Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P Ch-23 Atoms
Uploaded by
mysoftinfo.incOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P Ch-23 Atoms
Uploaded by
mysoftinfo.incCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 23
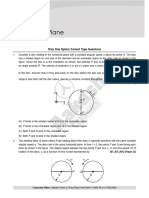
Atoms
Only One Option Correct Type Questions
1. The largest wavelength in the ultraviolet region of the hydrogen spectrum is 122 nm. The smallest wavelength
in the infrared region of the hydrogen spectrum (to the nearest integer) is [IIT-JEE-2007 (Paper-1)]
(A) 802 nm (B) 823 nm
(C) 1882 nm (D) 1648 nm
2. Which one of the following statements is WRONG in the context of X - rays generated from a X-ray tube?
[IIT-JEE-2008 (Paper-1)]
(A) Wavelength of characteristic X-rays decreases when the atomic number of the target increases
(B) Cut-off wavelength of the continuous X-rays depends on the atomic number of the target
(C) Intensity of the characteristic X-rays depends on the electrical power given to the X-ray tube
(D) Cut-off wavelength of the continuous X-rays depends on the energy of the electrons in the X-ray tube
3. The wavelength of the first spectral line in the Balmer series of hydrogen atom is 6561 Å. The wavelength of
the second spectral line in the Balmer series of singly-ionized helium atom is [IIT-JEE-2011 (Paper-1)]
(A) 1215 Å (B) 1640 Å
(C) 2430 Å (D) 4687 Å
4. If Cu is the wavelength of K X-ray line of copper (atomic number 29) and Mo is the wavelength of the K X-
ray line of molybdenum (atomic number 42), then the ratio Cu /Mo is close to [JEE (Adv)-2014 (Paper-2)]
(A) 1.99 (B) 2.14
(C) 0.50 (D) 0.48
One or More Option(s) Correct Type Questions
5. The radius of the orbit of an electron in a Hydrogen-like atom is 4.5 a0, where a0 is the Bohr radius. Its orbital
3h
angular momentum is . It is given that h is Planck constant and R is Rydberg constant. The possible
2
wavelength(s), when the atom de-excites, is (are) [JEE (Adv)-2013 (Paper-2)]
9 9
(A) (B)
32R 16R
9 4
(C) (D)
5R 3R
6. Highly excited states for hydrogen-like atoms (also called Rydberg states) with nuclear charge Ze are defined
by their principal quantum number n, where n >> 1. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true?
[JEE (Adv)-2016 (Paper-1)]
(A) Relative change in the radii of two consecutive orbitals does not depend on Z
(B) Relative change in the radii of two consecutive orbitals varies as 1/n
(C) Relative change in the energy of two consecutive orbitals varies as 1/n3
(D) Relative change in the angular momenta of two consecutive orbitals varies as 1/n
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
ARCHIVE - JEE (Advanced) PHYSICS
7. A free hydrogen atom after absorbing a photon of wavelength a gets excited from the state n = 1 to the state
n = 4. Immediately after that the electron jumps to n = m state by emitting a photon of wavelength e. Let
the change in momentum of atom due to the absorption and the emission are pa and pe, respectively. If
1
a / e , which of the option(s) is/are correct?
5
[Use hc = 1242 eV nm; 1 nm = 10–9 m, h and c are Planck’s constant and speed of light, respectively]
[JEE (Adv)-2019 (Paper-2)]
(A) e = 418 nm
1
(B) pa / pe
2
1
(C) The ratio of kinetic energy of the electron in the state n = m to the state n = 1 is
4
(D) m = 2
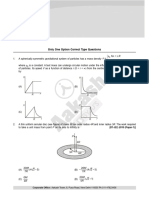
8. A particle of mass m moves in circular orbits with potential energy V(r) = Fr, where F is a positive constant
and r is its distance from the origin. Its energies are calculated using the Bohr model. If the radius of the
particle’s orbit is denoted by R and its speed and energy are denoted by v and E, respectively, then for the
nth orbit (here h is the Planck’s constant) [JEE (Adv)-2020 (Paper-1)]
(A) R n1/3 and v n2/3 (B) R n 2/3 and v n1/3
1/3 1/3
3 n 2h2F 2 n 2 h 2F 2
(C) E (D) E 2
2 42 m
42 m
9. In an X-ray tube, electrons emitted from a filament (cathode) carrying current I hit a target (anode) at a distance
d from the cathode. The target is kept at a potential V higher than the cathode resulting in emission of
I
continuous and characteristic X-rays. If the filament current I is decreased to , the potential difference V
2
d
is increased to 2V, and the separation distance d is reduced to , then
2
[JEE (Adv)-2020 (Paper-2)]
(A) The cut-off wavelength will reduce to half, and the wavelengths of the characteristic X-rays will remain the
same
(B) The cut-off wavelength as well as the wavelengths of the characteristic X-rays will remain the same
(C) The cut-off wavelength will reduce to half, and the intensities of all the X-rays will decrease
(D) The cut-off wavelength will become two times larger, and the intensity of all the X-rays will decrease
10. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct about the spectrum of hydrogen atom?
