Professional Documents
Culture Documents
125-Tutotial-Question-For-Dld-Exit-Exam (1) T
Uploaded by
hayuasamad2Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
125-Tutotial-Question-For-Dld-Exit-Exam (1) T
Uploaded by
hayuasamad2Copyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
125 Tutotial Question for DLD Exit Exam
digital logic design (Haramaya University)
Scan to open on Studocu
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
Adama Science & Technology University
School of Electrical Engineering & Computing
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
Tutorial question for Exit Exam of Digital Logic Design Course
1. Which of the following majorly determines the number of emitters in a TTL digital circuit?
A. Fan – in
B. Fan – out
C. Propagation delay
D. Noise immunity
2. What are the basic gates in MOS logic family?
A. NAND and NOR
B. AND and OR
C. NAND and OR
D. AND and NOR
3. How must the output of a gate in a TTL digital circuit act when it is HIGH?
A. Acts as a voltage source
B. Acts as a current sink
C. Acts as a current source
D. Acts as a voltage sink
4. The negative numbers in the binary system can be represented by
A. sign magnitude
B. 2\s complement
C. 1\s complement
D. all the above
5. Convert the octal number 7401 to Binary.
A. 1.111e+11
B. 1.1111e+11
C. 1.111e+11
D. 1.11e+11
6. Find the hex sum of (93)16 + (DE)16.
A. (171)16
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
B. 271)16
C. (179)16
D. (181)16
7. Perform 2’s complement subtraction of (7)10 − (11)10.
A. 1100 (or -4)
B. 1101 (or -5)
C. 1011 (or -3)
D. 1110 (or-6)
8. What is the gray equivalent of (25)10
A. 1101
B. 110101
C. 10110
D. 10101
9. Conversion of fractional number 0.6875 into its equivalent binary number:
A. 0.1011
B. 0.1111
C. 0.10111
D. 0.0101
10. Convert the decimal number 82.67 to its binary, hexadecimal and octal equivalents
A. (1010010.10101011)2; (52. ab)16.
B. (1010010.10101011)2; (52. ab)16.
C. (1010010.10101011)2; (52. ab)16.
D. (1010010.
11. Add 648 and 487 in BCD code.
A. 1135
B. 1136
C. 1235
D. 1138
12. (65.535)10 =(X)16 FIND X
A. (41.88f5c28)16.
B. (42.88f5c28)16.
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. (41.88f5c)16.
D. (42.88f5c)16.
13. Convert the decimal number 430 to Excess-3 code:
A. 110110001
B. 110110000
C. 110110011
D. 110100001
14. following subtraction (i) 11001-10110 using 1’s complement
A. 11
B. 111
C. 10
D. 10011
15. The hexadecimal number for (95.5)10 is
A. (5f.8) 16
B. (9a.b) 16
C. (2e.f) 16
D. (5a.4) 16
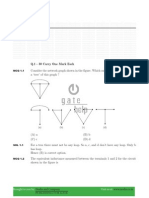
16. How many two-input AND and OR gates are required to realize Y=AB+CD+E?
A. 2, 2
B. 2, 3
C. 3, 3
D. 3, 2
17. If a 3-input NOR gate has eight input possibilities, how many of those possibilities will result in a HIGH
output?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 7
D. 8
18. If a signal passing through a gate is inhibited by sending a LOW into one of the inputs, and the output is
HIGH, the gate is a(n):
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. AND
B. NAND
C. NOR
D. OR
19. The format used to present the logic output for the various combinations of logic inputs to a gate is called
a(n):
A. Boolean constant
B. Boolean variable
C. Truth table
D. Logic function
20. What does the small bubble on the output of the NAND gate logic symbol mean?
A. open collector output
B. tristate
C. The output is inverted.
D. none of the above
21. A logic probe is again applied to the pins of a 7421 IC with the following results. Is there a problem with
the circuit and if so, what is the problem?
PIN Indicator PIN Indicator
1 ON 14 ON
2 PULSING 13 ON
3 DIM 12 ON
4 ON 11 DIM
5 ON 10 OFF
6 PULSING 9 PULSING
7 OFF 8 OFF
A. Pin 6 should be ON
B. Pin 8 should be ON.
C. Pin 8 should be pulsing.
D. no problem
22. What are the pin numbers of the outputs of the gates in a 7432 IC?
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. 3, 6, 10, and 13
B. 1, 4, 10, and 13
C. 3, 6, 8, and 11
D. 1, 4, 8, and 11
23. Logically, the output of a NOR gate would have the same Boolean expression as a(n):
A. NAND gate immediately followed by an inverter
B. OR gate immediately followed by an inverter
C. AND gate immediately followed by an inverter
D. NOR gate immediately followed by an inverter
24. The circuit of the given figure realizes the function
A. (A’+B’)C+ (DE)’
B. A’+B’+C’+D’+E’
C. AB+C+DE
D. AB+C(D+E)
25. Minimum number of 2-input NAND gates required to implement the function F=(X+Y)(W+Z) is
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
26. The minimum number of NOR gates required to implement the Boolean function A+AB+ABC is equal to
A. 0
B. 1
C. 4
D. 7
27. In the given figure, A = B = 1 and C = D = 0. Then Y =
A. 0
B. 1
C. Either 0 or 1
D. Indeterminate
28. In the circuit of the given figure, Y =
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. 0
B. 1
C. X
D. X’
29. The digital logic family which has the lowest propagation delay time is
A. ECL
B. TTL
C. CMOS
D. PMOS
30. The logic circuit given figure below converts a binary code ABC into
A. Excess-3 Code
B. Gray Code
C. BCD code
D. Hamming Code
31. In the circuit shown below in Fig-1, Transistor Q & Diode D are ideal with negligible collector-to-emitter saturation voltage
and negligible voltage drops across diode under forward bias. If Vcc , is +5 V X and Y are digital signals with DV as logic d
and Vcc as logic 1, the Boolean expression for Z is
A.
B. X Y
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. X Y
D. X Y
32. The logical expression Y A A B is equivalent to
A. Y AB
B. Y A B
C. Y A B
D. Y A B
33. The Boolean function A + BC is a reduced form of
A. AB + BC
B. (A + B). (A + C)
C. A’B+ ABC
D. (A + C).B
34. The minimized form of the logical expression (A’B’C’ + A’BC’ A’BC ABC’ ) is
A. AC BC AB
B. AC BC AB
C. AC + BC +AB
D. A’C’ A’B BC’
35. The Boolean expression for the truth table shown is
K L M Y
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0
A. L(K M)(K’ M’)
B. L(K M’)(K’ M)
C. L (K M) (K’ M’)
D. L’(K M)(K M’)
36. If A = 1 in the logic equation
[A+ C{B’+ (C’+ AB’)]{A’+C’(A+B)}= 1, then
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. B=C
B. B = C’
C. C=0
D. C=1
37. The Boolean expression (X +Y)(X +Y’) (X’Y’) + X’ simplifies to
A. X
B. Y
C. XY
D. X+Y
38. The Minimum Boolean expression for the following circuit is
A. A+B+C
B. A+B
C. AB+AC+BC
D. A+BC
39. An order of precedence of operations for Boolean algebra is
A. highest to lowest priority is NOT, then OR, then AND
B. highest to lowest priority is NOT, then AND, then OR
C. lowest to highest priority is NOT, then AND, then OR
D. lowest to highest priority is NOT, then OR, then AND
40. Which of the following Boolean algebra statements represent distributive law
A. A+BC = A.B + A.C
B. A + BC = A(B+C)
C. A + BC = (A+B).C
D. A + BC = (A + B) (A + C)
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
41. Which of the following Boolean algebra statements represent distributive law
A. A+BC = A.B + A.C
B. A + BC = A(B+C)
C. A + BC = (A+B).C
D. A + BC = (A + B) (A + C)
42. Which of the following Boolean algebra statements represent commutative law
A. A. (A+B)+CA+(B+C)
B. B. A.(B+C)(A.B)+(A.C)
C. C. A+BB+A
D. D. A+AA
43. Match the List-I with List –II select correct answer
List-I List=II
1. Commutative Law a) A+B=B+A
2. Associative Law b) (A+B).(A+C)=A.A+A.C+B.A+B.C
3. Distributive Law c) A B A B
4. Demorgans law d) A.(B.C)=(A.B). C
A. 1-b, 2-d, 3-a, 4-c
B. 1-a, 2-c, 3-b, 4-d
C. 1-a, 2-d , 3-b, 4-c
D. 1-a 2-b 3-c 4-d
44. K-map is used to minimize the number of
A. Flip-flops in digital circuits
B. Layout spaces in digital circuits for fabrication
C. Functions of 3, 4, 5 or 6 variables
D, Registers in CPU
45. The simplified expression for 𝐹(𝐴, 𝐵, 𝐶, 𝐷) = ∏(1, 3, 6, 9, 11, 12, 14)
A. F = BD + B'D' + A'C'D'
B. F = C'D' + AB' + CD'
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. F = AC' + AD + C'D + AB'C
D. F = A'C' + AD' + C'D + AB'C
46. For the K map in the given figure the simplified Boolean expression is
A. A’C’ + A’D’ + ABC
B. A’C + A’D’ + ABC
C. A’C + A’D’ + ACD
D. A’C’ + A’D’ + ABC’
47. The simplified form of (A'B'C'D' + AC'D' + B'CD' + A'BCD + BC'D)
A. F =BD + A'B + B' D'
B. F = B' D' +A'BD + ABC'
C. F = BD + B'D' + A'D'
D. F = B'D' + BCD + A'BD + A'BC
48. Which of the following logic circuits is a
realization of the function F whose
Karnaugh map is shown in figure.
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
49. The K- Map for Boolean function is shown below in figure. The number of the essential prime implicates
for the function is
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 8
50. A function of Boolean variables, X, Y and Z is expressed in
terms of the min-terms as
F(X, Y, Z) = (1, 2, 5, 6, 7). Which one of the product of sums given below is equal to the function
F(X, Y, Z )
A. (X’+ Y’+ Z’).(X’+ Y+ Z).(X +Y’+ Z’)
B. (X+ +Y+ Z).(X+ Y’+ Z’).(X’+ Y+ Z)
C. (X’+ ‘Y+ Z).(X’+ Y+ Z’).(X+ Y+ Z’) (X+ Y+ ‘Z).(X+ Y+ Z’)
D. (X +Y+ Z’).(X’+ Y+ Z’).(X’ +Y+ Z) (X’+ Y’+ Z).(X’+ Y’+ Z’)
51. Following is the K-map of a Boolean function of five variables P, Q, R, S and X. The minimum sum of-
product (SOP) expression for the function is
A. P’Q’SX +’ PQ’SX’+ QR’S’X+ QRS’X
B. Q’SX’+ QS’X’
C. Q’SX+ QS’X’
D. Q’S+ QS’
52. The number of product terms in the minimized sum of-product expression obtained through the following
K-map is (where, "d" denotes don't care states)
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
53. Which one of the following gives the simplified sum of products expression for the Boolean function F =
m 0 + m 2 + m 3 + m 5, where m 0, m 2, m 3 and m 5 are minterms corresponding to the inputs X, Y and
Z with X as the MSB and Z as the LSB?
A. X’Y+ X’Y’Z’+ XY’Z
B. X’Z’+ XY’+ XY’Z
C. X’Z’+ X’Y+ XY’Z
D. X’YZ+ X’Z’+ XY’Z
54. A function F(A B, C) defined by three Boolean variables A, B and C when expressed as sum of products
is given by F = A’.B.C+ A’.B.’C+ A.B’.C’ where, A’, B , and C’ are the complements of the respective
variables, The product of sums (POS) form of the function F is
A. =(A’+ B’+ C’).(A’+ B+C’).(A+ B’+ C’)
B. F= (A’+ B’+ C’(A’+ B+ C’).(A+ B’+C’)
C. F= (A+ B+ C)(A+ B+ C’). (A+ B’+ C’)(A’+ B’+ C’)
D. F= (A’+ B’+ C)(A’+ B+ C).(A+ B’+C).(A+ B+ C’) .(A+ B+ C)
55. The simplified form of (A'B'C'D' + AC'D' + B'CD' + A'BCD + BC'D)
A. F =BD + A'B + B' D'
B. F = B' D' +A'BD + ABC'
C. F = BD + B'D' + A'D'
D. F = B'D' + BCD + A'BD + A'BC
56. The simplified expression for F(A, B, C, D) = ∏(1, 3, 6, 9, 11, 12, 14)
A. F = BD + B'D' + A'C'D'
B. F = C'D' + AB' + CD'
C. F = AC' + AD + C'D + AB'C
D. F = A'C' + AD' + C'D + AB'C
57. The number of select lines ‘m’, required to select one out of ‘n’ input lines is
A. 𝑚 = 𝑙𝑜𝑔2 𝑛
B. 𝑚 = log 𝑛
C. 𝑚 = ln 𝑛
D. 𝑚 = 2𝑛
58. How many 3-line-to-8-line decoders are required for a 1-of-32 decoder?
A. 1
B. 2
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. 4
D. 8
59. For the device shown here, let all D inputs be LOW, both S inputs be HIGH, and the input be LOW. What
is the status of the Y output?
A. LOW
B. HIGH
C. Don't Care
D. Cannot be determined
60. For the device shown here, assume the D input is LOW, both S inputs are HIGH, and the input is HIGH.
What is the status of the outputs?
A. All are HIGH.
B. All are LOW.
C. All but Y0'are LOW.
D. All but Y0'are HIGH.
61. One application of a digital multiplexer is to facilitate:
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. data generation
B. serial-to-parallel conversion
C. parity checking
D. data selector
62. Consider the 2-bit multiplexer (MUX) shown in the figure. For OUTPUT to be the XOR of C and D, the
values for A0, A1, A2 and A3 are ___________.
A. A0 = 0, A1= 0, A2 =1,A3 =1
B. A0 = 1, A1= 0, A2 =1,A3 =0
C. A0 = 0, A1= 1, A2 =1,A3 =0
D. A0 = 1, A1= 1, A2 =0, A3 =0
63. Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The Boolean expression F implemented by the circuit is
A. X’Y’Z’ + XY+ Y’Z
B. X’ Y Z’ + XZ+ Y’Z
C. X’Y Z’ + XY+ Y’Z
D. X’Y’Z’ + XZ+ Y’Z
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
64. Identify the circuit below.
A. Binary to Gray code converter
B. Binary to Excess 3 code converter
C. Gray to Binary Converter
D. Excess 3 code converter to Binary
65. A 2-bit binary multiplier can be implemented using
A. 2 Input AND gates only
B. 2 Number of 2 Input XOR gates and 6 number of 2 input AND gates
C. Two 2 input NOR gates and one XNOR notes
D. XOR gate and shift registers
66. The Boolean function realized by the logic circuit shown is
A. F = m( 0,1,3,5,9,10,14)
B. F = m( 2,3,5,7,8,12,13)
C. F = m( 1,2,4,5,11,14,15)
D. F = m( 2,3,5,7,8,9,12)
67. The device shown here is most likely a ________.
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. Comparator
B. Multiplexer
C. Demultiplexer
D. Parity Generator
68. A 4:1 multiplexer is to be used for generating the output carry of a full adder. A and B are the bits to be added
while 𝐶in is the input carry and 𝐶out is the output carry. A and B are to be used as the select bits with A being
the more significant select bit.
Which one of the following statements correctly describes the choice of signals to be connected to the
inputs I0, I1, I2 and I3 and so that the output is C?
A. I0 =0 , I1 = Cin, I2 = Cin , I3 = 1
B. I0 =1 , I1 = Cin, I2 = Cin , I3 = 1
C. I0 = Cin , I1 = 0, I2 = 1, I3 = Cin
D. I0 =0 , I1 = Cin, I2 = 1 , I3 = Cin
69. A four-variable Boolean function is realized using 4 1 multiplexers as shown in the figure.
The minimized expression for F(U, V, W, X) is
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. (UV + U’V’) W’
B. (UV + U’V’) (W’X’+W’X)
C. (UV’ + U’V) W’
D. (UV’ + U’V) (W’X’+W’X)
70. What are the minimum number of multiplexers required to generate a 2 input AND gate and a 2 input Ex-OR
gate.
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 1 and 1
D. 2 and 2
71. 3 bits full adder contains ________
A. 3 combinational inputs
B. 4 combinational inputs
C. 6 combinational inputs
D. 8 combinational inputs
72. What is the function of an enable input on a multiplexer chip?
A. To apply Vcc
B. To connect ground
C. To active the entire chip
D. To active one half of the chip
73. Which digital system translates coded characters into a more useful form?
A. Encoder
B. Display
C. Counter
D. Decoder
74. Which IC is used for the implementation of 1-to-16 DEMUX?
A. IC 74154
B. IC 74155
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. IC 74139
D. IC 74138
75. Which error detection method uses one’s complement arithmetic?
A. Simple parity check
B. Two-dimensional parity check
C. CRC
D. Checksum
76. Which gates are ideal for checking the parity bits?
A. AND
B. NAND
C. EX-OR
D. EX-NOR
76. A ripple counter's speed is limited by the propagation delay of…………….
A. Each flip-flop
B. All flip-flops and gates
C. The flip-flops only with gates
D. Only circuit gates
77. To operate correctly, starting a ring counter requires……………
A. Clearing all the flip-flops
B. Presetting one flip-flop and clearing all the others
C. Clearing one flip-flop and presetting all the others
D. Presetting all the flip-flops
78. What type of register would shift a complete binary number in one bit at a time and shift all the stored bits
out one bit at a time?
A. PIPO
B. SIPO
C. PISO
D. SISO
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
79. Synchronous counters eliminate the delay problems encountered with asynchronous (ripple) counters
because the:
A. Input clock pulses are applied only to the first and last stages
B. Input clock pulses are applied only to the last stage
C. Input clock pulses are not used to activate any of the counter stages
D. Input clock pulses are applied simultaneously to each stage
80. The truth table for an S-R flip-flop has how many VALID entries?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 3
81. When both inputs of a J-K flip-flop cycle, the output will ………………
A. Be invalid
B. Change
C. Not change
D. Toggle
82. Which of the following is correct for a gated D-type flip-flop?
A. The Q output is either SET or RESET as soon as the D input goes HIGH or LOW
B. The output complement follows the input when enabled
C. Only one of the inputs can be HIGH at a time
D. The output toggles if one of the inputs is held HIGH
83. A basic S-R flip-flop can be constructed by cross-coupling of which basic logic gates?
A. AND or OR gates
B. XOR or XNOR gates
C. NOR or NAND gates
D. AND or NOR gates
84. Whose operations are faster among the following?
A. Combinational circuits
B. Sequential circuits
C. Latches
D. Flip-flops
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
85. The sequential circuit is also called ___________
A. Flip-flop
B. Latch
C. Strobe
D. Adder
86. The basic latch consists of ___________
A. Two inverters
B. Two comparators
C. Two amplifiers
D. Two adders
87. What is a trigger pulse?
A. A pulse that starts a cycle of operation
B. A pulse that reverses the cycle of operation
C. A pulse that prevents a cycle of operation
D. A pulse that enhances a cycle of operation
88. The circuits of NOR based S-R latch classified as asynchronous sequential circuits, why?
A. Because of inverted outputs
B. Because of triggering functionality
C. Because of cross-coupled connection
D. Because of inverted outputs & triggering functionality
89. In S-R flip-flop, if Q = 0 the output is said to be ___________
A. Set
B. Reset
C. Previous state
D. Current state
90. A NAND based S’-R’ latch can be converted into S-R latch by placing ____________
A. D latch at each of its input
B. An inverter at each of its input
C. It can never be converted
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
D. Both a D latch and an inverter at its input
91. How many types of flip-flops are?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
92. The characteristic equation of S-R latch is ____________
A. Q(n+1) = (S + Q(n))R’
B. Q(n+1) = SR + Q(n)R
C. Q(n+1) = S’R + Q(n)R
D. Q(n+1) = S’R + Q'(n)R
93. One major difference between a NAND based S’-R’ latch & a NOR based S-R latch is __
A. The inputs of NOR latch are 0 but 1 for NAND latch
B. The inputs of NOR latch are 1 but 0 for NAND latch
C. The output of NAND latch becomes set if S’=0 & R’=1 and vice versa for NOR latch
D. The output of NOR latch is 1 but 0 for NAND latch
94. When is a flip-flop said to be transparent?
A. When the Q output is opposite the input
B. When the Q output follows the input
C. When you can see through the IC packaging
D. When the Q output is complementary of the input
95. A J-K flip-flop with J = 1 and K = 1 has a 20 kHz clock input. The Q output is ________
A. Constantly LOW
B. Constantly HIGH
C. A 20 kHz square wave
D. A 10 kHz square wave
96. What is the significance of the J and K terminals on the J-K flip-flop?
A. There is no known significance in their designations
B. The J represents “jump,” which is how the Q output reacts whenever the clock goes high and the J
input is also HIGH
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. The letters were chosen in honor of Jack Kilby, the inventory of the integrated circuit
D. All of the other letters of the alphabet are already in use
97. Four J-K flip-flops are cascaded with their J-K inputs tied HIGH. If the input frequency (fin) to the first
flip-flop is 32 kHz, the output frequency (fout) is ________
A. 1 kHz
B. 2 kHz
C. 4 kHz
D. 16 kHz
98. Determine the output frequency for a frequency division circuit that contains 12 flip-flops with an input
clock frequency of 20.48 MHz
A. 10.24 kHz
B. 5 kHz
C. 30.24 kHz
D. 15 kHz
99. In D flip-flop, D stands for _____________
A. Distant
B. Data
C. Desired
D. Delay
100. Which statement describes the BEST operation of a negative-edge-triggered D flip-flop?
A. The logic level at the D input is transferred to Q on NGT of CLK
B. The Q output is ALWAYS identical to the CLK input if the D input is HIGH
C. The Q output is ALWAYS identical to the D input when CLK = PGT
D. The Q output is ALWAYS identical to the D input
101. Which of the following describes the operation of a positive edge-triggered D flip-flop?
A. If both inputs are HIGH, the output will toggle
B. The output will follow the input on the leading edge of the clock
C. When both inputs are LOW, an invalid state exists
D. The input is toggled into the flip-flop on the leading edge of the clock and is passed to the output
on the trailing edge of the clock
102. The characteristic equation of D-flip-flop implies that ___________
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. The next state is dependent on previous state
B. The next state is dependent on present state
C. The next state is independent of previous state
D. The next state is independent of present state
103. The flip-flops which has not any invalid states are _____________
A. The S-R, J-K, D
B. S-R, J-K, T
C. J-K, D, S-R
D. J-K, D, T
104. Which of the following is the Universal Flip-flop?
A. S-R flip-flop
B. J-K flip-flop
C. Master slave flip-flop
D. D Flip-flop
105. The term synchronous means ____________
A. The output changes state only when any of the input is triggered
B. The output changes state only when the clock input is triggered
C. The output changes state only when the input is reversed
D. The output changes state only when the input follows it
106. A counter circuit is usually constructed of ____________
A. A number of latches connected in cascade form
B. A number of NAND gates connected in cascade form
C. A number of flip-flops connected in cascade form
D. A number of NOR gates connected in cascade form
107. The parallel outputs of a counter circuit represent the __________. (d)
A. Parallel data word
B. Clock frequency
C. Counter modulus
D. Clock count
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
109.A shift register is made up of how many flip-flops? (c)
A. One
B. Two
C. Three or more
D. None of the above
110.What is the difference between a serial and parallel shift register?(a)
A. A serial shift register shifts in data serially, while a parallel shift register shifts in data in parallel.
B. A serial shift register shifts out data serially, while a parallel shift register shifts out data in
parallel.
C. A serial shift register shifts out data serially, while a parallel shift register shifts out data serially
as well.
D. A serial shift register shifts out data in parallel, while a parallel shift register shifts out data in
parallel as well.
111.Which type of shift register is used to implement a digital up-down counter? (a)
A. Serial in/serial out (SISO) type
B. Serial in/parallel out (SIPO) type
C. Parallel in/serial out (PISO) type
D. Parallel in/parallel out (PIPO) type
112.A bidirectional 4-bit shift register is storing the nibble 1110. Its input is LOW. The nibble 0111 is waiting
to be entered on the serial data-input line. After two clock pulses, the shift register is storing ________
(d)
A. 1110
B. 0111
C. 1000
D. 1001
113.In a parallel in/parallel out shift register, D0 = 1, D1 = 1, D2 = 1, and D3 = 0. After three clock pulses, the
data outputs are ________ (b)
A. 1110
B. 0001
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
C. 1100
D. 1000
114.What type of register would have a complete binary number shifted in one bit at a time and have all the
stored bits shifted out one at a time? (c)
A. Parallel-in Parallel-out
B. Parallel-in Serial-out
C. Serial-in Serial-out
D. Serial-in Parallel-out
115.How much storage capacity does each stage in a shift register represent? (a)
A. One bit
B. Two bits
C. Four bits
D. Eight bits
116.What is the maximum possible number of flip-flops in a decade counter? (b)
A. 1n
B. 2n
C. 2n+1
D. 3n
117. The __________ is programmable logic device with a fixed OR array and a programmable AND
array.
A. PAL
B. PROM
C. PLA
D. None of the above
118.In Hamming Code technique, if the data does not have any error, then C is equivalent to_________.
A. 10001
B. 1001
C. 0000
D. 1111
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
119. Types of ROM memories are____________.
A. EPROM
B. PROM
C. EEPROM
D. All of these
120.To construct 2k × n ROM for given k inputs and n outputs, how many OR gates are needed?
A. 2 𝑛
B. n + 1
C. 2n
D. n
121. To construct 2k × n ROM for given k inputs and n outputs, which decoder is needed?
A. 2 𝑛 decoder
B. k × 2k decoder
C. k × 2n decoder
D. k × 2n decoder
122. Original Hamming Code is used to _________________.
A. detect only a single error
B. detect and correct multiple errors
C. detect and correct only a single error
D. detect multiple errors only
123.The applications of PLA and PAL are followings.
A. To implement combinational circuits
B. Register PALs can be used to implement sequential circuits
C. They can be programmed to use as code converters
D. All of the above
124.How many locations are addresses using 18 address bits?
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
A. 262560
B. 262144
C. 262146
D. 250000
125.How many address bits are needed to operate a 2k × 8 ROM?
A. 9
B. 10
C. 11
D. 12
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|26125627
Downloaded by Hayu A/samad (hayuasamad2@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Testpaper - 1 NTDocument13 pagesTestpaper - 1 NTGattu SadashivaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document59 pagesChapter 5Humna DubbiiNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics and CircuitsDocument12 pagesDigital Electronics and CircuitsGuruKPONo ratings yet
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Digital Electronic CircuitsDocument66 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Digital Electronic Circuitsedwinaustine100% (4)
- Digital ElectronicsDocument19 pagesDigital ElectronicsNitysNo ratings yet
- Digitals Electronics Important MCQ With SolutionDocument20 pagesDigitals Electronics Important MCQ With SolutionPradeep Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Questions: Chapters 1-7, 9 of Nelson's TextDocument6 pagesExam 1 Study Questions: Chapters 1-7, 9 of Nelson's TextNUrul Aqilah MusNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument22 pagesDigital Electronics: Multiple Choice QuestionsSenthilkumar KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- RRB Junior Electronics Engineer Study Material 3Document66 pagesRRB Junior Electronics Engineer Study Material 3thirumalNo ratings yet
- X Input D Q Y Output D Q D Q: CLK CLKDocument6 pagesX Input D Q Y Output D Q D Q: CLK CLKMeenakshi SundaramNo ratings yet
- Typical Questions and AnswersDocument158 pagesTypical Questions and Answersiragire viateurNo ratings yet
- Exercise1 Digital System (LAB)Document39 pagesExercise1 Digital System (LAB)Phong ĐâyNo ratings yet
- IES - Electrical Engineering - Analog and Digital CircuitsDocument81 pagesIES - Electrical Engineering - Analog and Digital CircuitsVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- ECE213 Solved QuestionsDocument89 pagesECE213 Solved QuestionsJundeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Exercises With AnswersDocument157 pagesDigital Electronics Exercises With Answersdineshdkj83% (6)
- BEST Question Bank - Digital ElectronicsDocument157 pagesBEST Question Bank - Digital Electronicsabhinav_pundir0% (1)
- DE09 SolDocument157 pagesDE09 SolRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ece30 QZ 1Document6 pagesEce30 QZ 1Dyan FayeNo ratings yet
- BCA T 113 Digital Electronics Question BankDocument9 pagesBCA T 113 Digital Electronics Question BankAhana MalhotraNo ratings yet
- MsqsDocument5 pagesMsqsYusra MehmoodNo ratings yet
- DE Quiz SnehDocument8 pagesDE Quiz Snehavnesh joshiNo ratings yet
- VCBVDocument8 pagesVCBVavnesh joshiNo ratings yet
- DigitalDocument182 pagesDigitalYeshoda MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Gcet Question Papers-2005Document10 pagesComputer Science Gcet Question Papers-2005Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Gatye TempDocument116 pagesGatye Tempram1calNo ratings yet
- Common Interview QuestionDocument4 pagesCommon Interview QuestionimmamNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Number Systems and Boolean AlgebraDocument8 pagesModule 4 - Number Systems and Boolean AlgebraSuyog ChavanNo ratings yet
- GATE - CS - Digital LogicDocument22 pagesGATE - CS - Digital LogicAnonymous 8pCXXsNo ratings yet
- Gate Ec - 2004 QDocument46 pagesGate Ec - 2004 QRakesh AseryNo ratings yet
- Digital Circuits For GATE ExamDocument15 pagesDigital Circuits For GATE ExamSAMIT KARMAKAR100% (1)
- 1 Number SystemDocument14 pages1 Number SystemhemanthNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering: 1. Prove The Boolean Theorems: (A) X + X X (B) X + Xy X (M/J-16)Document18 pagesDhanalakshmi College of Engineering: 1. Prove The Boolean Theorems: (A) X + X X (B) X + Xy X (M/J-16)Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern Digital Electronics R P Jain Solution ManualDocument167 pagesModern Digital Electronics R P Jain Solution ManualHarpreet PaliaNo ratings yet
- (Solutions) : Page (1/4)Document4 pages(Solutions) : Page (1/4)stellargirl123No ratings yet
- DEDocument10 pagesDEVineetaSinghNo ratings yet
- Morning Session Problems SolutionDocument60 pagesMorning Session Problems SolutionDang XmanNo ratings yet
- DE - 2 MarksDocument30 pagesDE - 2 Markskarthimegs100% (1)
- Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterDocument37 pagesRajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterAmrita VenkitaramaniNo ratings yet
- 2004 IE Theory PaperDocument26 pages2004 IE Theory PaperRafael Mario da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ec1312 QBDocument7 pagesEc1312 QBGopinathan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Practice2Document9 pagesMCQs For Practice2gsvsainiNo ratings yet
- LDST Supplementary 2012Document2 pagesLDST Supplementary 2012yazdanieNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument10 pagesQuestion BankTEIT38 prasad PansareNo ratings yet
- Two Mark & 12 Mark QuestionsDocument42 pagesTwo Mark & 12 Mark QuestionsAnas Ricky ANo ratings yet
- Digital CircuitsDocument29 pagesDigital CircuitsgmsshamaafreenNo ratings yet
- Section C - Digital MCQ1Document6 pagesSection C - Digital MCQ1viki awsacNo ratings yet
- EC 2008 With SolutionsDocument45 pagesEC 2008 With SolutionsBedadipta BainNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesFrom EverandDigital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsFrom EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Siemens S7 Ethernet (Eng) PDFDocument6 pagesSiemens S7 Ethernet (Eng) PDFAlex OrtegaNo ratings yet
- A.C Servo System CatelougeDocument525 pagesA.C Servo System Catelougespectra-twNo ratings yet
- ExosDocument4 pagesExosAi ChaNo ratings yet
- Ce G 3150 Lab 4 Traffic LightDocument22 pagesCe G 3150 Lab 4 Traffic LightAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Lab ManualDocument50 pagesDigital Electronics Lab Manualmohanbabu0% (1)
- Newbie's Guide To AVR Timers: Dean CameraDocument27 pagesNewbie's Guide To AVR Timers: Dean CameracoraztoNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Prof. Richa Sharma Submitted By: Rakhi Yadav 0901eo221049 Eeiot (2 Yr, 3 Sem)Document10 pagesSubmitted To: Prof. Richa Sharma Submitted By: Rakhi Yadav 0901eo221049 Eeiot (2 Yr, 3 Sem)itsmerakhi8940No ratings yet
- ModelSim - Tutorial VHDL PDFDocument21 pagesModelSim - Tutorial VHDL PDFValentina Gomez IsazaNo ratings yet
- D 06 Uservol 2Document374 pagesD 06 Uservol 2cnrk777No ratings yet
- 8253 NotesDocument8 pages8253 NotesSushmita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keil Emulator For C166 InfeneonDocument31 pagesKeil Emulator For C166 Infeneonciwic85343No ratings yet
- PISO - VerilogDocument5 pagesPISO - Verilogshabbir470No ratings yet
- DCS Objective QuestionDocument20 pagesDCS Objective QuestionravigwlNo ratings yet
- Digital InstrumentsDocument29 pagesDigital InstrumentsakshayaNo ratings yet
- MCX514 User's Manual: NOVA ElectronicDocument285 pagesMCX514 User's Manual: NOVA ElectronicvliNo ratings yet
- CS 4141 Digital Systems Lab Report Cover Sheet: ExperimentDocument6 pagesCS 4141 Digital Systems Lab Report Cover Sheet: Experimentoddjobhat@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- CS 2202 - Digital Principles and Systems DesignDocument3 pagesCS 2202 - Digital Principles and Systems DesignDhilip PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- DPSD Model Question Bank With AnswersDocument7 pagesDPSD Model Question Bank With AnswersAkash SanjeevNo ratings yet
- DS1624Document17 pagesDS1624superpuma86No ratings yet
- Carel Ecobox PZHB PYHBDocument50 pagesCarel Ecobox PZHB PYHBcristo.nieto1No ratings yet
- PLC XGBDocument38 pagesPLC XGBmegawati istiqomahNo ratings yet
- 03 Elektor USA May June 2015 PDFDocument132 pages03 Elektor USA May June 2015 PDFvpsampathNo ratings yet
- AWB2528-1508-User Manual EASY500-700 PDFDocument304 pagesAWB2528-1508-User Manual EASY500-700 PDFverde24No ratings yet
- PLC Lab ManualDocument64 pagesPLC Lab ManualNaveen Kumar100% (4)
- HIMAP A2 Eventbuilder EDocument48 pagesHIMAP A2 Eventbuilder EmaronnamNo ratings yet
- 04 Delays, Counters, and TimersDocument47 pages04 Delays, Counters, and TimersFatimaAlarconBlancoNo ratings yet
- EE200 Exp 09Document4 pagesEE200 Exp 09pilim32No ratings yet
- 02 - Modulo-5 CounterDocument4 pages02 - Modulo-5 CounterUsman QadeerNo ratings yet
- Programmable Communication Interface and Programmable Interval TimerDocument48 pagesProgrammable Communication Interface and Programmable Interval TimerMahendra Singh MeenaNo ratings yet