Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C Sol Ch-12 Surface Chemistry
Uploaded by
mysoftinfo.incOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C Sol Ch-12 Surface Chemistry
Uploaded by
mysoftinfo.incCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12
Surface Chemistry
1. Answer (C)
Coagulating power of a electrolyte is dependent on the valency of effective ion and Sb2S3 is negatively charged
sol.
Answer is Al2(SO4)3.
2. Answer (B)
The adsorption of methylene blue on activated charcoal is physiosorption which is exothermic, multilayer and
does not have energy barrier.
3. Answer (D)
A solution of CH 3OH and water shows positive deviation from Raoult's law, it means by adding
intermolecular force of attraction decreases and hence surface tension decreases.
By adding KCl in water, intermolecular force of attraction bit increases, so surface tension increases by
small value.
By adding surfactant like CH3(CH2)11OSO3–Na+, surface tension decreases rapidly and after forming micelle
it slightly increases.
4. Answer (A, B, D)
At high temperature, sufficient activation energy for chemical adsorption is provided.
Hadsorption for chemical lies between 200-400 kJ/mole.
5. Answer (A, D)
Lyophobic colloids carry either +ve or –ve charge. In order to acquire stability the colloidal particles attract
oppositely charged ions forming a diffused layer. A potential is developed between fixed layer and diffused layer
called zeta potential. Higher the value of zeta potential higher will be the stability of lyophobic colloid.
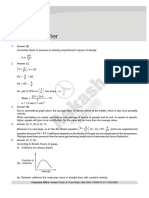
6. Answer (A, C)
Under mild conditions of temperatures extent of physisorption decreases with increasing temperature so
graph (I) is correct. As initial temperature provided meets the necessary activation energy needed for chemical
bond formation for chemisorption so graph (II) is also correct. Finally graph (IV) is correct for chemisorption
as plot is now of potential energy vs distance of molecule from surface. Hence, answer is (A, C).
7. Answer (B, C, D)
Reaction on metal surface
M M e
O2 e
O2
This is an example of chemisorption.
8. Answer (A, C)
Adsorption is an exothermic process and is accompanied by decrease is entropy,
H 0, S 0
sys sys
More is critical temperature (Tc), more are intermolecular forces of attraction.
More is extent of adsorption.
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
CHEMISTRY ARCHIVE - JEE (Advanced) (Solutions)
9. Answer (B, C)
Select the correct statements.
(A) The process of precipitating colloidal sol by an electrolyte is called peptization - False, (It is process of
converting precipitate into colloid)
(B) Colloidal solution freezes at a higher temperature than the true solution at the same concentration - True
(colligative properties)
(C) Surfactants form miscelle above critical miscelle concentration (CMC). CMC depends on temperature -
True
(D) Miscelles are macromolecular colloids - False, As misceles are associated colloids.
10. Answer (A, D)
(A) First statement is correct as chemisorption results in a unimolecular layer and physisorption result in a
multimolecular layer.
(B) Second statement is incorrect as enthalpy change during physisorption is of the range of (20 – 40) kJ mol–1.
(C) Chemisorption is an exothermic process with (80 – 240) kJ mol–1 as the enthalpy of adsorption.
(D) Lowering the temperature results in increase in the extent of physisorption.
Hence (A) and (D) are correct.
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph.011-47623456
You might also like
- Quantum Physics and The Power of The Mind - Nancy PattersonDocument92 pagesQuantum Physics and The Power of The Mind - Nancy PattersonRanjan KarnNo ratings yet
- 1995, Edzwald, Principles and Applications of Dissolved Air Flotation PDFDocument23 pages1995, Edzwald, Principles and Applications of Dissolved Air Flotation PDFDaniel Alejandro Jara PaineanNo ratings yet
- Assertion Reasoning Questions All Chapters - AnswersDocument10 pagesAssertion Reasoning Questions All Chapters - AnswersSheeba Sathyan Mohan70% (10)
- Turbine Start UpDocument15 pagesTurbine Start UprobiansahNo ratings yet
- Davit Design Calculation: L 1 D V H V H V DDocument2 pagesDavit Design Calculation: L 1 D V H V H V DSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1011 Final Lab ExamDocument4 pagesCHEM 1011 Final Lab ExamKeigh KimmNo ratings yet
- Exam #1 KeyDocument9 pagesExam #1 KeyCaitlynNo ratings yet
- Basic Education Department (SHS) : Qualifying Examination - ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic Education Department (SHS) : Qualifying Examination - Chemistryismael jaafarNo ratings yet
- Cary 100/300/4000/5000/ 6000i Spectrophotometers: Hardware Operation ManualDocument44 pagesCary 100/300/4000/5000/ 6000i Spectrophotometers: Hardware Operation ManualHydroPotatoesNo ratings yet
- Aspen For Chem RXN PART 2Document50 pagesAspen For Chem RXN PART 2hakita86No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Part - 2Document29 pagesChemical Kinetics Part - 2smi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Class-12 Chemistry ElectroDocument4 pagesClass-12 Chemistry ElectroHemant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry-03-Assignments (New)Document11 pagesSurface Chemistry-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry MCQ CH 5Document95 pages12 Chemistry MCQ CH 5Anshika Tripathi100% (1)
- MCQs For Class XII ChemistryDocument29 pagesMCQs For Class XII Chemistryjkc collegeNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment # 02: Chemistry SECTION-I: (I) Only One Option Correct Type 3 (-1) 1Document6 pagesRevision Assignment # 02: Chemistry SECTION-I: (I) Only One Option Correct Type 3 (-1) 1KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physical Test - Q - 05.07.2021Document3 pagesPhysical Test - Q - 05.07.2021joydeep17590No ratings yet
- General Instructions: Examination Question PaperDocument8 pagesGeneral Instructions: Examination Question PaperAakriti RoyNo ratings yet
- The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus Chemistry Class:11Document5 pagesThe City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus Chemistry Class:11api-262668586No ratings yet
- Final Model Foe Grade 12 2011 May (Recovered) PDFDocument18 pagesFinal Model Foe Grade 12 2011 May (Recovered) PDFwondimu0% (1)
- CH 10 Practice Test Liquids Solids-And-Answers-ComboDocument17 pagesCH 10 Practice Test Liquids Solids-And-Answers-ComboHARSHNo ratings yet
- Class 12chemistry - Solutions - McqsDocument18 pagesClass 12chemistry - Solutions - McqsSnekha TNo ratings yet
- GRP 11Document5 pagesGRP 11Dishu BNo ratings yet
- Chem. Assig.Document8 pagesChem. Assig.aryan asliaNo ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry 2014 Part 1 PDFDocument2 pagesHSC Chemistry 2014 Part 1 PDFdgkulkarniNo ratings yet
- Che Paper6Document7 pagesChe Paper6deepasankunyNo ratings yet
- Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument6 pagesSingle Answer Type Questionspinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- MCQS Special TopicsDocument18 pagesMCQS Special TopicsPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Chem PaperDocument4 pagesChem PaperPrasad YarraNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Q.P.Document5 pages12 Chemistry Q.P.Aradhya SinghNo ratings yet
- !2014 Excel G-12 Chemistry Model - 2Document11 pages!2014 Excel G-12 Chemistry Model - 2henotech HDNo ratings yet
- Mock TestDocument3 pagesMock Testariasinghhh07No ratings yet
- Soal KimdasDocument13 pagesSoal KimdasNur SyahrainiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemDocument9 pagesChemistry: Daily Practice ProblemZeroNo ratings yet
- Questions On Gases and SolutionsDocument12 pagesQuestions On Gases and SolutionsChemist Mohamed MohyNo ratings yet
- Sem-2 Board Questions 2017-2019Document21 pagesSem-2 Board Questions 2017-2019roblox guardNo ratings yet
- 13 Worked ExamplesDocument13 pages13 Worked Examplesnttkim0201No ratings yet
- PT-1 Chemistry (SET-A) 2023-24Document4 pagesPT-1 Chemistry (SET-A) 2023-24Manraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Colloids and Interface Science Communications: P.M. Biesheuvel, H.V.M. Hamelers, M.E. SussDocument5 pagesColloids and Interface Science Communications: P.M. Biesheuvel, H.V.M. Hamelers, M.E. SussTheDreamMNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 3 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - Edited.edited Copy - EditedDocument12 pagesSummative Test 3 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - Edited.edited Copy - EditedJV Subang PatindolNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cells MCQsDocument10 pagesFuel Cells MCQsFareeha ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sheet Haxked - 5Document7 pagesChemistry Sheet Haxked - 5manasgandhi684No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry XII PaperDocument4 pages12 Chemistry XII PaperPrinceNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Important 3 Marks Questions With Answers PDFDocument25 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Important 3 Marks Questions With Answers PDFDipti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Liquid SolidDocument9 pagesContoh Liquid Solidloey scaa100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics and ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics and ElectrochemistryB NithuNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of MatterDocument25 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of MatterAnidhya TiwariNo ratings yet
- 111-1 環化第1次段考詳解 V2Document5 pages111-1 環化第1次段考詳解 V2Kyle LuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Chemical KineticsDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - Chemical KineticsShubh MishraNo ratings yet
- 11.5 JK - 11.5 JK 23 JK: Topic: ThermochemistryDocument5 pages11.5 JK - 11.5 JK 23 JK: Topic: ThermochemistryGopal PenjarlaNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2343 Chemistry Assignment PaperDocument8 pagesALPS 2343 Chemistry Assignment PaperchiragNo ratings yet
- Victoria Junior College JC 2 Preliminary Examinations Higher 2Document20 pagesVictoria Junior College JC 2 Preliminary Examinations Higher 2saffronNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Ncert NotesDocument99 pagesClass 10 Ncert Notescrapjorust123No ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument4 pagesSample Papermahima mishraNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Diamond and Graphite Are Examples ofDocument6 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Diamond and Graphite Are Examples ofsalim pradhan100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Question Bank - Part 3Document23 pagesThermodynamics Question Bank - Part 3Upendra YadavNo ratings yet
- ISC 2014 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperDocument23 pagesISC 2014 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperMd Saif UddinNo ratings yet
- 5 Surface-ChemistryExerciseDocument4 pages5 Surface-ChemistryExercisepinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- First Pre-Board Examination (2019-2020) Class: Xii Subject: CHEMISTRY Date: 12.12.2019Document9 pagesFirst Pre-Board Examination (2019-2020) Class: Xii Subject: CHEMISTRY Date: 12.12.2019gaming with skdNo ratings yet
- Nov 2015Document54 pagesNov 2015dharshanaabNo ratings yet
- Courses Science Chemistry 1555934239 2019 Chemistry HSC Past PaperDocument21 pagesCourses Science Chemistry 1555934239 2019 Chemistry HSC Past PaperCullen LumNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-PQ XII 22-23Document12 pagesChemistry-PQ XII 22-23Tanushree KarwatkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquaDocument10 pagesChemical Reactions and Equas sachinNo ratings yet
- Science Class WorkDocument190 pagesScience Class Workrrrprivate777No ratings yet
- 1 Pre-Board Examination - 2020-21: Dav Public Schools, Odisha, Zone-IiDocument9 pages1 Pre-Board Examination - 2020-21: Dav Public Schools, Odisha, Zone-IiAshutosh sahooNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsFrom EverandPhysical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsMitsuru NagasawaNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-21 HydrocarbonsDocument8 pagesC Sol Ch-21 Hydrocarbonsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-01 - Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument2 pagesC - Sol - Ch-01 - Some Basic Concepts of Chemistrymysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-07 - Redox Reactions and Volumetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesC - Sol - Ch-07 - Redox Reactions and Volumetric Analysismysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-09 SolutionsDocument6 pagesC Sol Ch-09 Solutionsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-14 The S-Block ElementsDocument1 pageC Sol Ch-14 The S-Block Elementsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-16 General+Principles+and+Processes+OfDocument4 pagesC Sol Ch-16 General+Principles+and+Processes+Ofmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-23 AtomsDocument5 pagesP Ch-23 Atomsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-12 Kinetic+Theory+of+GasesDocument2 pagesP Ch-12 Kinetic+Theory+of+Gasesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-04 States of MatterDocument3 pagesC Sol Ch-04 States of Mattermysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-11 - Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear ChemistryDocument8 pagesC - Sol - Ch-11 - Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistrymysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-10 WavesDocument7 pagesP Ch-10 Wavesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-03 Laws+of+MotionDocument5 pagesP Ch-03 Laws+of+Motionmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- P Ch-02 Motion+in+a+PlaneDocument3 pagesP Ch-02 Motion+in+a+Planemysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-18 IntegralsDocument2 pagesM Ch-18 Integralsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-15 Limits and DerivativesDocument3 pagesM Ch-15 Limits and Derivativesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-07 DeterminantsDocument3 pagesM Ch-07 Determinantsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-11 CircleDocument6 pagesM Ch-11 Circlemysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Ch-26 BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesC Ch-26 Biomoleculesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-02 Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesM Ch-02 Quadratic Equationsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Ch-24 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument22 pagesC - Ch-24 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Ch-28 - Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument1 pageC - Ch-28 - Chemistry in Everyday Lifemysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- M Ch-08 Trigonometric FunctionsDocument8 pagesM Ch-08 Trigonometric Functionsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Ch-18 Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument7 pagesC Ch-18 Co-Ordination Compoundsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Ch-23 - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument6 pagesC - Ch-23 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethersmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C - Ch-17 - The D - F - Block ElementsDocument2 pagesC - Ch-17 - The D - F - Block Elementsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- C Ch-10 ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesC Ch-10 Electrochemistrymysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Kích thước để chế tạo Robot Delta kiểu ba khớp trượt ngang - LTĐịnhDocument22 pagesKích thước để chế tạo Robot Delta kiểu ba khớp trượt ngang - LTĐịnhLê Thúc ĐịnhNo ratings yet
- User Manual For Remote Midea Mission II Air ConditionersDocument8 pagesUser Manual For Remote Midea Mission II Air Conditionerscostica_dinaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ModelingDocument13 pagesDC Motor ModelingMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Teachnical & Service Manual ARV 7 T1 All DC Inverter series 8-36 hp V1Document163 pagesTeachnical & Service Manual ARV 7 T1 All DC Inverter series 8-36 hp V1sssddssNo ratings yet
- P11 Wk18 WS 2021 Work and Impulse - 1632832373354 - 8fkdqDocument3 pagesP11 Wk18 WS 2021 Work and Impulse - 1632832373354 - 8fkdqRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- 5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Almas TalibNo ratings yet
- Capacity of Cone-Shaped Hollow Flexible ReinforcedDocument14 pagesCapacity of Cone-Shaped Hollow Flexible ReinforcedG.RameshNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument35 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes Haloalkanes and HaloarenesAshish rathoreNo ratings yet
- PNTC Colleges: Activity SheetDocument10 pagesPNTC Colleges: Activity SheetPagtakhan Mary JoyNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Torque de Diametros Grandes Asme B16 47 Metallic GasketsDocument4 pagesTabla de Torque de Diametros Grandes Asme B16 47 Metallic GasketsQuiroa, Antonio JNo ratings yet
- Operating Process For Access To Gas Insulated SwitchgearDocument19 pagesOperating Process For Access To Gas Insulated SwitchgearMaharajaNo ratings yet
- SR 1761Document205 pagesSR 1761apoorva aapoorvaNo ratings yet
- R10-E01 Rev 1 Mar 2017 Instrument Piping and Tubing Systems CriteriaDocument10 pagesR10-E01 Rev 1 Mar 2017 Instrument Piping and Tubing Systems CriteriaSALMANNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum: (Práctica Tomada y Adaptada de David. H - Loyd - PLM)Document6 pagesConservation of Momentum: (Práctica Tomada y Adaptada de David. H - Loyd - PLM)MORENO RANGEL YERAY DARIONo ratings yet
- Building Construction: Century, Andrea Palladio Presented A Design of Truss Bridge Based On ADocument2 pagesBuilding Construction: Century, Andrea Palladio Presented A Design of Truss Bridge Based On Aallyssa monica duNo ratings yet
- FLEXOGUM - Ver 2.0Document3 pagesFLEXOGUM - Ver 2.0Query TANo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 2Document8 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 2Okiror GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Thermoelastic Analysis of A Thin Circular Plate With Radiation Type ConditionsDocument6 pagesThermoelastic Analysis of A Thin Circular Plate With Radiation Type ConditionssijyvinodNo ratings yet
- Batra Ring: DescriptionDocument2 pagesBatra Ring: DescriptionxzarrandikoNo ratings yet
- L 5 The Normal CurveDocument37 pagesL 5 The Normal CurveAiza mae MontiagodoNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Linear Partial Differential Equations With Constant CofficentsDocument17 pagesHomogeneous Linear Partial Differential Equations With Constant CofficentsSerial SpyNo ratings yet
- Construction of Series and Parallel Circuits Using ResistorsDocument7 pagesConstruction of Series and Parallel Circuits Using ResistorsBisma QamarNo ratings yet
- SMC-3 Specs PDFDocument3 pagesSMC-3 Specs PDFManuelNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project PhysicsDocument8 pagesInvestigatory Project PhysicsRonald100% (1)