Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 05 - Forced Vibration
Uploaded by
snafuxxspartanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 05 - Forced Vibration
Uploaded by
snafuxxspartanCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 05: Dynamics and Vibration (UME 513)
Forced Vibrations Response (Undamped/Damped systems)
1. A machine part of mass 1.95 kg vibrates in a viscous medium. Calculate the damping
coefficient when a harmonic exciting force of 24.46 N results in a resonating amplitude of
12.7 mm with a period of 0.20 seconds. (Ans: c = 61.3 N.s/m)
2. For a viscously damped system excited by a harmonic force, F = F0 sint, the resonating
amplitude is found to be 5.8 mm. At 80% of the resonating frequency, the amplitude is
observed as 4.6 mm. Calculate the damping factor for the system from the observed data.
(Ans: =0.18)
3. A machine part having a mass of 2.5 kg vibrates in a viscous medium. A harmonic exciting
force of 30 N acts on the part and causes a resonant amplitude of 14 mm with a period of 0.22
seconds. Find the damping coefficient.
If the frequency of the exciting force is changed to 4 Hz, determine the increase in the
amplitude of the forced vibrations upon the removal of the damper.
[75.04N/m/s; 49.7mm]
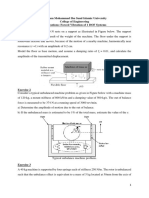
4. A single cylinder vertical diesel engine has a mass of 400 kg and is mounted on a steel chassis
frame. The static deflection owing to the weight of the chassis is 2.4 mm. The reciprocating
masses of the engine amount to 18 kg and the stroke of the engine is 160 mm. A dashpot with
a damping coefficient of 2 N/mm/s is also used to dampen the vibrations. In the steady-state
of the vibrations, determine the
i. Amplitude of the vibrations if the driving shaft rotates at 500 rpm.
ii. Speed of the driving shaft when the resonance occurs.
[7.2mm; 610.5rpm]
5. Consider an automobile traveling over a rough road at a speed of v km/hr. The suspension
system has a spring constant of 40kN/m and a damping ratio of = 0.1. The road surface
varies sinusoidally with an amplitude of Y = 0.05 m and a wavelength of 6m. Find the
displacement amplitude of the automobile for the following conditions: (a) mass of the
automobile = 600 kg (empty), 1000 kg (loaded) (b) velocity of the automobile (v): 10 km/hr,
50 km/hr, 100 km/hr.
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DOM Unit II AssignmentDocument1 pageDOM Unit II AssignmentKeshav PagarNo ratings yet
- DOM Unit 4 & 5 QBDocument6 pagesDOM Unit 4 & 5 QBRayleighNo ratings yet
- Single DOF System Excited Vibrations ProblemsDocument3 pagesSingle DOF System Excited Vibrations ProblemsghulmNo ratings yet
- 4.forced Damped VibrationDocument4 pages4.forced Damped VibrationAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Forced VibrationsDocument3 pagesForced VibrationsshethNo ratings yet
- Machinery vibration question bankDocument1 pageMachinery vibration question bankhumkisisekamnahi 82No ratings yet
- Assignment 06cDocument3 pagesAssignment 06cDhiraj NayakNo ratings yet
- Forced Vibration123Document4 pagesForced Vibration123Himanshu KhannaNo ratings yet
- M.tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Document2 pagesM.tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Rutvik ShethNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 3Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter 3Siti ShuhadaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: Single Degree Free VibrationDocument14 pagesSolved Problems: Single Degree Free Vibrationprem adhikariNo ratings yet
- Forced Vibration of 1 DOF Systems ExercisesDocument12 pagesForced Vibration of 1 DOF Systems ExercisesMohammed Al HelaylNo ratings yet
- Machine Dynamics and Vibration-Forced Vibration AssignmentDocument4 pagesMachine Dynamics and Vibration-Forced Vibration AssignmentVijay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Single Degree of Freedom Systems Question BankDocument4 pagesSingle Degree of Freedom Systems Question Bankxing007No ratings yet
- Find beam dimensions limit motor vibration to 0.5 cmDocument2 pagesFind beam dimensions limit motor vibration to 0.5 cmJuma AlaydiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery Question PapersDocument22 pagesDynamics of Machinery Question PapersMohan Babu S0% (1)
- Previous Questions DomDocument5 pagesPrevious Questions DomSafeer MNo ratings yet
- 5 Longitudinal and Transverse VibrationsDocument4 pages5 Longitudinal and Transverse Vibrationsenggsantu0% (1)
- Sheet 6 EM214Document2 pagesSheet 6 EM214Ahmed M. RezkNo ratings yet
- ME 353 - Assgn1Document4 pagesME 353 - Assgn1Amar KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment (4) Forced Vibration of SDOF Systems PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment (4) Forced Vibration of SDOF Systems PDFKarim FangaryNo ratings yet
- Mechanism MechanicsDocument5 pagesMechanism MechanicsEzmel KazimNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Iyyappan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- DSMV Assignment IIDocument3 pagesDSMV Assignment IIRajakumar SaiNo ratings yet
- Panimalar Engineering College Mechanical Engineering IA-II Dynamics of MachinesDocument4 pagesPanimalar Engineering College Mechanical Engineering IA-II Dynamics of MachinesThamizh Selvan SNo ratings yet
- Balancing of Rotating Masses and Forces in MachinesDocument5 pagesBalancing of Rotating Masses and Forces in MachinesSridhar KanagarajNo ratings yet
- S6 QB MeDocument18 pagesS6 QB MevenkiteshksNo ratings yet
- M.tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Document2 pagesM.tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Rutvik ShethNo ratings yet
- Damped Vibration and Critical Speed AnalysisDocument4 pagesDamped Vibration and Critical Speed AnalysisDhinakaran VeemanNo ratings yet
- BE - 2019 - Dynamics of MachineryDocument5 pagesBE - 2019 - Dynamics of Machineryparthadhav2020.mech1No ratings yet
- M.Tech Semester-II Structural Dynamics TutorialDocument2 pagesM.Tech Semester-II Structural Dynamics TutorialRutvik ShethNo ratings yet
- ME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDocument4 pagesME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsMukul Chandra0% (1)
- Anna University Madras Institute of Technology: 718 R.P.M N 843 R.P.M)Document4 pagesAnna University Madras Institute of Technology: 718 R.P.M N 843 R.P.M)veeyeskay_2006No ratings yet
- Master of Science-Technology-Mechanical System Design Batch 1 Semester IV - Phase 1 Advanced Mechanical Vibrations Test-1Document2 pagesMaster of Science-Technology-Mechanical System Design Batch 1 Semester IV - Phase 1 Advanced Mechanical Vibrations Test-1Ananda Babu ArumugamNo ratings yet
- DOM Asst Question - IIIDocument1 pageDOM Asst Question - IIIAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Mechanical SystemsDocument3 pagesVibration Analysis of Mechanical Systemsrkumaravelan100% (1)
- Balancing of rotating and reciprocating massesDocument3 pagesBalancing of rotating and reciprocating massesBhavesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Worked Out Problems - Vibrations-DOMDocument103 pagesWorked Out Problems - Vibrations-DOMTom TambeNo ratings yet
- Machinery Dynamics Question Bank GuideDocument2 pagesMachinery Dynamics Question Bank GuideArun ManoNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesImportant QuestionsdineshbabuNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY MODEL QUESTION PAPERDocument4 pagesMECHANICAL ENGINEERING DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY MODEL QUESTION PAPERNirman ParasharNo ratings yet
- B F1040 Pages: 4: Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 MarksDocument4 pagesB F1040 Pages: 4: Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 MarksVaisakhan.A.SNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 Vibrations 2017Document3 pagesAssignment-1 Vibrations 2017Arpit Sharma0% (1)
- Practice Problems Based On Free & Forced Vibrations of SDOF SystemDocument3 pagesPractice Problems Based On Free & Forced Vibrations of SDOF Systemzeeshanahmad111No ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 3Document2 pagesTutorial Chapter 3hanaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit IIDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank Unit IISachin BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Damping coefficient and resonant amplitude of vibrating machine partDocument10 pagesDamping coefficient and resonant amplitude of vibrating machine partAlhji AhmedNo ratings yet
- Damping ExerciseDocument5 pagesDamping ExerciseArif NecNo ratings yet
- Au Qp-Me8594 PDFDocument18 pagesAu Qp-Me8594 PDFMariappan VNo ratings yet
- 8 Mechanical VibrationsDocument10 pages8 Mechanical VibrationsTsihatesfaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering Tutorial - Instrument Acceleration DampingDocument1 pageEarthquake Engineering Tutorial - Instrument Acceleration DampingRutvik ShethNo ratings yet
- University QuestionsDocument4 pagesUniversity QuestionsMartin De Boras PragashNo ratings yet
- D04FA48908744891B70ED91613E5E5ABDocument4 pagesD04FA48908744891B70ED91613E5E5AByashvantNo ratings yet
- ME351 MDV Jan14 DampedFreeVibrationTutorial Tut02 PDFDocument4 pagesME351 MDV Jan14 DampedFreeVibrationTutorial Tut02 PDFJim HarrisNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet