Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary
Uploaded by
Hussain AhmedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary
Uploaded by
Hussain AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Private Costs: costs paid for by a business or the consumer of a product.
Private Benefits: gains to a business or the consumer of a product.
External Costs: costs paid for by the rest of society, other than the business.
External Benefits: gains to the rest of society, other than the business.
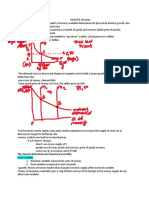
Social Costs = External costs + Private costs.
Social Benefits = External benefits + Private benefits.
If the social benefit exceeds social costs, the scheme will likely be accepted; the government/local community will
probably refuse permission
Exchange Rate: the price of one currency in terms of another currency.
For example, 1 Euro is equivalent to 1.2 Dollars
Currency Appreciation: when the value of a currency increases. It can buy more of another currency
1 euro = 1.2 dollars, to 1 euro = 1.5 dollars.
Currency Depreciation: when the value of a currency decreases. It can buy less of another currency.
1 euro = 1.2 dollars, to 1 euro = 1 dollar.
2 things influence the exchange rate of a currency: Demand for the Currency: if many people want to buy the
currency, the price will increase because it is a limited’ number of currencies (so it leads to appreciation).
Supply of Currency: if the central bank prints more money, the supply increases, but the demand is still the same, so
the value is lower (leading to depreciation).
If it is appreciated, then Import prices fall: since your currency can buy more of the other currency
If its depreciated, then Import prices will rise: Your currency is worth less, so you need more to buy other currencies
You might also like
- Depreciation and AppreciationDocument2 pagesDepreciation and AppreciationBobbyNicholsNo ratings yet
- "Techniques of Controlling Foreign Exchange Exposure Used byDocument56 pages"Techniques of Controlling Foreign Exchange Exposure Used byAshirvad MayekarNo ratings yet
- mgnt-4670-ch-10-foreign-exchange-fall-2007-1194589053952028-3-đã chuyển đổiDocument68 pagesmgnt-4670-ch-10-foreign-exchange-fall-2007-1194589053952028-3-đã chuyển đổiDương Thị Kiều TrangNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 + Lecture: Foreign Exchange MarketDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 10 + Lecture: Foreign Exchange Marketradhika1991No ratings yet
- Week 1 SummaryDocument7 pagesWeek 1 SummaryjuanpablooriolNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQsDocument6 pagesSample MCQsRubal GargNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange RateDocument6 pagesForeign Exchange RateAshutosh BishtNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument8 pagesCh02 Foreign Exchange MarketsPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument8 pagesCh02 Foreign Exchange MarketsPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates - NewDocument28 pagesExchange Rates - Newrishitar101No ratings yet
- International EconmyDocument2 pagesInternational Econmydonatello499No ratings yet
- Exchange Rates and The Open EconomyDocument50 pagesExchange Rates and The Open Economybanjorene100% (1)
- Undervalued Currency Part 2Document1 pageUndervalued Currency Part 2SilverGengarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document13 pagesChapter 18Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Open EconomyDocument17 pagesChapter 4 Open EconomyProveedor Iptv EspañaNo ratings yet
- 9 Determinants of The Exchange Rate Purchasing Power Parity and Interest RateDocument13 pages9 Determinants of The Exchange Rate Purchasing Power Parity and Interest RateOlga LiNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange RateDocument50 pagesForeign Exchange RatekanhaiyabattaseNo ratings yet
- IE 3 Final SkriptaDocument54 pagesIE 3 Final SkriptaVeljko KerčevićNo ratings yet
- Euro EconomyDocument26 pagesEuro EconomyJinal ShahNo ratings yet
- (TCQT) Slide - Group 1Document53 pages(TCQT) Slide - Group 1hoangminh01122019No ratings yet
- TTQ-group 4Document13 pagesTTQ-group 4Phan ThọNo ratings yet
- Foreignexchangemarket 190712100000Document79 pagesForeignexchangemarket 190712100000Prasanjit BiswasNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument29 pagesThe Foreign Exchange MarketSam Sep A Sixtyone100% (1)
- Determination of Exchange RateDocument14 pagesDetermination of Exchange RateAshish Tagade100% (2)
- Report in MacroeconomicsDocument4 pagesReport in MacroeconomicsNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- IB HL Global Economics Chapter 16 - Exchange Rates NotesDocument12 pagesIB HL Global Economics Chapter 16 - Exchange Rates NotescharryNo ratings yet
- Sale of Government Bonds CB Sells Bonds To The Public and Gets Cash in Return SucksDocument55 pagesSale of Government Bonds CB Sells Bonds To The Public and Gets Cash in Return SucksDora IskandarNo ratings yet
- Exchange RatesDocument32 pagesExchange RatesStuti BansalNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Currency Dealing and Exchange Rate QuotationsDocument6 pagesMechanics of Currency Dealing and Exchange Rate Quotationsvijayadarshini vNo ratings yet
- R21 Currency Exchange Rates IFT NotesDocument35 pagesR21 Currency Exchange Rates IFT NotesMohammad Jubayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight: 8. Foriegn Exchange MarketsDocument26 pagesChapter Eight: 8. Foriegn Exchange MarketsNhatty WeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Foreign Currecies Exchange MarketDocument47 pagesChapter 1 - Foreign Currecies Exchange MarketThư Trần Thị AnhNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange MarketDocument42 pagesForeign Exchange MarketJafaryNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates: Exchange Rate Relative Price of CurrenciesDocument25 pagesExchange Rates: Exchange Rate Relative Price of CurrenciesBhavvesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document27 pagesChap 1kimngan.nguyen8803No ratings yet
- Econ 28Document2 pagesEcon 28Paige BurgosNo ratings yet
- Business of Banking (Volumul II) PDFDocument328 pagesBusiness of Banking (Volumul II) PDFminusdas540No ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Determination: T.J. JosephDocument58 pagesExchange Rate Determination: T.J. JosephArshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Currency ConversionDocument33 pagesCurrency ConversionSruthi NairNo ratings yet
- Trepp Week 3 Real Exchange Rates and Nominal Exchange RatesDocument33 pagesTrepp Week 3 Real Exchange Rates and Nominal Exchange RatesXuân BìnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4Proveedor Iptv EspañaNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange Market: Unit 5 SectionDocument6 pagesThe Foreign Exchange Market: Unit 5 SectionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 IEDocument22 pagesChapter 6 IEYu ZanNo ratings yet
- Egzamin Z BiznesuDocument5 pagesEgzamin Z BiznesuBeata WesolowskaNo ratings yet
- Forex ManagementDocument42 pagesForex ManagementRavinder YadavNo ratings yet
- Jpmorgan Chase Quant Finance Mentorship Case Study 2024Document25 pagesJpmorgan Chase Quant Finance Mentorship Case Study 2024anshikamittal2626No ratings yet
- Fx-ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesFx-Considerationsюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Chapter One and TwoDocument50 pagesChapter One and Twomikialeabrha23No ratings yet
- Pairs Stock MarketDocument3 pagesPairs Stock MarketManish HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- DevaluationDocument5 pagesDevaluationसागर मोहन पाटीलNo ratings yet
- 344 ch2Document18 pages344 ch2Vishal NigamNo ratings yet
- C6 Money and InflationDocument31 pagesC6 Money and InflationStefan VasileNo ratings yet
- Kavita IbDocument19 pagesKavita IbKaranPatilNo ratings yet
- 12 International Corporate Finance (Session 25, 26) - ForumDocument16 pages12 International Corporate Finance (Session 25, 26) - ForumcreamellzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Proveedor Iptv EspañaNo ratings yet
- Internatinal Financial Markets, Rates and QuotesDocument13 pagesInternatinal Financial Markets, Rates and QuotesShivani Goyal100% (1)
- Lecture 1: Exchange Rates and The Foreign Exchange Market: FT Chapter 13Document10 pagesLecture 1: Exchange Rates and The Foreign Exchange Market: FT Chapter 13asdNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. FOREIGN EXCHANGE RateDocument6 pagesUnit 5. FOREIGN EXCHANGE Rateswaroop msNo ratings yet
- Econ 161 SQMand PDocument4 pagesEcon 161 SQMand PSZNo ratings yet
- Exel Work in Vacations EtcDocument2 pagesExel Work in Vacations EtcHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Maths Project Term 2Document10 pagesMaths Project Term 2Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- End of Semester 2 Material Clover For Grade 7Document2 pagesEnd of Semester 2 Material Clover For Grade 7Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- 11._OTHER_PAYABLES_AND_OTHER_RECEIVABLESDocument42 pages11._OTHER_PAYABLES_AND_OTHER_RECEIVABLESHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Question 4 Page 27Document2 pagesChapter 2 Question 4 Page 27Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Market ResearchDocument50 pagesChapter 11 Market ResearchHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- KSA Project 2Document8 pagesKSA Project 2Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- PE ProjectDocument5 pagesPE ProjectHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Islamic ProjectDocument11 pagesIslamic ProjectHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- KSA ProjectDocument7 pagesKSA ProjectHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit1 2+representing+soundDocument11 pagesUnit1 2+representing+soundHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics ProjectHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Quran ProjectDocument7 pagesQuran ProjectHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Encryption: Symmetric and Asymmetric EncryptionDocument24 pages2.3 Encryption: Symmetric and Asymmetric EncryptionHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Softwrae Worksheet2Document6 pagesUnit4 Softwrae Worksheet2Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit1 2+representing+characters+and+character+setsDocument22 pagesUnit1 2+representing+characters+and+character+setsHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 2+error+detection+methodsDocument24 pages2 2+error+detection+methodsHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 2+automatic+repeat+query+ (ARQ)Document9 pages2 2+automatic+repeat+query+ (ARQ)Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit1 1+signed+integers+using+two's+complementDocument27 pagesUnit1 1+signed+integers+using+two's+complementHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements - Part ADocument36 pagesFinancial Statements - Part AHussain AhmedNo ratings yet