Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiplexer and Demultiplexer - 22
Uploaded by
senpaixd01100 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Multiplexer and Demultiplexer_22
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesMultiplexer and Demultiplexer - 22
Uploaded by
senpaixd0110Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
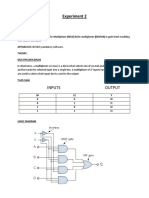
Objectives:
1. Multiplexers:
a. 4-to-1 Multiplexers.
b. Design of 8:1 Multiplexers.
2. Demultiplexers.
3. Encoders.
4. Examples.
1. Multiplexers
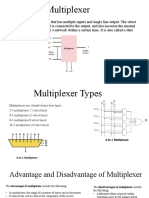
A Multiplexers (MUX) is a combinational logic component that has several
inputs and only one output.
MUX directs one of the inputs to its output line by using a control bit word
(selection line) to its select lines.
Multiplexer contains the followings:
o data inputs
o selection inputs
o a single output
o Selection input determines the input that should be connected to the
output.
The multiplexer sometime is called data selector.
The multiplexer acts like an electronic switch that selects one from
different.
A multiplexer may have an enable input to control the operation of the
unit.
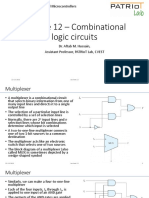
a) 4-to-1 Multiplexers
ü 4-data input MUX
ü , - Select lines.
ü , , , - Input lines.
ü - Single output line.
Select
Output
lines
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
MUX implementation
b) Design of a 8:1 multiplexer
How to construct a 8:1 MUX from two 4:1 MUX.
ü and are the two output lines of two 4:1 MUX
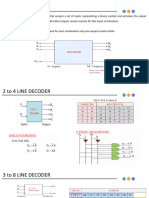
2. Demultiplexers
The demultiplexer is a combinational logic circuit that performs the
reverse operation of multiplexer (Several output lines, one input
line).
Explain:
inputs Output
Two select lines four outputs
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 1
You might also like
- Microprocessor Architectures and Systems: RISC, CISC and DSPFrom EverandMicroprocessor Architectures and Systems: RISC, CISC and DSPRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Exper-8 Multiplexer and DemultiplexerDocument2 pagesExper-8 Multiplexer and DemultiplexerMohammed Dyhia Ali100% (1)
- Our Presentation: Shajnin Binte Noor ID:191031002 Marium Akter Chompa ID:191031005 Nawshin Tabassum Mumu ID:191031015Document9 pagesOur Presentation: Shajnin Binte Noor ID:191031002 Marium Akter Chompa ID:191031005 Nawshin Tabassum Mumu ID:191031015Shariful IslamNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportabuzarkazmi779No ratings yet
- Multiplexer: By: Teknik Elektro 2Document89 pagesMultiplexer: By: Teknik Elektro 2joxNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4noirNo ratings yet
- DLLec7c NotesDocument4 pagesDLLec7c NotesChintan MandalNo ratings yet
- 220644-665-666, DLD Lab#10Document11 pages220644-665-666, DLD Lab#10Muhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Com Bi National LogicDocument168 pagesCom Bi National LogicpinokyuNo ratings yet
- Encoder and MUXDocument41 pagesEncoder and MUXsulthan_81No ratings yet
- Multiplexers & DemultiplexersDocument14 pagesMultiplexers & DemultiplexersSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- EEE 304 Experiment No. 04 Name of The Experiment: Design of Decoder/Encoder/Multiplexer CircuitDocument5 pagesEEE 304 Experiment No. 04 Name of The Experiment: Design of Decoder/Encoder/Multiplexer CircuitAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- EEE 304 - Exp4 PDFDocument5 pagesEEE 304 - Exp4 PDFAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii: Design With Msi DevicesDocument16 pagesUnit Iii: Design With Msi DevicesArjun SeshadhryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Combinational Logic Circuits: EC2.101 - Digital Systems and MicrocontrollersDocument19 pagesLecture 12 - Combinational Logic Circuits: EC2.101 - Digital Systems and MicrocontrollersAnurag DubeyNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 2022 2Document2 pagesLab 11 2022 2CuongNo ratings yet
- EEE 357 Lecture 10 Mux, DemuxDocument15 pagesEEE 357 Lecture 10 Mux, DemuxShuvodip Das100% (1)
- Combinational Logic TechnologiesDocument38 pagesCombinational Logic TechnologiesJanvier IyakaremyeNo ratings yet
- MUXs & DEMUXsDocument93 pagesMUXs & DEMUXsAssistance WorldNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer and DemultiplexerDocument5 pagesMultiplexer and DemultiplexerAdebayo AdebariNo ratings yet
- Chapter4: Combinational Logic: Originally by Reham S. Al-MajedDocument14 pagesChapter4: Combinational Logic: Originally by Reham S. Al-Majedرغوووودي رغووووديNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document24 pagesTopic 3tanay.s1No ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - Multiplexer and Demultiplexer Using NAND GatesDocument6 pagesExperiment 6 - Multiplexer and Demultiplexer Using NAND GatesPrr PrrNo ratings yet
- MultiplexerDocument22 pagesMultiplexerMa. Patricia PalibinoNo ratings yet
- Combinational Circuits: Dr. Bernard Chen PH.DDocument41 pagesCombinational Circuits: Dr. Bernard Chen PH.DJacob JayaseelanNo ratings yet
- Full Adder and Subtractor Using MUXDocument3 pagesFull Adder and Subtractor Using MUXdevonlaratt359No ratings yet
- EC-322 Multiplexer & DemultiplexerDocument31 pagesEC-322 Multiplexer & DemultiplexersuryanshNo ratings yet
- Digital TechniqueDocument33 pagesDigital Techniquekhalique demonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 MUX DEMUXDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 MUX DEMUXMD Sadique AnsariNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT No 5 - MuX and DeMuxDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT No 5 - MuX and DeMuxSaksham DhawanNo ratings yet
- Lec 13 Multiplexer Demux XORDocument23 pagesLec 13 Multiplexer Demux XORPiyooshTripathiNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: Combinational Circuit: Multiplexers-De-multiplexers Decoder-EncoderDocument22 pagesUnit-5: Combinational Circuit: Multiplexers-De-multiplexers Decoder-EncoderFaizan KhanNo ratings yet
- Expt 4. 16x1 Mux Using 4x1 MuxDocument6 pagesExpt 4. 16x1 Mux Using 4x1 Muxanon_64997028367% (3)
- MultiplexerDocument14 pagesMultiplexerjenny khan100% (1)
- LOGIC DESIGN-Lecture24Document12 pagesLOGIC DESIGN-Lecture24muktikantaNo ratings yet
- Military College of Signals Digital Logic Design: Lab Engr HammadDocument9 pagesMilitary College of Signals Digital Logic Design: Lab Engr Hammadahmad khanNo ratings yet
- MultiplexerDocument16 pagesMultiplexerPARTEEK RANANo ratings yet
- Unit2 LD DssDocument36 pagesUnit2 LD Dssrajthkumar122333No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 FinalDocument9 pagesExperiment 4 Finalliddleme33No ratings yet
- 271 7Document0 pages271 7Usman Sabir100% (1)
- Data Processing CircuitsDocument19 pagesData Processing CircuitsBhaskar MNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit-2Document25 pagesCoa Unit-2PARTEEK RANANo ratings yet
- Sistem Digital - Mux DemuxDocument12 pagesSistem Digital - Mux DemuxFilio DaffaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Inputs OutputDocument6 pagesExperiment 2: Inputs OutputSdoNo ratings yet
- 33 DLD Lec 33 Multiplexer, Demultiplexer 01 Dec 2022 Lecture SlidesDocument26 pages33 DLD Lec 33 Multiplexer, Demultiplexer 01 Dec 2022 Lecture SlidesZuha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Verilog Assigment 1Document12 pagesVerilog Assigment 1Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- Jana 22BLC1032Document26 pagesJana 22BLC1032janardhanan1711No ratings yet
- Lab 10 Mux & DeMuxDocument9 pagesLab 10 Mux & DeMuxsafdarmunir070No ratings yet
- Digital Logic ProblemsDocument30 pagesDigital Logic ProblemsKeithKrNo ratings yet
- Functions of Multiplexers in A Data Communication Network PDFDocument8 pagesFunctions of Multiplexers in A Data Communication Network PDFAbdu AlhaddiNo ratings yet
- CS 8351 Digital Principles and System Design: MultiplexersDocument25 pagesCS 8351 Digital Principles and System Design: Multiplexerspadmaa1No ratings yet
- 1 Fulladder Draw The Block DiagramDocument11 pages1 Fulladder Draw The Block DiagramAbcdNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 FinalDocument8 pagesExperiment 5 Finalliddleme33No ratings yet
- VHDL Lab RecordDocument13 pagesVHDL Lab RecordRajBhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignDocument37 pagesChapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignSruthy SasiNo ratings yet
- Combinational circuitMUX - AdderDocument12 pagesCombinational circuitMUX - AdderHARI HARAN REDDYNo ratings yet
- DD Module-2 Part-2 (Comparator, Encoder, Decoder, Mux)Document43 pagesDD Module-2 Part-2 (Comparator, Encoder, Decoder, Mux)Aneal SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch#3 Logic DesignDocument38 pagesCh#3 Logic DesignErmiyas AbrahaNo ratings yet
- Mult and DemultDocument8 pagesMult and Demultkarim mohamedNo ratings yet
- 202004021910157352aksingh Phy Adder SubtractorDocument8 pages202004021910157352aksingh Phy Adder SubtractorJai SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1VI CharacteristicsDocument11 pages1VI Characteristicssenpaixd0110No ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument70 pagesFinal Reportsenpaixd0110No ratings yet