Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key U7
Uploaded by
kimchi20122005Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key U7
Uploaded by
kimchi20122005Copyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 7: SEE, SMELL, HEAR
What things can you see, hear, smell, taste or touch? Gimme 5 sentences
5 senses of human:
Taste
There are thousands of taste buds on the tongue that sense five types of taste, sweet, salty, bitter, sour,
and umami. The signals sent from the taste buds are processed in the gustatory cortex. A combination
of taste and smell leads to flavor. This is why food "tastes" different when your nose is stuffy.
Smell
There are a large number of receptors in the upper reaches of the nose. These olfactory receptors sense
smell using mucus-covered cilia, which are like tiny hairs that respond to "smelly" molecules. The
olfactory cortex that receives and processes these signals is in the front of the brain.
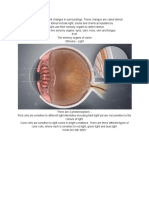
Sight
The sight receptors are in the back of the eye on the retina. Rods are used for black and white vision,
while cones are for color vision. Vision is processed in the occipital cortex. The right side of the visual
cortex processes signals from the left visual field and the right visual field is processed in the left visual
cortex.
Hearing
Hearing involves a complex chain of processes but ends up in the inner ear in a spiral-shape cavity called
the cochlea, where the mechanical signal is turned into an electrical signal to send it to the auditory
cortex in the center of the brain.
Touch
The skin is the body's largest organ. It has millions of touch receptors that respond to touch, pressure,
pain, and temperature. The somatosensory cortex processes these signals. There are more of these
receptors in fingertips, lips, and eyelids.
See/hear/smell/feel/notice/watch + Object + V-ing: cấu trúc này được sử dụng khi người nói chỉ chứng
kiến 1 phần của hành động.
See/hear/smell/feel/notice/watch + Object + V: cấu trúc này được sử dụng khi người nói chứng kiến
toàn bộ hành động
You might also like
- Sensory Organs: What Are The Sense Organs?Document3 pagesSensory Organs: What Are The Sense Organs?ajay kalangiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The World Through Our SensesDocument38 pagesChapter 1: The World Through Our SensesJamel GriffinNo ratings yet
- Is Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIs Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesHafizah Ghany HayudinnaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2Document9 pagesScience Form 2yvonne vonne vonneNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument9 pagesSense OrgansЕкатерина КовальNo ratings yet
- Sense OrganDocument14 pagesSense OrganAna Concepcion IsraelNo ratings yet
- Sensory OrganDocument20 pagesSensory OrganJaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Science (Form 2)Document128 pagesChapter 1-Science (Form 2)Yeoh Hui KoonNo ratings yet
- Five Human Senses, What & Why? : 3rd Grade Science Books Series: Third Grade BooksFrom EverandFive Human Senses, What & Why? : 3rd Grade Science Books Series: Third Grade BooksNo ratings yet
- SensesDocument1 pageSensesDaniela Medrano LujanNo ratings yet
- The World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter OneDocument10 pagesThe World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter Onegan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- Sistem SensoriDocument2 pagesSistem SensoriCitra Lestari LudjiNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Class 5 PPT On Human Sense OrganDocument16 pagesClass 5 PPT On Human Sense OrganGizaw TadesseNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organ PDFPerry Sin75% (4)
- Laporan SenseDocument16 pagesLaporan SenseladylomoNo ratings yet
- SENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Document6 pagesSENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Karl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- 5 Senses ReadingDocument4 pages5 Senses ReadingAdrian Trincado FernandezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansMelanie GialogoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionNoralizah IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Stimuli and Responses in HumansDocument6 pagesScience Form 3 Stimuli and Responses in HumansSharvin JananeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 8Document8 pagesLesson Proper For Week 8Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Sensory Perception (Notes)Document5 pagesCH 14 Sensory Perception (Notes)Olivia DoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Olfaction and Gustation: What Does A Snake Smell/taste Like?Document23 pagesOlfaction and Gustation: What Does A Snake Smell/taste Like?Abiy Tewelde TekleNo ratings yet
- Crash Course Taste and SmellDocument2 pagesCrash Course Taste and SmellReem SleemNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionReduan Ibrahim100% (3)
- Sex and SensesDocument1 pageSex and SensesEmie EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument13 pagesSensation and PerceptionRiza Roncales100% (1)
- Five Sense: DR - Rr. Sri Ratna Rahayu M.Kes, PHDDocument37 pagesFive Sense: DR - Rr. Sri Ratna Rahayu M.Kes, PHDDewi Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- The Sense Organs and It'S PartsDocument38 pagesThe Sense Organs and It'S PartsSk Laila AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial Sensesvivian.obadeNo ratings yet
- Five SensesDocument41 pagesFive SensesJobel Sibal CapunfuerzaNo ratings yet
- Form 2-Chapter 1-The World Through Our SensesDocument8 pagesForm 2-Chapter 1-The World Through Our SensesMathew Hon Jun YoonNo ratings yet
- Soc AssignmentDocument3 pagesSoc AssignmentIsraq AhmmedNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 (Special Sense Organs)Document7 pagesUNIT 5 (Special Sense Organs)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- SensesDocument25 pagesSensesMia FENTONNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument36 pagesTaste and SmellKarthikeyan Balakrishnan100% (2)
- The Human Skin - The Sense of Touch: Receptors - Special Sensory Structures in Your Skin Ends (Terminal Branches ofDocument8 pagesThe Human Skin - The Sense of Touch: Receptors - Special Sensory Structures in Your Skin Ends (Terminal Branches ofdindi1818No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesNurul Ain RazaliNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Document5 pagesPsychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Lyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Document49 pagesSCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Nurul NasaruddinNo ratings yet
- Mine AnkdsjcsDocument2 pagesMine AnkdsjcsKarl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentapi-614390592No ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 08Document12 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 08Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Science Form 2Document29 pagesChapter 1 Science Form 2Minh HayatNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses NotesizabelaNo ratings yet
- 5 SensesDocument1 page5 SensespsathishthevanNo ratings yet
- PARAFRASEODocument4 pagesPARAFRASEOAllegroNo ratings yet
- Let's Remember: Understanding How Your Sense OrgansDocument1 pageLet's Remember: Understanding How Your Sense OrgansJohn LimNo ratings yet
- YihalemDocument16 pagesYihalemyihalemasmamawNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception (Contd.) The Other Senses Depth Perception Perception MovementDocument14 pagesSensation and Perception (Contd.) The Other Senses Depth Perception Perception MovementNael Nasir ChiraghNo ratings yet
- L5 - Special SensesDocument39 pagesL5 - Special SensesNana Boakye Anthony AmpongNo ratings yet
- Senses: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument29 pagesSenses: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleRea AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Five SensesDocument4 pagesThe Five SensesMadalina CiurdeaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7Document19 pages2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7ENOCH NAPARI ABRAMANNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument5 pagesSensation and PerceptionCamille Nathalie JuloyaNo ratings yet
- I Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandI Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Scent 07102020Document4 pagesScent 07102020OrsiNo ratings yet
- Look, Listen, Taste, Touch, and Smell: Learning About Your Five SensesFrom EverandLook, Listen, Taste, Touch, and Smell: Learning About Your Five SensesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)