5 pagesNotes On Queue
A queue is a linear data structure that follows first-in, first-out (FIFO) principles. Elements are added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front. Common operations include enqueue, which inserts an element to the rear, and dequeue, which removes an element from the front. Queues have many applications where ordering or processing is required, such as job scheduling, network packet transmission, and printing/resource sharing.
Uploaded by
sheetal85076Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd