Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychological Assessment Prefinals
Uploaded by
ale.cristianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psychological Assessment Prefinals
Uploaded by
ale.cristianCopyright:
Available Formats
PSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT (PREFINALS)
THE SOURCES OF MEASUREMENT ERROR
RELIABILITY
There can be several
errors with the process of
test construction, it
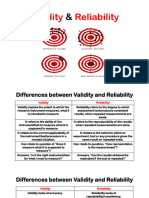
Reliability is the degree to which an assessment includes the test items
tool produces stable and consistent results. In and the item sampling
other words, a psychological test or assessment itself.
would only be considered valuable if it can get the
same results upon each administration. In other words, the items
included in a test and how
Example: A ruler would give the same results every they were selected could
single time we would use it to measure the length produce measurement
of an object which is why it is considered as errors in a test when it
reliable. Test Construction comes to its
construction. It is
A reliability coefficient is an index of reliability, a possible that the items
proportion that indicates the ratio between the true included In a test does not
scored variance on a test and the total variance. In really measure the
other words, reliability coefficient refers to the desired construct, it
numerical index or the value of the reliability of a could also because the
test, meaning to say it expresses whether or not a test maker was not able to
test or an assessment is reliable. select the questions
properly.
Usually, reliability coefficient ranges from 0 to 1. A
score of 0 to 0.60 means that the test is not reliable
while a grade from 0.70 to 1 indicates that it is in
fact reliable. In other words, unlike the classical When it comes to the test
test theory, reliability coefficient is numerical in administration factors
such as environment, test
nature.
taker, and test
administrator (examiner
related variables such as
THE CONCEPT OF RELIABILITY Test Administration appearance and
treatment) could become
The Classical Test Theory is a score on a test that is the reason for the
presumed to reflect not only the true score of the existence of errors in a
test taker on the ability being measured but also test or assessment.
the error. The said theory claims that the observed
score (X) is formulated through the combination of
the true score (T) and error (E). It means that what As for the errors in the test
we get from a test is only the observed score since scoring and interpretation
true score can only be acquired if there is an there are actually two
absence of error which is not possible in the real Test Scoring and types of them, test and
world. However, classical test theory cannot be Interpretation pencil test errors and
numerically translated. digital errors.
CLASSICAL TEST THEORY FORMULA When it comes to digital
errors, the most common
X (observed score) = T (true score) + E (error) factors that contribute to
its existence in a test
include the internet TYPES OF RELIABILITY
connection, the device
that is being used, etc.
On the other hand, in a
test and pencil setting the
primary issue is what is It is a test of reliability
called subjective scoring obtained by
also known as bias correlating pairs of
grading which is scores from the same
commonly present during people on two
the scoring of projective different
tests. administrations of the
same test. The test-
retest reliability could
be considered high if
INTERPRETING TEST RESULTS the score from the
initial and final testing
A reliability coefficient can range from a value of 0
correlates with each
to a value of 1. The reliability of a test needs to be
other.
around a score of 0.70 (70%) and above in order to
be considered as reliable (high reliability). A high However, when it
reliability indicates that the test is measuring comes to test-retest
something (its desired variable) while a low reliability have to
reliability means that the measurements made consider the construct
through the use of the said test are only due to or the variable being
coincidence. Furthermore, a score of flat 1 Test-Retest measured. If it is
indicates that the test does not have any presence Reliability consistently changing
of error (which is impossible). such as states, test-
retest reliability would
Additionally, if the reliability coefficient is lower be useless.
than .70 it means that the majority of the test
variance is error which means that most of the test Test-retest reliability
scores are only out of chances. often deals with test
administration errors
A high reliability is a requirement for high validity, since the test needs to
meaning to say a test cannot be valid without being be administered twice
reliable, however, it can be reliable without being which makes it prone
valid. In simpler terms, in order for test to be to errors during the
considered valid it needs to be capable of time period between
measuring a variable accurately with the same the initial and final
testing.
level of precision while on the other hand, a test
can have a high level of precision but low level of
The statistical tools
accuracy. that can be used in this
type of reliability are
either Pearson R or
Spearman Rho.
It refers to the
measure of reliability
obtained by It is the consistency of
administering results among two or
different versions of an more different forms
assessment tool (both of a test.
versions must contain
items that probe the Parallel Form and
same construct, skill, Alternative-Form
knowledge, base, etc) Reliability are
to the same group of somewhat similar with
individuals. The scores each other since both
from the two versions of them is in need of
can then be correlated having large number of
in order to evaluate the test questions that
consistency of results measure the same
across alternate construct and then
versions. they would be split
into two separate
In simpler terms, in tests. However, in
this type of reliability parallel form the mean
the test taker would of the test scores of
need to take different both tests are
tests which measure identical while on the
the same construct. Alternative-Form other hand, in
Parallel Forms Reliability alternative-form, the
Reliability Usually, test makers mean of the two tests
create a vast number is not that similar with
of test questions each other. The
which they would then statistical tool used for
split into two in order the both of them are
to have two different either Spearman Rho
tests which measure or Pearson R.
same construct.
In Alternative-Form
The Parallel Forms Reliability, the errors
Reliability deals with are mainly due to the
errors from test test administration
administration due to because of the time
the time interval interval and test
between the testing construction since the
and the test more test questions
construction since it is are formulated the
possible that the items higher the risk of the
in the tests are not presence of
consistent with the inconsistency.
construct needed to
be measured.
It is a measure of
reliability used to
assess the degree to
which different judges
or raters agree in their
It this type of reliability, assessment
a test for a single decisions.
construct is split into
two parts (odd and In this type of reliability
even numbers) and there are three raters
then both parts are that are tasked to rate
given to the same the test in question. If
group at the same the data from the
time. After that the raters are in line with
scores from both parts each other they can
of the test are Inter-Rater agree that the test is
correlated. The Reliability indeed reliable.
difference between
Parallel Form, In this type of reliability
Alternative-Form, and there is only a single
Split-Half Reliability is test administration
that the former have to and test being
be administered with assessed.
time interval while the Furthermore, most of
Split-Half Reliability latter does not need the errors that occur in
to. this type of test are
due to test scoring and
The errors in this type interpretation. While
or reliability are mainly on the other hand, the
due to test statistical tool that
construction since it can be used in this
has a large number of type of reliability is the
items which increases Pearson R.
the risk of having some
of them being
inconsistent with the It is the type of
construct being reliability that refers to
measured. the degree of
correlation among all
In Split-Half Reliability, items on a scale. It
there is only a single means that it deals
test administration with the test item,
and two numbers of Internal Consistency about how consistent
tests (odd and even). the function of the
The statistical tool items is, unlike in the
used in this type of Parallel Form and
reliability is Pearson R. Alternative-Form that
deal with the
performance of the
test taker. It only has
single administration.
It is useful in assessing with five or seven
the homogeneity of choices in place.
the test. Meaning to
say how good is an
item (question) when it
comes to the THE NATURE OF THE TEST
measurement of a
Closely related to considerations concerning the
single variable.
purpose and use of a reliability coefficient are
Kuder-Richardson 20 those concerning the nature of the test itself.
is a statistical tool Included here are considerations such as whether:
used only if the test
1. The test is heterogeneous or
items are highly
homogeneous in nature. To specify further,
homogenous which
means it only homogeneous means it is uniform
measures a single throughout, it only measures one factor or
variable. On the other variable all throughout, it indicates that
hand, it is also used if there is a high possibility that the test has
the difficulty of the a high internal consistency since the items
items is different with are most probably related to each other.
each other. On the other hand, if it is heterogeneous, it
Additionally, it is also means that the test measures more than
used if the test is one trait which also indicates that it is
binary, it means that it highly possible that the internal
is only answerable by
consistency of it is significantly low due to
yes or no.
the presence of multiple types of
questions that aim to measure different
However, if the level of variables.
difficulty of each item
varies from each other 2. The characteristic, ability, trait being
the statistical tool that measured is presumed to be dynamic or
would be needed to static. Dynamic refers to the type of test
use is the Kuder- that is ever changing while static is the
Richardson 21. opposite of it.
Assuming that the variable that is needed
Coefficient Alpha or to be measured is dynamic the best type of
Cronbach Alpha is
reliability to use would be inter item
appropriate for use on
consistency since it is only a single
tests containing non
dichotomous items. It administration. On the other hand, when it
means that it is used if comes to static variables the best type of
the test is designed to reliability would be test-retest since it is
be answered by two or built to measure constructs that do not
more responses, this change frequently.
would be the proper
tool for the job. An
example would be a
Likert Scale which
allows the test taker to
answer the question
3. The range of test scores is or is not ALTERNATIVES TO THE TRUE SCORE
restricted. MODEL
If the variance of either variable in a
correlational analysis is restricted by the DOMAIN SAMPLING THEORY
sampling procedure, then the resulting
correlations tend to be lower. In simpler It states that each item in a test is an
terms, if the participants that were chosen independent trait or ability being
were gathered based on a criterion, there measured. This theory states that if the
is a possibility that the correlation would reliability of the test is low, the only thing
be lower. that is needed to be done is to add more
items to the test (double the number of
On the other hand, If it is inflated by the items to be specific).
sampling procedure, then it tends to be
higher. It means that if the participants The larger the sample, the more likely that
were chosen randomly, there is a the test will represent true characteristics.
possibility that the correlation would be
higher.
4. The test is a speed or a power test. When
we say power test, it means that the speed
of the test taker when it comes to
answering the test, instead, it focuses on
the right answers that he/she managed to
get. Usually, power tests are those that
contain a hard set of questions.
On the other hand, in the speed test the
factor being considered is the time limit. It
usually has a uniform level of difficulty.
The type of reliability to use could be
Alternative-Forms Reliability or Test-
Retest Reliability since they mainly focus
on the performance of the test taker.
5. The test is or is not criterion-referenced
test. If the test is criterion-referenced, the
type of reliability that is needed to be used
should be Inter-Rater Reliability, Parallel
Form Reliability, or Alternative-Form
Reliability. While on the other hand, if the
test is not criterion-referenced, all the
types of reliability can be used, it would
only depend on the construct being
measured.
You might also like
- Summary Chapter Vi To X (Io Psych Aamodt)Document16 pagesSummary Chapter Vi To X (Io Psych Aamodt)Joseanne Marielle100% (2)
- Subfields in PsychologyDocument3 pagesSubfields in PsychologyJoel AugustusNo ratings yet
- Different Types of ReliabilityDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of ReliabilityminnalecvaNo ratings yet
- Notes Ec PsychassDocument25 pagesNotes Ec PsychassalbzkeNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Dr. Ghias Ul Haq. Submitted By: Noorulhadi Qureshi (PHD Scholar)Document27 pagesSubmitted To: Dr. Ghias Ul Haq. Submitted By: Noorulhadi Qureshi (PHD Scholar)iqraNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment HW #7Document8 pagesPsychological Assessment HW #7maerucelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RecruitmentDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Recruitmenthallie PalmerNo ratings yet
- 02-C. Selection TechniquesDocument52 pages02-C. Selection TechniquesJomalyn7No ratings yet
- Week 2 Readings (CH 4-5)Document33 pagesWeek 2 Readings (CH 4-5)Bethany LongNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methodology: 11. Reliability and Validity Assessment in Study Design, BDocument6 pagesStatistical Methodology: 11. Reliability and Validity Assessment in Study Design, BShalini A/P SurianarayananNo ratings yet