[JEE (Adv)-2021 (Paper-1)]
9
(A) The ratio of the longest wavelength to the shortest wavelength in Balmer series is
5
(B) There is an overlap between the wavelength ranges of Balmer and Paschen series
1
(C) The wavelengths of Lyman series are given by 1 2 0 , where 0 is the shortest wavelength of
m
Lyman series and m is an integer
(D) The wavelength ranges of Lyman and Balmer series do not overlap
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
PHYSICS ARCHIVE - JEE (Advanced)
Linked Comprehension Type Questions
Paragraph for Q. Nos. 11 to 13
In a mixture of H – He+ gas (He+ is singly ionized He atom), H atoms and He+ ions are excited to their respective first
excited states. Subsequently, H atoms transfer their total excitation energy to He+ ions (by collisions). Assume that the
Bohr Model of atom is exactly valid. [IIT-JEE-2008 (Paper-1)]
Choose the correct answer :
11. The quantum number of n of the state finally populated in He+ ions is
(A) 2 (B) 3
(C) 4 (D) 5
12. The wavelength of light emitted in the visible region by He+ ions after collisions with H atoms is
(A) 6.5 10 –7 m
(B) 5.6 10 –7 m
(C) 4.8 10 –7 m
(D) 4.0 10 –7 m
13. The ratio of the kinetic energy of the n = 2 electron for the H atom to that of He+ ion is
1 1
(A) (B)
4 2
(C) 1 (D) 2
Paragraph for Q. Nos. 14 to 16
When a particle is restricted to move along x-axis between x = 0 and x = a, where a is of nanometer dimension,
its energy can take only certain specific values. The allowed energies of the particle moving in such a restricted
region, correspond to the formation of standing waves with nodes at its ends x = 0 and x = a. The wavelength of
this standing wave is related to the linear momentum p of the particle according to the de Broglie relation. The energy
p2
of the particle of mass m is related to its linear momentum as E . Thus, the energy of the particle can be
2m
denoted by a quantum number ‘n’ taking values 1, 2, 3,... (n = 1, called the ground state) corresponding to the
number of loops in the standing wave.
Use the model described above to answer the following three questions for a particle moving in the line x = 0 and
x = a. Take h = 6.6 × 10–34 J s and e = 1.6 × 10–19 C. [IIT-JEE-2009 (Paper-1)]
Choose the correct answer :
14. The allowed energy for the particle for a particular value of n is proportional to
(A) a–2 (B) a–3/2
(C) a–1 (D) a2
15. If the mass of the particle is m = 1.0 × 10–30 kg and a = 6.6 nm, the energy of the particle in its ground state is
closest to
(A) 0.8 meV (B) 8 meV
(C) 80 meV (D) 800 meV
16. The speed of the particle, that can take discrete values, is proportional to
(A) n–3/2 (B) n–1
(C) n1/2 (D) n
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
ARCHIVE - JEE (Advanced) PHYSICS
Paragraph for Q. Nos. 17 to 19
The key feature of Bohr’s theory of spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantization of angular momentum when an
electron is revolving around a proton. We will extend this to a general rotational motion to find quantized rotational
energy of a diatomic molecule assuming it to be rigid. The rule to be applied is Bohr’s quantization condition.
[IIT-JEE-2010 (Paper-2)]
Choose the correct answer :
17. A diatomic molecule has moment of inertia l. By Bohr’s quantization condition its rotational energy in the nth level
(n = 0 is not allowed) is
1 h2 1 h2
(A) (B) n 2
n 2 8 2I 8 I
h2 2 h
2
(C) n 2 (D) n 2
8 I 8 I
18. It is found that the excitation frequency from ground to the first excited state of rotation
4
for the CO molecule is close to 1011 Hz. Then the moment of inertia of CO molecule
about its centre of mass is close to (Take h = 2 × 10–34 J s)
(A) 2.76 × 10–46 kg m2 (B) 1.87 × 10–46 kg m2
(C) 4.67 × 10–47 kg m2 (D) 1.17 × 10–47 kg m2
19. In a CO molecule, the distance between C (mass = 12 a.m.u.) and O (mass = 16 a.m.u.), where 1 a.m.u.
5
10 –27 kg , is close to
3
(A) 2.4 × 10–10 m (B) 1.9 × 10–10 m
(C) 1.3 × 10–10 m (D) 4.4 × 10–11 m
Matrix-Match / Matrix Based Type Questions
20. Some laws/processes are given in Column I. Match these with the physical phenomena given in Column II and
indicate your answer by darkening appropriate bubbles in the 4 × 4 matrix given in the ORS.
[IIT-JEE-2007 (Paper-1)]
Column I Column II
(A) Transition between two atomic energy levels (p) Characteristic X-rays
(B) Electron emission from a material (q) Photoelectric effect
(C) Mosley’s law (r) Hydrogen spectrum
(D) Change of photon energy into kinetic (s) -decay
energy of electrons
Integer / Numerical Value Type Questions
21. Consider a hydrogen atom with its electron in the nth orbital. An electromagnetic radiation of wavelength
90 nm is used to ionize the atom. If the kinetic energy of the ejected electron is 10.4 eV, then the value of n
is (hc = 1242 eV nm) [JEE (Adv)-2015 (Paper-1)]
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
PHYSICS ARCHIVE - JEE (Advanced)
22. An electron is an excited state of Li2+ ion has angular momentum 3h/2. The de Broglie wavelength of the
electron in this state is pa0 (where a0 is the Bohr radius). The value of p is [JEE (Adv)-2015 (Paper-2)]
23. A hydrogen atom in its ground state is irradiated by light of wavelength 970 Å. Taking hc/e = 1.237 × 10–6 eV m
and the ground state energy of hydrogen atom as –13.6 eV, the number of lines present in the emission
spectrum is [JEE (Adv)-2016 (Paper-1)]
24. An electron in a hydrogen atom undergoes a transition from an orbit with quantum number ni to another with
Vi
quantum number nf. Vi and Vf are respectively the initial and final potential energies of the electron. If V = 6.25,
f
then the smallest possible nf is [JEE (Adv)-2017 (Paper-1)]
25. Consider a hydrogen-like ionized atom with atomic number Z with a single electron. In the emission spectrum
of this atom, the photon emitted in the n = 2 to n = 1 transition has energy 74.8 eV higher than the photon
emitted in the n = 3 to n = 2 transition. The ionization energy of the hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV. The value of
Z is ______. [JEE (Adv)-2018 (Paper-2)]
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
You might also like
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument14 pagesAtomic Structure PDFbunny reedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Jee Main SelectedDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure Jee Main SelectedfopjfvmhdNo ratings yet
- Atom McqsDocument13 pagesAtom McqsMrunmayee ManeNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3Document5 pagesSheet 3atharvabari9No ratings yet
- Chemistry Physical PDFDocument95 pagesChemistry Physical PDFKaushik Barman50% (2)
- 226 ELP 72 Student Copy KT01 6201 PDF Modern Physics EL JindalJi247Document2 pages226 ELP 72 Student Copy KT01 6201 PDF Modern Physics EL JindalJi247arorayash603No ratings yet
- Final Lap (Chemistry) ATMDocument341 pagesFinal Lap (Chemistry) ATMAnwesh SahaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024Document3 pagesAtomic Structure - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024armughank708No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure BookletDocument20 pagesAtomic Structure Bookletsiddharth rambhiaNo ratings yet
- WB JEE Master Question Bank Chapter Wise PC-20210707093717556734Document51 pagesWB JEE Master Question Bank Chapter Wise PC-20210707093717556734PRIYANSHNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 1 2022-23 BoardDocument11 pagesPhysics Set 1 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- 14 SQPDocument8 pages14 SQPdipanshu76612No ratings yet
- Xii QP Physics VSTDocument5 pagesXii QP Physics VSTkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- Physics Set 2 2022-23 BoardDocument10 pagesPhysics Set 2 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure-DTS-2 Main (Archive)Document3 pagesAtomic Structure-DTS-2 Main (Archive)Halfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Practice SheetDocument6 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter Practice SheetHi MeNo ratings yet
- Optics and Modern Physics Adv1Document22 pagesOptics and Modern Physics Adv1kamlesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Main) CWS01 (Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Chemical Bonding) (SAG Mam) PDFDocument3 pages2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Main) CWS01 (Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Chemical Bonding) (SAG Mam) PDFvidhit dlNo ratings yet
- Exercise-I: Section (A) : Calculation Related To NucleusDocument9 pagesExercise-I: Section (A) : Calculation Related To NucleusAshwani kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure DTS-1Document2 pagesAtomic Structure DTS-1Aashish GoyalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PracticeDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure Practicerajesh.justiceNo ratings yet
- PM Shri Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPM Shri Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024maxers.xdNo ratings yet
- Physics XII QP Set 1Document10 pagesPhysics XII QP Set 1meme MachineNo ratings yet
- Vmts Jee Part Test 7Document15 pagesVmts Jee Part Test 7harshit pandeyNo ratings yet
- Atoms PYQDocument8 pagesAtoms PYQAyaanNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Support Material Final-1 - Removed - RemovedDocument70 pagesClass XII Physics Support Material Final-1 - Removed - RemovedIshu RaoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structrue XPPDocument14 pagesAtomic Structrue XPPruchikumari76543No ratings yet
- Race-26 - Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesRace-26 - Atomic StructureItish maanNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 7: (Dual Nature of Matter, Atoms and Nuclei)Document6 pagesUnit Test 7: (Dual Nature of Matter, Atoms and Nuclei)padhi8480No ratings yet
- Physics Mock-1Document7 pagesPhysics Mock-1rachyalbert89No ratings yet
- Ii Pre Board Class XiiDocument14 pagesIi Pre Board Class XiiPrithibiNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPDocument42 pagesPhysics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPOJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- Bhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1Document9 pagesBhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1niladriputatunda1No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument29 pagesStructure of AtomSayantan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Atomic Structure Important QuestionsDocument22 pagesJEE Advanced Atomic Structure Important QuestionsPooja SainiNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter Practice Model QuestionDocument3 pagesDual Nature of Matter Practice Model Questionmohammedfaisalimran5No ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 22-23Document7 pagesPre Board 1 22-23VAIBHAW VAIBHAWNo ratings yet
- XII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Document6 pagesXII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Anuradha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Dpyq Full Syllabus Paper-6Document5 pagesJee Main Dpyq Full Syllabus Paper-6Yash ParateNo ratings yet
- Quanta Atomic SheetDocument55 pagesQuanta Atomic SheetVenkatarao KankanalaNo ratings yet
- N 4, 5, 6 To N 1: SL No - Question Correct AnswerDocument7 pagesN 4, 5, 6 To N 1: SL No - Question Correct Answermahil parmarNo ratings yet
- DPP 04Document3 pagesDPP 04urmomNo ratings yet
- Physics: Rapid Crash CourseDocument12 pagesPhysics: Rapid Crash CourseHudsun HornetNo ratings yet
- Exam Papers 2023Document19 pagesExam Papers 2023supbolte12No ratings yet
- Jee Main-2023 - Important Replica QS - PhysicsDocument106 pagesJee Main-2023 - Important Replica QS - PhysicsAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- 10nov - Physics WorkDocument8 pages10nov - Physics Workpratyushmehta3No ratings yet
- Physics XII - Set 3Document6 pagesPhysics XII - Set 3ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Question Bank On Atomic Structure-2Document7 pagesQuestion Bank On Atomic Structure-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Matter-Wave Exercise 1 - 4 Module-6Document14 pagesMatter-Wave Exercise 1 - 4 Module-6Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 Sample PaperDocument7 pagesPhysics Class 12 Sample PaperAkhilesh ArdcNo ratings yet
