Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Literary Techniques
Uploaded by
Sohania Roopai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesLiterary Techniques
Uploaded by
Sohania RoopaiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Literary Techniques to learn
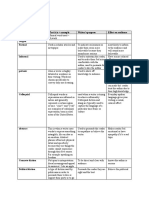
Similes Personification Symbolism 5 Senses
One thing is like or as another Writer describes a non-human thing Use symbols to portray and idea Describe settings by appealing to the
As thin as a beanpole Using human-like actions and (What it looks like) reader’s 5 senses
Metaphors emotions White dove - peace It adds depth
More direct The sea roars
No like or as
The stars were diamonds
Foreshadowing Tone Punctuation + font Rhetorical questions
The writer hints something is going Writer’s attitude towards what he Comma: used to create urgency and Make audience think more deeply
to happen writes or towards the readers abundance about an issue or to prove a point.
Sneak peak to create suspense Tone can change suddenly Colons and semi-colons:
E.g. in fiction: a stormy sky Tone must adapt to audience create a short break In narrative pieces it may indicate a
P1: when commenting on writer’s divert attention to words after the struggle.
tone, don’t be vague colon or semi-colon.
P2: adopt tone to audience you Capitals + bold fonts grab attention Useful in P2
write for Hyphens and brackets add additional
Modality information
Writer’s attitude towards the world. Sometimes connection between
write and audience
Repetition Alliteration Onomatopoeia Juxtaposition
Useful in speeches and persuasive Same consonants placed together A word is formed from a sound Contrasting ideas/words are placed
articles. Used to mimic sounds or create Creates lively and noisy atmosphere close together
Used to prove a point rhythm Thud, slam Oxymorons
To create certain effect Contrasting ideas are placed side-
The snake slithers by-side
Deafening silence
Juxtapositions and Oxymorons are
used to create emphasis
Hyperbole Allusion Tense Sentence length
Exaggerated statement Indirect reference is made to a To create tone Short sentence: to create fear and
“You told me this a million times” person/event/place. Past tense: nostalgia suspense.
Helps to reflect feelings of Use the familiar to describe Present tense: urgency, despair Long sentence: long and windy idea
annoyance something less familiar. We experience what the character is
experiencing
Future tense: effect of determination
“I will wake up at 4:00”
Point of view Puns Jargon Neologism
First person “I”, “myself”. Word-play that used words/phrases A technical term to do with a New word created by writer
See things through the writer’s eyes. that sound familiar but mean totally technical field that people outside the “eater-tainment”
different things. field may find difficult to understand.
Second person Create interest, focus. Targeted to a specific audience. Aspect
Personal pronouns “you”, “you’re”, “I am so fed up with chocolate” Writer creates a bond with audience Perfect She will call you
“your” because only they are familiar with it. Progressive (continuous)
Speeches and persuasive writing She was running late
Writer appears to speak directly to
the audience.
Third person “he”, “she”, “they”
Writer describes another person’s
feelings and experiences.
Asyndeton Irony Verbs, adverbs, + adjectives Showing, not telling
A conjunction is omitted from a A message/idea which uses Verb: action word Imply something, not explicitly
sentence. language that means the opposite of “bellowed” not “shouted” stating it.
“I stopped, turned, ran”. what the writer is trying to say. Hot: “My T-shirt is sticking to my
Increases pace of story. Creates humorous effect. Adverb: describes the verb body”
Makes writer sound breathless. “bellowed ferociously”
Adjective: describes a noun
“enormous man”
Paradox Euphemism Amplification Dialogue
Statement that seems false but could A term used instead of an offensive Add extra information to enhance the Conversation.
be true. one. idea. To create fear, happiness, anger
Makes us think. Writer is considerate.
“All animals are equal but soe are Newspapers – crime
more equal than others”
Triadic structure Stream of consciousness Syntax Tautology
Things are placed in groups of 3 Character’s thoughts/emotions are Order of words in a phrase/sentence Repeat single idea using different
“sugar, spice and all things nice” described continuously. Changing syntax diverts the focus. words.
Creates pleasant rhythm. Natural thought process, does not “never have I lied to you” “last and final call”
Readers cling to the idea. have to be grammatically correct. Emphasises “never”. Emphasises
It connects the reader to the
characters (he knows what they are
thinking).
You might also like
- English Language and Literature Key Terms DictionaryDocument7 pagesEnglish Language and Literature Key Terms Dictionarysynxz2kNo ratings yet
- Stylistic Devises & Their EffectsDocument2 pagesStylistic Devises & Their EffectsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Literary Techniques GlossaryDocument3 pagesYear 8 Literary Techniques GlossaryMUBASHIR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Figurative LanguageDocument2 pagesFigurative LanguageNoel Krish ZacalNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Poetic Terminology IGCSEDocument4 pagesGlossary of Poetic Terminology IGCSEhappytingsNo ratings yet
- Table of Poetic TermsDocument6 pagesTable of Poetic TermsVincey LuNo ratings yet
- Better Team On The Day: The Slippery Slithering SnakeDocument4 pagesBetter Team On The Day: The Slippery Slithering SnakenerdasdasdNo ratings yet
- HhnxcbaDocument31 pagesHhnxcbaGael GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Literary Technique Explanation and ExampleDocument7 pagesLiterary Technique Explanation and Exampleapi-615425726100% (1)
- Y11 Persuasive Writing Devices BookletDocument7 pagesY11 Persuasive Writing Devices BookletJack LarkinNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument3 pagesLiterary DevicesMara BravoNo ratings yet
- Knowing The Language of Creative Writing 2Document1 pageKnowing The Language of Creative Writing 2JM AsisNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review For 1st Periodical Test in Creative WritingDocument7 pagesPointers To Review For 1st Periodical Test in Creative Writingrose abalosNo ratings yet
- Diction: Type What It Is + Example Writer's Purpose Effect On Audience Slang Jargon FormalDocument3 pagesDiction: Type What It Is + Example Writer's Purpose Effect On Audience Slang Jargon FormalAisyah AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument1 pageLiterary DevicesBrano HanesNo ratings yet
- Language TechniquesDocument5 pagesLanguage TechniquesPhilip VuuNo ratings yet
- Keep Forever-Literary LexiconDocument3 pagesKeep Forever-Literary Lexiconart niyetliNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language-Group 2Document16 pagesFigurative Language-Group 2authelia esmeeran fusunNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Creative WritingDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Creative WritingBecca Olorvida-Roquid100% (1)
- Rhetorical Devices Handout PDFDocument4 pagesRhetorical Devices Handout PDFNashie Omar RomancapNo ratings yet
- ReportingDocument10 pagesReportingdyesaendaya06No ratings yet
- Analyze Literary and Nonfiction TextsDocument5 pagesAnalyze Literary and Nonfiction TextsWayne HNo ratings yet
- Language Techniques KS4Document1 pageLanguage Techniques KS4THE PSYCONo ratings yet
- English Year 7 Spring 1 KO - Narrative and Descriptive WritingDocument3 pagesEnglish Year 7 Spring 1 KO - Narrative and Descriptive WritingDarien DCostaNo ratings yet
- Some Possible Aims Rhetorical Devices, Other Strategies Phrases For The AnalysisDocument3 pagesSome Possible Aims Rhetorical Devices, Other Strategies Phrases For The AnalysisHannahNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices 1. Alliteration - Alliteration Is TheDocument5 pagesLiterary Devices 1. Alliteration - Alliteration Is TheDona Sabucdalao SacoteNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument31 pagesLiterary DevicesMarvin PilienNo ratings yet
- 21st Lit Module 4 Non+FictionDocument25 pages21st Lit Module 4 Non+FictionJennie KImNo ratings yet
- Literary ElementsDocument2 pagesLiterary ElementsnettextsNo ratings yet
- ReviewerlitDocument3 pagesReviewerlitQuinperl DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing - Q1 - M4Document10 pagesCreative Writing - Q1 - M4Aldous AngcayNo ratings yet
- Subject Terminlogy ListDocument5 pagesSubject Terminlogy Listkomalsaeed265No ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument6 pagesLiterary DevicesZaira UsmanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Prelim)Document4 pagesReviewer (Prelim)stream boy by treasureNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument4 pagesLiterary Devicesjuned ansariNo ratings yet
- LANGUAGE of CW Figures of SpeechDocument41 pagesLANGUAGE of CW Figures of Speechkhryslerbongbonga30No ratings yet
- Australian Poetry Booklet 2023Document62 pagesAustralian Poetry Booklet 2023orla earnshaw100% (1)
- Foreign Carol Ann DuffyDocument14 pagesForeign Carol Ann DuffyBao ngoc pham duongNo ratings yet
- Literary Techniques - 2Document3 pagesLiterary Techniques - 2Roozbeh ElaviaNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction - Weeks 1-2Document44 pagesCreative Nonfiction - Weeks 1-2Dorothy Shane PradasNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices in RhetoricDocument4 pagesLiterary Devices in Rhetoricapi-369556537No ratings yet
- Ib Middle Years Program English Theory v1Document24 pagesIb Middle Years Program English Theory v1felvin kwofieNo ratings yet
- English BIBLEDocument7 pagesEnglish BIBLELachlan PurnellNo ratings yet
- Bildschirmfoto 2022-08-30 Um 12.27.48Document3 pagesBildschirmfoto 2022-08-30 Um 12.27.48Alison LiskenNo ratings yet
- Litterary TechniquesDocument16 pagesLitterary Techniquesbenjamin_hoatsonNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing ReviewerDocument7 pagesCreative Writing ReviewerKendall JennerNo ratings yet
- (GR) Devices Writers Use To Create EffectsDocument4 pages(GR) Devices Writers Use To Create EffectshariNo ratings yet
- Poetry Matching Cards For Review 8thDocument6 pagesPoetry Matching Cards For Review 8thAbigail CornelNo ratings yet
- English 8 PoetryDocument24 pagesEnglish 8 PoetryXysti Moncada100% (1)
- 12EA Language TechniquesDocument5 pages12EA Language TechniquesAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Lesson 1Document34 pagesCreative Writing Lesson 1Raekiey JujuNo ratings yet
- The Wonderful World of PoetryDocument27 pagesThe Wonderful World of PoetryMary Jo LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Mod1a RD PresentationDocument79 pagesMod1a RD Presentationapi-486324042No ratings yet
- PoetryDocument22 pagesPoetryAngel FyraNo ratings yet
- 10B Poetic Device DefinitionDocument3 pages10B Poetic Device DefinitionMalika MamajonovaNo ratings yet
- Additional Authors Craft Notes WhyDocument2 pagesAdditional Authors Craft Notes WhyMohamedNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument4 pagesFigure of Speechjoanna gurtizaNo ratings yet
- CW ReviewerDocument16 pagesCW ReviewerrxnnvalenzuelaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument8 pagesTensesMuhammad Fauzi AndriansyahNo ratings yet
- Present Tense - TableDocument2 pagesPresent Tense - TableAlexandru BorzaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Would, Should, Ought To, Had Better, Might, Used ToDocument4 pagesReported Speech: Would, Should, Ought To, Had Better, Might, Used ToOstein VittorioNo ratings yet
- Feeble SlidesCarnival..Document7 pagesFeeble SlidesCarnival..Alya FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Makalah Present Perfect Tense Etc OthersDocument8 pagesMakalah Present Perfect Tense Etc OthersIan SariantoNo ratings yet
- TM 6-7 Learning-Description MDocument10 pagesTM 6-7 Learning-Description MAgustinNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect Speech Gr10-1Document18 pagesDirect & Indirect Speech Gr10-1joshdevree3No ratings yet
- Conditionals Part 1: If I Cook More, I'll Get Better at CookingDocument6 pagesConditionals Part 1: If I Cook More, I'll Get Better at CookingLidia Mateos RomeroNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Gr.10 Week 1 Day 1Document6 pages4th Quarter Gr.10 Week 1 Day 1BellNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ExerciseDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Voice ExercisedthaaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Past and Past Continuous TenseDocument18 pagesThe Simple Past and Past Continuous TenseBrenda KimNo ratings yet
- Toynbee MW Visitor's Guide ST LucianDocument33 pagesToynbee MW Visitor's Guide ST Lucianavocetave100% (1)
- Quran GrammarDocument197 pagesQuran GrammarYourHand100% (1)
- Assignment 222Document5 pagesAssignment 222Dincer Dinc100% (2)
- Japanese Class VerbDocument7 pagesJapanese Class VerbHarihara SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Adesty Dwi Andansari 1902420Document18 pagesAdesty Dwi Andansari 1902420Maysa HasanahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan:: Present Perfect TenseDocument4 pagesLesson Plan:: Present Perfect TenseMalika NamazbekovaNo ratings yet
- Crashcourse LojbanDocument4 pagesCrashcourse LojbanMaria Perla Araújo MoraisNo ratings yet
- English 3 Weeks 6-7Document9 pagesEnglish 3 Weeks 6-7yilber castellanosNo ratings yet
- English Module F1Document21 pagesEnglish Module F1syarhan channelNo ratings yet
- Nabella Lestari 2017002022 Pscho 7CDocument16 pagesNabella Lestari 2017002022 Pscho 7CBella LestariNo ratings yet
- 3 Sounds of The PluralDocument6 pages3 Sounds of The PluralpatrililianNo ratings yet
- Tenses in English LanguageDocument44 pagesTenses in English LanguageГалина РоманчукNo ratings yet
- Laminas PDFDocument25 pagesLaminas PDFCharalNo ratings yet
- English Grade 12 Lesson Note 2Document7 pagesEnglish Grade 12 Lesson Note 2Kaleab AlebachewNo ratings yet
- Iit Indore Cse SyllabusDocument199 pagesIit Indore Cse SyllabusVenuSrivatsavaNo ratings yet
- Ditar 2.6Document3 pagesDitar 2.6egla berberiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VI TelephoningDocument14 pagesCHAPTER VI TelephoningolaonlyNo ratings yet
- Materyal Tasarim Fi̇nal Projesi̇Document32 pagesMateryal Tasarim Fi̇nal Projesi̇Esra Nur EDİŞNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tenses: by Salsabila Naqiyyah Xiia1Document13 pagesPerfect Tenses: by Salsabila Naqiyyah Xiia1Salsabila NaqiyyahNo ratings yet