- Clinical Interpretation of "Test-Retest Reliability of The Evaluation Tool of Children's Handwriting-Manuscript"Document3 pagesClinical Interpretation of "Test-Retest Reliability of The Evaluation Tool of Children's Handwriting-Manuscript"Lena CoradinhoNo ratings yet
- Characteristicsofagoodtest 120403015022 Phpapp01Document23 pagesCharacteristicsofagoodtest 120403015022 Phpapp01Marlon BlasaNo ratings yet
- The Research of Reliability and Validity On Computer Courses Network Test SystemDocument3 pagesThe Research of Reliability and Validity On Computer Courses Network Test SystemnandarizqiapradanaNo ratings yet
- 8602 Unit 6Document19 pages8602 Unit 6Masooma Ishrat100% (1)
- B.Ed Course 8602Document19 pagesB.Ed Course 8602Hub e BattolNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment HW #6Document16 pagesPsychological Assessment HW #6maerucelNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 8602Document22 pagesUnit 6 8602ilyas100% (1)
- Kuliah 9 - Kesahan Dan Kebolehpercayaan InstrumenDocument31 pagesKuliah 9 - Kesahan Dan Kebolehpercayaan InstrumenAINATY BT MD. YUSOF WATTY -No ratings yet
- Validity and Reliability: Joanna Ochoa VDocument15 pagesValidity and Reliability: Joanna Ochoa VFitri EmiNo ratings yet
- A) There Are Different Types of Reliability. B) It Is Seldom An All-Or-None Matter. C) Tests Are Reliable To Different Degrees. D) All of The AboveDocument2 pagesA) There Are Different Types of Reliability. B) It Is Seldom An All-Or-None Matter. C) Tests Are Reliable To Different Degrees. D) All of The AbovedanielNo ratings yet
- Concept of Reliability and ValidityDocument6 pagesConcept of Reliability and ValidityAnjaliNo ratings yet
- 8602 2nd AssignmentDocument48 pages8602 2nd AssignmentWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument5 pagesValidity and Reliabilityrawan.taha2000.rtmNo ratings yet
- Reliability - On The Reproducibility of Assessment DataDocument8 pagesReliability - On The Reproducibility of Assessment Datagus_lionsNo ratings yet
- 6499e3fbd5519 Explain Approaches To Gathering Reliability and Validity Evidence For Specific Psychological Testing PurposesDocument6 pages6499e3fbd5519 Explain Approaches To Gathering Reliability and Validity Evidence For Specific Psychological Testing PurposesNgacha hitsNo ratings yet
- AZA3462 2019 Lecture 3Document20 pagesAZA3462 2019 Lecture 3Mbali TshabalalaNo ratings yet
- OnlundDocument12 pagesOnlundapi-3764755100% (2)
- Week 2 LecturesDocument13 pagesWeek 2 LecturesBethany LongNo ratings yet
- 9 ReliabilityDocument10 pages9 Reliabilitystephen allan ambalaNo ratings yet
- IO Chapter6 FinalDocument10 pagesIO Chapter6 FinalJulia MoplaNo ratings yet
- Selection Method Standards: Types of Reliability EstimatesDocument4 pagesSelection Method Standards: Types of Reliability Estimatesjohn randelNo ratings yet
- Reliability (Statistics) : Navigation SearchDocument3 pagesReliability (Statistics) : Navigation SearchN. SivaNo ratings yet
- PT PresentaionDocument25 pagesPT PresentaionNoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 9 - Kesahan Dan Kebolehpercayaan InstrumenDocument31 pagesKuliah 9 - Kesahan Dan Kebolehpercayaan InstrumenMardhiah Ramlan100% (1)
- ValidityDocument26 pagesValidityRathiNo ratings yet
- Qualities of An Evaluation ToolDocument42 pagesQualities of An Evaluation ToolShijiThomasNo ratings yet
- Bunga Refira - 1830104008 - Resume 3Document6 pagesBunga Refira - 1830104008 - Resume 3Bunga RefiraNo ratings yet
- Reliability Vs Validity in ResearchDocument12 pagesReliability Vs Validity in ResearchnurwadiaNo ratings yet
- 4 Essential Criterions of A Good TestDocument31 pages4 Essential Criterions of A Good TestWasan AbdulbasetNo ratings yet
- Research Instrument: Dr. Eunice B. Custodio PhilippinesDocument12 pagesResearch Instrument: Dr. Eunice B. Custodio PhilippinesJerico Refamonte ValezaNo ratings yet
- HRM Lesson 4Document16 pagesHRM Lesson 4john randelNo ratings yet
- MBA Free EbooksDocument56 pagesMBA Free EbooksedholecomNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument15 pagesValidity and ReliabilityMelii SafiraNo ratings yet
- Quantitative SherlockDocument13 pagesQuantitative SherlockCARL JUSTINE LADRANo ratings yet
- A Hitchhiker's Guide To Reliability: Charles DarrDocument2 pagesA Hitchhiker's Guide To Reliability: Charles DarrRIKKA JELLEANNA SUMAGANG PALASANNo ratings yet
- Reliability, Validity, 2015Document15 pagesReliability, Validity, 2015swethashakiNo ratings yet
- Employee Testing and Selection: Presented By: Group 6Document20 pagesEmployee Testing and Selection: Presented By: Group 6Nguyen Thuy LinhNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Validity PresentationDocument22 pagesResearch Methodology Validity PresentationJuhiNo ratings yet
- Equiz No. 5 Abac, Regina Claire G.Document4 pagesEquiz No. 5 Abac, Regina Claire G.Regina AbacNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Educ 105 ModifiedDocument28 pagesModule 3 Educ 105 ModifiedMaria Zobel CruzNo ratings yet
- 8602 Assignment No 2Document24 pages8602 Assignment No 2Fatima YousafNo ratings yet
- What Is TestDocument10 pagesWhat Is TestAmmar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Validity and ReliabilityDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Validity and ReliabilityWinifridaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Lesson1 Assessment MethodDocument31 pagesChapter 3-Lesson1 Assessment MethodAires Mae Cafe TagalogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Understanding Test Quality-Concepts of Reliability and ValidityDocument10 pagesChapter 3: Understanding Test Quality-Concepts of Reliability and ValidityRose DumayacNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning: Proverbs 3:3Document2 pagesAssessment of Learning: Proverbs 3:3Elisa R. VisccaNo ratings yet
- Validity Types - Test ValidityDocument3 pagesValidity Types - Test ValidityCiobanu IuliaNo ratings yet
- Umamah ValidityDocument6 pagesUmamah ValidityJoozher ElifNo ratings yet
- Validity in TestingDocument18 pagesValidity in Testingreza jazmiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Reliability-1Document90 pages6 - Reliability-1Samantha TavaresNo ratings yet
- Evaluating a Psychometric Test as an Aid to SelectionFrom EverandEvaluating a Psychometric Test as an Aid to SelectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Psychological Assessment RRL Group 7Document8 pagesPsychological Assessment RRL Group 7ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Psychological AssessmentDocument16 pagesAssignment in Psychological Assessmentale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Field Methods in Psychology PrelimsDocument22 pagesField Methods in Psychology Prelimsale.cristianNo ratings yet
- GROUP-Will of DDocument32 pagesGROUP-Will of Dale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Field Methods in Psychology MidtermsDocument12 pagesField Methods in Psychology Midtermsale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Research in FMP CHAPTER 1 TO 3 Okay Na Chapter 2Document27 pagesResearch in FMP CHAPTER 1 TO 3 Okay Na Chapter 2ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Straus Kinnard WilliamsneglectDocument30 pagesStraus Kinnard Williamsneglectale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment (Midterms)Document20 pagesPsychological Assessment (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry (Midterms)Document3 pagesBiological Chemistry (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Lem4 - 500x200 - Garnet EspDocument276 pagesLem4 - 500x200 - Garnet Esphannah goldNo ratings yet
- Trunk Impairment ScaleDocument11 pagesTrunk Impairment Scale林良駿No ratings yet
- Research Paper Using Likert ScaleDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Using Likert Scaleafmcwqkpa100% (1)
- 32040-Article Text-118939-1-10-20230705Document17 pages32040-Article Text-118939-1-10-20230705dian febriaNo ratings yet
- Studi Kepuasan Konsumen Pada Tempat Penyedia Makanan Di Kampus Universitas Negeri JakartaDocument6 pagesStudi Kepuasan Konsumen Pada Tempat Penyedia Makanan Di Kampus Universitas Negeri JakartaB074GioVanesa Hana FaizaNo ratings yet
- PsychometricsDocument11 pagesPsychometricsmattew657No ratings yet
- Item Difficulty and Item DiscriminationDocument19 pagesItem Difficulty and Item Discriminationbhagavathishree131200No ratings yet
- (Updated) Pactt Nov 2022 Exam Guidelines & List of TakersDocument79 pages(Updated) Pactt Nov 2022 Exam Guidelines & List of TakersadieNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Reliability ValidityDocument29 pagesQuestionnaire Reliability Validityprateek sachdevaNo ratings yet
- 2 Kyj2fr2Document32 pages2 Kyj2fr2Alibhaa AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 (Section B)Document14 pagesAssignment2 (Section B)Nur SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Establishing Test Validity and ReliabilityDocument29 pagesEstablishing Test Validity and ReliabilityRowena RetarinoNo ratings yet
- IOP4861 B0 LS05 003 Moerdyk 2022Document12 pagesIOP4861 B0 LS05 003 Moerdyk 2022qgvb2th7mqNo ratings yet
- Mastering Modern Psychological Testing Theory and Methods 1st Edition Reynolds Test BankDocument25 pagesMastering Modern Psychological Testing Theory and Methods 1st Edition Reynolds Test BankDonnaMoorefspo100% (53)
- Methods of Study in PsychologyDocument6 pagesMethods of Study in PsychologySumair AhmadNo ratings yet
- 5m-Standardized TestsDocument91 pages5m-Standardized TestsZachwieNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 4: Analisis Daya Beda Soal Uji Coba Tes Representasi MatematisDocument2 pagesLampiran 4: Analisis Daya Beda Soal Uji Coba Tes Representasi MatematisAhmad Safi'iNo ratings yet
- الصدق والثبات في البحوث الاجتماعيةDocument17 pagesالصدق والثبات في البحوث الاجتماعيةhbh33564No ratings yet
- Social - Confirmitu Scale by Dhapola & Satyendra SinghDocument15 pagesSocial - Confirmitu Scale by Dhapola & Satyendra Singhsrohityadav5612No ratings yet
- Psychometric Properties of A Good TestDocument44 pagesPsychometric Properties of A Good TestJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- UNAUDITED Updated BATAX2 TAX 2 1st Semester 2023 2024 OFFICIAL Ms Grace Gural Jolina Joaquin Ravene Dela Cruz Version 3Document6 pagesUNAUDITED Updated BATAX2 TAX 2 1st Semester 2023 2024 OFFICIAL Ms Grace Gural Jolina Joaquin Ravene Dela Cruz Version 3Cancino, Marvin S.No ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1667922102175 6995772344844495176Document6 pagesOrca Share Media1667922102175 6995772344844495176Antonette DublinNo ratings yet
- Mueller & Knapp 2018 Reliability and Validity (In The Reviewers Guide To Quantitative Methods in The Social Sciences 2nd)Document5 pagesMueller & Knapp 2018 Reliability and Validity (In The Reviewers Guide To Quantitative Methods in The Social Sciences 2nd)Víctor FuentesNo ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument33 pagesMarketing ResearchiherbfirstorderNo ratings yet
- قياس دافعية الإنجاز بين الاختبارات الإسقاطية والسيكوميترية مدخل نظريDocument11 pagesقياس دافعية الإنجاز بين الاختبارات الإسقاطية والسيكوميترية مدخل نظريmayaadreams88No ratings yet
- Reporting Reliability, Convergent and Discriminant Validity With Structural Equation Modeling: A Review and Best Practice RecommendationsDocument39 pagesReporting Reliability, Convergent and Discriminant Validity With Structural Equation Modeling: A Review and Best Practice Recommendationskiki13336586No ratings yet
- Exam Schedule 1Document12 pagesExam Schedule 1foreverkings900No ratings yet
- Public Health Nursing - 2022 - Winquist - Climate Health and Nursing Tool CHANT A Confirmatory Factor AnalysisDocument7 pagesPublic Health Nursing - 2022 - Winquist - Climate Health and Nursing Tool CHANT A Confirmatory Factor AnalysispcNo ratings yet
- DM s2022 100 Nqesh ResultsDocument141 pagesDM s2022 100 Nqesh ResultsTheSummitExpress94% (16)