- As Wet-4Document8 pagesAs Wet-4Rsrao JNo ratings yet
- Mathongo Jee Main 2019 12 January Evening ShiftDocument33 pagesMathongo Jee Main 2019 12 January Evening ShiftMadhurNo ratings yet
- 10 Atomic StructureDocument9 pages10 Atomic StructurearcNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems: C-B (Level-B)Document3 pagesDaily Practice Problems: C-B (Level-B)Ved NarsekarNo ratings yet
- B1 Physics PaperDocument9 pagesB1 Physics PaperJotika DeviNo ratings yet
- 2020 12 SP PhysicsDocument22 pages2020 12 SP PhysicsRiya NinanNo ratings yet
- Physics SQPDocument7 pagesPhysics SQPGopa DeyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 02 (Atomic Structure and Basic Concepts of Chemistty) (VSK Sir)Document4 pagesWorksheet - 02 (Atomic Structure and Basic Concepts of Chemistty) (VSK Sir)Daksha SubrhamanyaNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- C - Ch-17 - The D - F - Block ElementsDocument2 pagesC - Ch-17 - The D - F - Block Elementsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-21 HydrocarbonsDocument8 pagesC Sol Ch-21 Hydrocarbonsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Ch-13 HydrogenDocument1 pageC Ch-13 Hydrogenmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-09 SolutionsDocument6 pagesC Sol Ch-09 Solutionsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-16 General+Principles+and+Processes+OfDocument4 pagesC Sol Ch-16 General+Principles+and+Processes+Ofmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-14 The S-Block ElementsDocument1 pageC Sol Ch-14 The S-Block Elementsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-07 - Redox Reactions and Volumetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesC - Sol - Ch-07 - Redox Reactions and Volumetric Analysismysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Aakash Alternating Current MCQDocument3 pagesAakash Alternating Current MCQINDIAN ARMYNo ratings yet
- P Ch-03 Laws+of+MotionDocument5 pagesP Ch-03 Laws+of+Motionmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-12 Surface ChemistryDocument2 pagesC Sol Ch-12 Surface Chemistrymysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-11 - Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear ChemistryDocument8 pagesC - Sol - Ch-11 - Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistrymysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-16 Current+Electricity PDFDocument10 pagesP Ch-16 Current+Electricity PDFRamesh kamatNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-04 States of MatterDocument3 pagesC Sol Ch-04 States of Mattermysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-01 - Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument2 pagesC - Sol - Ch-01 - Some Basic Concepts of Chemistrymysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-08 Mechanical+Properties+of+FluidsDocument10 pagesP Ch-08 Mechanical+Properties+of+Fluidssumitsrs2011No ratings yet
- P Ch-07 Mechanical+Properties+of+SolidsDocument2 pagesP Ch-07 Mechanical+Properties+of+Solidssumitsrs2011No ratings yet
- P Ch-11 Thermal+Properties+of+Matter PDFDocument5 pagesP Ch-11 Thermal+Properties+of+Matter PDFlaksh jainNo ratings yet
- P Ch-10 WavesDocument7 pagesP Ch-10 Wavesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-06 GravitationDocument5 pagesP Ch-06 Gravitationpriyalagrawal78No ratings yet
- M Ch-15 Limits and DerivativesDocument3 pagesM Ch-15 Limits and Derivativesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-12 Kinetic+Theory+of+GasesDocument2 pagesP Ch-12 Kinetic+Theory+of+Gasesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-02 Motion+in+a+PlaneDocument3 pagesP Ch-02 Motion+in+a+Planemysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-12 Conic+SectionsDocument12 pagesM Ch-12 Conic+Sectionspriyalagrawal78No ratings yet
- M Ch-24 ProbabilityDocument10 pagesM Ch-24 ProbabilityBossNo ratings yet
- M Ch-22 Vector AlgebraDocument7 pagesM Ch-22 Vector AlgebraBossNo ratings yet
- M Ch-23 Three Dimensional GeometryDocument6 pagesM Ch-23 Three Dimensional GeometryBossNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives: Only One Option Correct Type QuestionsDocument11 pagesApplication of Derivatives: Only One Option Correct Type QuestionsSachin MalikNo ratings yet
- M - Ch-20 - Area Under CurveDocument3 pagesM - Ch-20 - Area Under CurveBossNo ratings yet
- M Ch-11 CircleDocument6 pagesM Ch-11 Circlemysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet