Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3Q L2 Economics As An Applied Science
Uploaded by
shanehfernandez18Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3Q L2 Economics As An Applied Science
Uploaded by
shanehfernandez18Copyright:
Available Formats
wrote about applying
the "general
principles of political
APPLIED ECONOMICS economy" to
3Q L2 "ascertain the rule of
action of any
combination of
circumstances
presented to us”
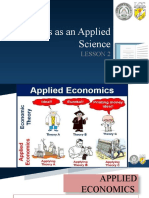
Economics is an applied science because
economics deals with the analysis on how members ECONOMIC THEORY VS APPLIED ECONOMICS
of society interacts with each other on the creation ❖ Economic Theory
and utilization of wealth. - is all about thinking things up
❖ Applied Economics
What makes economics an applied science is the - is about trying things out
formulation of general theories through testing,
mainly using data from the past. POINTS TO LEARN
❖ Robust background in applied economics
APPLIED ECONOMICS allows people to make informed forecasts
• is the study of economics in relation to real life about future trends.
situations ❖ Knowledge in applied economics provides the
• is the application of economic principles and student with a broader perspective on the
theories to actual situations, and trying to application of economic theory to real world
predict what the outcomes might be issues but less knowledge of core economic
• is the study of observing how theories work in theory.
practice ❖ Applied economics is the application of
• Applied economics may be practiced at these economic theory and econometrics in specific
two levels below: settings (Market Business News 2016)
o Microeconomic
- analyzing individual consumers ECONOMIC THEORIES
o Macroeconomic ❖ Theory
- the whole, aggregate economy and • is a well substantiated explanation of some
companies aspects of the natural world.
- started to be used nearly 200 years ago in the ❖ Economic Theory
writing of Jean-Baptiste Say and John Stuart • is a theory on commercial activities such as the
Mill production and consumption of goods.
2 EARLY ECONOMIC THEORIES
MALTHUSIAN THEORY OF
POPULATION GROWTH
- By Thomas Robert Malthus
Jean-Baptiste Say John Stuart Mill - He was an English cleric and
(1767-1832) (1806-1873) scholar
French economist British political - examined the relationship
and businessman economist, between population growth and resources
philosopher, and civil - the human population grows more rapidly than
servant the food supply until famines, war or disease
famous for “Say’s “Principles of Political reduces the population
Law” Economy with Some - control of the growth of the population is
- also called “law of Their Applications important to sustain the population. Positive
of market” to Social Philosophy” checks restore the balance between the
- the ability to - published in 1848
increased growth rate of population and food
purchase - examines
supply.
something fundamental
depends on the economic - Ex: If every member of a family tree
ability to produce process upon reproduces, the tree will continue to grow with
and thereby which society is each generation.
generate income based
ADAM SMITH AND THE WEALTH FREE MARKET
OF NATIONS - Laissez-faire
- By Adam Smith - is a doctrine
- He was a Scottish economist - claims that an economic system should be
and philosopher free from government intervention or
- He was a pioneer in political moderation and be driven only by the market
economy and modern economics forces
- Father of Economics or Father of Capitalism - is centered on the belief that when humans
are self-interested and, when they are not
- "An Inquiry into the Nature and Cause of the interfered, a balanced system of production
Wealth of Nations" and exchange, arises.
- commonly called "The Wealth of Nations”
- is his best-known work MODERN ECONOMIC THEORIES
- published in 1776 1. Consumerism
- The book offers a detailed description of - states that an increasing consumption of
life and trade in English society. goods is economically beneficial
- It also scientifically describes the basic 2. Keynesianism
principles of economics. - popularized by John Maynard Keynes
- advocates government monetary and
fiscal programs intended to stimulate
ECONOMIC IDEAS OF ADAM SMITH business activity and increase
Productivity and Wealth employment.
• Smith observed that labor becomes more - most significant work is about the role of
productive as each worker becomes more the government in a capitalist economy
skilled at a single job. 3. Liberalism
• He also said that new machinery and the - advocates free competition and self-
division and specialization of labor would lead regulating market.
to an increase in production and greater wealth 4. Monetarism
for the nation. - states that variation in unemployment
Invisible Hand and the rates of inflation are usually
• self-regulation of economy/no government caused by changes in the supply of money.
intervention 5. Utilitarianism
• One of Smith's most important contributions - bases the moral worth of an action upon
deals with the competition in the marketplace. the number of people who derive
• He argued that competition, together with the happiness or pleasure from it
free market system, would act as an invisible - is used when making social, economic, or
hand that would guide resources to their most political decision for the "betterment of
productive use. society."
• He also believed that under competitive
conditions, individuals acting naturally in their ECONOMETRICS
own self-interest would bring the greatest - is the application of statistical and
good for society as a whole. mathematical theories in economics for the
• Became basic idea of free-market economy or purpose of testing hypotheses and forecasting
capitalism future trends.
• He believed that all individuals act in their self-
- it takes economic models to be tested through
interest, and can produce and purchase by
statistical trials.
themselves
- the results are then compared and contrasted
Laissez-Faire
against real-life examples.
• The Wealth of Nations was ridiculed by
- Is divided into two major categories:
aristocracy in parliament at that time.
o theoritical
• Business people, however, were delighted to
o applied
have a moral justification for their growing
wealth power.
• Eventually, the doctrine of laissez-faire,
meaning no government intervention in
economic affairs, became the watchword of the
day in Great Britain.
POINTS TO LEARN
- Theoretical Econometrics
o uses a combination of economic
theory, math, and statistical
inferences to quantify and analyze
economic theories by leveraging tools
such as frequency distributions,
probability and probability
distributions, statistical inference,
simple and multiple regression
analysis, simultaneous equations
models, and time series methods.
• Example of real-life application of
econometrics would be to study to income
effect.
o An economist may hypothesize that as
a person increases his income, his
spending will also increase. The
hypothesis can be tested and proven
using econometric tools like
frequency distributions or multiple
regression analysis.
GOALS OF STUDY ECONOMETRICS
Without evidence, economic theories are abstract
and might have no bearing on reality.
According to Judge (2017), the following are the
goals of studying econometrics:
1. Test Hypothesis
- first goal
- allows you to conduct applied econometric
studies of your own, which can be very
useful if you are also doing a dissertation
2. Critically Assess the Empirical Work of Others
- 2nd goal
- helpful when discussing the relevant
academic literature in any other module
and to be able to comment on why a
particular technique may or may not be
appropriate can often be impressive
Reference Materials
“Applied Economics - Intro - Part 2 - Senior High
School and College Students”
by Melchor Roque on YTR
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UGwbBVTv0qY
You might also like
- Econ - DevelopmentDocument7 pagesEcon - DevelopmentLouisse Homer NarcisoNo ratings yet
- APECO Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesAPECO Midterms ReviewerSOLEDAD LONo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 LESSON 2 Economics As An Applied ScienceDocument25 pagesUNIT 1 LESSON 2 Economics As An Applied ScienceElla CaraanNo ratings yet
- The History of Economic Thought & Development (Versoza)Document41 pagesThe History of Economic Thought & Development (Versoza)LykaBernadetteVersozaNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Reviewer (1st Periodical)Document12 pagesApplied Economics Reviewer (1st Periodical)casumbalmckaylacharmianNo ratings yet
- Nomos Meaning Management Household: Choices. - Means That Our ChoicesDocument3 pagesNomos Meaning Management Household: Choices. - Means That Our ChoicesnicNo ratings yet
- 01 Understanding EconomicsDocument41 pages01 Understanding EconomicsMicheleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (1) EconomicsDocument76 pagesChapter 1 (1) Economicsshahriar sNo ratings yet
- Investing in Mutual FundsDocument22 pagesInvesting in Mutual FundsIan PatrickNo ratings yet
- Nature of Economics Lecture 1Document73 pagesNature of Economics Lecture 1Shekainah BNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics/Basic EconomicsDocument9 pagesMicro Economics/Basic EconomicsJashi SiosonNo ratings yet
- Basic Consept in EconomicsDocument32 pagesBasic Consept in EconomicsSri HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Microeconimics Handout Chapter 1Document8 pagesMicroeconimics Handout Chapter 1John Henry ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Econ C1Document57 pagesIntroduction in Econ C1Casey keith GarciaNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ L1Document42 pagesApplied Econ L1Marie Christine PajanilNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Macro ThoughtDocument32 pagesCh2 Macro ThoughtLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Economics - Study MaterialDocument3 pagesBasic Concept of Economics - Study MaterialEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy 01 - Lecture Notes - (Sankalp (UPSC 2024) )Document11 pagesIndian Economy 01 - Lecture Notes - (Sankalp (UPSC 2024) )nikunjNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To EconomicsNicole ViernesNo ratings yet
- Economics As Applied Science (PT1.2)Document15 pagesEconomics As Applied Science (PT1.2)Sha NENo ratings yet
- Syllabus Class: - BBA I Year Subject: - Micro EconomicsDocument64 pagesSyllabus Class: - BBA I Year Subject: - Micro EconomicsHasan HamidNo ratings yet
- Economic Theory PowerpointDocument11 pagesEconomic Theory PowerpointLawrence Gabrielle BernalesNo ratings yet
- Economic and Development ReviewDocument16 pagesEconomic and Development ReviewMary Justine GallanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Economics - 9914937e c0f1 4fa8 9418 Bb9f4270ae76Document34 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Economics - 9914937e c0f1 4fa8 9418 Bb9f4270ae76riteshhpatel0945No ratings yet
- Applied EconomicsDocument2 pagesApplied EconomicsRaquel GuinucudNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, NijhuDocument9 pagesLecture 1, NijhuNizhum FarzanaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document8 pagesTopic 1Gwen Stefani DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 EconDocument4 pagesLesson 1 EconMonique DanielleNo ratings yet
- Notes On Macro Economics With Keynes Theory PDFDocument46 pagesNotes On Macro Economics With Keynes Theory PDFShalini Singh IPSANo ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To EconomicsMurshedul ArafinNo ratings yet
- Presentation EconomicsDocument93 pagesPresentation EconomicsAlexander EspinaNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomicsDocument60 pagesEngineering EconomicsAbhineet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Final 2 Hons I Year PDFDocument23 pagesManagerial Economics Final 2 Hons I Year PDFSANYAM PATILNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - MacroeconDocument26 pagesLecture 01 - MacroeconzNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MicroEconomicsDocument29 pagesModule 1 MicroEconomicsjustin vasquezNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Economics NotesDocument86 pagesAgricultural Economics NotesGary Bhullar95% (61)
- HEALTH ECON - CHAP.1to5Document11 pagesHEALTH ECON - CHAP.1to5Christine EstradaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument181 pagesEconomicsChanpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro Economics: Economics and BCK NotesDocument172 pagesIntroduction To Micro Economics: Economics and BCK NotesUnknown 1No ratings yet
- Ca Foundation - Paper 4 - Economics: Chapter-1 Nature & Scope of Business Economics (By-Jatin Lamba)Document18 pagesCa Foundation - Paper 4 - Economics: Chapter-1 Nature & Scope of Business Economics (By-Jatin Lamba)Alexander SoniNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument6 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerAevan Joseph100% (1)
- Economics & Business Management (EBM) - Note. Free Download-Pdf - Manu K MDocument46 pagesEconomics & Business Management (EBM) - Note. Free Download-Pdf - Manu K MManu K M100% (5)
- Lesson 1 Introduction To EconomicsDocument56 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To EconomicsAthena LyNo ratings yet
- Reading Material 1 Introduction EconDocument19 pagesReading Material 1 Introduction Econisaiah menesesNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts - AgEconDocument21 pagesLecture Handouts - AgEconMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Economics NotesDocument86 pagesAgricultural Economics NotesManohar PawarNo ratings yet
- AECO141Document86 pagesAECO141anbukkaniNo ratings yet
- AECO141principle of Agricultural Economics PDFDocument86 pagesAECO141principle of Agricultural Economics PDFpraveenbabu50% (8)
- Lecture On Agicultural EconomicsDocument16 pagesLecture On Agicultural Economicsirish deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Dde PDFDocument253 pagesMacroeconomics Dde PDFPankaj GahlautNo ratings yet
- PPP4Document35 pagesPPP4Ebs DandaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument18 pagesEconomicsAbhay KuteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Managerial EconomicsmussaiyibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 PPT 1Document38 pagesLesson 1 PPT 1Marianne FiguraNo ratings yet
- Basic Econ Chapter 1Document45 pagesBasic Econ Chapter 1Yuuki Touya CaloniaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Economics. DZADocument57 pagesIndustrial Economics. DZAsrikantadas4912No ratings yet
- Ch2 Macro ThoughtDocument25 pagesCh2 Macro ThoughtProveedor Iptv EspañaNo ratings yet
- I. Economics and Its NatureDocument5 pagesI. Economics and Its NatureCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- Basics of Economics: DR Seema JhalaDocument82 pagesBasics of Economics: DR Seema JhalaYash MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Abraham Tilahun GSE 6950 15Document13 pagesAbraham Tilahun GSE 6950 15Abraham tilahun100% (1)
- Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 39Document14 pagesQuestions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 39Saurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Test of Proportions For Confirmation Testing: Craig G. Hysong May 6, 2014Document44 pagesChi Square Test of Proportions For Confirmation Testing: Craig G. Hysong May 6, 2014MickloSoberanNo ratings yet
- Grade Filipino 7 Week 1-2Document10 pagesGrade Filipino 7 Week 1-2SALEM DE LA CONCEPCIONNo ratings yet
- Chemical EtchDocument18 pagesChemical EtchznpfgNo ratings yet
- Introducing Python Programming For Engineering Scholars: Zahid Hussain, Muhammad Siyab KhanDocument8 pagesIntroducing Python Programming For Engineering Scholars: Zahid Hussain, Muhammad Siyab KhanDavid C HouserNo ratings yet
- Trackless Mining at Thabazimbi MineDocument7 pagesTrackless Mining at Thabazimbi MineYojan Ccoa CcopaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Heat Transfer in Steelwork Protected and Unprotected SteelworkDocument23 pages2.2 Heat Transfer in Steelwork Protected and Unprotected SteelworkMahbub AlamNo ratings yet
- 3 (Diffusivity of Gases)Document52 pages3 (Diffusivity of Gases)Nasir ShamsNo ratings yet
- MR Right - Case Study Test - Summer 2018Document7 pagesMR Right - Case Study Test - Summer 2018jadenNo ratings yet
- Boolean Algebra Part 2Document10 pagesBoolean Algebra Part 2Md. Masum Latif Chowdhury (201016006)No ratings yet
- DMGTDocument139 pagesDMGTPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Music and Emotion Theory Research Applications 0199230145 9780199230143 CompressDocument990 pagesHandbook of Music and Emotion Theory Research Applications 0199230145 9780199230143 CompressSmyth1702No ratings yet
- Applied Linerar Algebra FinalDocument193 pagesApplied Linerar Algebra FinalAslesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Positive Mental AttitudeDocument83 pagesPositive Mental AttitudemuetanianNo ratings yet
- Report Group 1Document67 pagesReport Group 11706112No ratings yet
- Application of Modern Technology For Fault Diagnosis in Power Transformers Energy ManagementDocument6 pagesApplication of Modern Technology For Fault Diagnosis in Power Transformers Energy ManagementCamila Caceres FloresNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Double EffectDocument3 pagesDoctrine of Double EffectRael VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Once Per Year (RPM Vision Planner) : How To Schedule Your RPM Plan UpdatesDocument1 pageOnce Per Year (RPM Vision Planner) : How To Schedule Your RPM Plan Updatestrav bae0% (1)
- Northern Cebu Colleges, Inc. San Vicente ST., Bogo City, Cebu Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP)Document6 pagesNorthern Cebu Colleges, Inc. San Vicente ST., Bogo City, Cebu Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP)Jilmore Caseda Cantal100% (1)
- Deep Well Submersible Pump (Hydraulic Calculations)Document2 pagesDeep Well Submersible Pump (Hydraulic Calculations)Imran Aziz100% (2)
- China Domestic Style Test ProcessDocument2 pagesChina Domestic Style Test ProcessPopper JohnNo ratings yet
- Models of Cultural Heritage Management: Transformations in Business and Economics January 2014Document23 pagesModels of Cultural Heritage Management: Transformations in Business and Economics January 2014aaziNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Industrial Laser Materials Processing (Rofin-Rinar Laser) (Z-Lib - Org) - 1Document143 pagesIntroduction To Industrial Laser Materials Processing (Rofin-Rinar Laser) (Z-Lib - Org) - 1bayou71usaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDFDocument4 pagesDokumen PDFI Komang Agus Adi Merta 07No ratings yet
- Experiment 03: Measurement of Absolute Viscosity of Fluid by A Saybolt ViscometerDocument4 pagesExperiment 03: Measurement of Absolute Viscosity of Fluid by A Saybolt Viscometer17044 AZMAIN IKTIDER AKASHNo ratings yet
- Euro CPKDocument20 pagesEuro CPKnovarhai100% (1)
- The Norwegian Oil Experience:: Helge RyggvikDocument58 pagesThe Norwegian Oil Experience:: Helge RyggvikhiyeonNo ratings yet
- Context of ArtDocument20 pagesContext of ArtFerdinand Fremista JrNo ratings yet
- Exercise Phase 4 - Team LeadershipDocument13 pagesExercise Phase 4 - Team LeadershipLUZ AMPARO MARTINEZNo ratings yet